V Biology - Nutrition in Plants
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Word equation for Photosynthesis
carbon dioxide + water —> glucose + oxygen
Balanced chemical equation for Photosynthesis
6CO2 + 6H2O —> C6H12O6 + 6O2
The process of Photosynthesis
Light energy is used to split water, releasing oxygen gas and hydrogen ions.
Carbon dioxide gas combines with the hydrogen to make glucose.
This is important in order for the plant to maintain/ gain energy and continue to grow
Use of Magnesium Ions
Chlorophyll
Magnesium Deficiency
Plant leaves appear yellow
Use of Nitrate Ions
Amino acids
Nitrate Deficiency
Poor growth and yellow leaves
Use of Mineral Ions
Growth
Bioaccumulation
Bioaccumulation occurs when toxins build up - or accumulate - in a food chain. The animals at the top of the food chain are affected most severely.
Biomagnification
The rise or increase in the contaminated substances caused by the intoxicating environment.
Causes of Eutrophication
Some pollutants affect the environment by disrupting the equilibrium in food chains:
Sewage
Nitrate Fertilisers
Pesticides
Adaptations of the leaf for Photosynthesis
Adaption | Large surface area |
|---|---|
Purpose | To absorb more light |
Adaption | Thin |
|---|---|
Purpose | Short distance for carbon dioxide to diffuse into leaf cells |
Adaption | Chlorophyll |
|---|---|
Purpose | Absorbs sunlight to transfer energy into chemicals |
Adaption | Network of veins |
|---|---|
Purpose | To support the leaf and transport water, mineral ions and sucrose (sugar) |
Adaption | Stomata |
|---|---|
Purpose | Allow carbon dioxide to diffuse into the leaf and oxygen to diffuse out |
Adaption | Epidermis is thin and transparent |
|---|---|
Purpose | To allow more light to reach the palisade cells |
Adaption | Thin cuticle made of wax |
|---|---|
Purpose | To protect the leaf from infection and prevent water loss without blocking out light |
Adaption | Palisade cell layer at top of leaf |
|---|---|
Purpose | To absorb more light and increase the rate of photosynthesis |
Adaption | Spongy layer |
|---|---|
Purpose | Air spaces allow gases to diffuse through the leaf |
Adaption | Palisade cells contain many chloroplasts |
|---|---|
Purpose | To absorb all the available light |
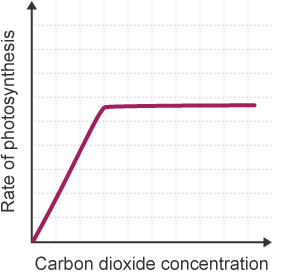
Effect of Carbon Dioxide on rate of photosynthesis
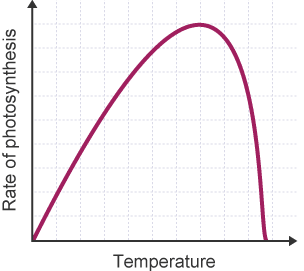
Effect of Temperature on rate of photosynthesis
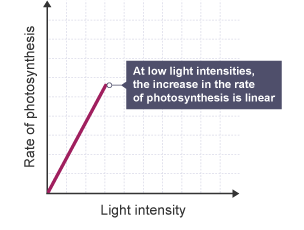
Effect of Light Intesity on rate of photosynthesis