AP Biology Unit 1 Terms
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
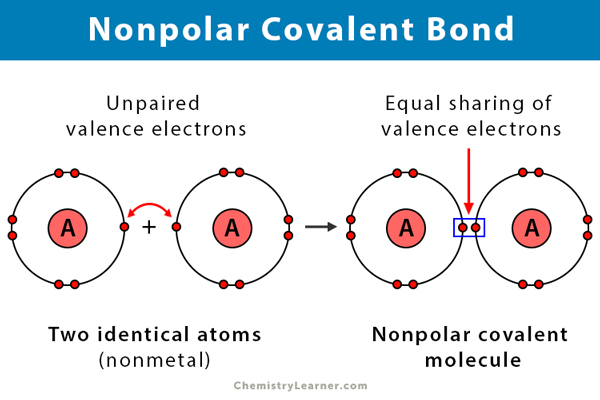
Covalent Bonds (non-polar)
Elements share one or more electrons.
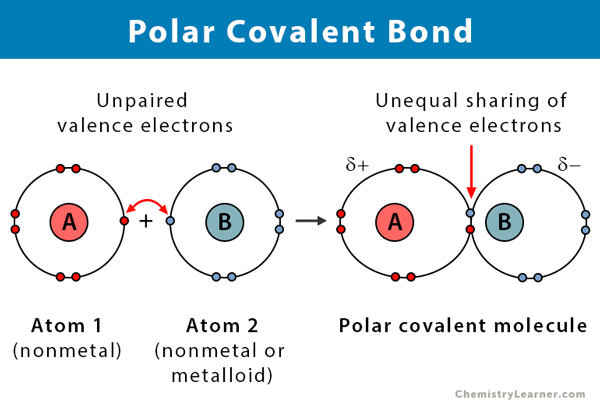
Covalent Bonds (polar)
Unequal sharing of electrons cause elements to have partial charges that are attracted to opposites.
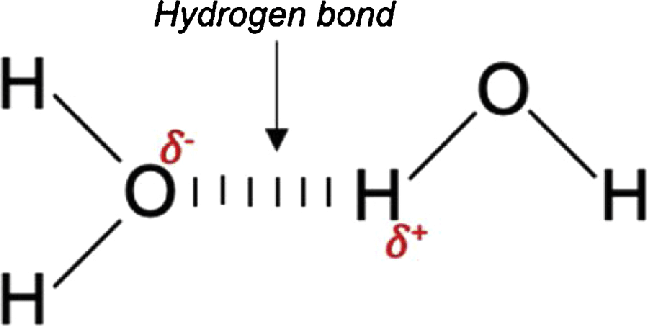
Hydrogen Bonds (H-Bonds)
Polar bond specifically with Hydrogen.
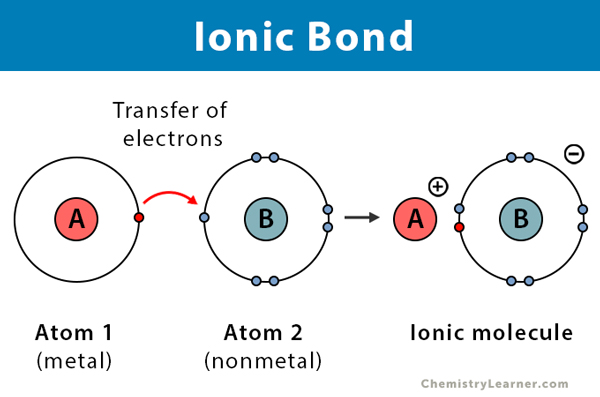
Ionic Bonds
Attraction between oppositely charged atoms causing a transfer of electrons.
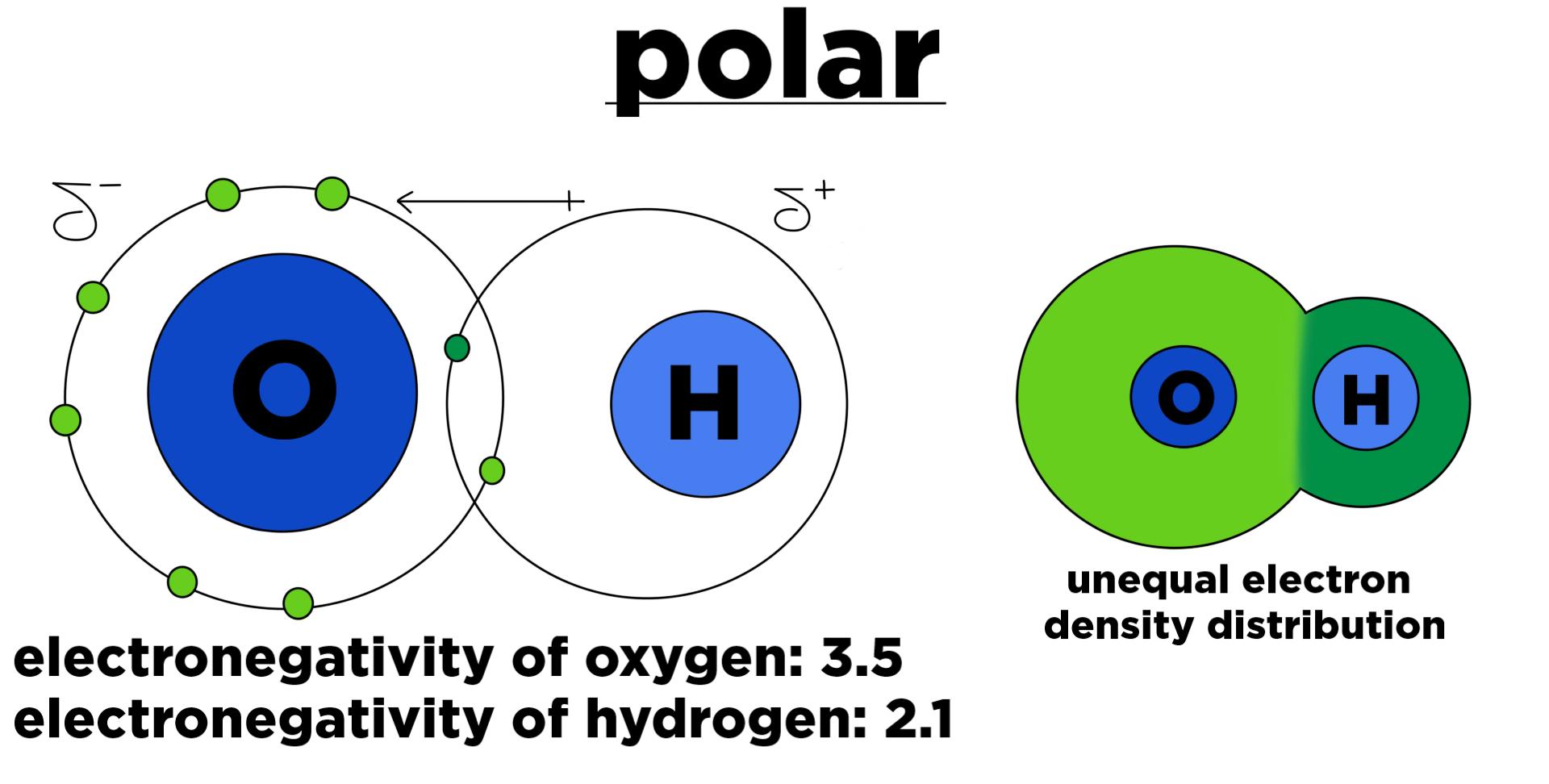
Polar
Molecules have partial charges.
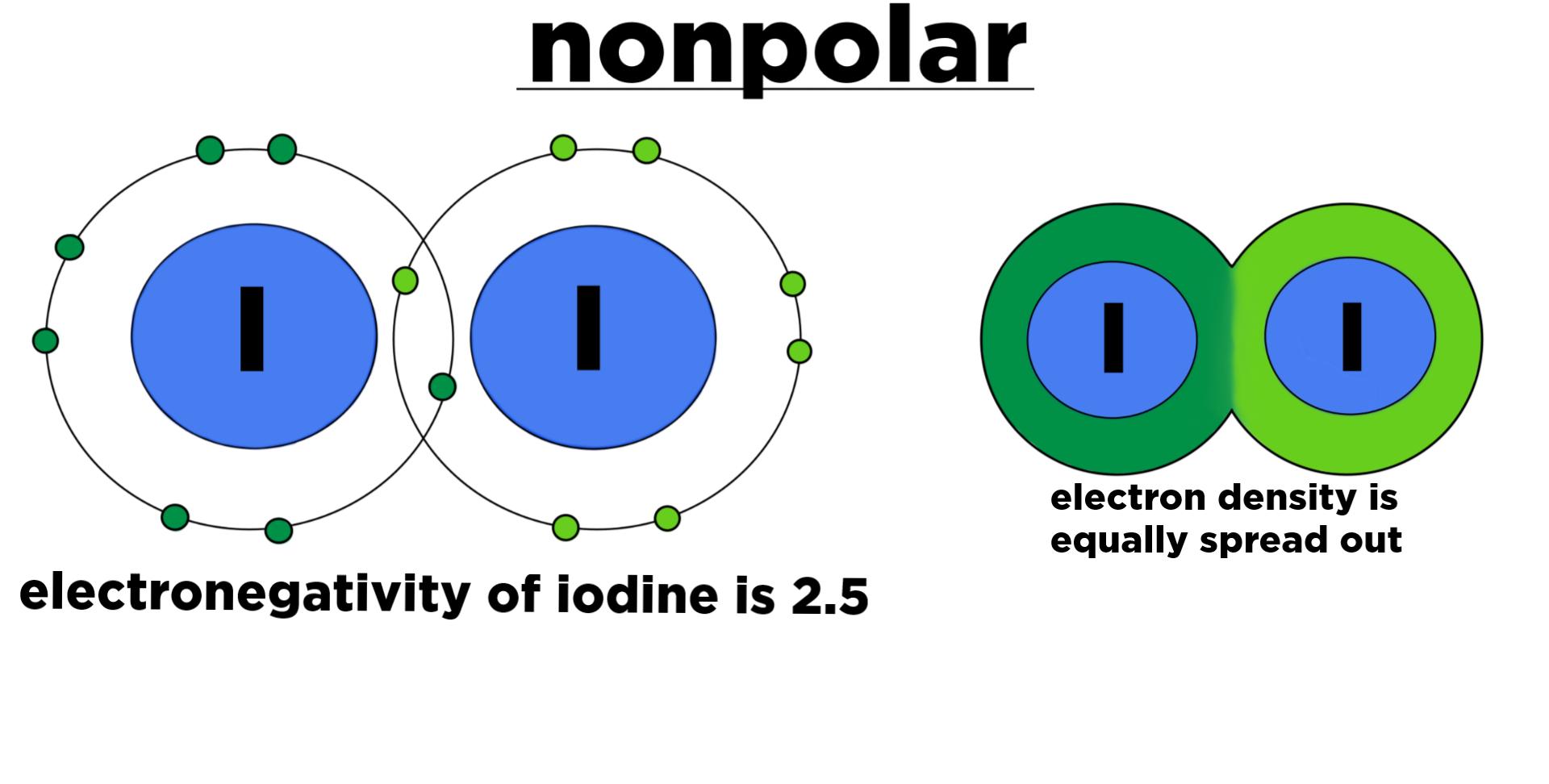
Non-polar
Molecules don't have partial charges, they equally share electrons (covalent bond) charges.
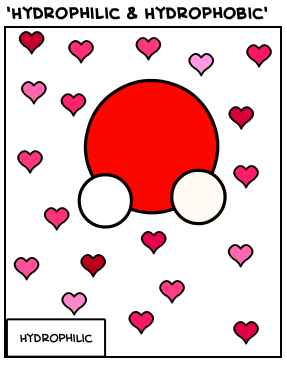
Hydrophilic
Molecules that love water; will point themselves towards water.
Hydrophobic
Molecules that hate water; will push themselves towards the middle to "hide" from water. |
Cohesion
Ability to stick to each other.
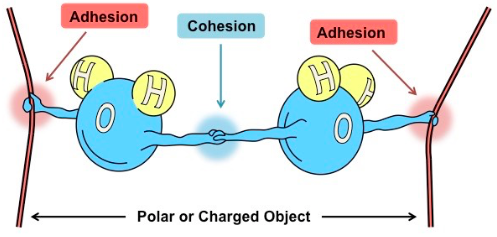
Adhesion
Ability to stick to other molecules/surfaces.
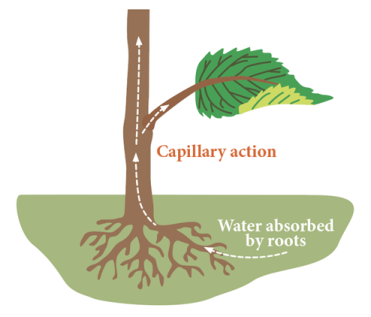
Capillary Action
Allows water to move up the body against gravity.
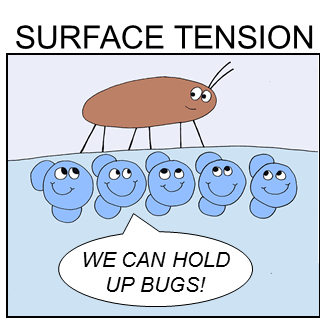
Surface Tension
Ability to resist separation when under tension or stress.
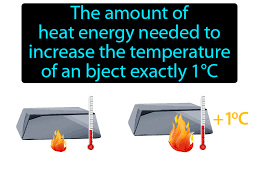
Heat Capacity
Amount of heat needed to raise 1g of water 1 degree Celsius.
Heat of Vaporization
Amount of heat needed to turn a liquid into gas.

Organic Chemistry
The study of compounds with covalent bonded carbon.
Organic Compounds
Compounds that contain carbon and hydrogen.
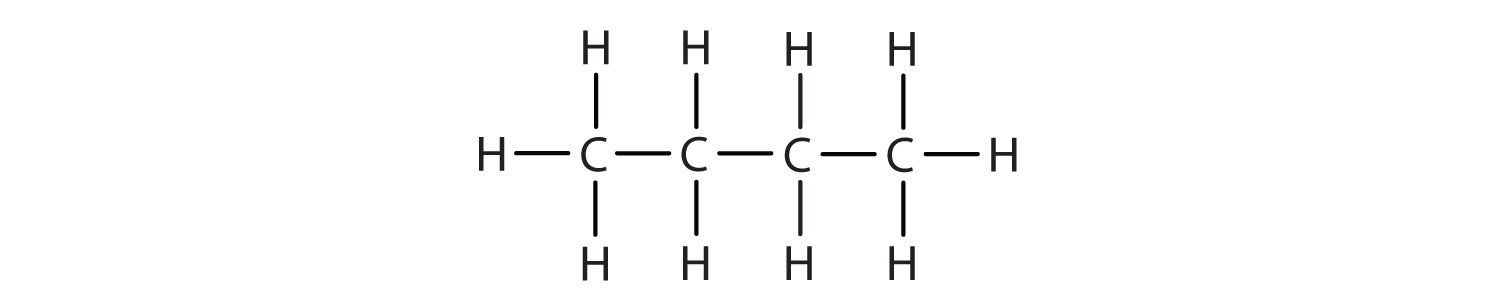
Carbon Chains
A line of connected carbon atoms.
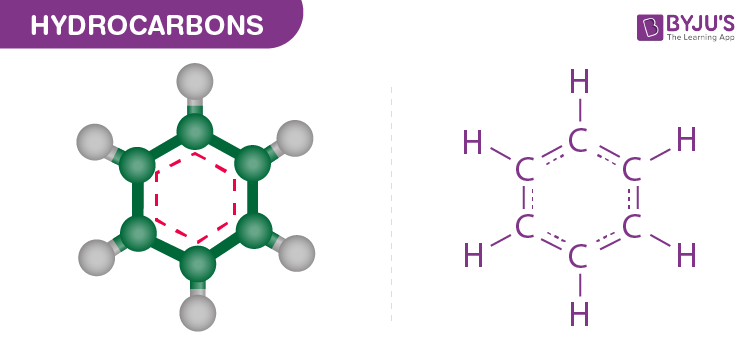
Hydrocarbons
Organic molecules consisting only of carbon and hydrogen.
Functional Groups
Chemical groups attached to the carbon skeleton that participate in chemical reactions.
Nitrogen
Builds proteins and nucleic acids.
Phosphorus
Builds nucleic acid and lipids.
Biological Macromolecules
Large molecules that are carbon-based and make up every living organism.
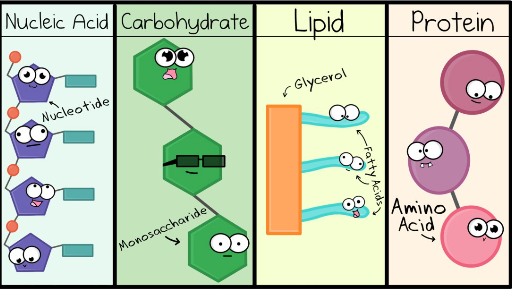
Carbohydrates
Saccharides (sugars) made from carbon chains or rings.
Proteins
Made from amino acids.
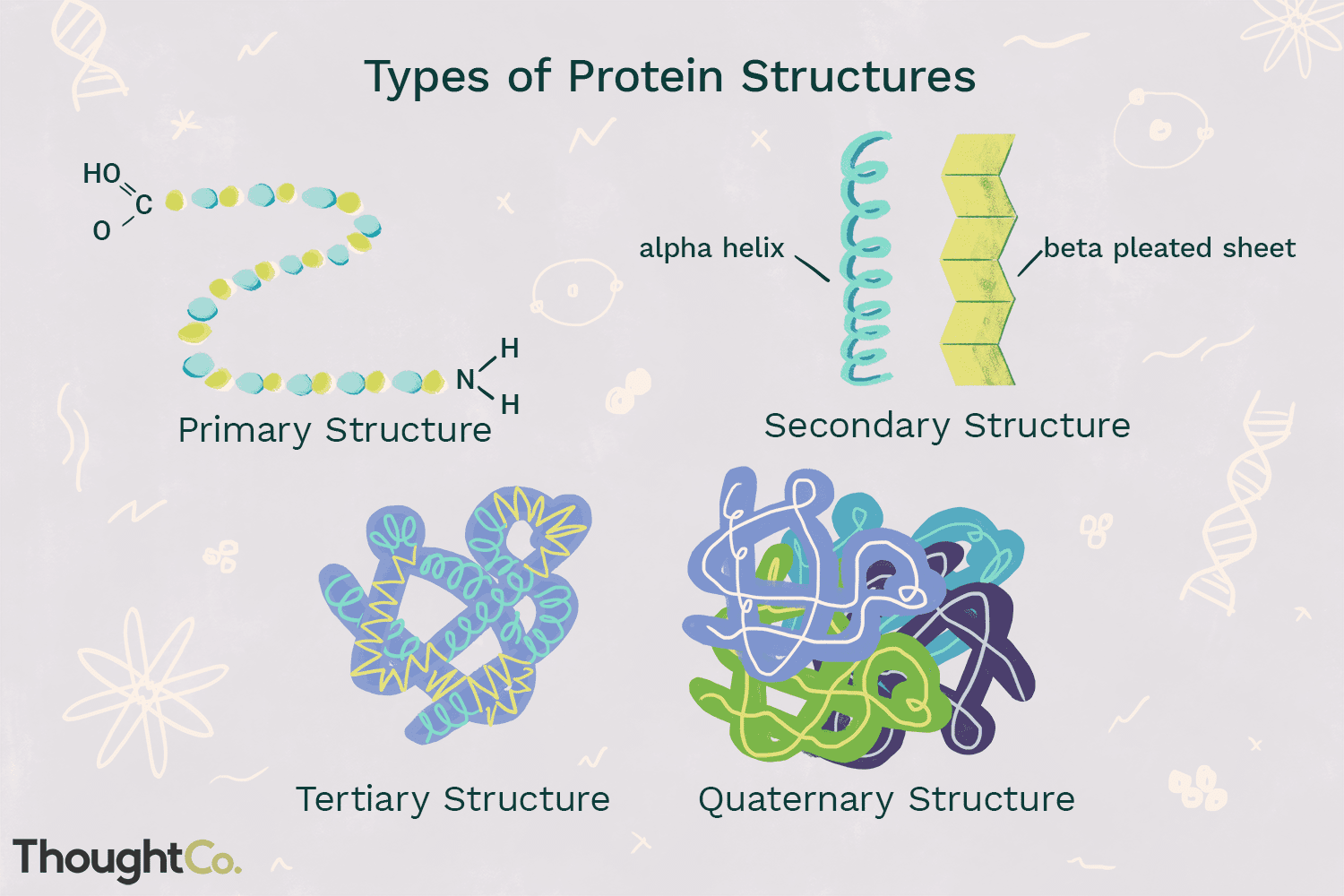
Lipids
Fats made of long carbon chains.
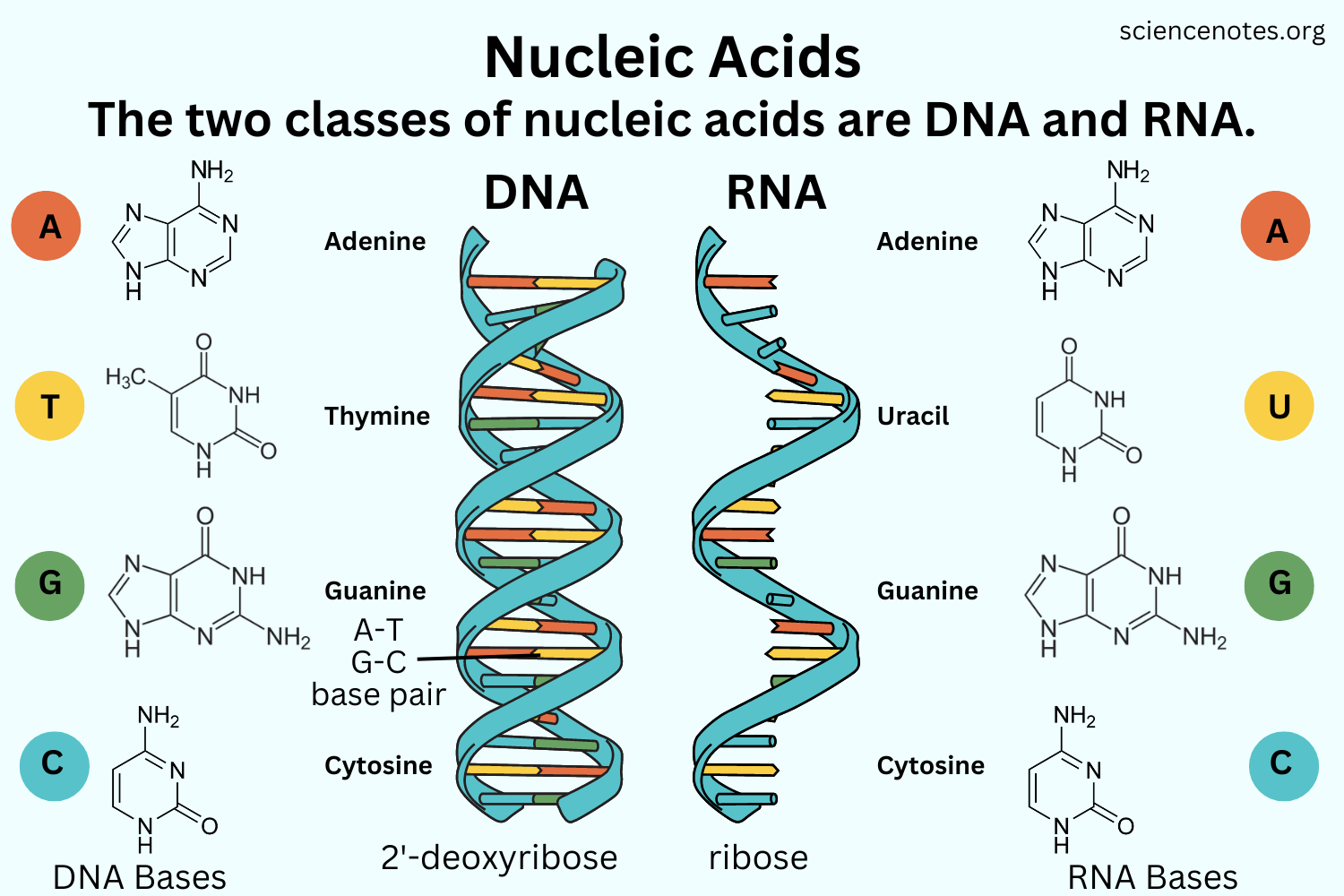
Nucleic Acids
DNA, RNA, ATP (energy).
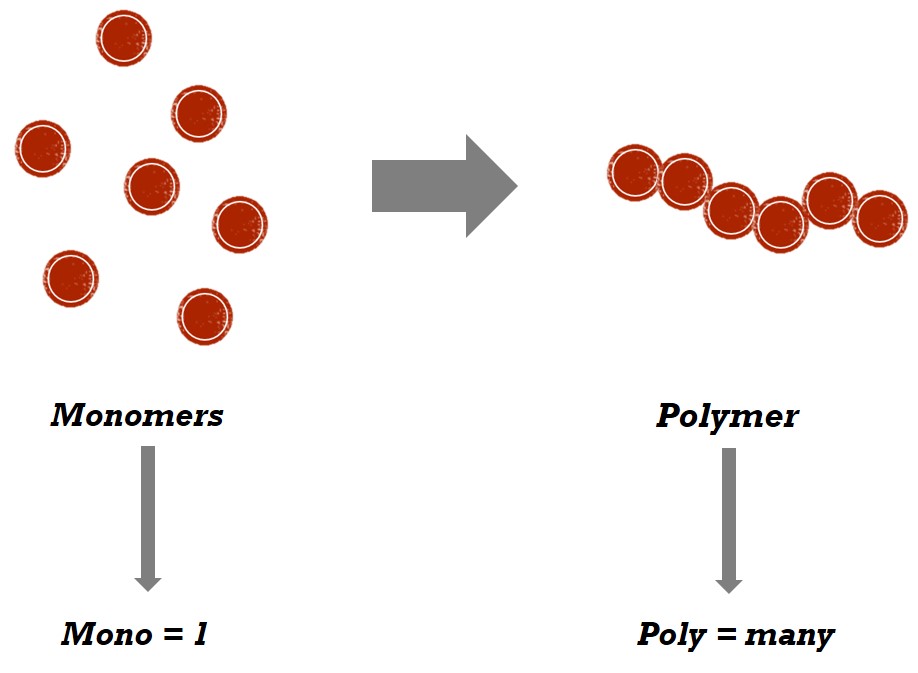
Monomers
Single macromolecules.
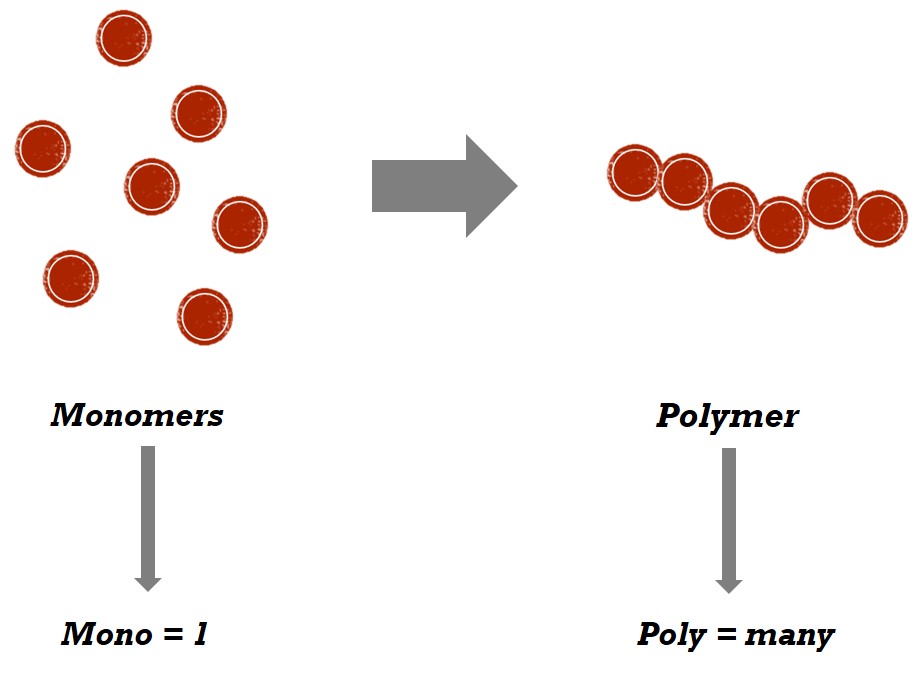
Polymers
Many monomers bonded together, forming a specific substance (repeating units).
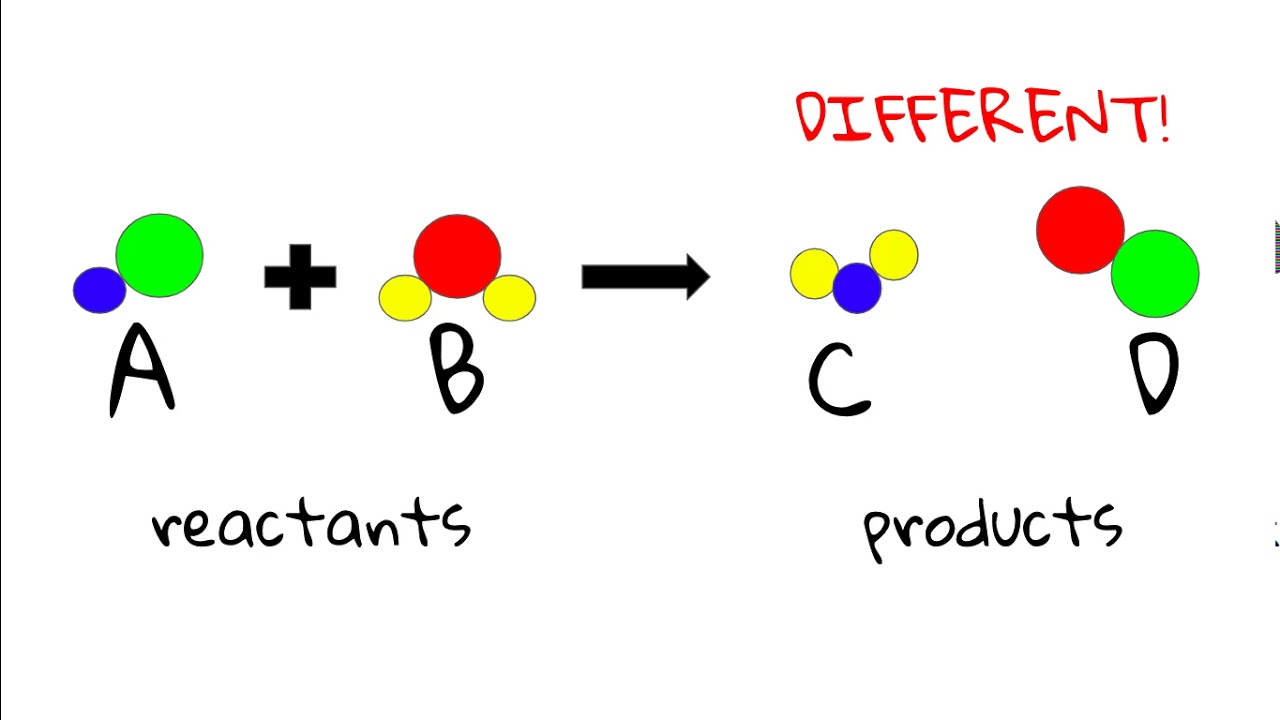
Reactants
Beginning molecules of the reaction.
Products
End molecules of the reaction.
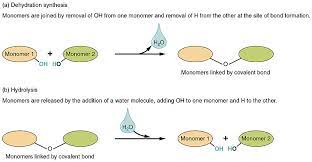
Dehydration Reaction
Bonds two monomers with the loss of H2O.
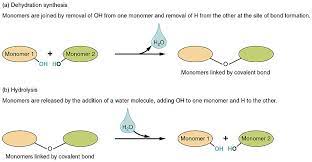
Hydrolysis
(Hydro = water, lysis = to break) = adding water to break bonds.
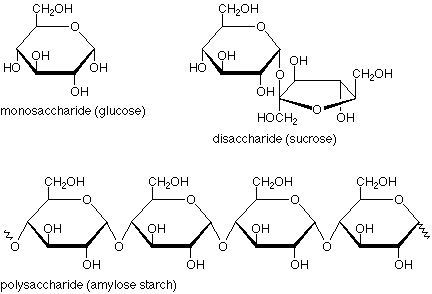
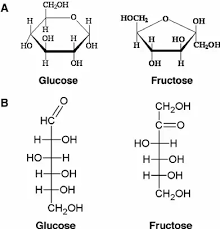
Monosaccharide
One sugar ring (ex./ glucose).
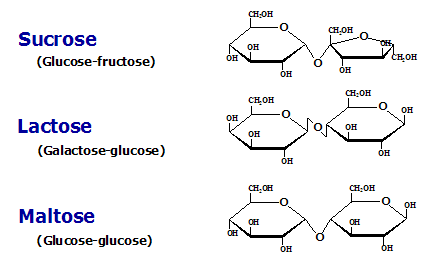
Disaccharide
Two sugar rings (ex./ sucrose).
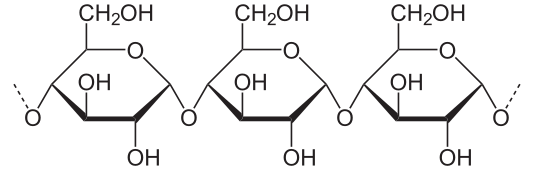
Polysaccharide
Three or more sugar rings (ex./ starch).
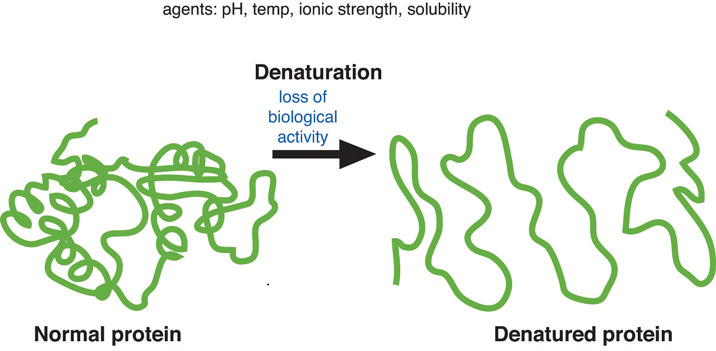
Denaturation
A process modifying the molecular structure of a protein, often due to changes in heat, salinity and pH.
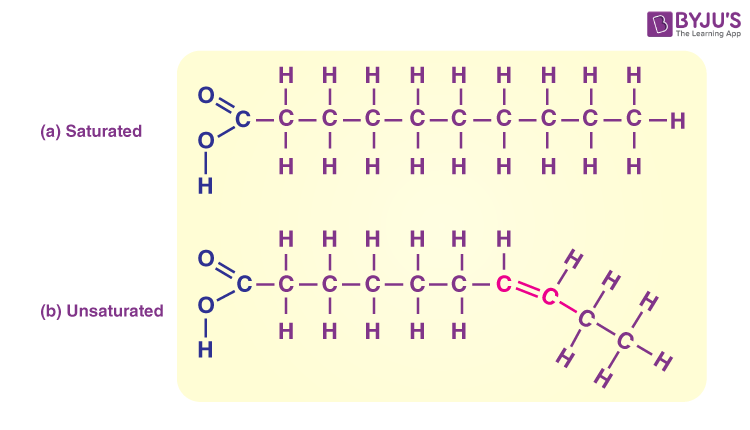
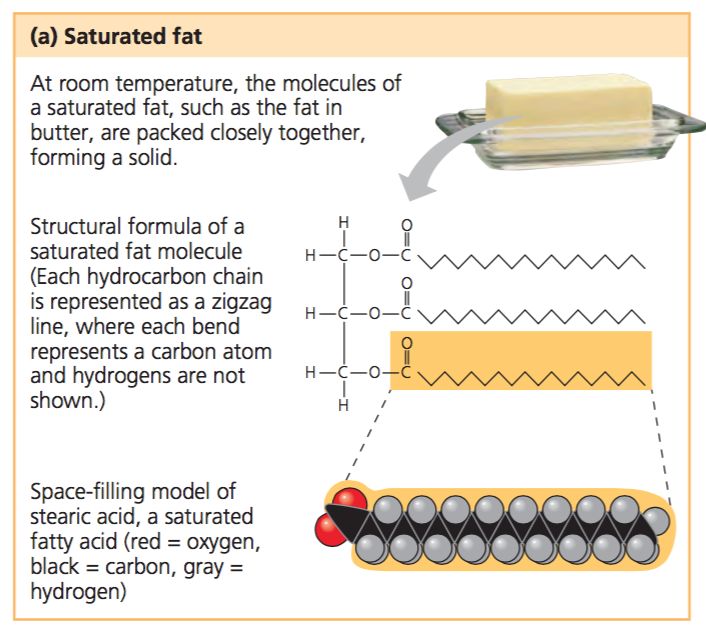
Saturated Fatty Acids
Lipids with a single bond that can be stacked together tightly; solid at room temperature.
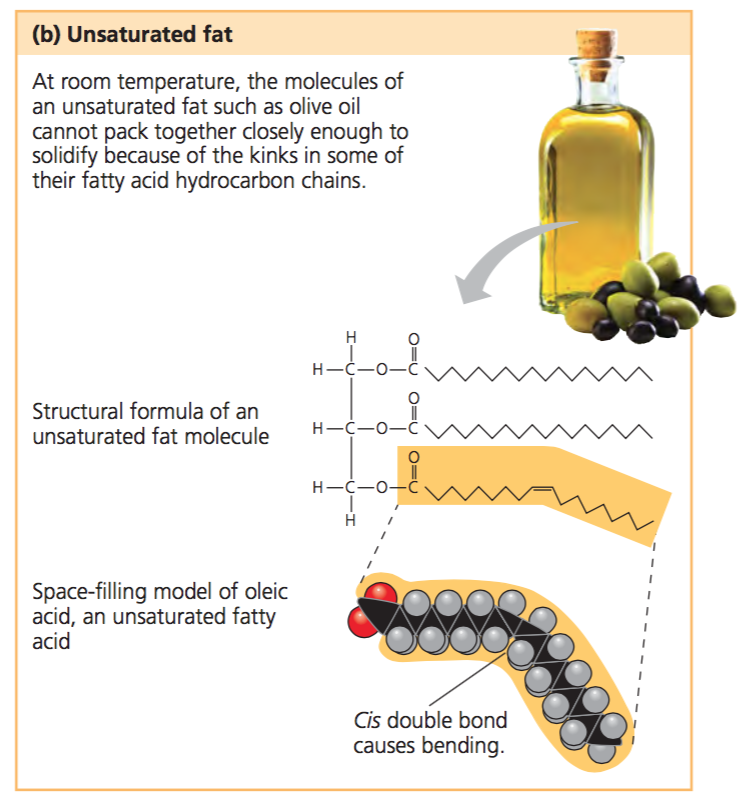
Unsaturated Fatty Acids
Lipids with at least one double bond that cannot bend or stack; liquid at room termperature.
Steroids
Lipids that are identifiable by their four fused rings.

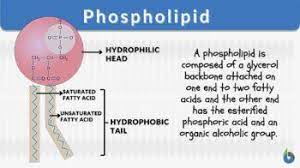
Phospholipids
A lipid with a hydrophillic (head) and hydrophobic (tail) part.