BIOL 1170 - Final Exam Review
1/56
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
The independent variable data value is located on the __ axis.
x-axis
The scale of a graph tells you ...
the value or quantity represented by the units on the axes.
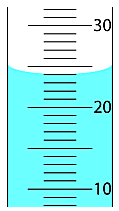
Assume the graduated cylinder pictured below is a 50ml graduated cylinder. How many milliliters of liquid are contained in this graduated cylinder?
24
![<p>Calculate the range for the following data set: [4, 8, 15, 16, 23, 42]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/0570b523-62a9-4f22-85ff-5a18e0db987b.png)
Calculate the range for the following data set: [4, 8, 15, 16, 23, 42]
38
What is the definition of a hypothesis in the scientific method?
A tentative explanation or prediction that can be tested through experimentation.
Which of the following is the best definition for the word Science?
The process of accumulating and interpreting knowledge in an organized manner.
What is the total magnification of an image viewed through a 15X ocular lens and a 40X objective lens?
600X
The Depth of Field is defined as . . .
The distance between the nearest and the farthest objects that are in acceptably sharp focus in an image.
Every observation should begin with the low power objective lens.
True
Resolution is defined as
The ability of an optical system to distinguish or separate details in an observed object.
Click on the image that displays the greatest field of view.
40X
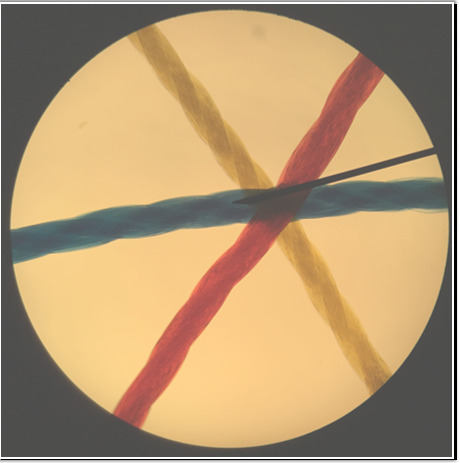
Complete the sentence below.
"The lens seen beneath the opening in the stage is the ________. This focuses a cone of light on the specimen. For most work, this lens should be at its upmost position."
substage condenser
A microscope is equipped with an objective lens having a numerical aperture (NA) of 0.65. The microscope is illuminated with light of a wavelength (λ) of 420 nanometers. Apply Abbe's equation to calculate the theoretical limit of resolution for this microscope. Approximate to the nearest tenth.
Abbe's equation:
R = (0.61λ) / NA
394.2 nm
List these optical structures of the compound microscope in the order that corresponds to the path that light travels.
Substage Condenser, Head/Prism Housing, Objective Lens, Ocular Lens/Eyepiece, Light Source, Iris Diaphragm
Light Source
Iris Diaphragm
Substage Condenser
Objective Lens
Head/Prism Housing
Ocular Lens/Eyepiece
Click on the image that displays the greatest depth of field.
40X
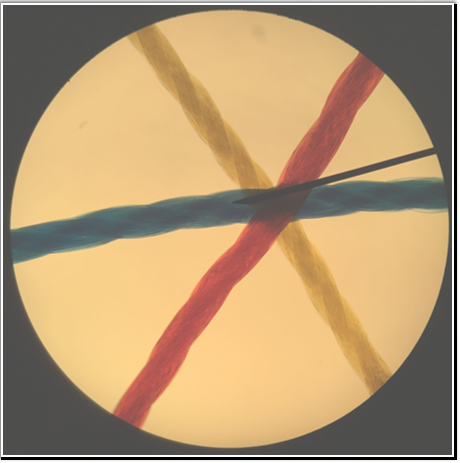

The image below is of the coaxial stage control knobs. There are two of these: one moves the stage forward and backward, the other moves the stage left and right.
Does the knob labeled '2' move the stage forward and backward, or left and right?
Left and Right
Iodine (iodine-potassium iodide) is a yellowish-brown solution which is used to detect the presence of starch. Iodine forms a complex with starch which is very stable and produces a color change. In the presence of starch, Iodine solution becomes _____.
Bluish Black
These are the four major groups of biological macromolecules.
carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids
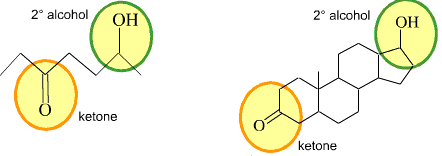
Alcohol groups and ketone groups, such as the ones highlighted below, are examples of specific groups of atoms within a molecule that are responsible for the characteristic chemical reactions of that molecule. What are these called?
functional groups

The picture below shows a hand holding a transfer pipette such as the one you have used in the lab. Approximately how much volume is being held inside the transfer pipette?
0.25 ml
Benedict’s reagent contains cupric ion (Cu2+) and appears blue in solution. When cupric ion (Cu2+) becomes reduced to cuprous ion (Cu+), the color of the solution changes to red. This occurs in the presence of ________.
Reducing sugars
In a study investigating the effectiveness of a new drug in inhibiting bacterial growth, researchers divided individuals with some particular infection into three groups: one which received the new drug, one which received no drugs, and one which received a known antibiotic for this infection. Identify the positive control, negative control, and the experimental group in this study.
Positive Control: Group with the known antibiotic.
Negative Control: Group with no drugs
Experimental Group: Group with the new drug
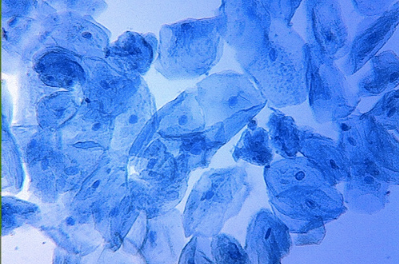
What type of cells are shown below?
Animal cells
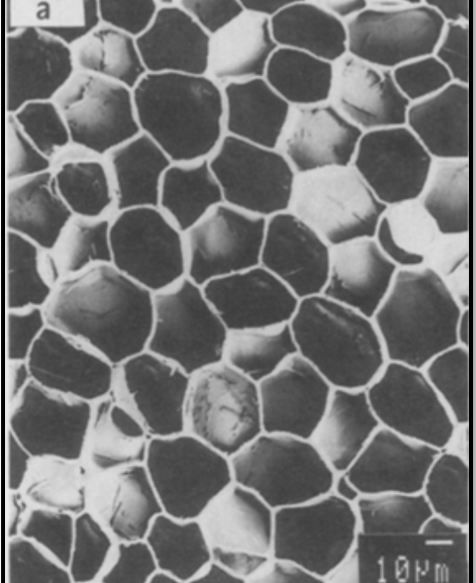

Which cell structure is most clearly visible in this image of cork cells?
Cell Wall
Which of the following are true of eukaryotic cells? Check all that apply.
They are generally larger than prokaryotic cells
They contain a nucleus
They contain ribosomes
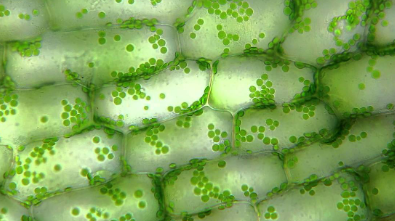
What is the name of the green discoid organelles in the cells below.
Chloroplasts

The movement of organelles around the periphery of the cell, that occurs as a result of a movement of the cytoplasm, is called __________.
cytoplasmic streaming
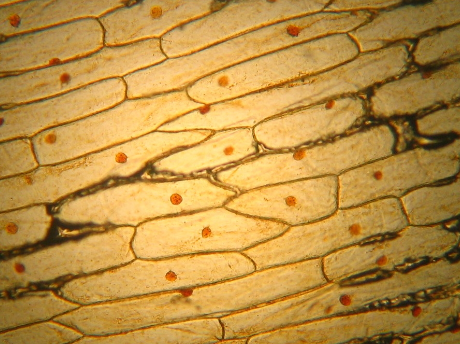
The image below shows a section of onion epidermis which has been stained with Iodine. What is the brown spherical structure within each cell?
nucleus
What role do enzymes play within living organisms?
They facilitate and speed up chemical reactions.
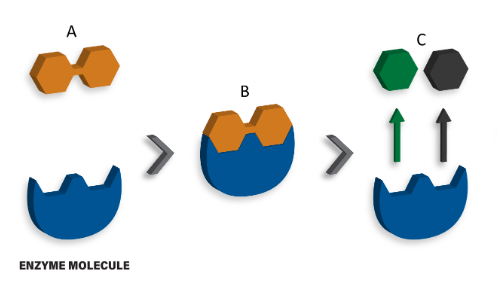
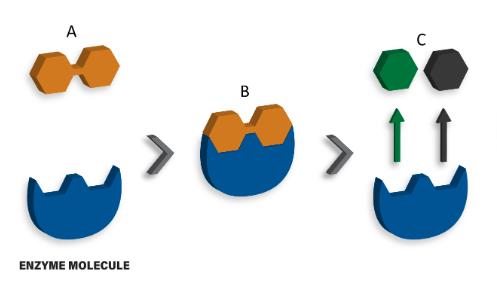
The image below depicts a disaccharide being hydrolyzed by an enzyme molecule into it's constituent monosaccharides. In this image, what is the term used for the disaccharides labeled B?
enzyme-substrate complex
The Benedict's test for reducing sugars requires that we do what to the reaction tube (the test tube containing the Benedict's reagent and the test solution)?
we need to gently boil it for approximately three minutes
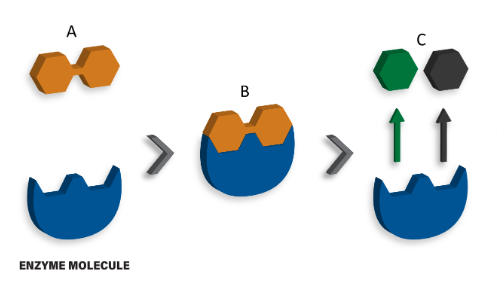
The image below depicts a disaccharide being hydrolyzed by an enzyme molecule into it's constituent monosaccharides. In this image, what is the term used for the disaccharides labeled A?
Substrate
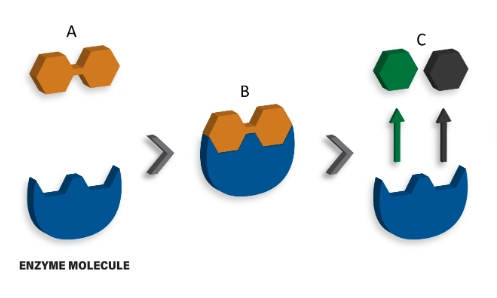
The image below depicts a disaccharide being hydrolyzed by an enzyme molecule into it's constituent monosaccharides. In this image, what is the term used for the disaccharides labeled C?
Products
Which of the following factors affect the rate at which enzymes catalyze chemical reactions? Check all that apply.
temperature
concentration of the substrate
concentration of the enzyme
pH
Enzymes belong to which class of biological macromolecules?
Proteins
At what temperature does water freeze?
-38 C, -38 F, 0 C, 0 F, 58 C, 58 F, 100 C, 100 F
0 C
At what temperature does water boil?
0 C, 0 F, 38 C, 38 F, 100 C, 100 F, 365 C, 365 F
100 C
If oxygen is absent, many organisms, such as the yeast we used in the lab, are able to reduce pyruvate to CO2 and ethanol via a process called ___________. Organisms that don't use oxygen for respiration are called anaerobes. The yeast we worked with in the lab are facultative anaerobes, which means they can undergo both aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
fermentation
Fermentation produces more ATP per glucose molecule than does aerobic respiration.
False
Why was NaF used in our cellular respiration/fermentation experiment?
NaF is an inhibitor of some enzymes of glycolysis
If oxygen is present, most organisms continue __________ by oxidizing pyruvate to CO2 via chemical reactions of the Krebs cycle. Organisms that use oxygen for _________ beyond glycolysis are called aerobes.
cellular respiration
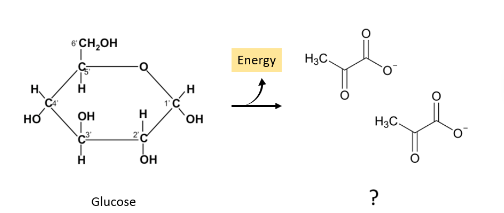
Glucose is a six-carbon molecule that is broken down to two three-carbon molecules in the final step of glycolysis. What is the name of this three-carbon molecule?
Pyruvate
What has happened to the amount of genetic material in a cell after the S phase of interphase?
It has doubled
Which is true about the chromosome content of gametes?
It is half of somatic cells
Your lab partner is examining an onion mitosis slide through the light microscope. She is looking for chromosomes in a cell that is in interphase, but is frustrated that she cannot see individual chromosomes in her slide. What should you tell her?
Chromosomes are not visible in interphase using a light microscope.
In genetics, a _______ refers to the specific physical location of a gene or DNA sequence on a chromosome.
locus
At the poles of the cell, the centrioles radiate an array of microtubules outward in addition to the spindle apparatus. These microtubules brace the centrioles against the cell membrane. This arrangement of microtubules radiating from a centriole is called an _________.
aster
What is the difference between homologous chromosomes and chromatids?
Homologous chromosomes may carry different alleles of a gene.
In which type of cells does meiosis occur?
cells that form sperm
Which event occurs only in meiosis (and not in mitosis)?
Crossing over occurs between homologous chromosomes during Prophase I.
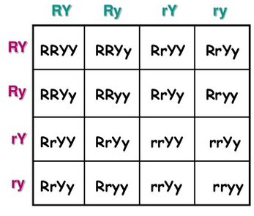
How many zygotes are round?
R=Rod-shaped and r=round. Rod-shaped is dominant
Y=Yellow and y=blue. Yellow is dominant.
4
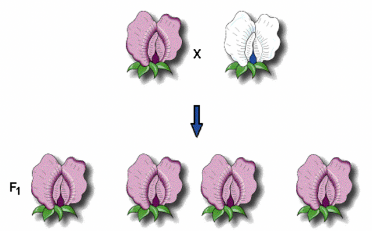
The white coloring on these flowers is ____________ phenotype.
Recessive
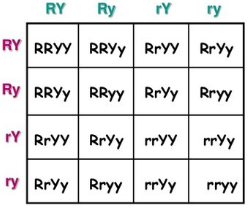
How many zygotes are yellow?
Y=Yellow and y=blue. Yellow is dominant.
R=Rod-shaped and r=round. Rod-shaped is dominant
12
What is true of a monohybrid cross?
A single character is involved. Such as Kernel Color:Yellow/purple
In which year did Gregor Mendel write his famous paper "Experiments in Plant Hybridization"?
1866
Gregor Mendel formulated three fundamental laws of genetics based on his experiments with pea plants. These laws laid the groundwork for our understanding of inheritance patterns and are known as Mendel's Laws or Mendelian Genetics. Which of the following were these?
Law of Independent Assortment
Law of Segregation
Law of Dominance
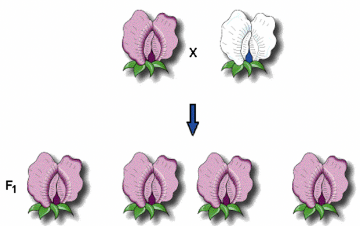
From the results above, the F1 generations phenotypic ratio is ______
100% Purple