medieval europe: all cards
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
when was the Magna Carta signed?
June 15, 1215.
who was forced to sign the Magna Carta?
King John of England was forced to sign the Magna Carta.
what is one significant impact of the Magna Carta?
influenced the development of constitutional law and limited government
what institution did the Magna Carta help establish?
helped lay the groundwork for the establishment of Parliament.
the Magna Carter =
the Great Charter
bubonic, pneumonic, septicaemic
the three types of plagues
Yersinia pestis
a bacteria; the cause of the disease
rat flea
the organism which is first infected by the bacteria
rats
the organism which is infected second
origin
541CE - Constantinople, capital of the Byzatine Empire and the largest city in the world
symptoms - bubonic
swollen lymbh nodes (buboes)
high fever
pain
coughing
vomiting blood
black dots over body
likelihood of death - bubonic
30-70%
spread - bubonic
human ➡ human
symptoms - pneumonic
coughing up blood
fever
headache
likelihood of death - pneumonic
90-95%. lived 2-4 days
spread - pneumonic
human ➡human (droplets coughed from the lungs of the infected, common in cold regions, extremely contagious)
causes of the black death
bitten by fleas, contamination of bodily fluids, poor hygeine
consequences
decline in population (approx. 1/3-2/3), loss of faith in the church, increased faith in God, peasants could ask for more pay
symptoms - septicaemic
bleeding
organ faliure
fever
internal bleeding ➡skin turned dark purple
see blood through the skin
likelihood of death - septicaemic
100%
spread- septicaemic
least common, most deadly, blood was infected by the bacterium, infection prevented body from forming blood clots (which would heal)
general role
protected from invasions, established power, home to nobility and peasants, built quickly, strong lines of defence
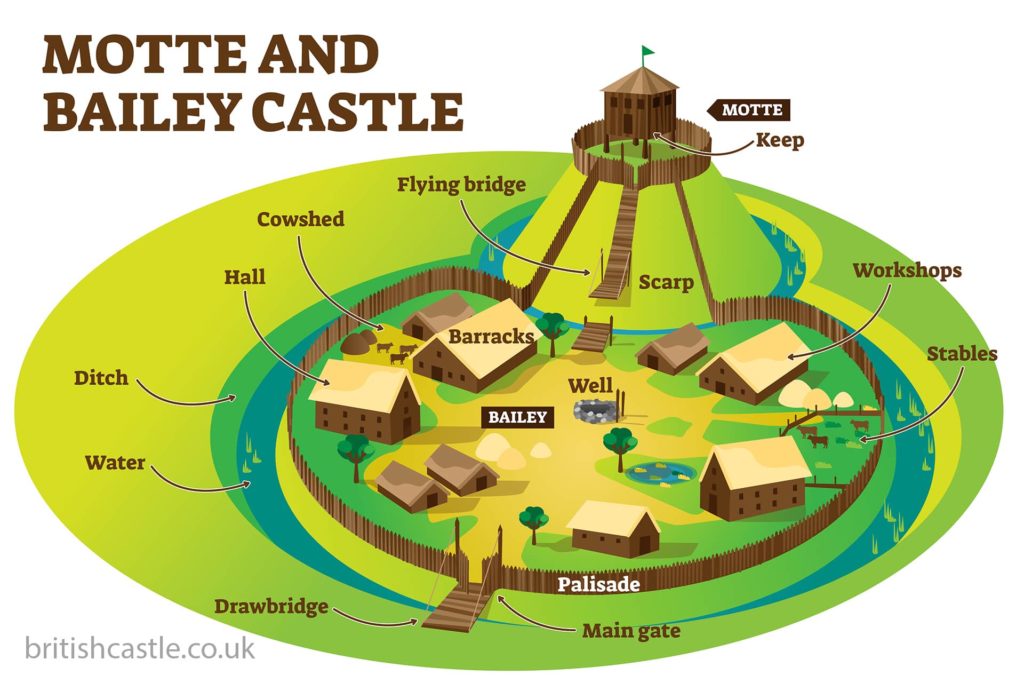
motte and bailey
quick to put up
easy to repair
big enough to house soldiers
had advantage height
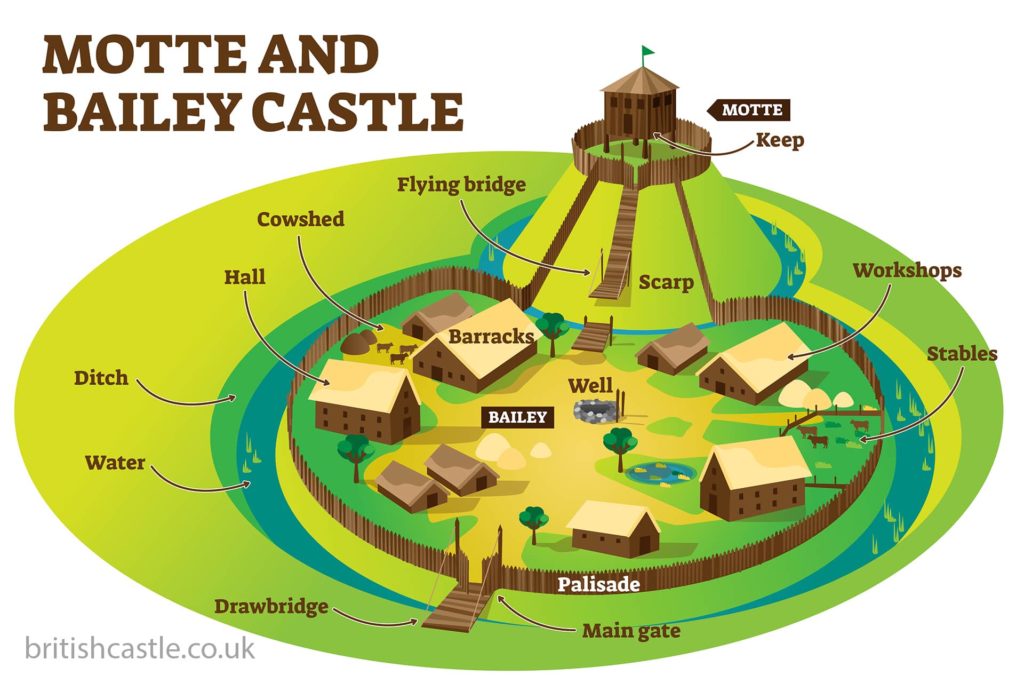
motte and bailey
wood is weak (rot, burn)
motte can collapse with weight of castle
not big enough to house big troops
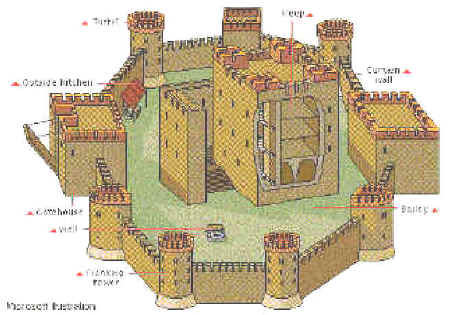
stone keep
stone lasts longer
can build taller castle
walls are thicker and strong
larger than motte and bailey
difficult to attack (size)
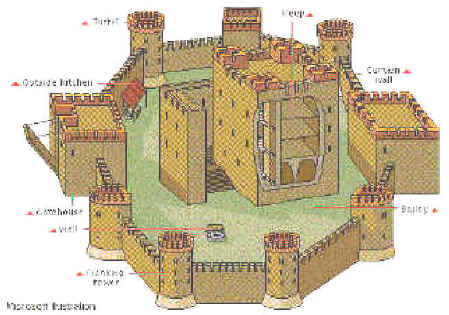
stone keep
enemy can go around it
starve you out
tunnel underneath
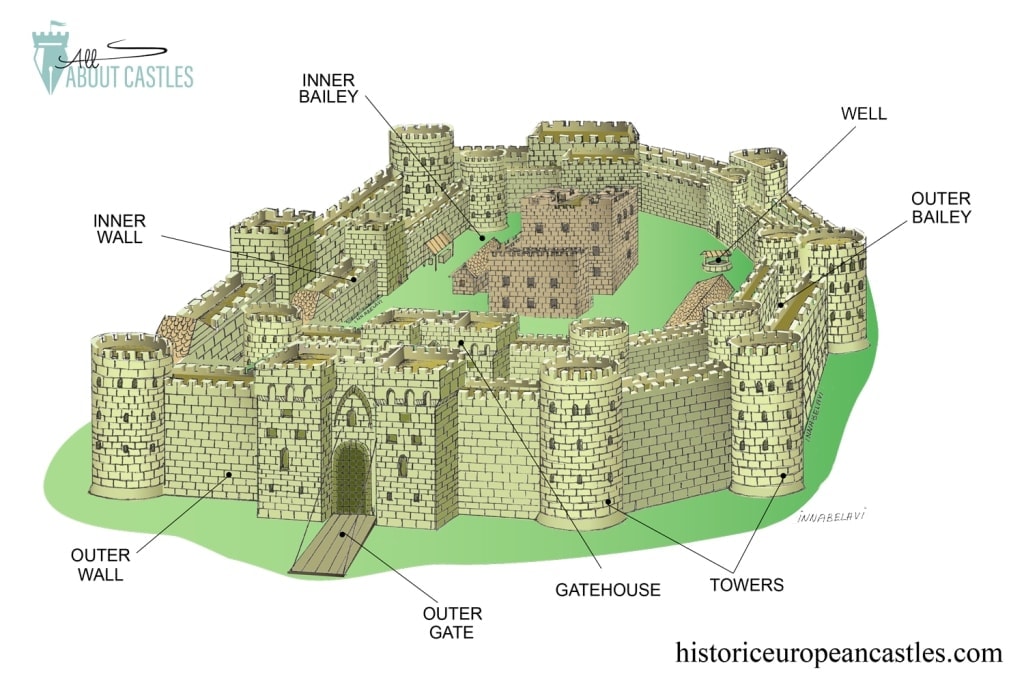
concentric castles
built to last
large, strong
could be defended easily
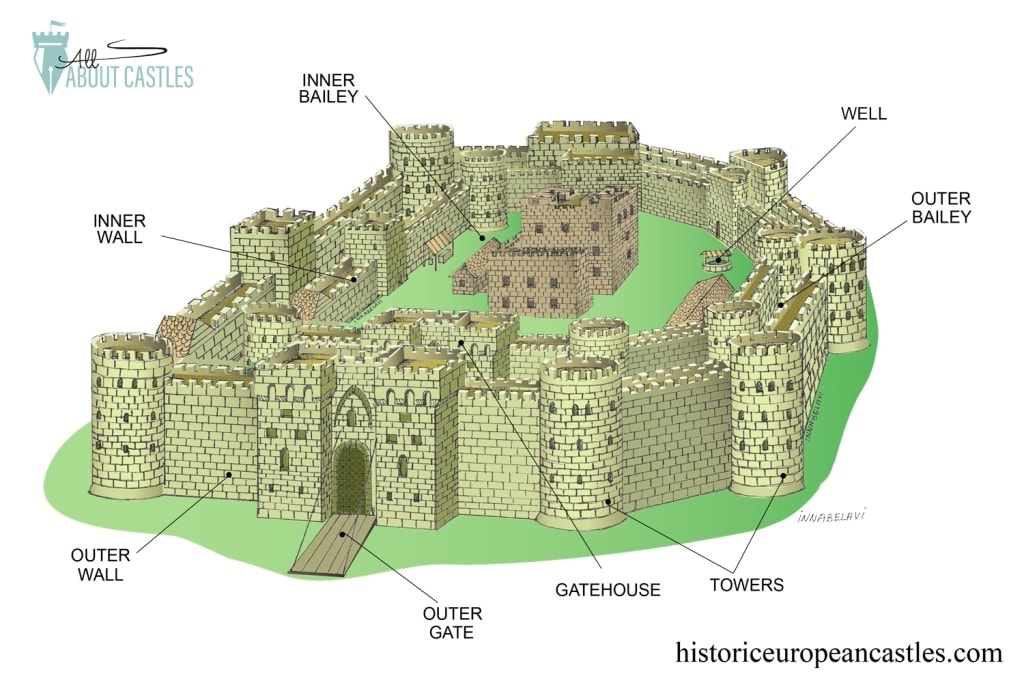
concentric castle
takes time to build
drawbridge
moveable bridge over moat; attached to gatehouse
moat
a ‘depression’ surrounding a fortification (castle, city, wall)
murder holes
holes in walls in which defenders pour or throw harmful substances through e.g., hot sand, scalding water, rocks, arrow, bowling oil
portcullis
a heavy castled door or gate made of metal strips
barbican
a fortified outpost/gateway
arrow slits
a narrow slit in a wall where archers can launch arrows
gatehouse
a strong, fortified building positioned to defend the entrance to a castle
structure of the church
pope, bishops, priests
wealth of the church
rich and powerful, everyone gave tithes (taxes), didn’t have to pay tax to king, wealthy people gave land
pilgrimages
spiritual journies holy sites
monasticism
a religious way of life, commit their lives to serving God
monastries
centres of learning, education, literature, hospitals
exocommunication
a religious act used to suspend membership in a religious community. it was believed that if you didn’t go to church, you would burn in hell after you died
tithes
10% of a person’s earnings
penances
paid money to the Churh to forgive your sins
levels of the system
King, Tenants in Cheif (barons/bishops), Knights (under-tenants), Peasants
definition
social hierarchy structure used during Medieval England; a way to orgnaise society
fief
a piece of land on loan from the king
divine right
a right give to a king by God to rule a country
bishop
a high-ranking member of the Catholic Church
hierachy
a system of ranking in order of power/importance
main idea
service for land
benefits
helped protect peasants from attacks and ensured they had food and clothing
disadvantages
controlling and restricted freedom
👑king
top leader; claimed all of the land and held it through ‘divine right’; divided it up between nobles; was pledged loyalty and soldiers
🏰nobles (tenants in chief)
barons and bishops; reported to the king and very powerful; in return for ‘fiefs’ they were loyal; governed the land given; fight in war; pay taxes; gave some land to knights
⚔knights
lesser nobles; loyalty to tenants in chief and king; divided land to peasants (protected them and recieve crops in the form of taxes)
🌱peasants
hard life; some were free (10% could be blacksmiths, bakers, etc.); serfs were slaves; couldn’t leave the land; pledged to their local lord; worked long days
the 4 claimants
Harold Hardrada, Harlod Godwinson, Edgar the Atheling, William Duke of Normandy
Edgar the Atheling
✅closest blood relative
❌only 14
Harald Hardrada
✅strong warrior
❌has to invade
William Duke of Normandy
✅apparently promised the throne
❌has to invade
Harold Godwinson
✅rich and powerful Earl
✅apparently promised the throne
❌his family killed Edward’s brother
Harold Godwinson
seized the throne after his death; last Saxon king
Harald Hardrada
sailed to England to invade but was killed by Godwinson
the Battle of Hastings
French duke - William - invaded England and was successful in killing Godwinson
changes made to England
English nobilty ➡ French
language changes as it mixed with Norman French
new styles of architecture (cathedrals and churches)
Fuedal system to help with control
increased cultural ties, especially with France
population
1 ½ million people
work of commoners
nearly everyone worked on the land
governance
Edward the Confessor; had a shaky rein and little power
defence
not well defended, and guarded by small hills called ‘embankments’
political connections
closer with Scandanavia, Denmark and Norway than the rest of Europe
earldoms
regions of England ruled by earls (nobility); many small villages
religion
belonged to Roman Catholic Church