L22 - Dams
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
what are hydroelectric dams?
dam that creates a reservoir of water and uses high → low elevation difference to drive turbines
picture of hydroelectric dam
goes from reservoir of high elevation, through turbine, and river of low elevation
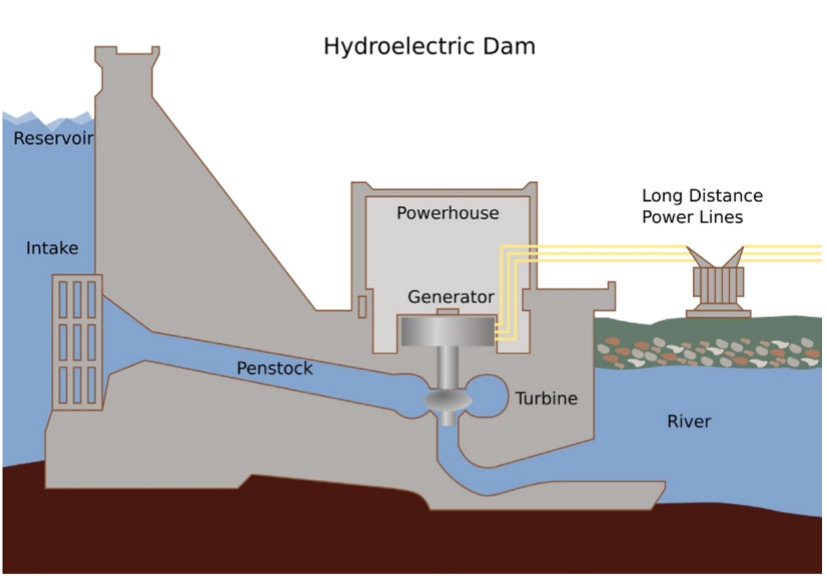
what are the pros of hydroelectric dams? (4)
long lifespan
low operating costs
domestic and renewable source of energy
stored as potential energy, which is ideal for meeting peak demands
what are the cons of hydroelectric dams? (5)
high capital cost
long construction periods
flood vast tracts of land
hurts fish/other wildlife habitats
risk to downstream communities from a dam in the event of a dam catastrophe
dam terminology picture
upstream:
gallery - room in left of dam for dam operations
downstream:
spillway: construction used to release excess reservoir water
sluiceway: dam opening near ground used to clear silt accumulation from reservoir
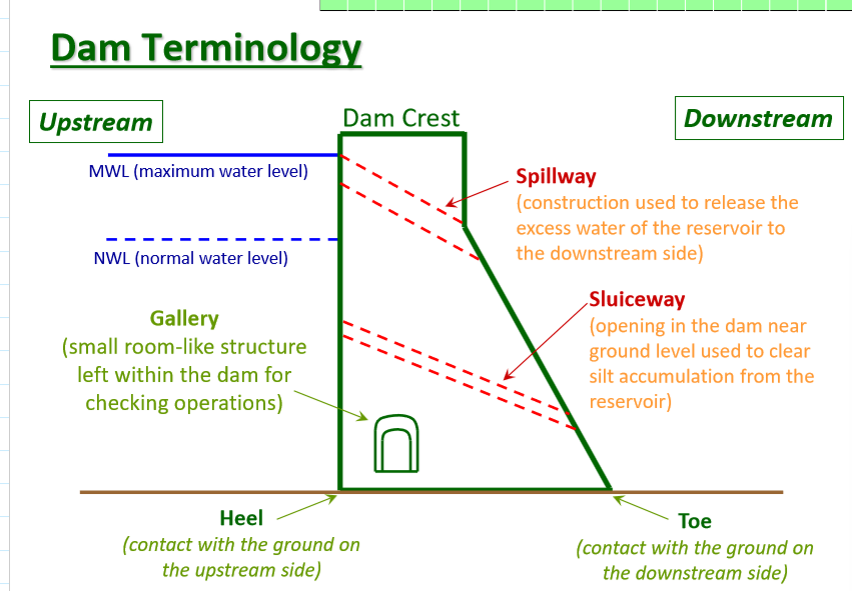
how are dams built? what four tools are used?
cofferdam: temporary barrier redirecting water into a diversion tunnel, preventing river flow through dam construction
abutments: sides of the valley where the dam structure rests
foundation: floor of valley where the dam sits
diversion tunnel: tunnels made to divert water before construction of the dam, keeping the river bed dry
what are the types of dams?
concrete dams
earth dams
composite dams (both concrete/earth)
what factors are considered when designing a dam?
dam stability
spillway
dam leakage
reservoir slopes
what are the types of concrete dams?
gravity
arch
buttress
concrete-face (hybrid)
what are the pros of concrete dams?
rigid and offers more resistance to compression
resistance to water erosion
resistance to overtopping and piping failure
can be shaped to support imposed loads
what are the cons of concrete?
concrete is expensive
lots of labour required
low tensile strength, susceptible to different settlements
how do gravity dams work? when are they best used?
use their bulk weight and a low centre of gravity to hold back water
best used for long distances over flat terrain (non-mountainous regions)
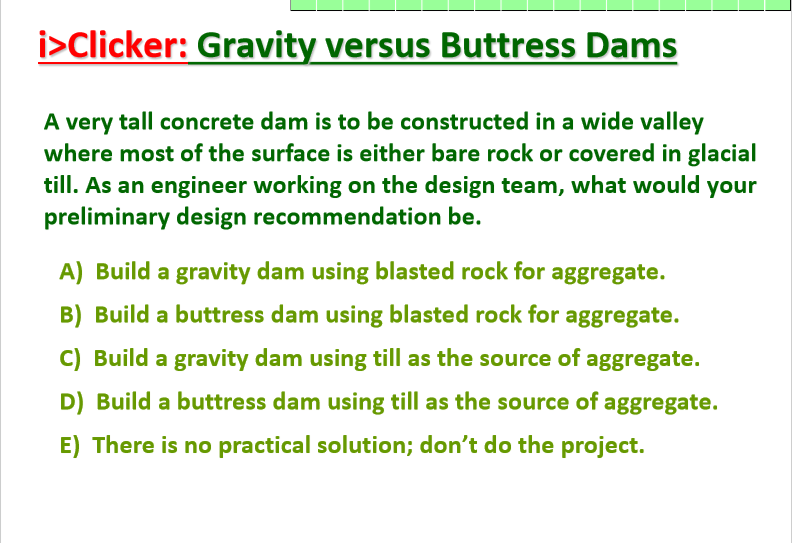
gravity vs buttress dams question
A: gravity dams can support tall loads, and till is uncertain and is not the best choice of aggregate.
what are buttress dams? what is their limitation?
dams that use multiple reinforced columns to support a dam with a thin structure
because it uses less concrete, this limits their height
what are arch dams? what is unique about them? contrast with gravity dams.
dams that utilize strength of an arc shape
uses less materials than gravity dams, but are more expensive due to the higher expertise needed to build them
where are arch dams built?
narrow, deep river gorges
can only be built where the walls of a canyon are definitely stable and will not leak
what are bad geological conditions for a dam’s foundation?
flat faults with sheared materials of low strength
folded rocks with thin, weak layers of shale, which has the potential for foundational failure
weak soils susceptible to liquefaction
highly permeable soils
what are earth dams. what is their shape like?
dams built with clay, sand, and gravel ( “earth fill”)
smaller in height, broad base, trapezoidal shape
what are the pros of earth dams?
can accommodate more differential settlement compared to concrete dams
safest dam type against risk of earthquake damage
what are the cons of earth dams?
large size of earth dams requires large volumes of suitable materials with varied grain sizes
susceptible to wave erosion
susceptible to catastrophic failure if overtopped/piping fail
not long-lasting
requires extra care with internal design
picture of earth dam components, list earth dam components
filter
shoulder
core
transition zone
toe drain
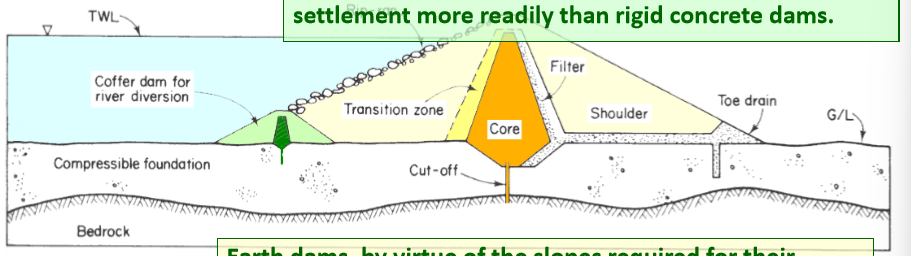
how does water pass through an earth dam?
through the filter, shoulder, then toe drain
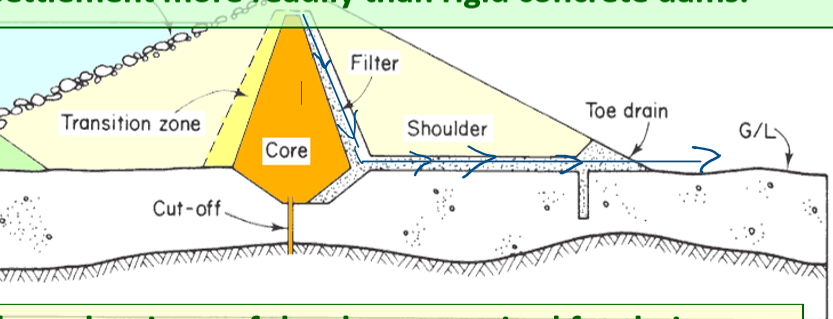
how do earth dams impose lower stresses on ground compared to concrete dams?
broad base
what kind of materials are needed for earth dam construction?
large amounts of clay, sand, and gravel
how do glacial deposits provide earth dam construction material (clay, sand, gravel)?
clay: deposited in still water in front of retreating glaciers or in glacier lakes
sand/gravel: eskers and outwash plans are easy/accessible sources for sand/gravel
how does overtopping work
overtopping causes erosive action of water
continuous water flow erodes through dam
what is the risk of pipe failure in dams?
if seepage is uncontrolled, then it can erode soil from foundation or dam, resulting in rapid failure of dam
what geomechanical and hydrogeological factors are there to consider when designing/maintaining an earth dam?
overtopping
piping - seepage due to water percolating through the dam/dam foundation, seepage must be controlled
seepage control
what are the causes of piping failures?
poor construction methods
using the wrong type of construction materials

during construction of an earth dam, great effort is taken to compact the clay core. Why?
E - both B (increase strength of the clay) and C (decrease permeability of the clay)