Energetics- enthalpy change definitions
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
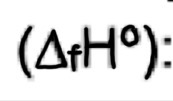
Enthalpy of formation
Enthalpy change when one mole of a substance is formed from its constituent elements with all substances in their standard states
exothermic (-ve) for most substances
E.g 2Na(s) + ½ O2(g) —> Na2O(s)

Enthalpy of combustion
Enthalpy change when one mole of a substance undergoes complete combustion in oxygen with all substances in standard states
Exothermic (-ve)
E.g H2(g) + ½ O2 (g) —> H2O (l)

Enthalpy of neutralisation
Enthalpy change when one mole of WATER is formed in a reaction between an acid and alkali under standard conditions
Exothermic (-ve)
e.g ½ H2SO4(aq) + NaOH (aq) —> ½ Na2SO4(aq) +H2O(l)
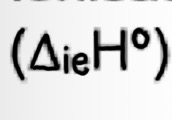
Ionisation Enthalpy (two definitions- 1st and 2nd ionisation energies)
FIRST ionisation energy= Enthalpy change when each atom in one mole of gaseous atoms loses one electron to form one mole of gaseous 1+ ions.
endothermic (+ve)
E.g Mg(g) —> Mg+(g) + e-
SECOND ionisation energy= Enthalpy change when each ion in one molecule of gaseous 1+ ions loses one electron to form one mole of gaseous 2+ ions
endothermic (+ve)
E.g Mg+(g) —> Mg2+(g) +e-

Electron affinity (2 definitions- first and second)
FIRST electron affinity= Enthalpy change when each atom in one mole of gaseous atoms gains one electron to form one mole of gaseous 1- ions.
exothermic (-ve) for many non-metals
E.g O(g) + e- —> O- (g)
SECOND electron affinity= Enthalpy change when each ion in one mole of gaseous 1- ions gains one electron to form one mole of gaseous 2- ions
endothermic (+ve) as adding -ve electron to -ve ion
E.g O-(g) + e- —> O2- (g)
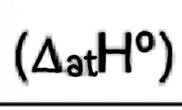
Enthalpy of atomisation
Enthalpy change when one mole of gaseous atoms is produced from an element in its standard state
endothermic (+ve)
E.g iodine : ½ I2(s) —> I(g)
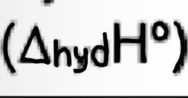
Hydration Enthalpy
Enthalpy change when one mole of gaseous ions become hydrated (dissolved in water)
exothermic (-ve)
E.g Mg2+ (g) + aq —> Mg2+ (aq)
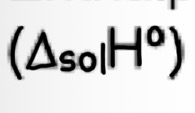
Enthalpy of solution
Enthalpy change when one mole of an ionic solid dissolves in an amount of water large enough so that the dissolved ions are well separated and do not interact with each other
exo/endothermic varies
E.g MgCl2(s) + aq —> Mg2+ (aq) + 2Cl- (aq)

Bond dissociation enthalpy
Enthalpy change when one mole of covalent bonds is broken in the gaseous state
endothermic (+ve)
E.g I-I bond (iodine): I2(g) —> 2 I(g)

Lattice enthalpy of formation
Enthalpy change when one mole of a solid ionic compound is formed into its constituent ions in the gas phase
exothermic (-ve)
E.g Mg2+(g) + 2Cl-(g) —> MgCl2(s)

Lattice enthalpy of dissociation
Enthalpy change when one mole of a solid ionic compound is broken up into its constituent ions in the gas phase
endothermic (+ve)
E.g MgCl2(s) —> Mg2+(g) + 2Cl-(g)
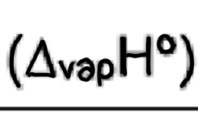
Enthalpy of vaporisation
Enthalpy change when one mole of a liquid is turned into a gas
endothermic (+ve)
E.g H2O(l) —> H2O(g)

Enthalpy of fusion
Enthalpy change when one mole of a solid is turned into a liquid
endothermic (+ve)
E.g Mg(s) —> Mg(l)