The brain and eye: Organism level systems: Biology: GCSE (9:1)
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Brain
A mass of nerve tissue consisting of billions of interconnected neurones that acts as the main control centre of the nervous system
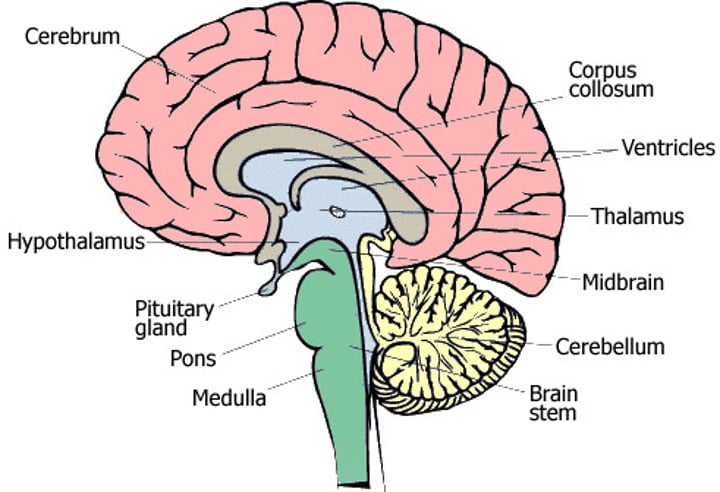
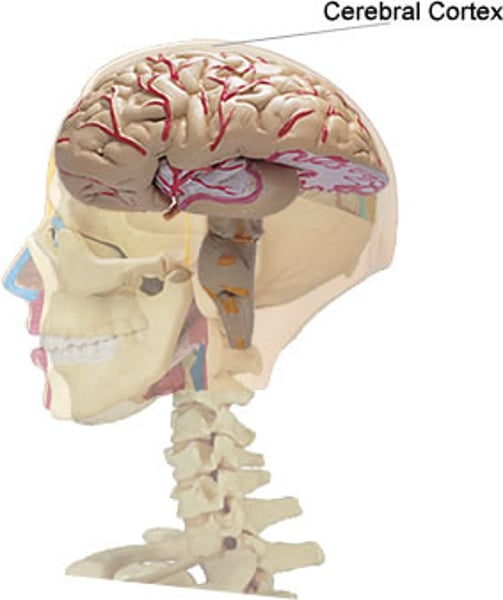
Cerebral cortex
The outer region of the cerebrum that contains sheets of nerve cells controlling memory, consciousness, language and intelligence
Cerebrum
The main part of the brain that is divided into a right hemisphere and a left hemisphere
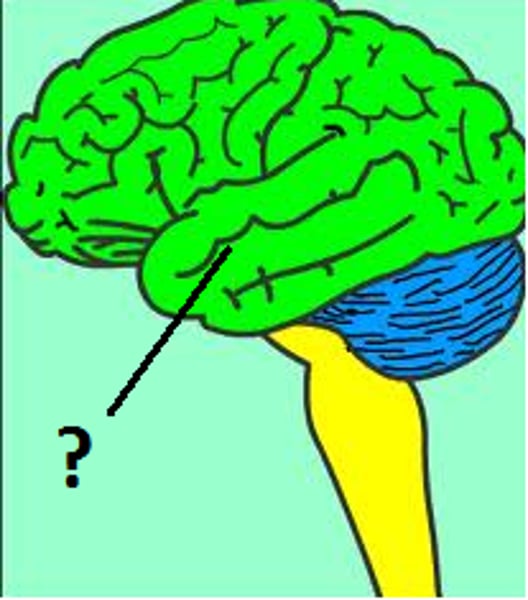
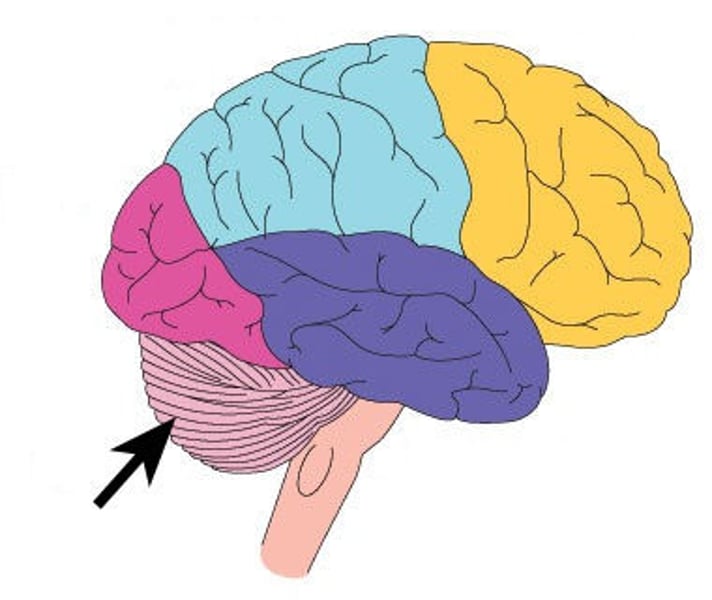
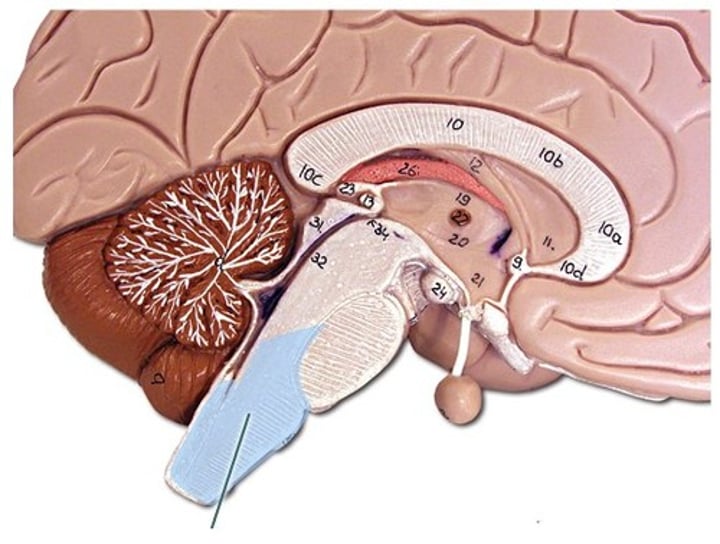
Cerebellum
A large structure of the hindbrain that controls fine motor skills including balance and movement
Hypothalamus
A small region at the base of the brain, it directs several maintenance activities such as eating, drinking and controlling body temperature
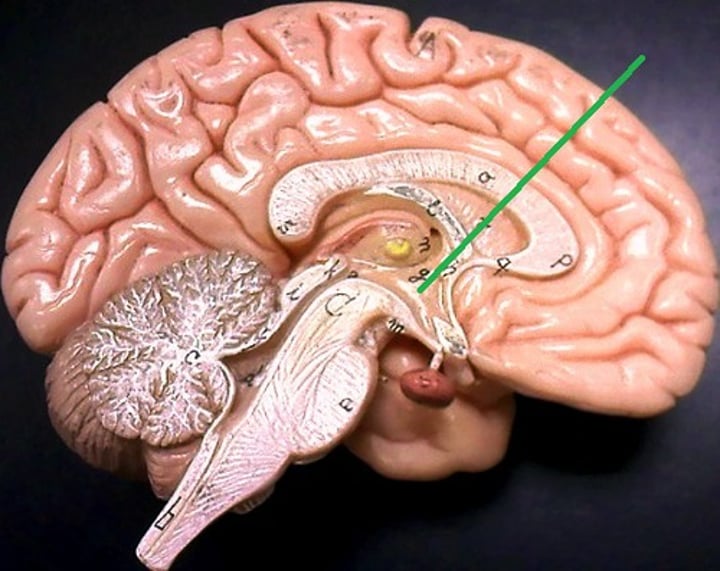
Pituitary gland
A master gland attached to the hypothalamus, responsible for releasing many different hormones that regulate specific processes and functions
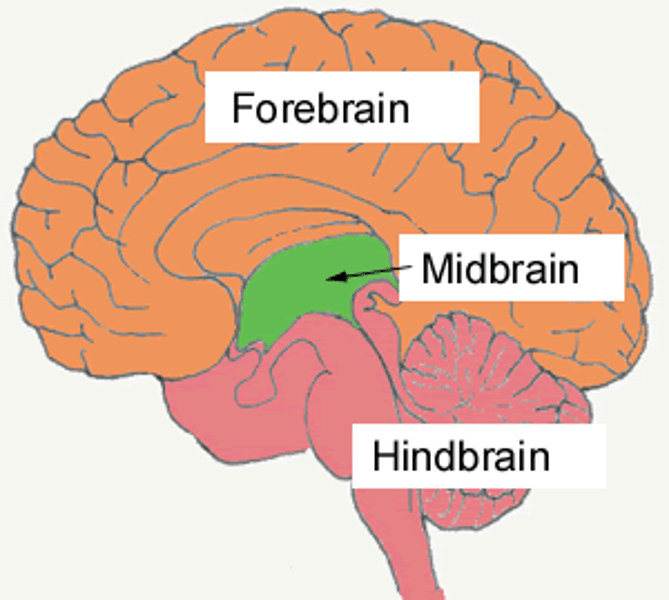
Hindbrain
The lower part of the brainstem that include the cerebellum
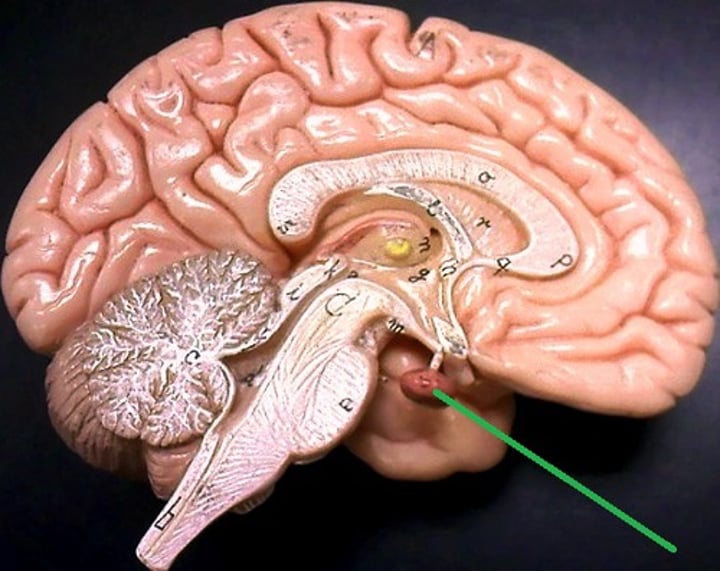
Medulla
The base of the brainstem which controls heartbeat and breathing
Eye
A sense organ that detects light and is responsible for vision
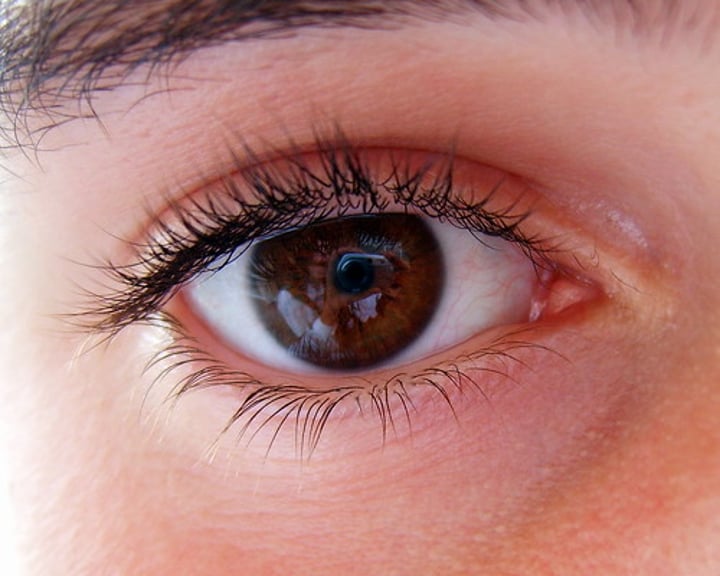
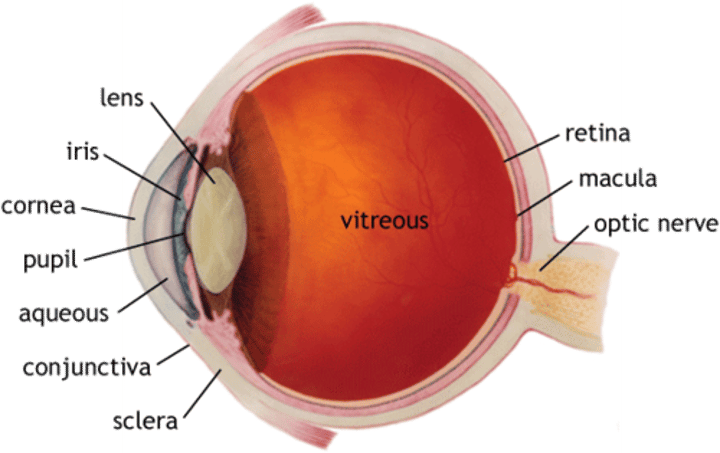
Sclera
The white outer part of the eye that provides protection
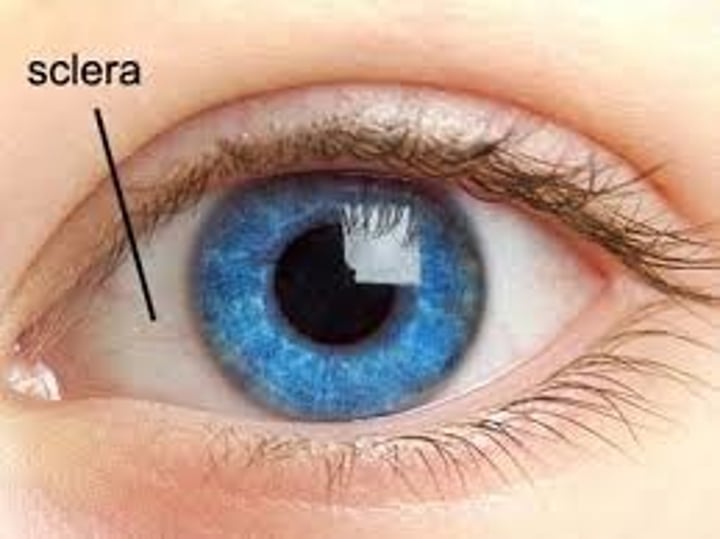
Cornea
The transparent tissue that covers the front of the eye, it controls and focuses the entry of light into the eye
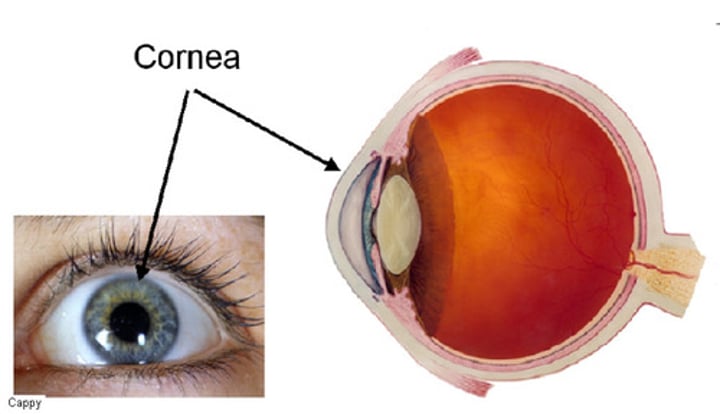
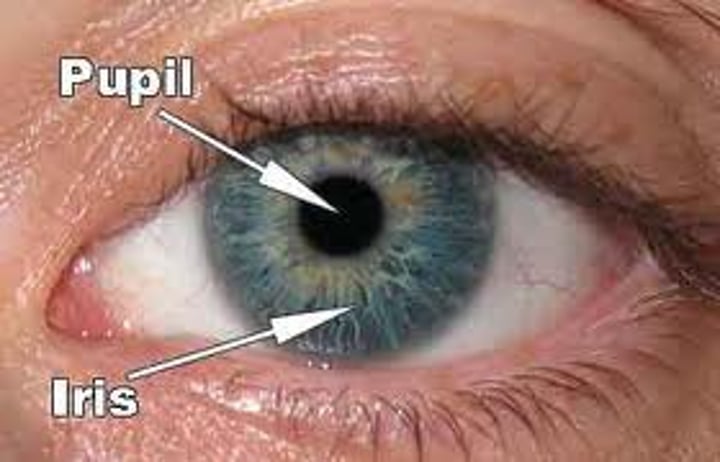
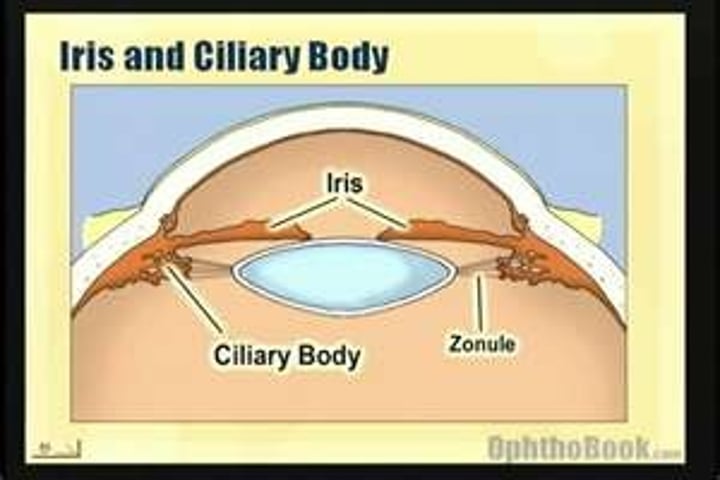
Iris
The coloured part of the eye behind the cornea that regulates the size of the pupil
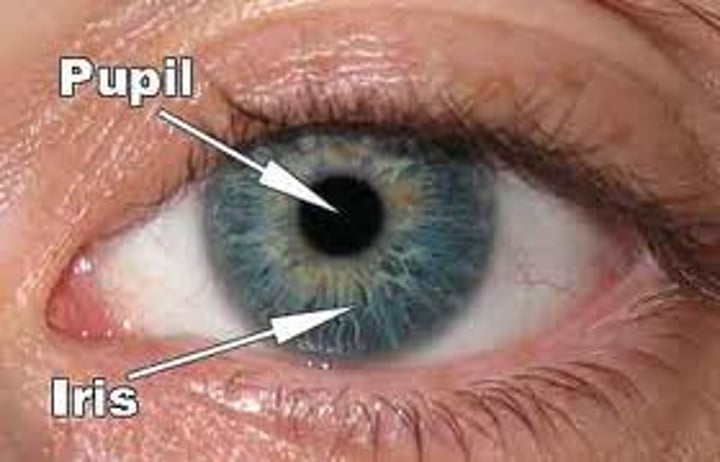
Pupil
The dark opening in the centre of the eye, it varies in size to regulate the amount of light that reaches the retina
Lens
A transparent structure located behind the iris that focuses light on the retina at the back of the eye
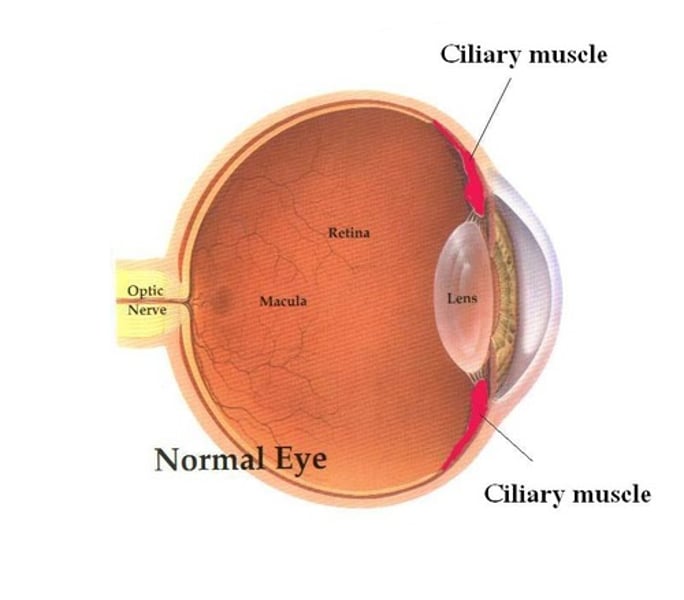
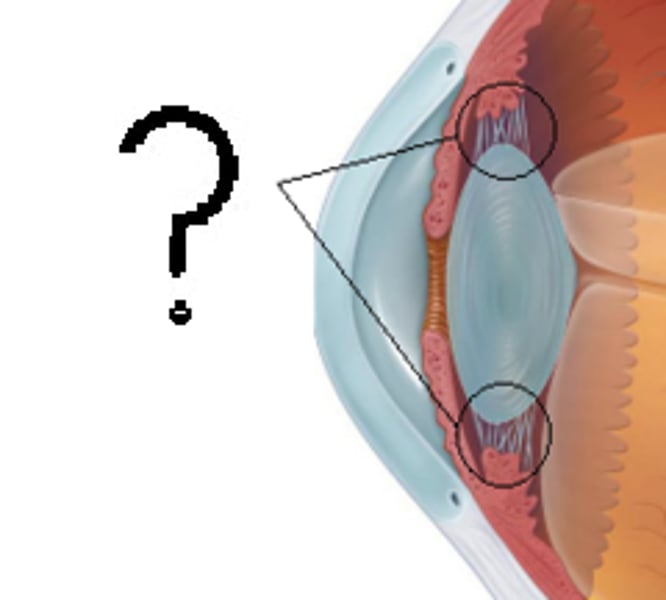
Ciliary muscles
Muscles which work with the suspensory ligaments to adjust the shape of the lens in order to focus on near or far objects
Suspensory ligaments
Ligaments which work with ciliary muscles to adjust the shape of the lens in order to focus on near or far objects
Retina
The light-sensitive surface at the back of the eye containing light and colour receptor cells
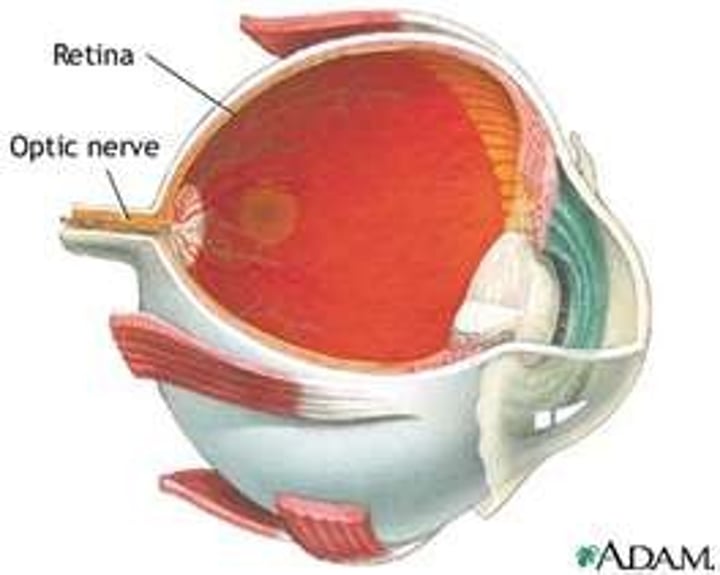
Optic nerve
The nerve that carries neural impulses from the receptor cells of the eye to the brain
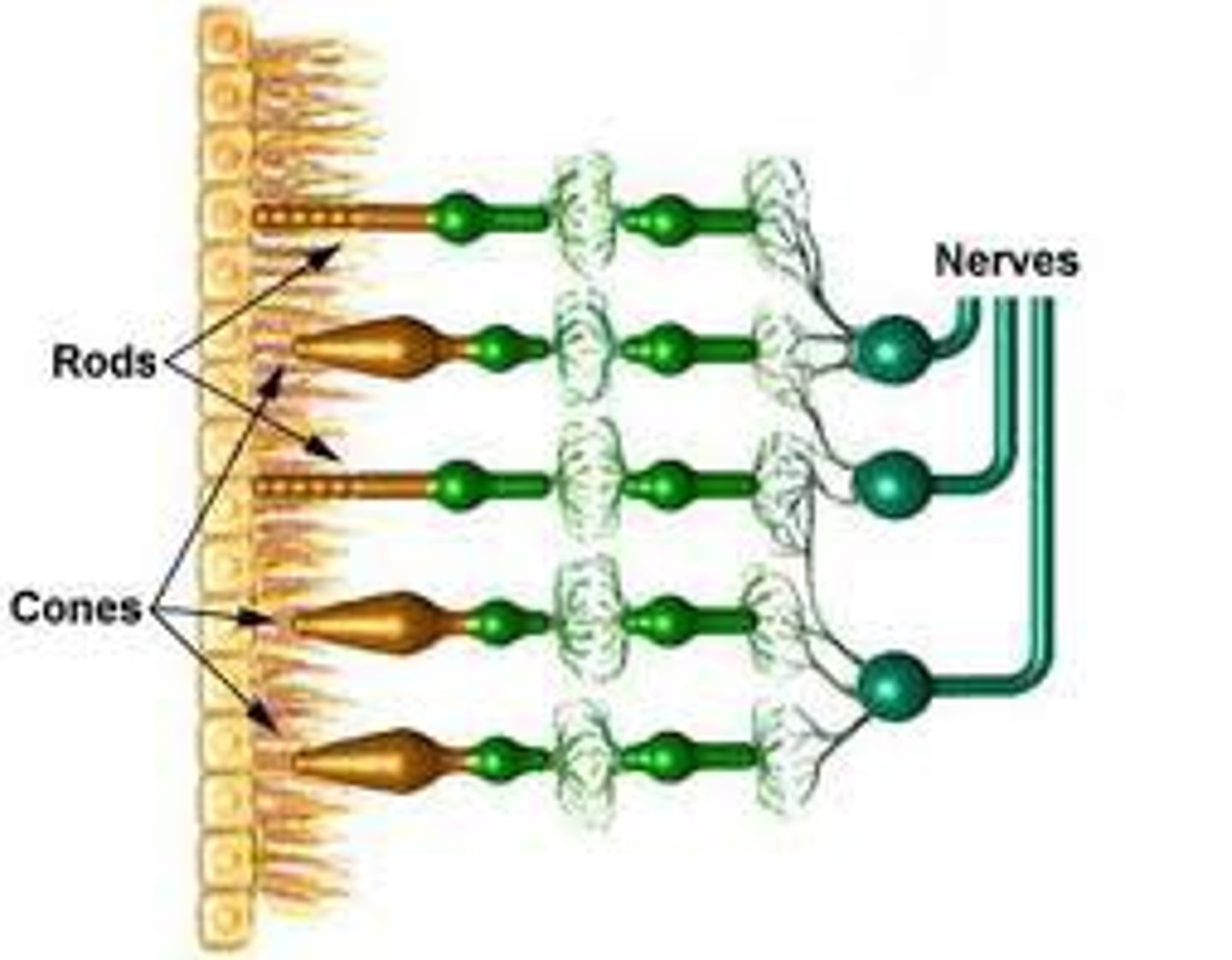
Light receptor cells
Also called rod cells, these are highly light sensitive and are responsible for vision in dimly-lit conditions
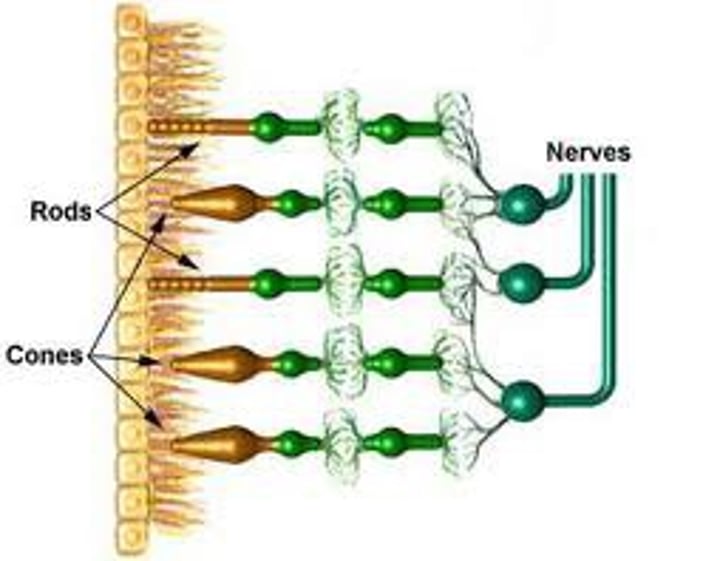
Colour receptor cells
Also called cone cells, these can detect a wide spectrum of light and are responsible for the perception of colour
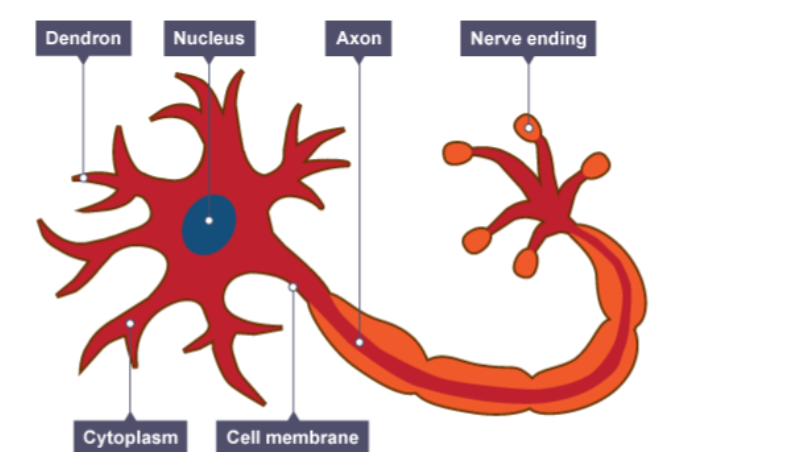
Neurons
aka nerve cells- basic elements of the nervous system.
Cell Body: The main processing centre of the cell.
Dendrites: Thin branching extensions of the cell body that conduct nerve impulses toward the cell body
Axon: A single branch which conducts nerve impulses away from the cell body. Myelin sheath is covering
Homeostasis
The regulation of conditions inside your body(and cells) to maintain a stable internal environment in response to both internal and external changes
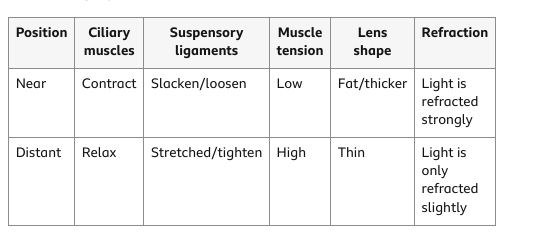
Eye focus
When objects are near:
-the ciliary muscle contracts
-the lens shape become fatter/thicker
When objects are far:
-the ciliary muscle relaxes
-the lens becomes thinner
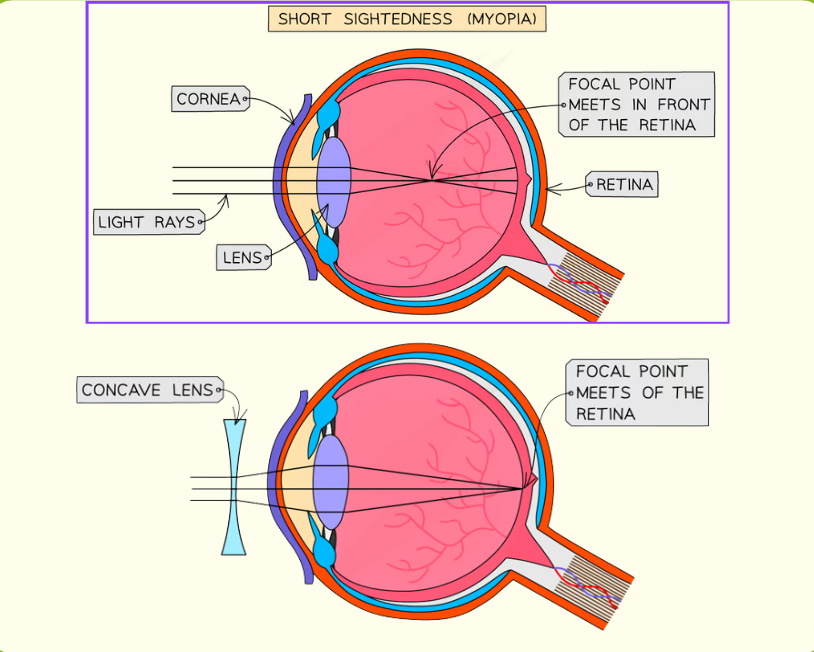
short sight
It is caused by:
the eyeball being elongated - so that the distance between the lens and the retina is too great
the lens being too thick and curved - so that light is focused in front of the retina
It can be corrected by concave lens->
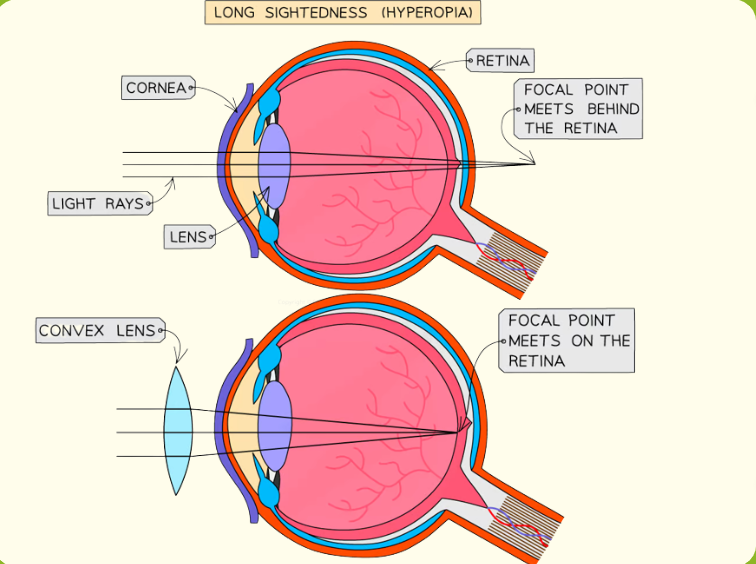
long-sight
It is caused by:
the eyeball being too short - so the distance between the lens and retina is too small
a loss of elasticity in the lens - meaning it cannot become thick enough to focus (which is often age-related)
<- It can be corrected by convex
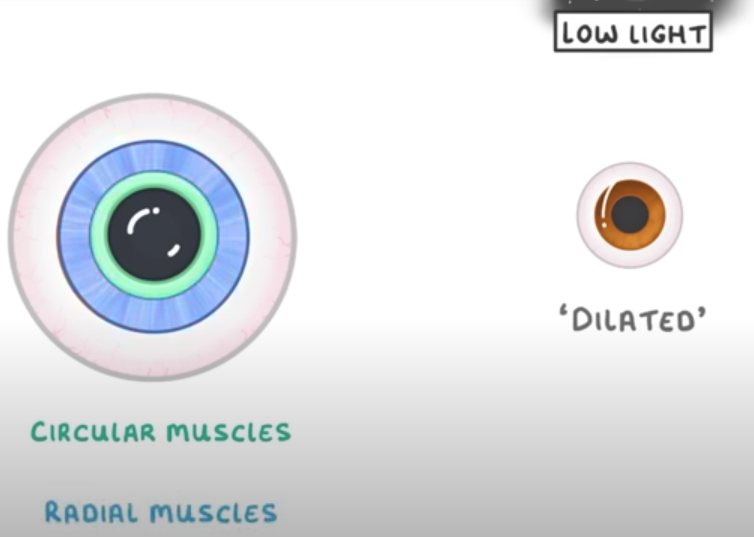
dilated
-radial muscles contract
-circular muscle relax
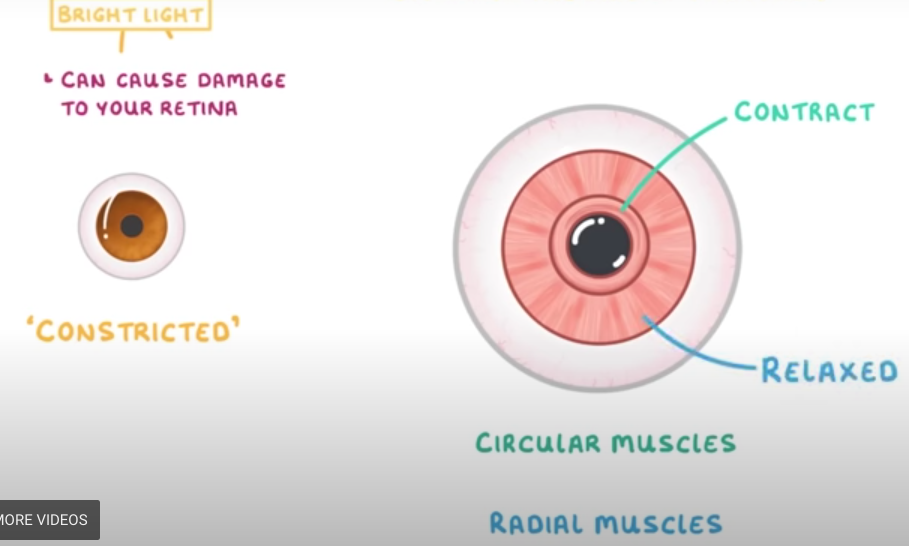
constricted
-radial muscles relax
-circular muscle contract
Why is brain hard to treat?
-many things can go wrong
-in skull (hard to access)
-complicated(hard to target with medicine)
-nervous tissue doesn’t repair the same as other tissue
-surrounding tissue may be damaged in procedure
accommodation
near to far:
the process of changing the shape of the lens to focus on near or distant objects
-light nees to refract less
-lens becomes thinner for less refraction
-ciliary muscle relaxes
-image is formed on retina
Scans
MRI (use strong magnetic fields and radio waves to show details of brain structure and function)
CT (series of x-rays from different angles)
PET (detect gamma rays that radiate from a chemical compound called a tracer.-metabolic reactions)
Explain process that takes place at the junction of two neurons:
chemicals release
cross synapse
arrive at receptor
starts up next neurons electrical impulse
Red-Green colour blindness
-genetic/hereditary
-affects receptors
-can’t differentiate red + green
no treatment available