Histo Lab- Digestive System (Aughey)
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
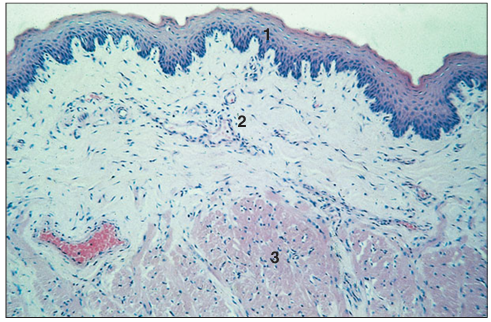
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2. __ 3.__
Stain used:
Tongue (cat). (1) Stratified squamous non-keratinized epithelium. (2) Vascular lamina propria with small projections. (3) Striated muscle fibres. H & E. ×25.
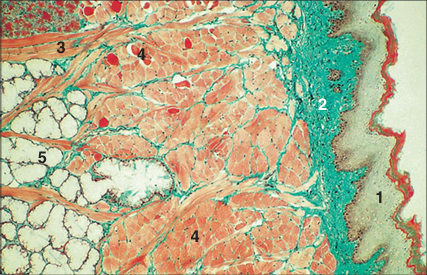
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2. __ 3.__ 4.__ 5.__
Stain used:
Tongue (dog). (1) Stratified squamous keratinized epithelium on the dorsum of the tongue. (2) Lamina propria. (3) Striated muscle fibres cut in longitudinal section and (4) in transverse section. (5) Mixed salivary gland. Masson’s trichrome. ×25.
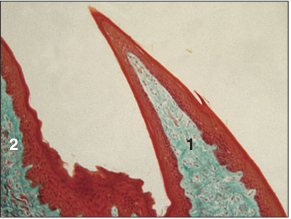
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2. __
Stain used:
Tongue (cow). (1) Filiform papilla. (2) Lenticular papilla. Masson’s trichrome. ×41.5.
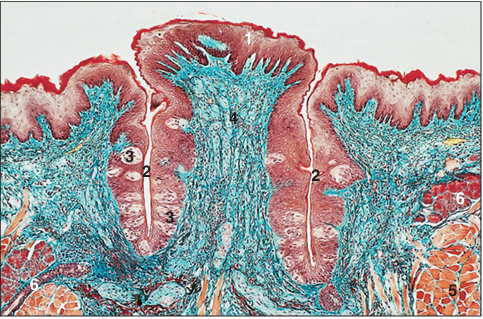
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2. __ 3.__ 4.__ 5.__ 6.__
Stain used:
Circumvallate papilla. Tongue (cow). (1) Stratified squamous epithelium. (2) Vallum. (3) Taste buds. (4) Lamina propria. (5) Striated muscle. (6) Mixed salivary gland. Gomori’s trichrome. ×100.
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2. __
Stain used:
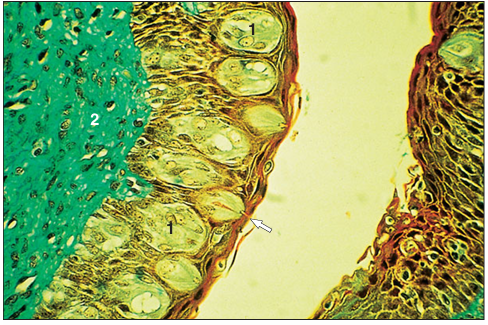
Tongue (cow). (1) Taste buds in the stratified squamous epithelium of the lateral wall of the papilla. The taste pore is arrowed. (2) Connective tissue lamina propria. Masson’s trichrome. ×250.
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Stain used:
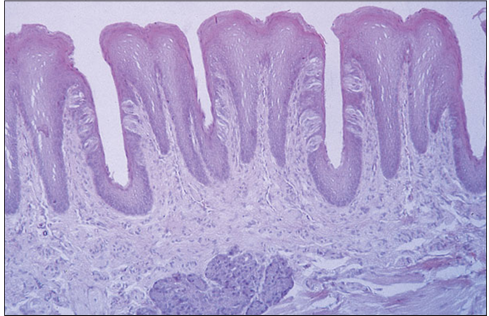
Foliate papilla. Tongue (rabbit). This papilla appears as a row of fungiform papillae. The taste buds are arranged along the lateral walls. H & E. ×62.5.
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2. __
Stain used:
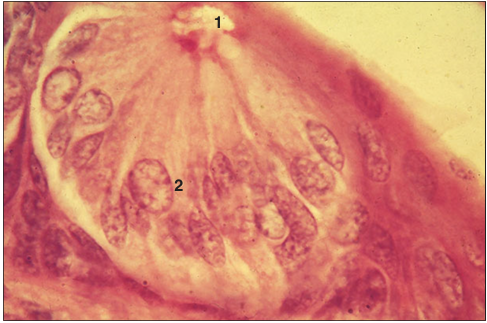
Taste bud. Tongue (cow). (1) Taste pore. (2) Taste receptor and sustentacular cells. H & E. ×62.5.
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2.__ 3.__
Stain used:
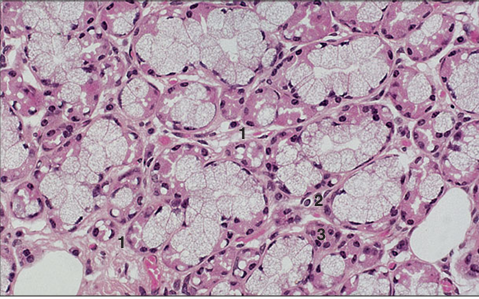
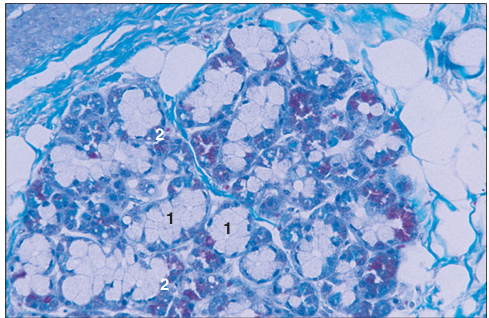
Mixed salivary gland (cow). The main mass of tissue is secretory units of seromucous acini. (1) Interlobular connective tissue with (2) blood vessels. (3) Interlobular ducts. H&E. ×125.
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2.__
Stain used:
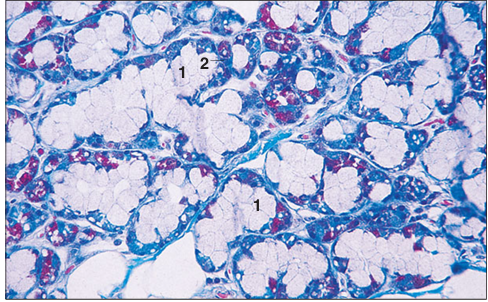
Mixed salivary gland (cow). Mixed seromucous acinus with (1) pale staining mucous cells and (2) darkly stained serous cells. Masson’s trichrome. ×125.
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2.__ 3.__ 4.__
Stain used:
Mixed salivary gland (dog). (1) Interlobular duct lined by a stratified columnar epithelium. (2) Connective tissue stroma. (3) Parasympathetic ganglion. (4) Seromucous acini. H & E. ×125.
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2.__
Stain used:
Mixed salivary gland (dog). (1) Pale staining triangular mucous cells with a basal nucleus. (2) Deeply staining serous cells with a round nucleus. Gomori’s trichrome. ×125.
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2.__ 3.__
Stain used:
Hard palate (ox). (1) Stratified squamous epithelium. (2) Lamina propria. (3) Mucus-secreting glands in the lamina propria. H & E. ×125.
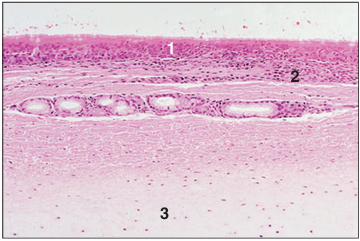
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2.__ 3.__
Stain used:
Soft palate (ox). (1) Respiratory epithelium. (2) Lymph nodule. (3) Bone. H & E. ×62.5.
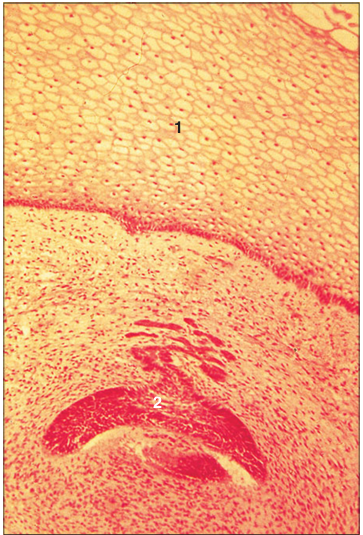
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2.__
Stain used:
Developing tooth (cat embryo). (1) Oral epithelium. (2) Enamel organ surrounded by mesoderm. H & E. ×12.5.
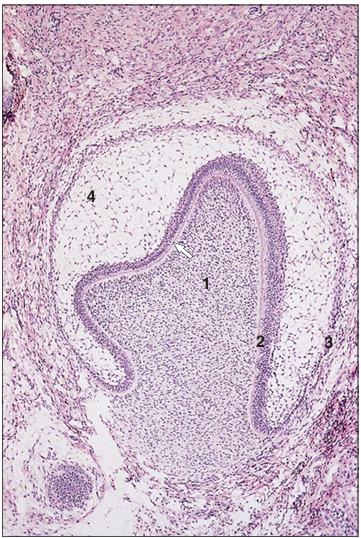
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2.__ 3.__ 4.__
Stain used:
Developing tooth (cat embryo). (1) Mesenchymal papilla with a layer of odontoblasts (arrowed). (2) Inner enamel epithelium, continuous with (3) the outer enamel epithelium. (4) Stellate reticulum. H & E. ×62.5.
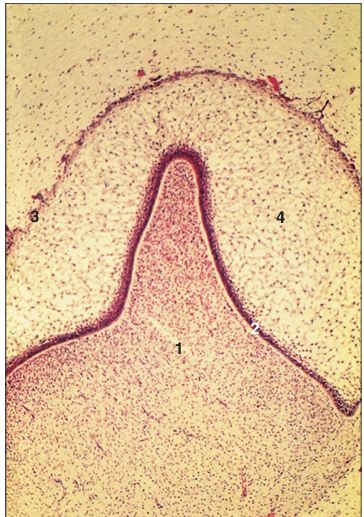
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2.__ 3.__ 4.__
Stain used:
Developing tooth (cat embryo). (1) Mesenchymal dental papilla. (2) Ameloblasts in the inner enamel epithelium. (3) Outer enamel epithelium. (4) Stellate reticulum. H & E. ×62.5.
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2.__ 3.__
Stain used:
Developing tooth (cat embryo). (1) Mesenchymal dental papilla lined by odontoblasts. (2) Inner enamel epithelium, ameloblasts, turns to become (3) outer enamel epithelium at the point of root development (arrowed). H & E. ×125.
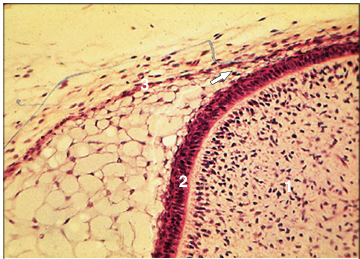
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Stain used:
Developing tooth (cat). The ameloblasts are tall columnar cells with a basal nucleus (arrowed). H&E. ×125
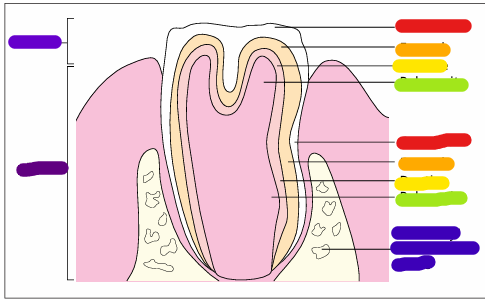
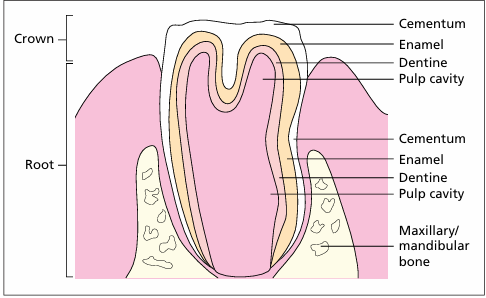
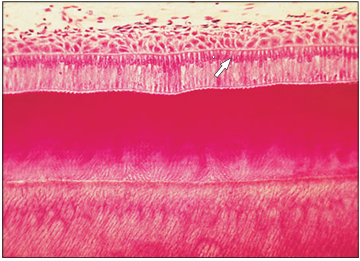
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2.__
Stain used:
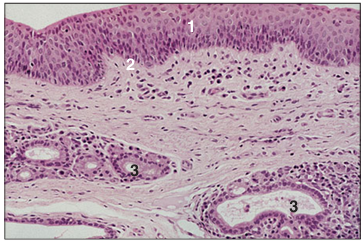
Oropharynx. (1) Stratified squamous epithelium. (2) Mucus secreting glands open onto the surface (arrowed). H & E. ×62.5.
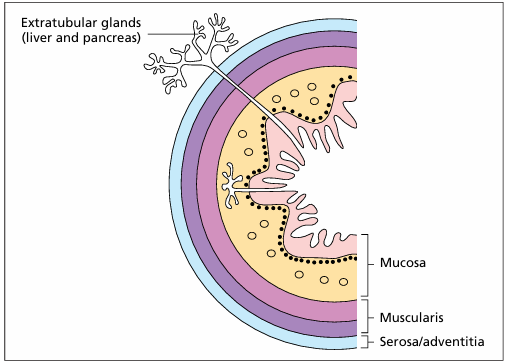
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2.__ 3.__ 4.__ 5.__
Stain used:
Oesophagus (cat). (1) Stratified squamous keratinized epithelium. (2) Lamina propria. (3) LS vein. (4) Inner layer of circular smooth muscle. (5) Outer layer of longitudinal smooth muscle. H & E. LP.
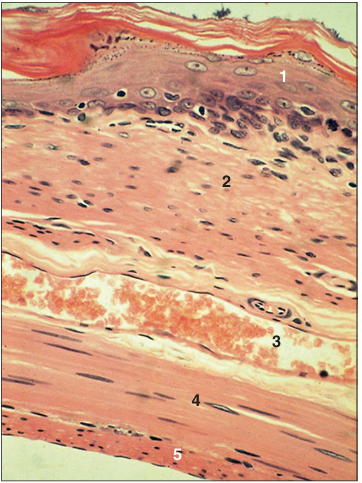
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2.__ 3.__ 4.__
Stain used:
Oesophagus (dog). (1) Stratified squamous epithelium. (2) Mucus-secreting glands in the lamina propria. (3) Inner layer of circular skeletal muscle. (4) Outer layer of longitudinal skeletal muscle. H & E. ×12.5.
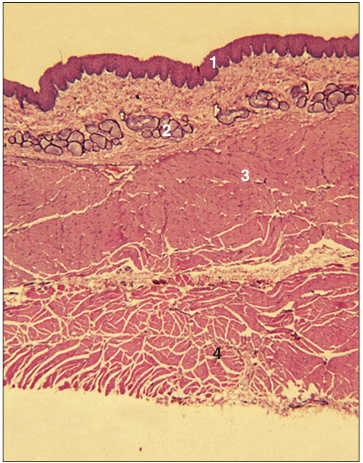
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2.__ 3.__ 4.__ 5.__
Stain used:
Oesophagus (cat). (1) Stratified squamous epithelium. (2) Lamina propria. (3) Muscularis mucosae. (4) Submucosal mucous glands. (5) Muscularis externa. Masson’s trichrome. ×12.5.
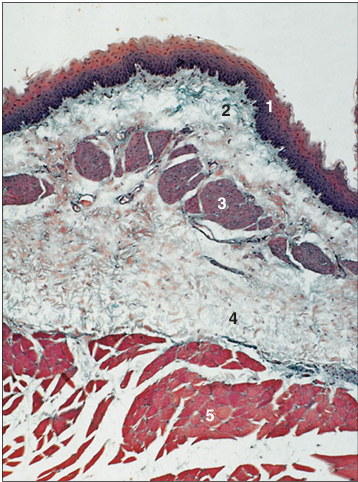
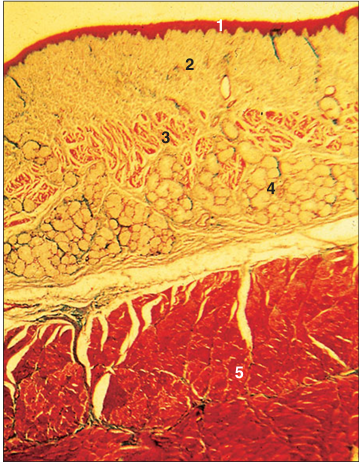
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2.__ 3.__ 4.__ 5.__
Stain used:
Oesophagus (dog). (1) Stratified squamous epithelium. (2) Lamina propria. (3) Muscularis mucosae. (4) Submucosal mucous glands. (5) Striated muscle of the muscularis externa. H & E. ×62.5.
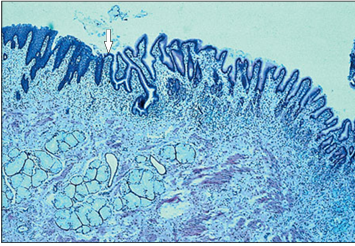
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Stain used:
Oesophageal/stomach junction (horse). The epithelium changes abruptly from stratified squamous to simple columnar at the junction (arrowed). H & E. ×62.5.
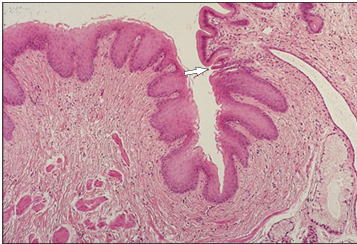
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Stain used:
Oesophageal/stomach junction (horse). The epithelium changes abruptly from stratified squamous to simple columnar at the junction (arrowed). H & E. ×100.
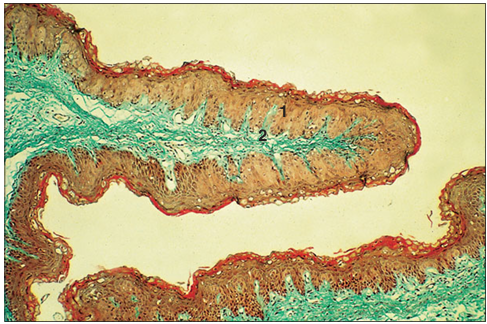
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2.__
Stain used:
Rumen (sheep). (1) Stratified squamous epithelium lines the rumen. (2) Lamina propria. Masson’s trichrome.×12.5.
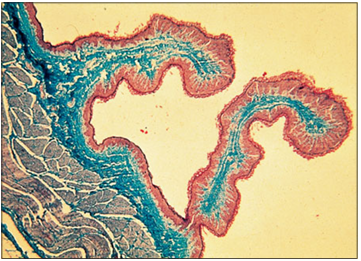
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Stain used:
Rumen (goat). The lining epithelium is stratified squamous. The lamina propria is loose connective tissue, stained green. Gomori’s trichrome. ×12.5.
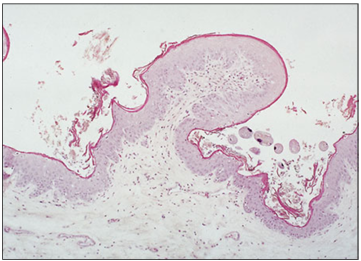
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Stain used:
Reticular groove (goat). The mucosa is folded; this allows stretching. The lining epithelium is stratified squamous. H & E. ×12.5.
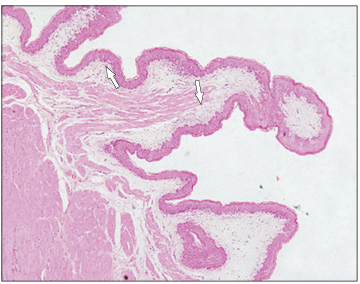
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Stain used:
Omasum (sheep). The muscularis mucosae is present in the long omasal folds (arrowed). H & E. ×12.5.
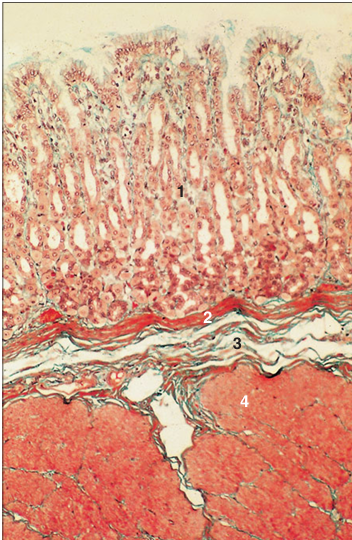
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2.__ 3.__ 4.__
Stain used:
Abomasum. Fundic region (goat). (1) Mucosa. (2) Muscularis mucosae. (3) Submucosa. (4) Muscularis externa. Masson’s trichrome. ×25.
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2.__ 3.__ 4.__
Stain used:
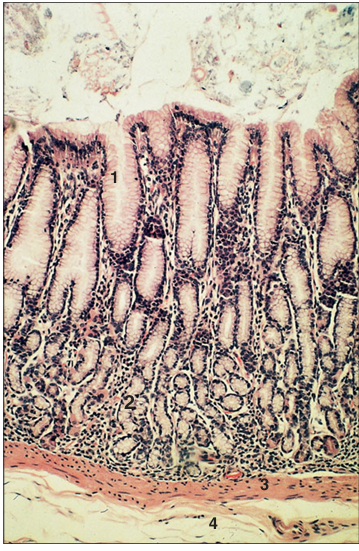
Abomasum. Pyloric region (goat). (1) The lining epithelium is simple columnar and mucus secreting. (2) Simple tubular mucus-secreting glands. (3) Muscularis mucosae. (4) Submucosa. H&E. ×62.5.
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2.__
Stain used:
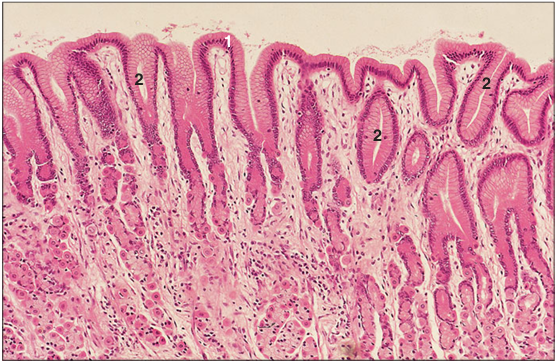
Stomach (horse). (1) Simple columnar mucus-secreting epithelium. (2) Gastric pits. H & E. ×62.5.
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2.__ 3.__
Stain used:
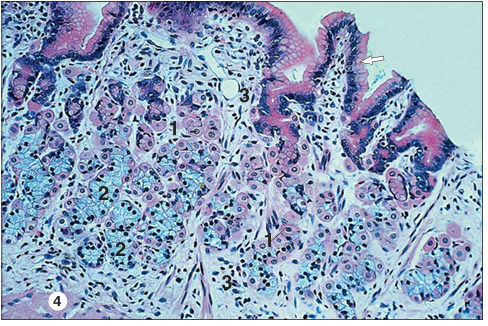
Cardiac glands. Stomach (horse). (1) Parietal cell. (2) Zymogen cell. (3) Lamina propria. H & E. ×125.
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2.__
Stain used:
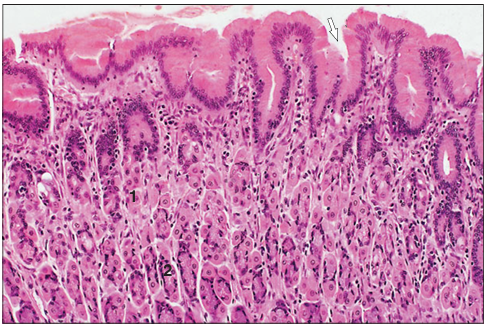
Fundic glands. Stomach (horse). Simple mucus-secreting epithelium extends into the gastric pits (arrowed). (1) Parietal cell. (2) Zymogen cell. H & E. ×250.
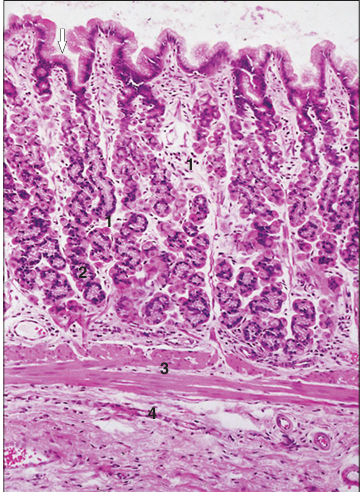
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2.__ 3.__ 4.__
Stain used:
Fundic glands. Stomach (dog). Simple columnar mucus-secreting epithelium extends into the gastric pits (arrowed). (1) Parietal cell. (2) Zymogen cell. (3) Muscularis mucosae. (4) Submucosa. H & E. ×125.
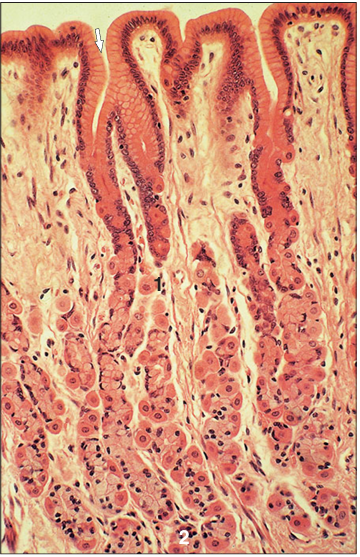
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2.__
Stain used:
Fundic glands. Stomach (dog). Simple columnar mucus-secreting epithelium extends into the gastric pits (arrowed). (1) Parietal cell. (2) Zymogen cell. H & E. ×160.
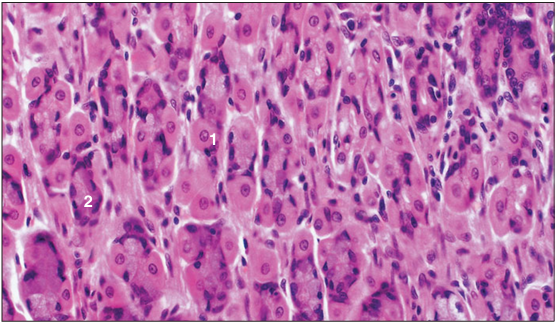
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2.__
Stain used:
Fundic gland. Stomach (cat). (1) Parietal cell. (2) Zymogen cell. H & E. ×250.
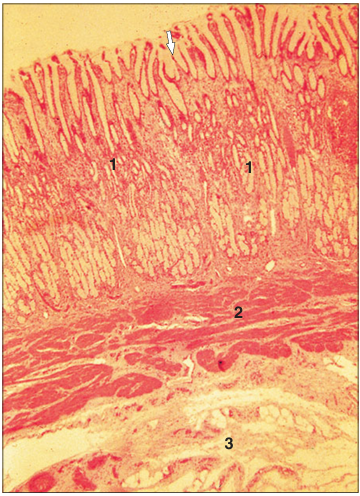
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2.__ 3.__
Stain used:
Pyloric glands. Stomach (pig). Simple columnar mucus-secreting epithelium extends into the gastric pits (arrowed). (1) Simple tubular mucus-secreting glands. (2) Muscularis mucosae. (3) Submucosa. H & E. ×25.
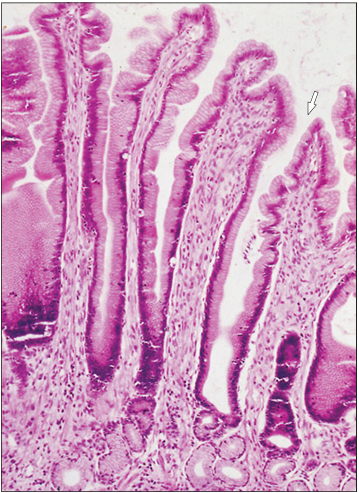
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Stain used:
Pyloric glands. Stomach (dog). Simple columnar mucus-secreting epithelium extends into the gastric pits (arrowed). Simple columnar epithelium lines the gland tubule seen here cut in transverse section. H & E. ×100.
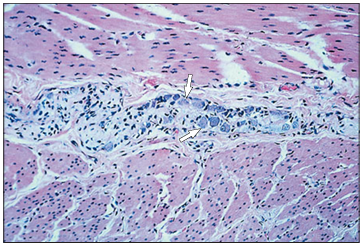
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Stain used:
Myenteric nerve plexus. Stomach (horse). Parasympathetic neuron cell bodies (arrowed) lie in the connective tissue between the smooth muscle layers. H&E. ×125.
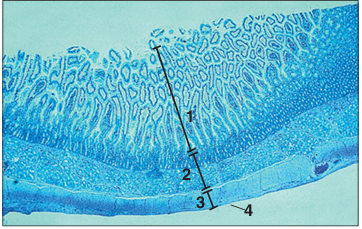
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2.__ 3.__ 4.__
Stain used:
Duodenum (dog). (1) Mucosa. (2) Submucosa. (3) Muscularis externa. (4) Serosa. H & E. ×25.
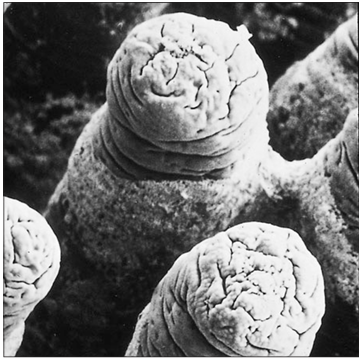
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Stain used:
Duodenal villi (dog). The finger-like villi project into the lumen of the duodenum. Scanning electron micrograph.×100.
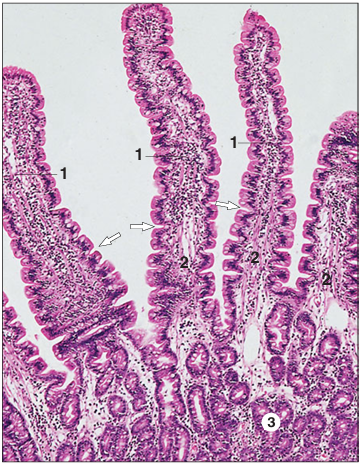
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2.__ 3.__
Stain used:
Duodenum (dog). (1) Villus covered by simple columnar epithelium. (2) Lamina propria forms the core of the villus; the contractile crypts are arrowed. (3) Mucosal glands. H & E. ×62.5.
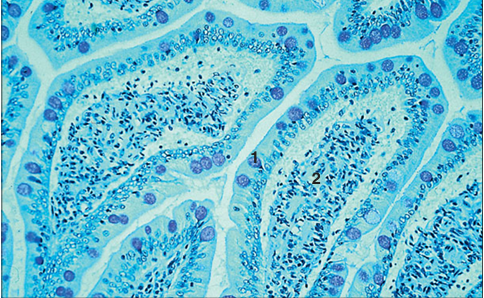
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2.__
Stain used:
Duodenum (horse). (1) Goblet cells in the epithelium are stained deep pink. (2) Lamina propria. Haematoxylin/PAS. ×125.
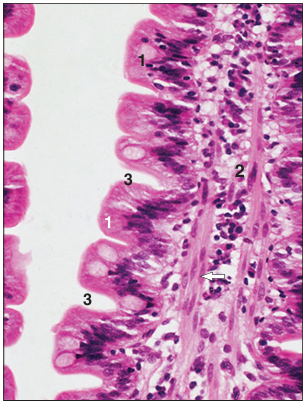
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2.__ 3.__
Stain used:
Duodenum (horse). (1) Simple columnar epithelium with goblet cells. (2) Lamina propria with smooth muscle fibres (arrowed). (3) Contractile crypts. H & E. ×250.
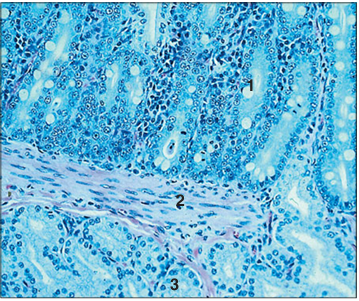
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2.__ 3.__
Stain used:
Duodenum (dog). (1) Mucosal glands. (2) Muscularis mucosae. (3) Submucosal glands. H & E. ×160.
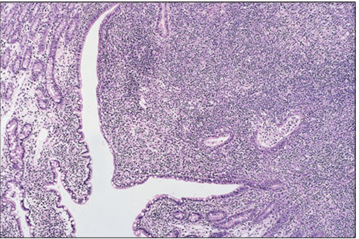
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Stain used:
Duodenum (dog). The lamina propria is filled with lymphatic tissue and lymphocytes are seen migrating through the epithelium (a Peyer’s patch). H.& E. ×12.5.
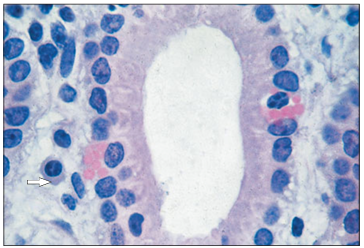
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Stain used:
Globular leucocyte (horse). The globular leucocyte (function unknown) is in the epithelium of the intestinal gland. A plasma cell is present in the lamina propria (arrowed). H & E. ×500.
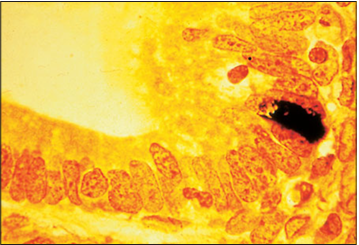
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Stain used:
Enteroendocrine argentaffin cell (cat). Argentaffin cell stains black in the intestinal gland epithelium. Methanamine silver/safranin. ×500.
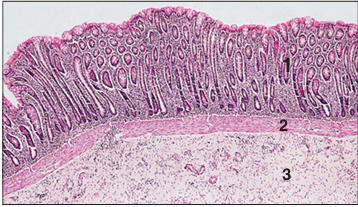
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2.__ 3.__
Stain used:
Colon (horse). (1) Mucosa. (2) Muscularis mucosae. (3) Submucosa. H & E. ×9.7.
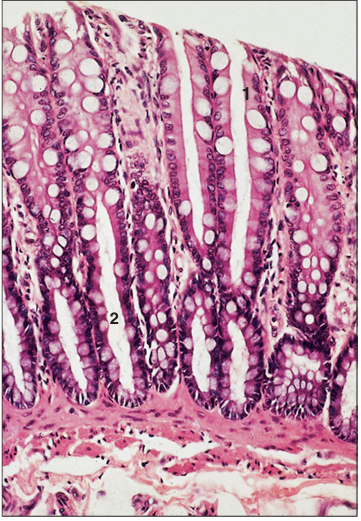
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2.__
Stain used:
Colon (horse). (1) Simple columnar epithelium with goblet cells. (2) Intestinal mucosal glands. H & E. ×125.
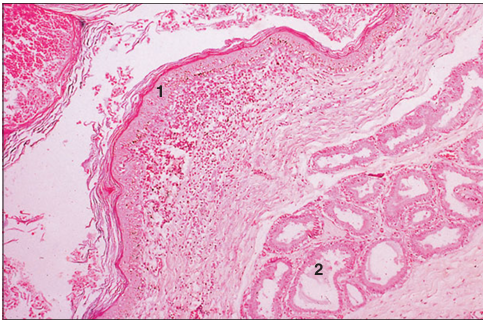
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2.__
Stain used:
Anal sac (dog). (1) Stratified squamous keratinized epithelium lines the sac. (2) Tubuloalveolar glands in the lamina propria. H & E. ×12.5.
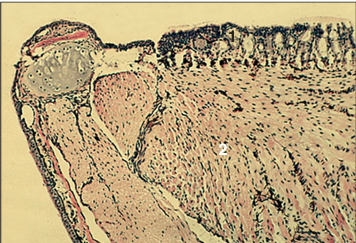
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2.__
Stain used:
Tongue of a poison-arrow frog (Dendrobatesspp.). The dorsal lingual surface (1) is covered by an unusual and complex epithelium composed of small, dark-staining cuboidal cells and acini of sticky mucin-secreting columnar cells that maintain a coating of adhesive mucus. The muscle fibres (2) are primarily arranged in a longitudinal direction and are attached at the front of the mandible. This facilitates the tongue being rapidly protruded and retracted in order to catch small invertebrates. H & E. ×12.5.
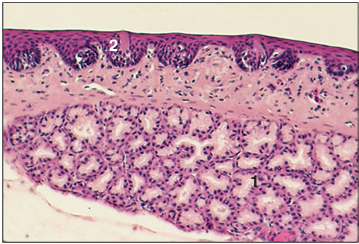
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2.__
Stain used:
The tongue of some lizards overlies a sublingual salivary gland (1), as is illustrated by this longitudinal section of the tongue of a small skink (Scincella lateralis). The dorsal surface is covered by a non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium (2) in which cup-shaped taste receptors are embedded. Some lizards (for example, many iguanines) possess tongues with a terminal tip composed of papillary projections that are kept moist and sticky with mucus secreted by goblet cells and several salivary glands. H & E. ×62.5.
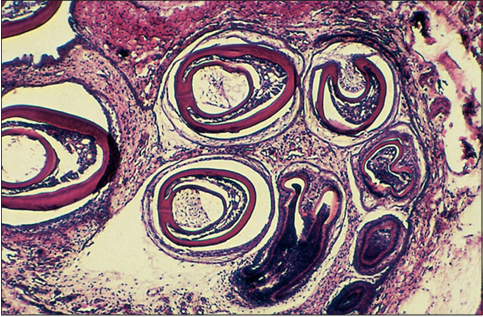
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Stain used:
The fangs of venomous snakes are continually being renewed. Illustrated are several teeth primordia of a juvenile rattlesnake (Crotalus spp.), forming modified fangs with a central enamel-lined channel through which venom is conducted. H & E. ×12.5.
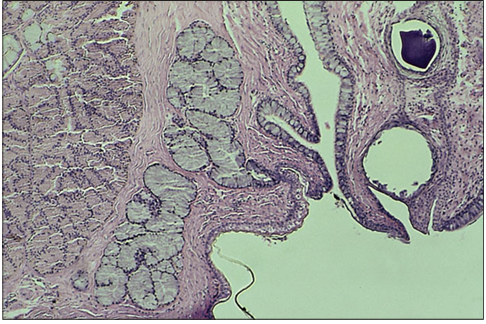
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Stain used:
Some non-venomous snakes possess modified (Duvernoy’s) maxillary and premaxillary salivary glands connected to short ducts that empty into the oral cavity. Current studies indicate that the secretions from some of these glands manifest venom-like bioactivity on the lower vertebrate prey of these snakes. Also, mild clinical envenomation of sensitive humans bitten by these snakes has been reported. Illustrated are two lobules of gland from a watersnake (Natrix cyclopion). H & E. ×62.5.
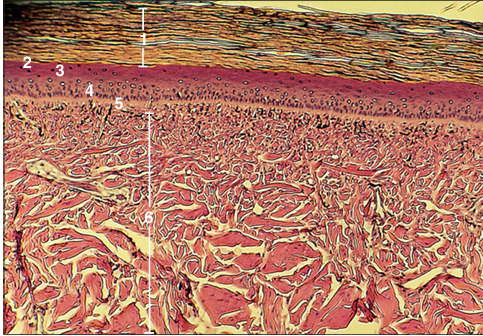
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2.__ 3.__ 4.__ 5.__ 6.__
Stain used:
The oesophageal lumen of many chelonians, such as this green sea turtle (Chelonia mydas), is heavily keratinized and lacks mucus-secreting goblet cells. These characteristics reflect the scabrous diet of these marine animals. (1) Stratum corneum. (2) Stratum lucidum. (3) Stratum granulosum. (4) Stratum spinosum. (5) Stratum basale. (6) Muscularis externa. H & E. ×12.5.

Identify the structure:
Specie:
Stain used:
The oesophagus of most snakes and many lizards is characterized by its extensive plaiting which permits the oesophagus to stretch to accommodate enormous prey. Illustrated is a cross-section of the oesophagus of a kingsnake (Lampropeltis triangulum). Because of the necessity for abundant lubrication during the swallowing of furry, feathered or scaly prey, the oesophageal lumen is lined by a mucous epithelium composed of simple non-keratinized columnar cells bearing basal nuclei. H & E. ×62.5.
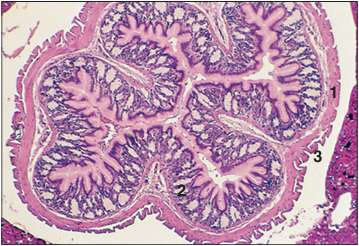
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2.__ 3.__
Stain used:
Whole mount cross-section of the fundic stomach of a small skink (Scincella lateralis). A very thin serosa covers the outermost visceral surface. The gastric wall is composed of an outer external longitudinal muscularis externa (1), a circular muscularis externa, the muscularis mucosa), and immediately beneath is the glandular mucosa (2) which is composed of pink staining granular chief cells and clear cells. The lumen is lined by tall mucus secreting columnar cells. Parietal cells, present in mammalian gastric mucosae, are lacking in amphibians and reptiles. The outermost surface of the stomach is covered by a delicate serosa (3) formed of non-keratinized squamous cells. H & E. ×12.5.
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2.__
Stain used:
Gastric mucosa of a boa constrictor (Boa constrictor). The lumen is covered by tall columnar epithelium. The gastric glands consist of only granular, cuboidal, pink staining chief cells (1) with large vesicular nuclei, and pale staining clear cells (2) whose nuclei are dark and basal. Some gastric pits are lined by both cell types. H & E. ×250.
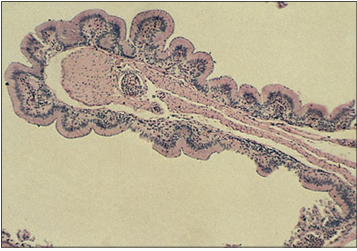
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Stain used:
The colon of some lizards, particularly folivorous species, is a highly modified sacculated organ divided into multiple chambers that are functionally analogous to the hindgut of lagamorphs and some (herbivorous/folivorous) rodents, and the forestomachs of ruminants. Digestion is enhanced because the villous surface of the colon is covered by a highly absorptive columnar mucosa across which nutrients processed from cellulose-digesting micro organisms are assimilated. The elongated villi that cover the surface are supported, and stiffened, by thin cores of smooth muscle. Illustrated is the sacculated colon of a green iguana (Iguana iguana). H & E. ×12.5.
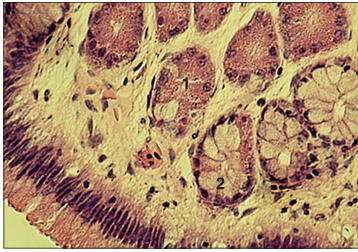
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__
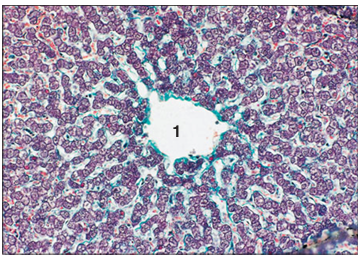
Stain used:
Liver (pig). The heaxagonal liver lobule is delineated by the green strands of the interlobular connective tissue. (1) Central vein. Masson’s trichrome. ×125.
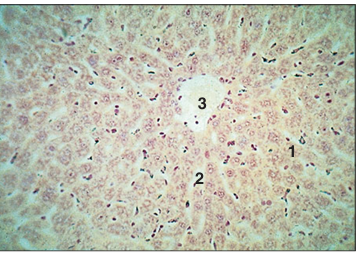
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2.__ 3.__
Stain used:
Liver (ox). (1) Hepatocytes arranged in cords. (2) Sinusoids lined by endothelial cells and macrophages open into (3) the central vein. Safranin/haematoxylin. ×125.
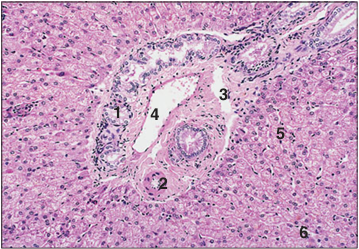
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2.__ 3.__ 4.__ 5.__ 6.__
Stain used:
Portal canal (triad) (sheep). (1) Branch of the bile duct. (2) Hepatic artery. (3) Lymphatic vessel. (4) Hepatic portal vein. (5) Liver cords. (6) Sinusoids. H & E. ×125.
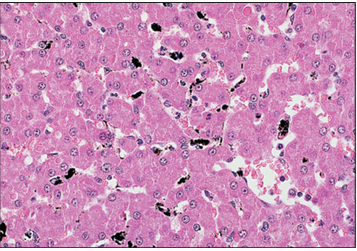
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Stain used:
Liver (dog). The macrophages have taken up the injected carbon and appear as black areas between the cords of hepatocytes. Carbon-injected with H & E counterstain.×125.
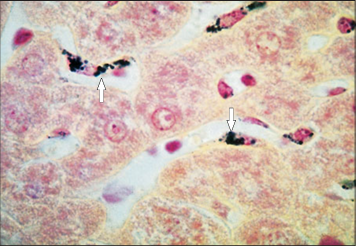
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Stain used:
Liver (dog). The hepatocytes lie in anastomosing cords separated by sinusoids lined by macrophages (arrowed). Safranin/haematoxylin after carbon injection. ×250.
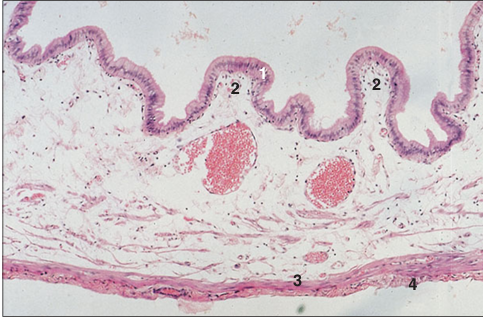
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2.__ 3.__ 4.__
Stain used:
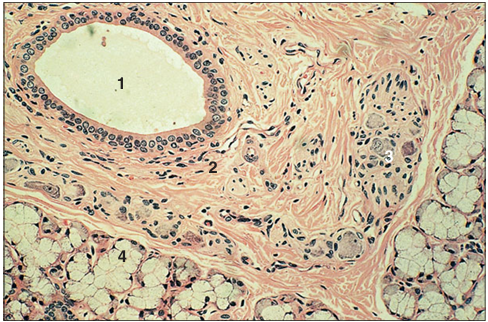
Gall bladder (cow). (1) Tall columnar epithelium lining the lumen. (2) Mucosal folds. (3) Muscularis. (4) Serosa. H & E. ×12.5.
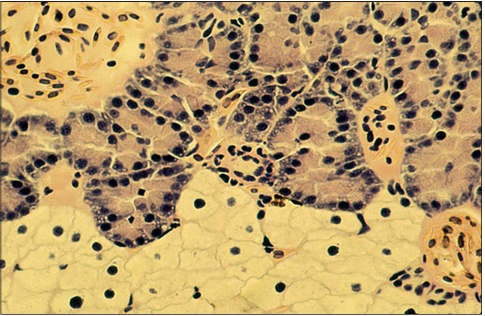
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Stain used:
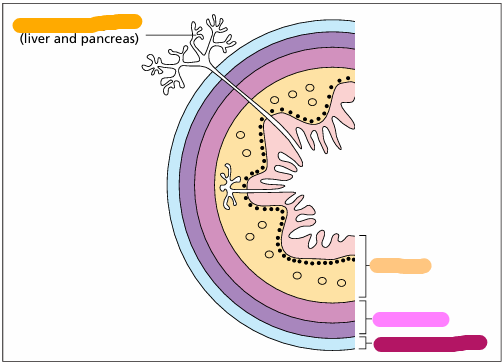
The liver and pancreas of some fish, amphibians and reptiles are fused or admixed with one another and form a hepatopancreas. Illustrated is a section of such a mixed organ in an axolotl, a neotenic form of the aquatic salamander (Ambystoma maculatum). The hepatocellular tissue is at the bottom of this section; the exocrine pancreatic portion is in the upper right; an islet is in the upper left. H & E. ×250.
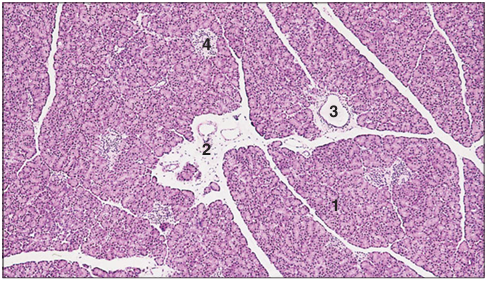
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2.__ 3.__ 4.__
Stain used:
Pancreas (dog). (1) Serous acini of the exocrine pancreas. (2) Interlobular connective tissue. (3) Interlobular duct. (4) Pancreatic islet, the endocrine pancreas. H & E. ×12.5.
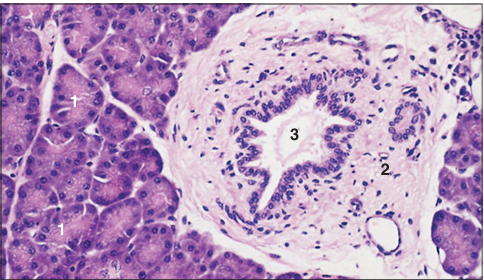
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2.__ 3.__
Stan used:
Pancreas (dog). (1) Serous acinus with a centroacinar cell (arrowed). (2) Interlobular connective tissue. (3) Interlobular duct. H & E. ×125.
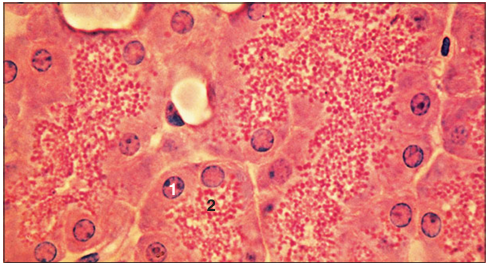
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2.__
Stan used:
Pancreas (dog). (1) Nucleus lies in the basal basophilic cytoplasm of the serous cell. (2) Eosinophilic granules (the secretion) lie in the luminal cytoplasm. H & E. ×250.
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2.__
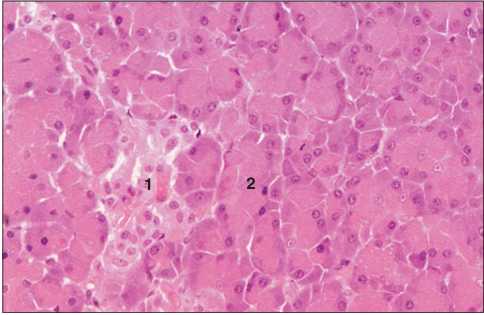
Stan used:
Pancreatic islet. Pancreas (cat). (1) Pale staining endocrine cells form cords associated with capillaries. (2) Exocrine acinus. H & E. ×125.
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Stain used:
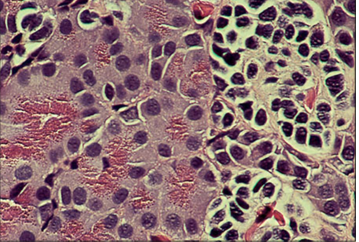
Pancreas of a salamander (Amphiuma tridactyla). Exocrine pancreatic cells characterized by their fine granular eosinophilic cytoplasm (on the left) extend a finger-like isthmus into the islet of paler staining endocrine cells bearing dense nuclei (on the right). The islet cells are arranged into nest-like lobules that are separated from each other and from the exocrine tissue by thin strands of connective tissue that support small blood vessels. H & E. ×250.
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Stain used:
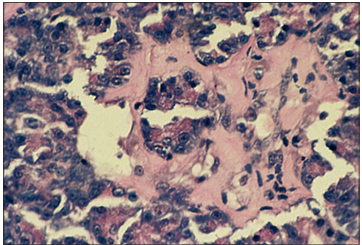
The splenopancreas of a milksnake (Lampropeltis triangulum). The spleen is on the right, a large aggregate of islet tissue is in the middle and a portion of the exocrine pancreatic tissue is on the left. The islet displays hyalinization. H & E. ×125.
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Stain used:
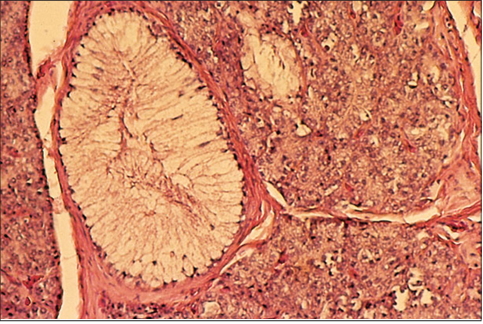
The pancreas of some snakes, particularly many pythons, is characterized by possessing endocrine cells formed into giant islets (often found at the edge of the lobule) rather than into many small nests of cells scattered randomly throughout the parenchyma. Illustrated is a section of the pancreas from a regal (ball) python (Python regius). H & E. ×125.
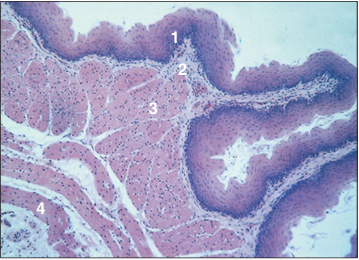
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2.__ 3.__ 4.__
Stan used:
Crop (bird). (1) Stratified squamous non-keratinized epithelium. (2) Lamina propria. (3) Muscularis mucosae. (4) Muscularis externa. H & E. ×12.5.
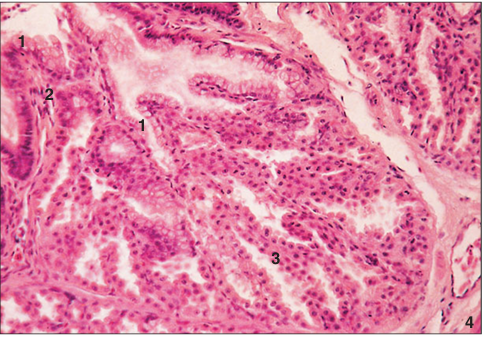
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2.__ 3.__ 4.__
Stan used:
Proventriculus (bird). (1) Simple columnar mucus-secreting epithelium. (2) Lamina propria. (3) Submucosal glands. (4) Muscularis externa. H & E. ×62.5.

Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2.__ 3.__ 4.__
Stan used:
Proventriculus (bird). (1) Simple columnar mucus secreting epithelium. (2) Lamina propria. (3) Submucosal glands. (4) Muscularis externa. Masson’s trichrome. ×25
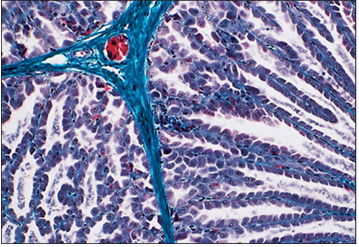
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Stain used:
Proventriculus (bird). The submucosal gland lobules are separated by thin strands of connective tissue. Masson’s trichrome. ×250.
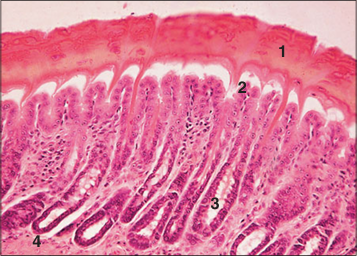
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2.__ 3.__ 4.__
Stan used:
Ventriculus, gizzard (bird). (1) Cornified lining. (2) Epithelium lining the gizzard. (3) Mucosal glands. (4) Lamina propria. H & E. ×25.
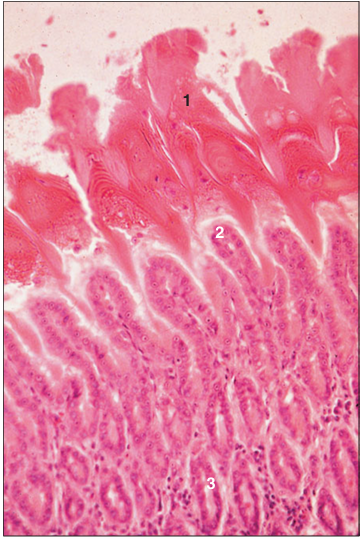
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2.__ 3.__
Stan used:
Ventriculus, gizzard (bird). (1) Cornified lining. (2) Lining epithelium. (3) Mucosal glands. H & E. ×125.
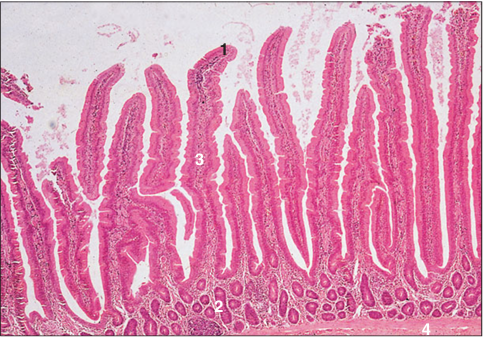
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2.__ 3.__ 4.__
Stan used:
Duodenum (bird). (1) Simple columnar epithelium. (2) Intestinal mucosal glands. (3) Connective tissue core of the villus. (4) Muscularis mucosae. H & E. ×62.5.
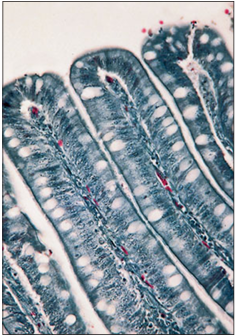
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Stain used:
Duodenum (bird). The simple columnar epithelium lining the duodenum has a striated border to allow absorption and goblet cells. Masson’s trichrome. ×125.
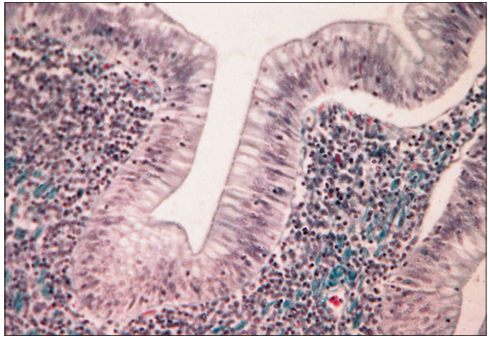
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Stain used:
Duodenum (bird). The simple columnar epithelium rests on a lamina propria with numerous lymphatic cells. Masson’s trichrome. ×250.
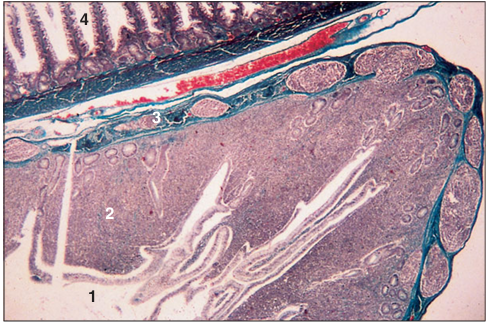
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2.__ 3.__ 4.__
Stan used:
Caecum (bird). (1) Lumen of the caecum. (2) Mucosa consists of a columnar epithelium and a lamina propria with extensive deposits of lymphatic tissue. (3) Muscularis. (4) Lumen of the duodenum. Masson’s trichrome. ×12.5.
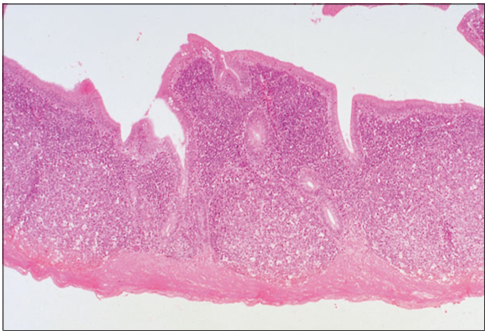
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Stain used:
Caecum (bird). Dense masses of lymphatic tissue fills the lamina propria. H & E. ×12.5.
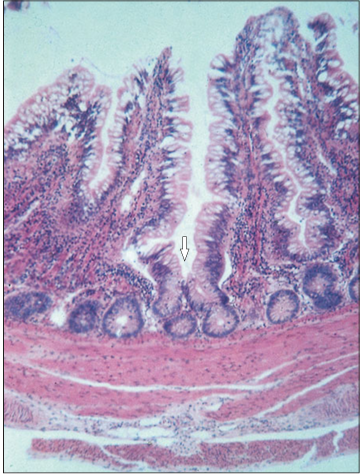
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Stain used:
Rectum (bird). The lining epithelium is simple columnar with goblet cells extending into the simple tubular mucosal glands (arrowed). H& E. ×62.5.
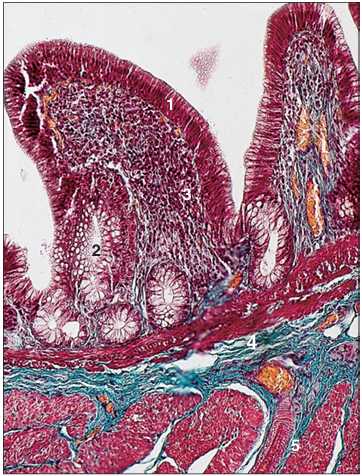
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2.__ 3.__ 4.__
Stan used:
Cloaca (bird). (1) Simple columnar lining epithelium. (2) Simple tubular glands. (3) Lamina propria with lymphatic tissue. (4) Muscularis mucosae. (5) Muscularis externa. Alcian blue/PAS. ×62.5.
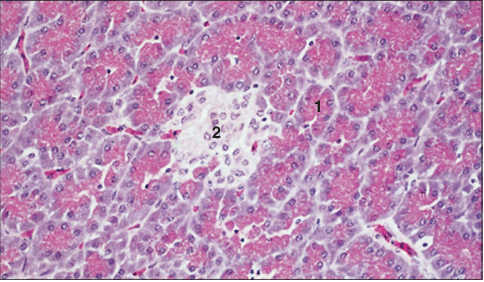
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2.__
Stan used:
Pancreas (bird). (1) Serous units of the exocrine gland. (2) Pancreatic islet, the endocrine gland. H & E. ×125.