asexual and sexual reproduction
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
traits def
charateristics that belong to an organism that make them unique
offspring def
children produced through reproduction
asexual reproduction (general def)
requires one parent
creates genetically identical offsprings (“clones”)
clone def
exact genetic replica of another organism
7 types of asexual reproduction
budding
binary fission
fragmentation
sporing
vegetative propagation
mitosis
parthenogenesis
budding
when offspring comes from an outgrowth/bud of the parent
occurs in plants, yeast, and animals
GENETICALLY IDENTICAL TO PARENT
binary fission
when parent copies its genetics then splits into 2
occurs in bacterica
GENETICALLY IDENTICAL TO PARENT
fragmentation
when parent splits into fragments, and each fragment becomes a clone
FRAGMENTATION AND REGENERATION ARE NOT THE SAME
occurs in animals (?)
GENETICALLY IDENTICAL TO PARENT
sporing
when parent produces spores that grow by attaching to something and making it mold (TLDR: mold are spores)
SPORES ARE NOT SEEDS
occurs in fungi
GENETICALLY IDENTICAL TO PARENT
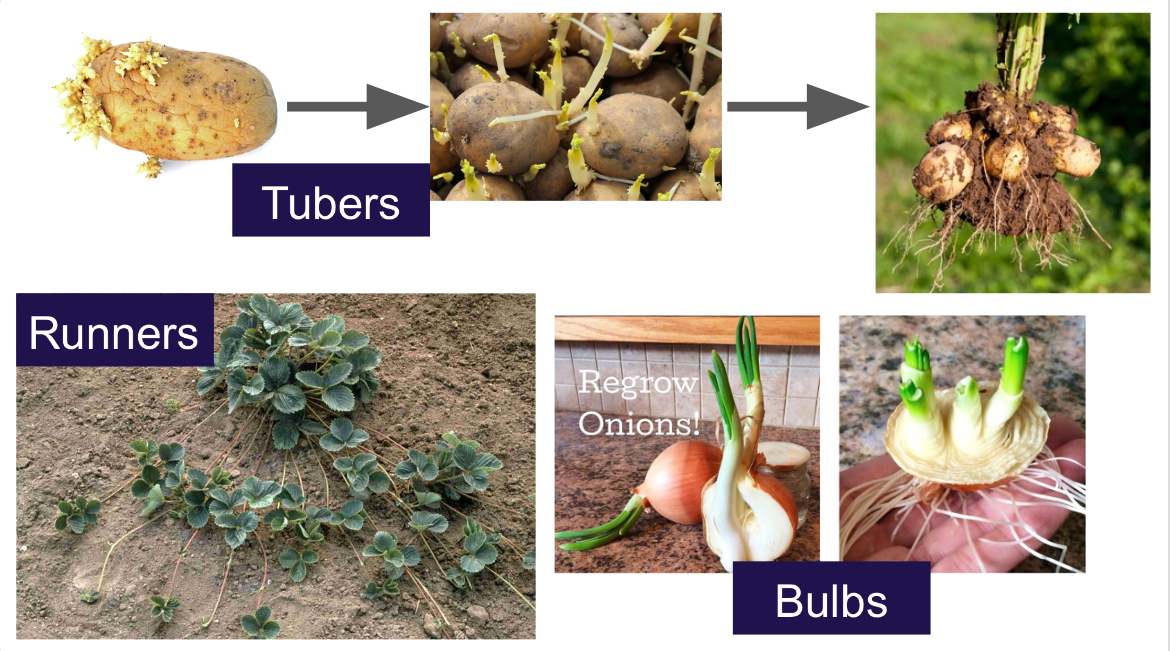
vegetative propagation (V.P for short)
when parent develops plant parts like stems, roots, leaves (NOT SEEDS OR SPORES) that create offspring
DIFFERENT TYPES OF V.P ARE RUNNERS, BULBS, AND TUBERS
occurs in plants
GENETICALLY IDENTICAL TO PARENT
mitosis
when human cells make more human cells to replace dead cells
occurs ONLY IN HUMAN CELLS
GENETICALLY IDENTICAL TO PARENT
parthenogenesis
when parent reproduces with an egg without fertilization from sperm
ONLY FEMALES CAN DO THIS BECAUSE THEY HAVE THE EGG
occurs in animals, plants, and fungi
GENETICALLY IDENTICAL TO PARENT
sexual reproduction (general def)
requires 2 parents
creates genetically DIFFERENT offspring
contains traits from both the mom and dad
4 types of sexual reproduction
fertilization (internal or external)
cross pollination
self pollination
conjugation
fertilization
when 2 gametes (sex cells) fuse together and make a zygote (the first cell that all organisms originate from
occurs mainly in animals
genetically DIFFERENT than parents
plant sexual reproduction crash course
most plants can reproduce asexually and sexually
most plants have both male and female parts (some can be either/or)
in plants male and female gametes unite to produce new offspring
cross-pollination
when the pollen/sperm of one plant is transferred to the female parts of another plant
usually achieved by wind or animals
genetically DIFFERENT than parents
self-pollination
when the pollen/sperm of a plant is transferred to the female part of the SAME flower
usually achieved by wind or animals
genetically DIFFERENT than parents
conjugation
2 bacteria swap portions of their DNA and create a new offspring with the new DNA
bacteria do this to mutate and become resistant to antibiotics and drugs
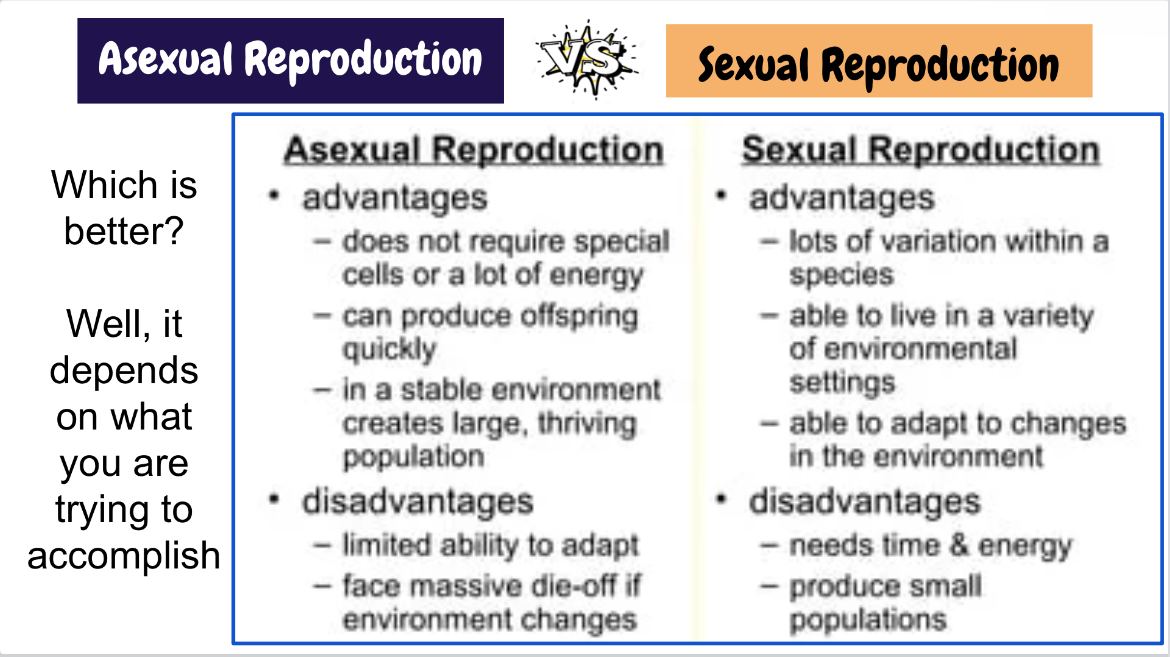
advantaged and disadvantages