Phyl 141 ( Exam 2 )
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Articular Cartilage
Protects the ends of the bones
Fat Pads
Protects the Cartilage
Ligaments
- Support the Joints
- Connect the bones to other bones
Bursa
- " Purses " of synovial fluid that cushion and reduce friction
3 types of Dynamic Motion
- Linear Movement (Gliding)
- Angular Movement
- Rotation
Gliding Joints
Sternoclavicular
Angular Movement
Hemeroulnar
Monaxial
1 axis
Biaxial
2 axes
Triaxial
3 axes
Sagittal plane
Divides the body into left and right
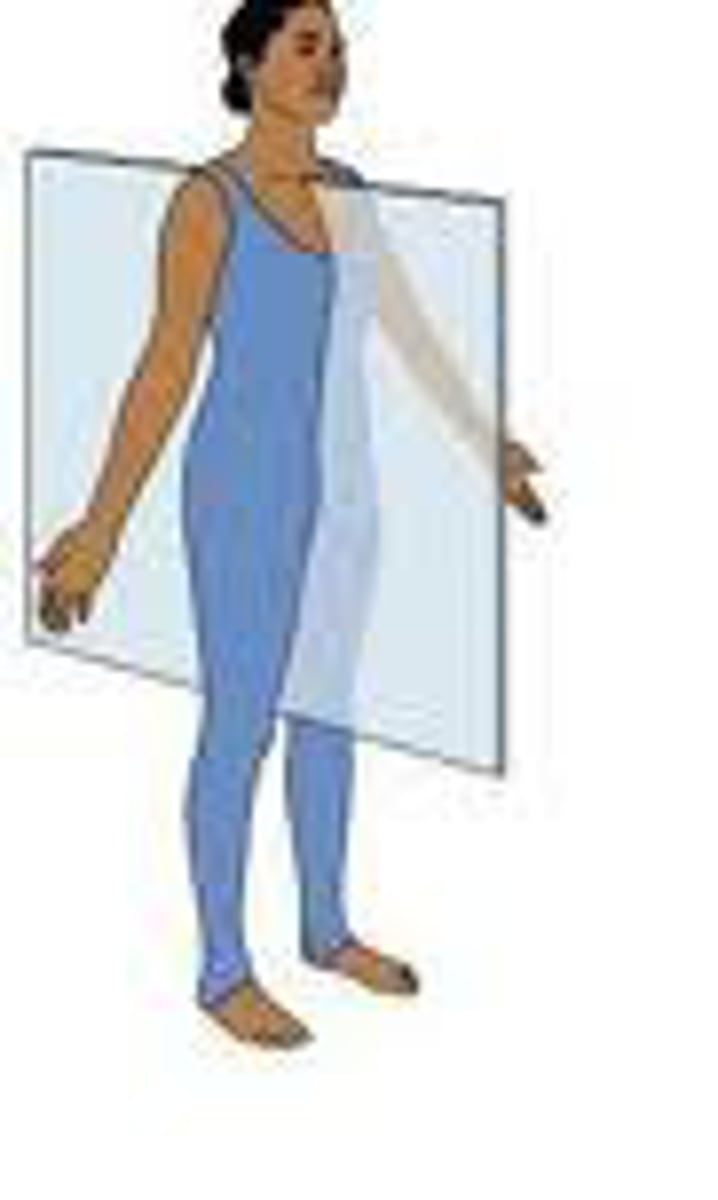
Frontal/Coronal
Divides the body into front and back
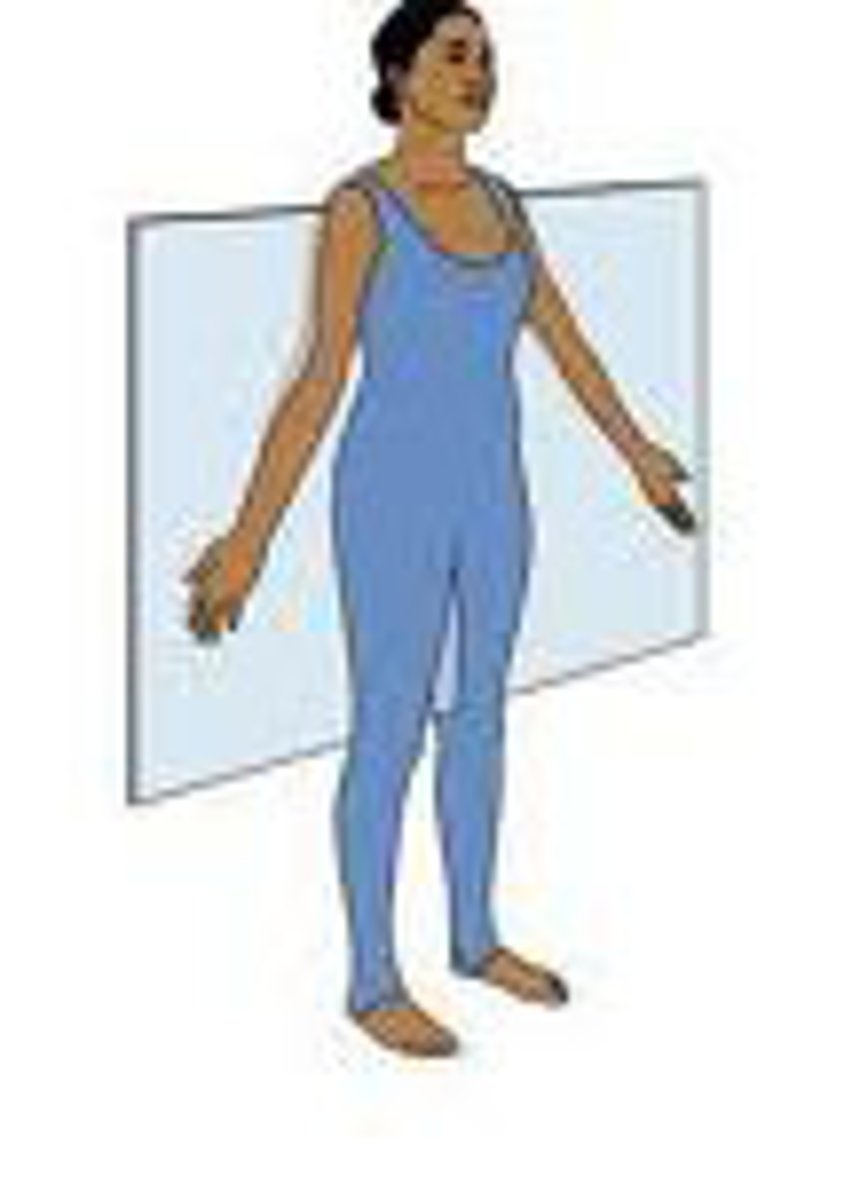

Horizontal/Transverse Plane
Divides the body in half: Superior and inferior parts
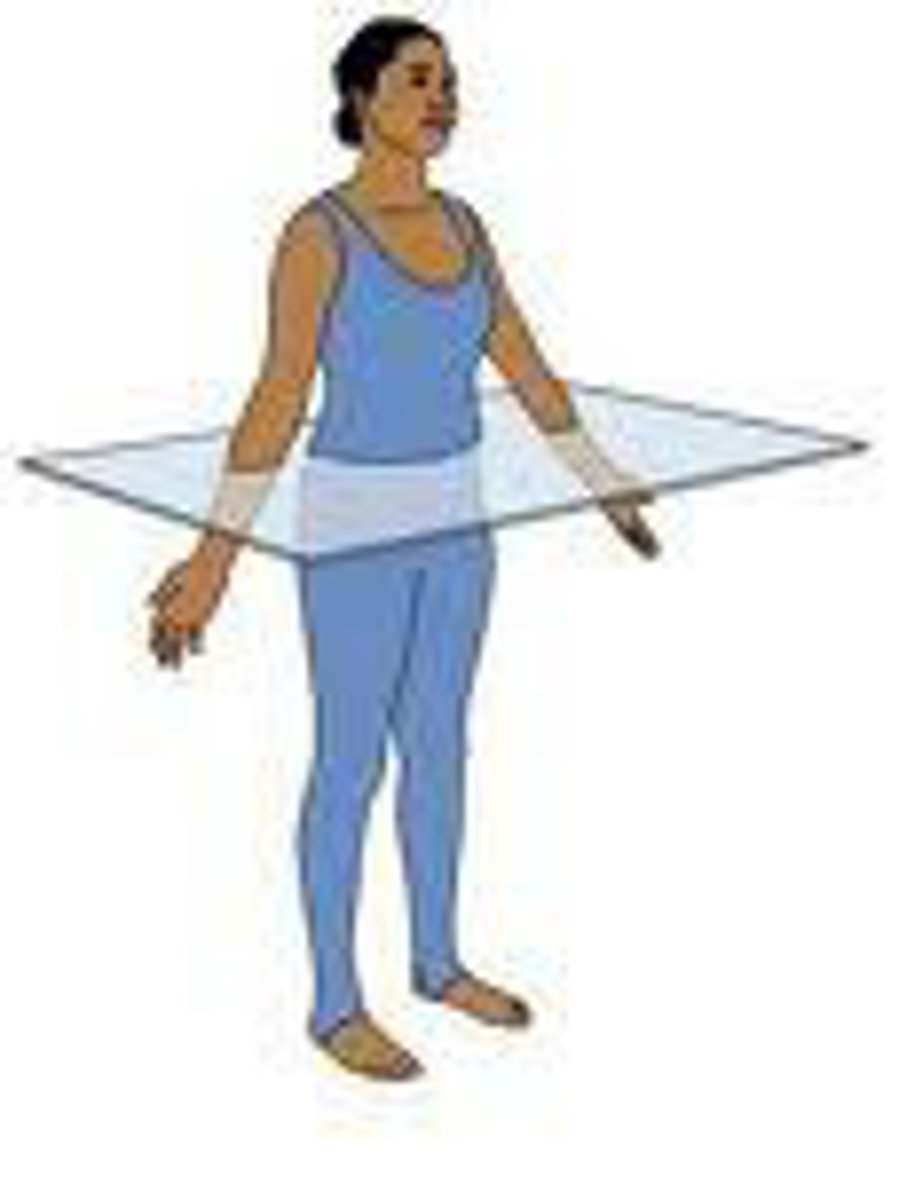
Biaxial Movement
Metacarpophalangeal
Triaxial Movement
Acetabulofemoral
Saddle Joint
Metacarpotrapezial
Metacarpophalangeal Abduction
Fingers spread
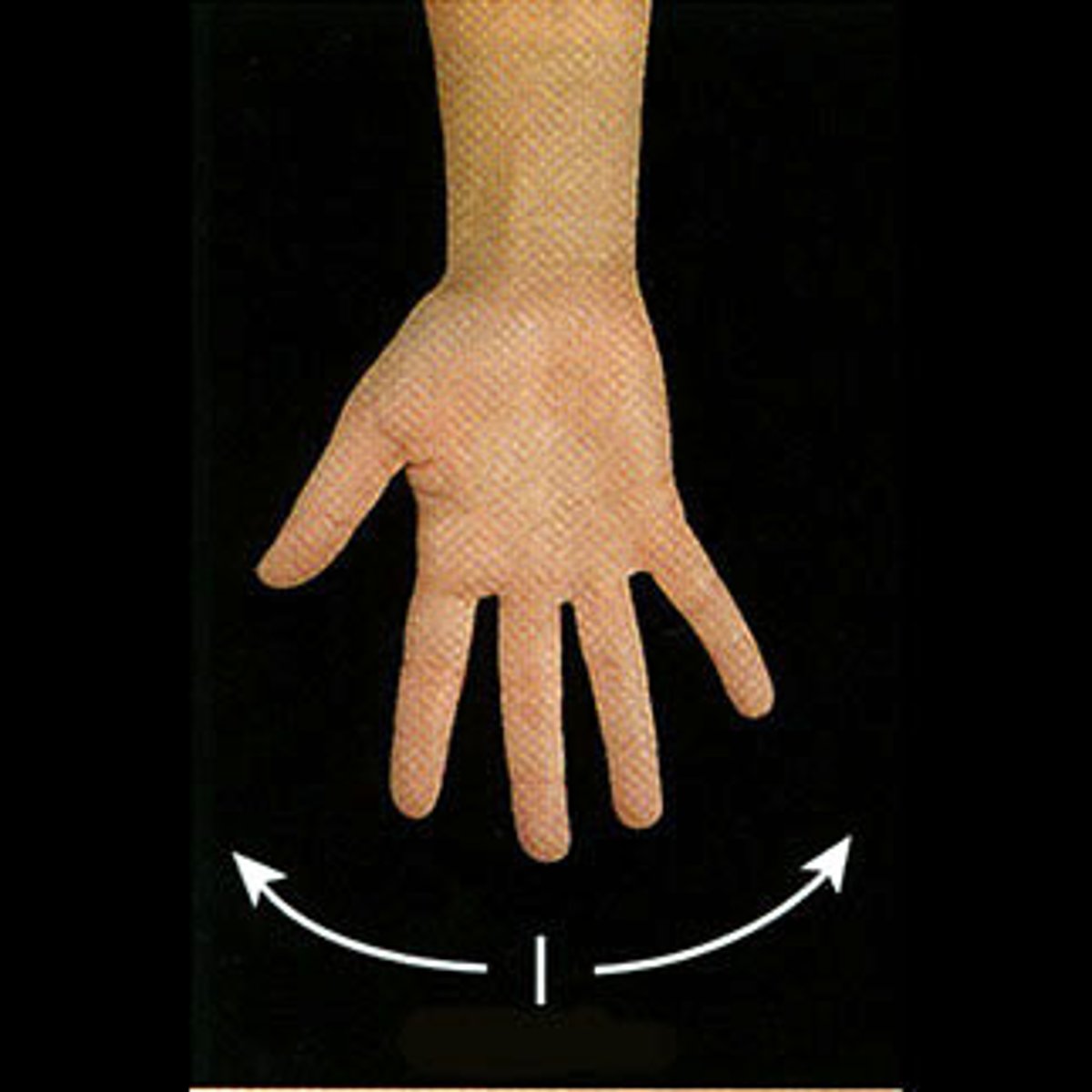
Metacarpophalangeal Adduction
Fingers together
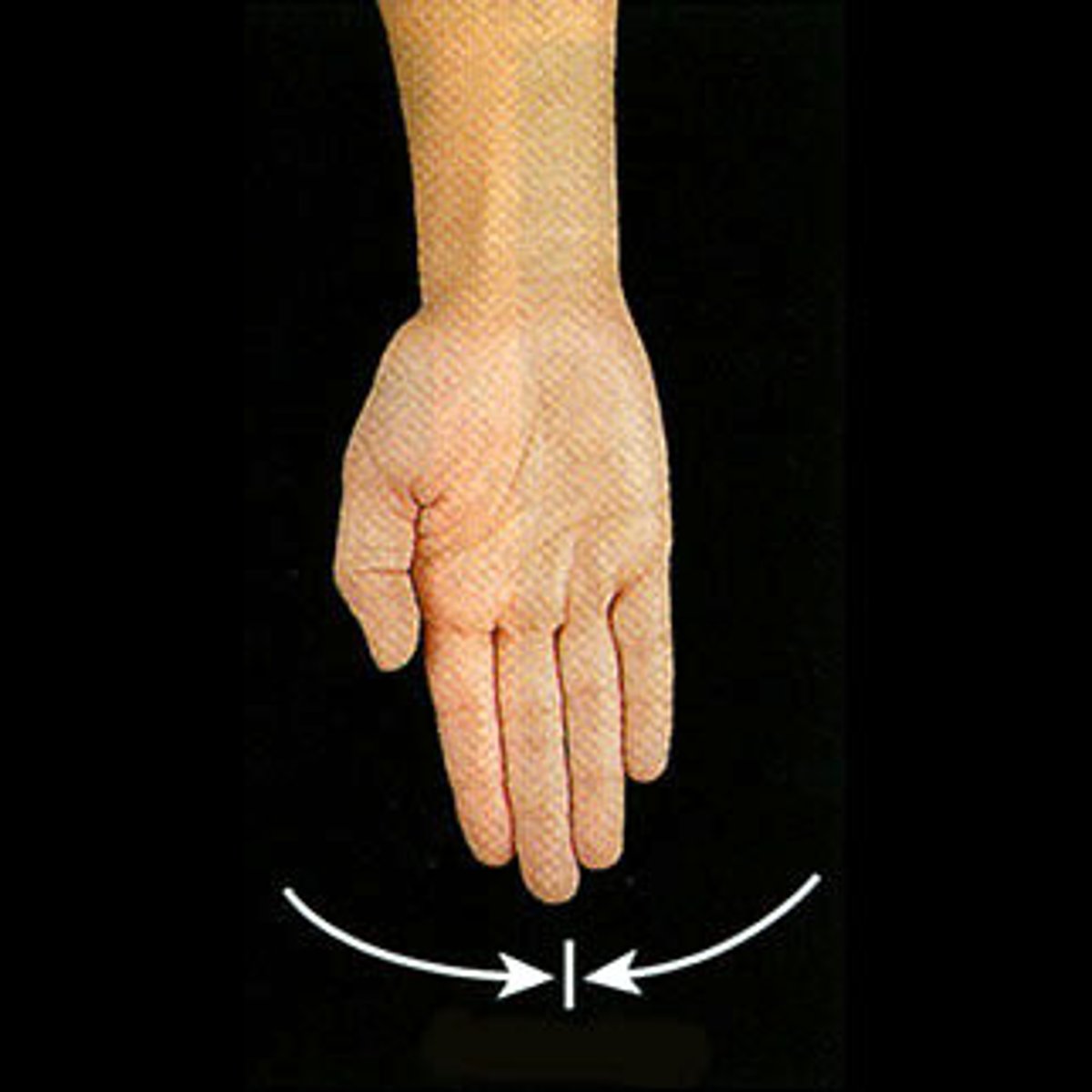
Dorsiflexion
Flexion at the ankle joint and the elevation of the sole
Protraction
Moving a body part anteriorly
Superior Rectus
Moves your eye up
Lateral Rectus
Moves eye left/right
Medial Rectus
Moves eye left/right
Inferior Rectus
Moves eye down
What happens during the power stroke?
The thin filaments slide toward the M line.
Which of the following is an example of an isometric contraction?
Holding a heavy stack of books above the ground
What is the effect of acetylcholine on the motor end plate of the muscle cell membrane?
Increasing the permeability to Na+, causing Na+ to diffuse into the muscle cell
All of the muscle fibers controlled by a single motor neuron constitute a __________.
motor Unit
The neurotransmitter required to trigger skeletal muscle contraction is __________.
Acetylcholine ( ACh )
Why is control over leg muscles LESS precise than control over the muscles of the eye?
Many muscle fibers are controlled by a single motor neuron.
How does the release of calcium ions from the terminal cisterns initiate contraction?
It triggers the binding of myosin to actin.
What causes the myosin head to reenergize itself once the power stroke has occurred?
The myosin head splits a fresh ATP molecule.
What happens when multiple stimuli are applied to a muscle fiber and tension production is gradually increasing?
Wave summation
The process of complete tetanus is reached by __________.
increasing the rate of stimulation until the relaxation phase is completely eliminated
Excitation-contraction coupling forms the link between __________.
Electrical activity in the sarcolemma and the initiation of the contraction
What is happening during the contraction phase of a single twitch?
The muscle is producing tension.
A muscle producing almost peak tension during rapid cycles of contraction and relaxation is said to be in __________.
incomplete tetanus
WEBSITE
http://www.easynotecards.com/notecard_set/28906