Lesson 2
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
Nervous system
The basis for our ability to perceive, adapt to, and interact with the world around us. Through this system, we receive, process, and then respond to information from the environment.
Neurons
Transmit electrical signals from one location to another in the nervous system.
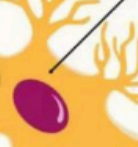
Soma
It contains the nucleus of the cell (the center portion that performs metabolic and reproductive functions for the cell), responsible for the life of the neuron and connects the dendrites to the axon.
Dendrites
Branch-like structures that receives information from other neurons.

Axon
A long, thin tube that extends from the soma and responds to the information, when appropriate, by transmitting an electrochemical signal, which travels to be terminus, where the signal can be transmitted to other neurons.
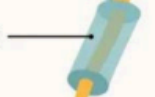
Myelin sheath
A white fatty substance that surrounds some of the axons of the nervous system, which accounts for some of the whiteness of the white matter of the brain. This sheat insulates interference by other neurons in the area, also speeds up the conduction of information.

Nodes of Ranvier
Small gaps in the myelin coating along the axon, which serve to increase conduction speed even more.

Terminal buttons
Small knobs found at the ends of the branches of an axon that do not directly touch the dendrites of the next neuron.
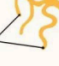
Synapse
Serve as a juncture between the terminal buttons of one or more neurons and the dendrites
Neuro transmitters
Serve as chemical messengers for transmission of information across the synaptic gap to the receiving dendrites of the next neuron.
Acetylcholine
D: Monoamine neurotransmitter synthesized from choline
GF: Excitatory in brain and either excitatory (at skeletal muscles) or inhibitory (at heart muscle) elsewhere in the body
SE: Believed to be involved in memory because of high concentration found in the hippocampus
Dopamine
D: Monoamine neurotransmitter synthesized from tyrosine
GF: Influences movement, attention, and learning: mostly inhibitory but some excitatory effects
SE: Parkison’s disease, characterized by tremors and limb rigidity, results from too little DA
Epinephrine and Norepinephrine
D: Monoamine neurotransmitter synthesized from tyrosine
GF: Hormones (also known as adrenaline and noradrenaline) involved in the regulation of alertness
SE: Involved in diverse effects in the body related to fight-or-flight reactions, anger, and fear
Serotonin
D: Monoamine neurotransmitter synthesized from tryptophan
GF: Involved in arousal, sleep and dreaming, and mood; usually inhibitory but some excitatory effects
SE: Normal inhibits dreaming: defects in this system are linked to severe depression
GABA (Gamma-aminobutyric acid)
D: Amino acid neurotransmitter
GF: General neuromodulatory effects resulting from inhibitory influences in presynaptic axons.
SE: Currently believed to influence certain mechanisms for learning and memory
Glutamate
D: Amino acid neurotransmitter
GF: General neuromodulatory effects resulting from excitatory influences on presynaptic axons
SE: Currently believed to influence certain mechanisms for learning and memory
Neuropeptides
D: Peptide chains serving as neurotransmitters
GF: General neuromodulatory effects resulting from influences on postsynaptic membranes
SE: Endorphins play a role in pain relief. Neuromodulating neuropeptides sometimes are released to enhance the effects of ach
Postmortem studies
After the patients die, the researchers examine the patients’ brains for lesions-areas where body tissue has been damaged, such as from injury or disease.
Cerebral cortex, Basal ganglia, Limbic systems, Thalamus, and Hypothalamus
Forebrain
Cerebral cortex
Involved in receiving and processing sensory information, thinking other cognitive processing, and planning and sending motor information
Basal ganglia
Crucial to the function of the motor system
Hippocampus, amygdala, and septum
Limbic systems
Limbic systems
Involved in learning, emotions, and motivation.
Thalamus
Primary relay station for sensory information coming into the brian: transmits information to the correct regions of the cerebral cortex.
Four key nuclei for sensory information
(1) from the visual receptors via optic nerves, to the visual cortex, permitting us to see; (2) from the auditory receptors, via auditory nerves, to the auditory cortex, permitting us to hear; (3) from sensory receptors in the somatic nervous system, to the primary somatosensory cortex, permitting us to sense pressure and pain: and (4) from the cerebellum (in the hindbrain) to the primary motor cortex, permitting us to sense physical balance and equilibrium
Hypothalamus
Controls the endocrine system; controls the autonomic nervous system, such as internal temperature regulation, appetite, and thirst regulation.
Superior colliculi, Inferior colliculi, and Reticular activating system
Midbrain
Superior colliculi (on top)
Involved in vision
Inferior colliculi (below)
Involved in hearing
Reticular activating system
Important in controlling consciousness (sleep arousal), attention, cardiorespiratory, function, and movement.
Cerebellum,, Pons, and Medulla oblongata
Hindbrian
Cerebellum
Essential to balance, coordination, and muscle tone
Pons
Involved in consciousness (sleep and arousal); bridges neural transmissions from one part of the brain to another; involved with facial nerves.
Medulla oblongata
Serves as a juncture at which nerves cross from one side of the body to the opposite side of the brain; involved in cardiorespiratory function, digestion, and swallowing.
Cerebral cortex
Forms a 1-3 millimeter layer that wraps the surface of the brain somewhat like the bark of a tree wraps around the trunk.
Right Cerebral hemisphere
Specialized for other kinds like receptors in the skin on the right side of the body, send information through the medulla to areas in the left hemisphere in the brain.
Left hemisphere
Directs the motor response on the right side of the body.
Dax
Treated more than 40 patients suffering from aphasia-loss of speech as a result of brain damage. He noticed a relationship between the loss of speech and the side of the brain in which damage had occurred.
Paul Broca
He claimed that an autopsy revealed that an aphasic stroke patient had a lesion in the left cerebral hemisphere of the brain.
He is also the person who was convinced that the left hemisphere of the brain is critical in speech. A view that has held up over time. The specific part of the brain that Broca identified, now called Broca's area, contributes to speech. Broca's area also plays a pivotal role in imitation.
Carl Wernicke
He studied language-deficient patients who could speak but whose speech made no sense
Frontal, Parietal, Temporal, and Occipital lobe
Lobes of the cerebral hemisphere
Karl Spencer Lashley
Often described as the father of neuropsychology.
Frontal lobe
Toward the front of the brain. Associated with motor processing and higher thought process, such as abstract reasoning, problem-solving, planning, and judgment.
Parietal lobe
The upper back portion of the brain is associated with somatosensory processing. It receives inputs from the neurons regariding touch, pain, temperature sense, and limb position.
Temporal lobe
Directly under your temples associated with auditory processing and comprehending language. Also involved in your retention of visual memories.
Occipital lobe
Associated with visual processing. This lobe contains numerous visual areas, each specialized to analyze specific aspects of a scene, including color, motion, location, and form.
Stroke, Brain tumors, and Head Injuries
Brain Disorders
Stroke
Vascular disorder. It occur when the flow of blood to the brin undergoes a sudden disruption.
Brain Tumors
Also called neoplasms, can affect cognitive functioning in very serious ways.
Head injuries
Can result from many causes, such as car accidents, contact with a hard object, and bullet wounds.
Closed-head and Opened-Head Injuries
Types of Head Injuries
Closed-head injuries
The skull remains intact but there is damaged to the brain, typically from the mechanical force of a blow to the head.
Open-head injuries
The skull does not remain intact but rather is penetrated, for example, by a bullet.