Static Occlusion
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Occlusion
Contact relationships of the teeth resulting from neuromuscular control of the masticatory system (musculature, TMJ, mandible, periodontium)
Physiologic occlusion
Occlusion-related pathosis is absent
Minimal muscle hyperactivity, limited stress to system
Traumatic occlusion
Occlusion as the causative factor in formation of lesions
Therapeutic occlusion
Treatment occlusion
Counteract structural relationships related to traumatic occlusion
Good occlusion
Optimal function
Absence of disease
Functional forms of teeth
Arrangement within dental arches
Relationship of mn to mx dental arch
Relation of mandible to maxilla
TMJ, muscles, nerves, ligaments
Factors that contribute to occlusion
Facial and lingual curvatures
Contact areas
Embrasures
Interproximal surfaces
Surface contact
Cusp and fossa apposition
Cusp and embrasure apposition
Ridge and sulcus apposition
Functional forms of teeth
Facial and lingual curvatures
Divert food away from the gingiva to prevent it from being traumatized
Crest of curvature on facial surfaces of all teeth
Cervical 1/3
Crest of curvature on lingual surfaces of anterior teeth
Cervical 1/3
Crest of curvature on lingual surfaces of posterior teeth
Middle 1/3
Contact areas
Positive contact relation M and D
COC on the proximal surface of crowns where a tooth touches adjacent tooth
Stabilize the tooth within the alveolus
Prevent food impaction
Protect the ID papilla
In all teeth, _____ contacts are more cervical except 44 and 34, and mandibular centrals
Distal
In 44 and 34, _____ contact is more cervical
Mesial
at the same level
Contact area of mandibular centrals
In all anterior teeth except maxillary 3, mesial contacts are in the
Incisal 1/3
Mesial contact of maxillary 3
Junction of incisal and middle 1/3
In all posterior teeth, mesial contacts are at the?
Junction of middle and occlusal 1/3
Which embrasures are larger?
Lingual embrasures
Between 11 and 21
Widest incisal embrasure
Incisal or occlusal embrasures
Shallow incisocervically and narrow faciolingually on anterior, broad on the posterior
Stamp cusps
Occlude in fossa of opposing teeth well within the perimeter of the crowns of teeth not exceeding 4 sq. mm the amount of tooth contact
Crush and cut food
Maintain vertical dimension of occlusion
Provide centric stops in centric occlusion
Shear cusps
Guiding cusps during contact with stamp cusps
Minimize tissue impingement
Shear the food, act as grabbing cusps
Give stability to mandible — providing tight and definite occlusal relationship when teeth occlude (maximum intercuspation)
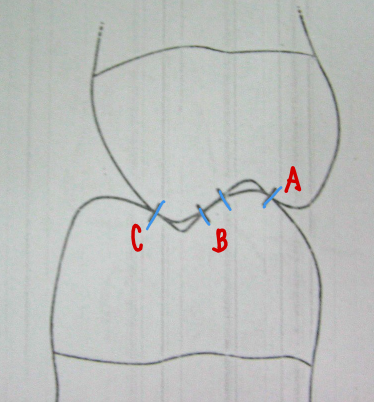
Shear cusp of mx → Stamp cusps of mn
Tooth Contact A
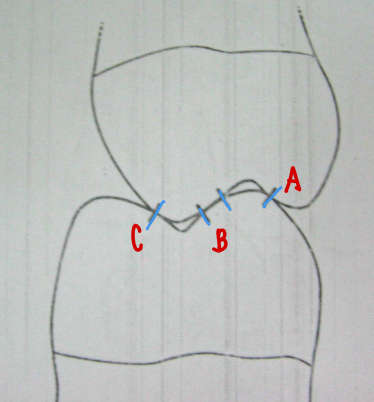
Stamp cusp of mx → Stamp cusp of mn
Tooth Contact B
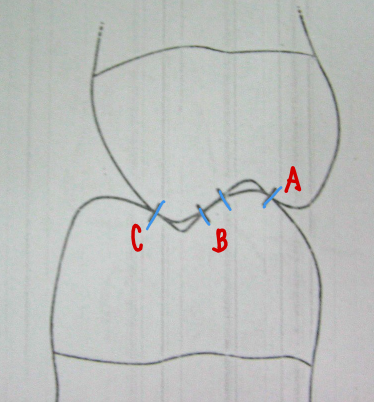
Stamp cusps of mx → Shear cusps of mn
Tooth Contact C
Tripodization
For every occluding tooth, three contact points are seen, this is called?
*this directs occlusal surfaces to the long axis of the tooth
counter contact; reciprocating force
For every tooth contact on an inclined surface, there is a _____ on another and opposite inclined surface, and a _____ to equalize occlusal forces
Cusp and fossa apposition
Most effective stabilizer of alignment
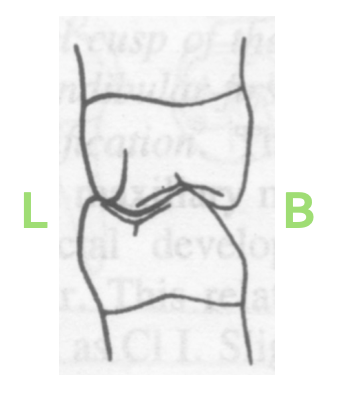
ML cusp; lingual embrasures
In cusp and embrasure apposition, ____________of all mandibular molars are in apposition with the _______________ of the maxillary molars
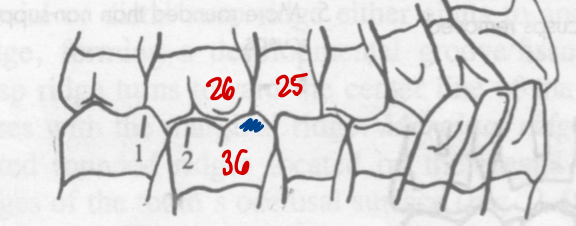
Ridge and sulcus apposition
Triangular ridges of the buccal cusps of mx molars → buccal grooves of the mn molars
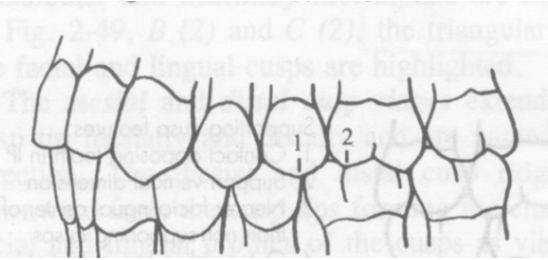
Ridge
Junction of 2 surfaces
Occlusal table
Area contained within the M and D edges of the occlusal surface
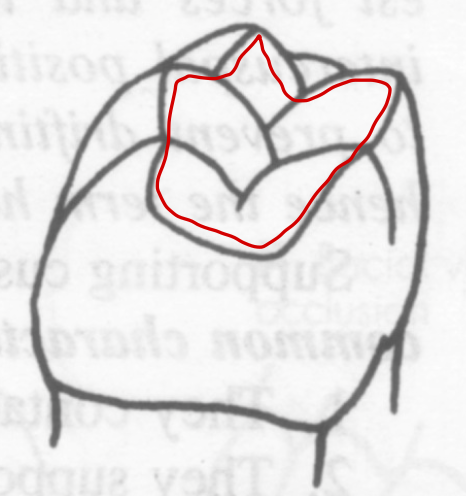
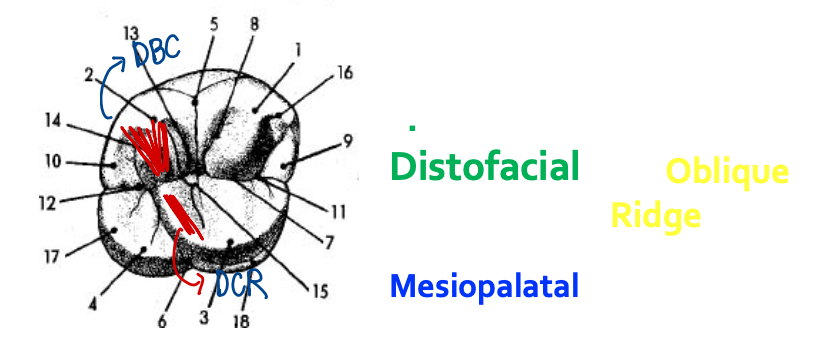
Distofacial cusps
Mandibular first molars have extra long triangular ridges on the _____ causing deviation of the central groove
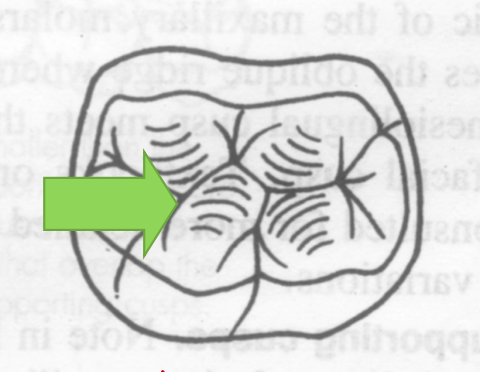
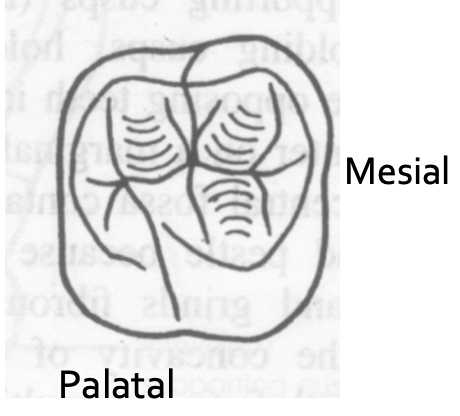
Which cusp is larger?
Mesiopalatal cusp
DCR of the MLC of 16/26 + Triangular ridge of the DBC
What forms the oblique ridge?