vitals and measurements (part two)
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
body measurements for adults and older children
height
weight
body measurements for infants
length
weight
head circumference
chest circumference
what is the purpose of taking body measurements?
provides baseline values for current condition and enables monitoring of growth and development of children
adult weight
each office visit
record to nearest quarter of a pound
height of adults
initial visit and yearly
record to nearest quarter of an inch
how do you take an adult’s height and weight?
obtain weight in a private area
make sure scale is balanced
assist patient on and off scale
document in chart if patient refuses
remove shoes for height
convert feet to inches
infant and child weight
medication dosage is based on weight in kilograms
convert pounds (lbs) to kilograms (kg)
lbs / 2.2 = kg
kg x 2.2 = lbs
height, head, and chest circumference
lay child on a paper-covered table
place mark at top of head and at heel of the flexed foot
measure head circumference at widest area (across eyebrows)
measure chest circumference (under arms)
return infant to caretaker
measure marks on the table in inches for height
body mass index (BMI)
not an indicator of health
used to correlate risk factors
based on height and weight
18.5 - 24.9 → normal
over 24.9 → overweight
over 30 → obese
over 40 → morbidly obese
high risk for diabetes and heart problems
diameter of limb
measure both to determine difference in size
what do you need to measure from a wound, bruise, or other injury?
length and width
pulse oximetry
not normally considered a vital sign
reading of oxygen saturation in blood
also displays pulse reading (heart rate)
probe is attached to finger or earlobe to obtain reading
nail polish blocks light and interferes with the test
normal reading is 95% or higher
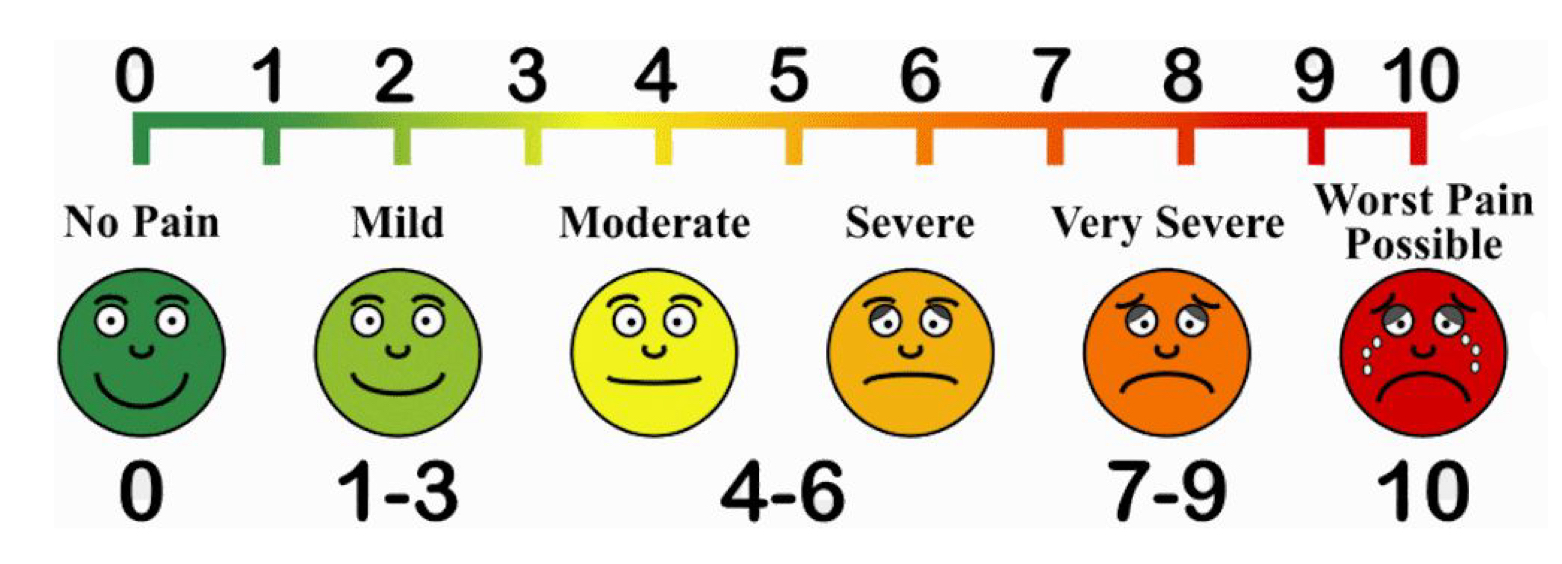
pain scale
subjective → difficult to interpret
rated on scale 1-10 (10 being the worst)
ask general questions to determine location, onset, and characteristics
document any medication used to relieve symptoms
adult height should be measured to the nearest
inch
quarter of an inch
eighth of an inch
sixteenth of an inch
quarter of an inch
adult weight should be measured
each office visit
initial visit
yearly
initial visit and yearly
each office visit
what is 10 lbs in kg?
4 kg
4.5 kg
20 kg
22 kg
4.5 kg
what is the first step in measuring an infant head and chest circumference?
place child in a paper-covered scale
lay child on scale
ask caretaker to hold the infant
place child in a paper-covered scale
what measurements are required to obtain a BMI measurement?
blood pressure and temperature
temperature and pulse
weight only
height and weight
height and weight
what does pulse oximetry measure?
pulse
oxygen levels in the blood
heat
pulse and oxygen levels in the blood
pulse and oxygen levels in the blood
which number on the pain scale is pain being at its least?
1
5
10
20
1
which of the following areas on the body provides the least accurate temperature reading?
axillary
rectal
temporal
tympanic
axillary
quint Gardner, a 35-year-old established patient, is in the office for his annual checkup. he says he feels great, and he appears to be in good physical condition. according to office policy, you check his blood pressure using the aneroid sphygmomanometer and his temperature using an axillary thermometer. his vital signs are: BP: 118/88, R: 16, T: 102.4, P: 62. given these vitals what would the medical assistant’s next step be?
recheck the blood pressure using an electronic sphygmomanometer
ask him to sit quietly for 15 minutes and then recheck his pulse
recheck his temperature using a different type of thermometer
ask him if he has had anything cold to drink in the last half hour
recheck his temperature using a different type of thermometer
which of the following is important when taking a rectal temperature?
rinse the thermometer under water before inserting it
insert the thermometer 2 inches into the rectum
hold the thermometer in place while taking the temperature
use a disposable thermometer
hold the thermometer in place while taking the temperature
how long should the MA count a pulse if it irregular?
20 seconds
30 seconds
60 seconds
120 seconds
60 seconds
in addition to the pulse rate, what else should you note about the patient’s pulse?
rhythm and volume
volume and effort
volume and tone
effort and rhythm
rhythm and volume