Set 7: Basic Digital Signal Processing
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
What is Digital Signal Processing (DSP)
DSP is representing a signal by digits, which is what computers do
Analogue
A continuous process/representation is called analog (analogue)
Digital
Discrete representations or processes are referred to as digital
Analogue vs. Digital
Analogue is continuous and Digital is discrete
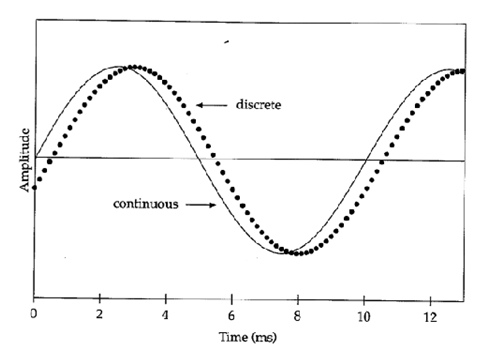
Samples
samples are discrete points in time
What are the 2 factors that we need to make a decision about when we convert to digital?
1. Sampling rate
2. Bit rate
Sampling rate
how often we sample is called the sampling rate. The more you sample, the more accurate the representation of the original analog signal.
What is the minimum sampling rate you need to be accurate?
Double the sample of the highest frequency you want to represent.
For a 100 Hz signal à need 200 Hz sampling rate
Nyquist Frequency
The highest-frequency component that can be captured with a sampling rate. It is always ½ of the sampling rate
What’s highest frequency of human hearing?
20,000 Hz
So you need 40,000 Hz sampling rate
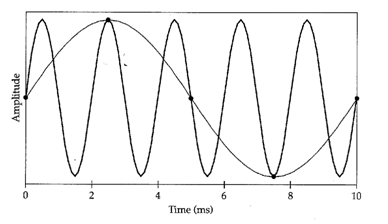
Aliasing
Aliasing is the misrepresentation of a signal because you have frequency components above the Nyquist. This happens when your sampling rate is not set high enough
Bit rate or Quantization
the amplitude of the signal at each sample point. The higher the bit rate, the more accurate we’ll be
Summary of recommendations for DSP
Sampling rate:
• Common advice is to record speech at 22,050 Hz because the amount of important information in speech above 10kHz is limited
• Human hearing extends to ~20kHz, which means that sampling at 44.1kHz is a more conservative approach (but that comes with size costs).
Bite rate: 16-bit