earth science carbon study guide
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
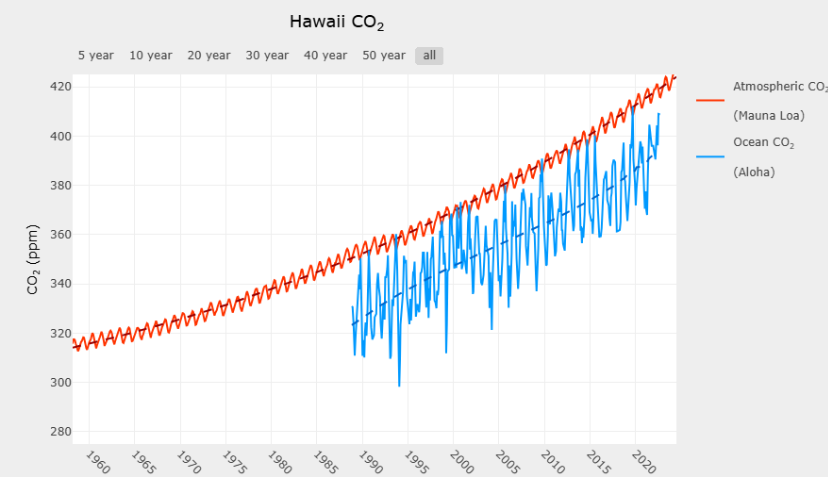
1.Notice how CO2 changes over the course of one year. These regular ups and downs are likely caused by:
photosynthesis and respiration
Next, notice how CO2 changes over the 60-year time period. The long-term, upward trend is likely caused by:
Burning of fossil fuels, aka human activities.
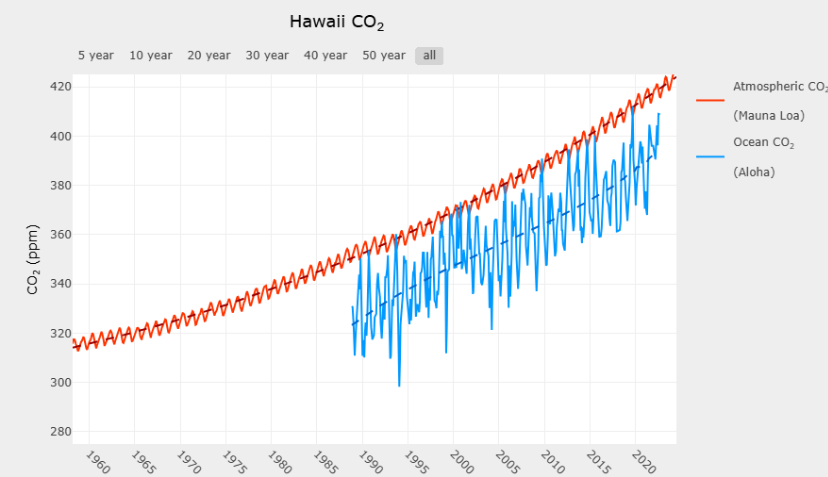
Which statement best describes the relationship between ocean CO2 and pH?
When CO2 increases, pH decreases and acidity increases
CO2 and pH both change in a predictable pattern from year to year. These regular ups and downs are not caused by carbon dioxide emissions in the atmosphere. Instead, they are likely caused by:
seasonal changes in both photosynthesis and respiration
When carbon dioxide enters the ocean, it reacts with water and carbonate to form:
bicarbonate
When carbon dioxide enters the ocean, the amount of carbonate available for shell-building animals:
decreases
What is the carbon cycle?
the continuous movement of carbon atoms throughout the Earth's systems, where carbon is exchanged between the atmosphere, living organisms, oceans, and soil, primarily through processes like photosynthesis, respiration, decomposition, and the burning of fossil fuels
What is the correct order for the carbon cycle, starting from “Carbon enters the atmosphere via carbon dioxide.”
Carbon enters the atmosphere via carbon dioxide.
Carbon dioxide is absorbed and used as energy.
Carbon compounds enter the food chain.
Carbon reenters the atmosphere via decomposition.
The carbon cycle repeats.
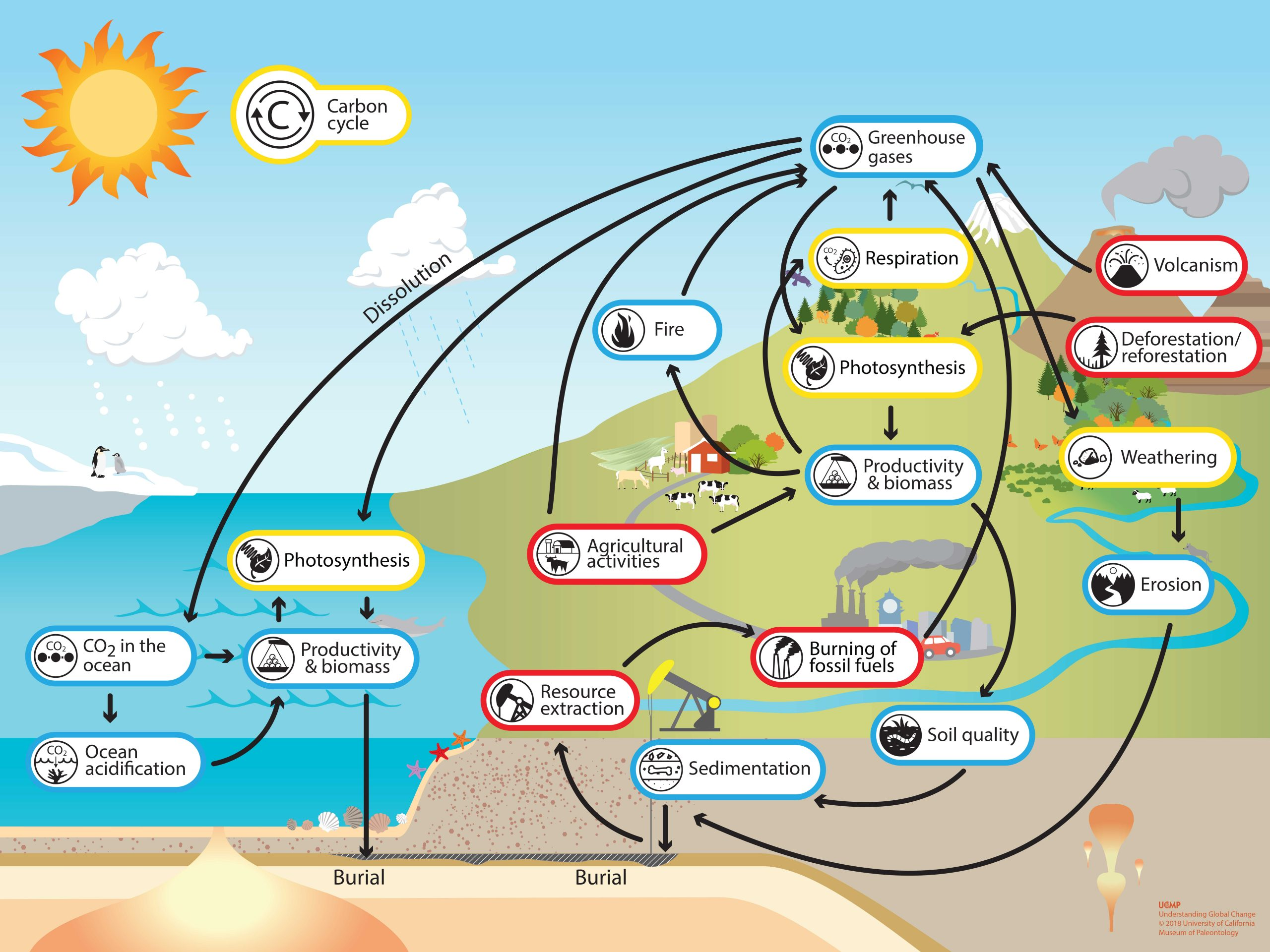
Look at the image.
I’ve looked at the image.
What is carbon capture?
capturing carbon dioxide (CO2) at emission sources, transporting and then storing or burying it in a suitable deep, underground location. It can also mean the removal of CO2 directly or indirectly from the atmosphere.
What is geological carbon sequestration?
a method of securing carbon dioxide (CO2) in deep geologic formations to prevent its release to the atmosphere and contribution to global warming as a greenhouse gas.
What is oceanic carbon sequestration?
the process where the ocean absorbs carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and stores it in the deep sea, essentially acting as a natural "carbon sink" by capturing and holding carbon
Technological challenges?
high energy consumption needed to capture CO2
The cost of implementing the technology
the need for large-scale infrastructure for storage
Potential leakage from storage sites
Concerns about the long-term safety and effectiveness of storage
The development of efficient capture methods for low-concentration CO2 sources
Regulatory challenges?
inconsistent frameworks across jurisdictions
lengthy permitting processes
unclear guidelines for CO2 transportation
lack of standardized storage regulations
potential issues with cross-state pipeline permitting
concerns around liability and long-term monitoring of storage sites
Financial challenges?
Without substantial efficiency improvements, the cost per tonne of CO2 captured is likely to exceed the revenue that the project can generate for each tonne captured
Using carbon scrubbers or towers that capture CO2 from the atmosphere
Direct capture
Storing carbon in subterranean (underground) rocks.
CO2 sinks
CO2 is captures from a gas mixture produced by partial oxidation of natural gas or biomass.
Pre combustion
Separation of CO2 from emission point sources or the atmosphere.
Carbon capture
Long-term liability for underground sites where carbon dioxide will be stored.
Regulatory challenges