Nervous System
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/114
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
115 Terms
1
New cards
Development of the Nervous System
- begins as a tube along the axis of the body
- folds over during development and is hollow as a result
- starts as 3 swellings after 4 weeks in the uterus (turns into 5)
- neural tube becomes the spinal cord
- folds over during development and is hollow as a result
- starts as 3 swellings after 4 weeks in the uterus (turns into 5)
- neural tube becomes the spinal cord
2
New cards
Rhombencephalon
Hindbrain
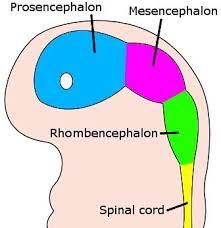
3
New cards
Mesencephalon
Midbrain
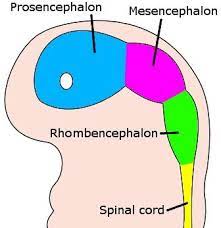
4
New cards
Prosencephalon
Forebrain
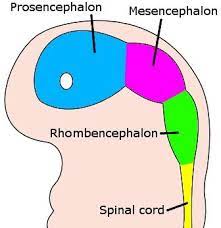
5
New cards
spina bifida
when the neural tube doesn't completely close at the caudal end
6
New cards
Central Nervous System
- brain
- spinal cord
- spinal cord
7
New cards
Peripheral Nervous System
- neural tissue outside of the CNS
- sensory and motor neurons
- sensory and motor neurons
8
New cards
Sensory Nervous System
contains receptors that transmit information to the CNS
9
New cards
Motor Nervous System
- transmits information for the CNS to the rest of the body
- sends motor information to effectors
- sends motor information to effectors
10
New cards
Somatic Sensory
- apart of the sensory nervous system
- voluntary actions
- voluntary actions
11
New cards
Visceral Sensory
- apart of the sensory nervous system
- involuntary actions
- involuntary actions
12
New cards
Somatic Motor
- apart of the motor nervous system
- voluntary actions
- voluntary actions
13
New cards
Autonomic Motor
- apart of the motor nervous system
- involuntary actions
- involuntary actions
14
New cards
Gray Matter
- consists of neural and glial cell bodies
- outer portion of the brain
- inner portion of the spinal cord
- outer portion of the brain
- inner portion of the spinal cord
15
New cards
White Matter
- consists of axons
- inner portion of the brain
- outer portion of the spinal cord
- inner portion of the brain
- outer portion of the spinal cord
16
New cards
Nerves
- cable like bundle of parallel axons
- surrounded by three layers of connective tissue
- surrounded by three layers of connective tissue
17
New cards
Endoneurium
delicate connective tissue around individual axons in nerve
18
New cards
Perineurium
the sheath of connective tissue that covers a bundle of nerve fibers (fascicles)
19
New cards
Epineurium
connective tissue surrounding the entire nerve
20
New cards
Synapse
- junction between two neurons that is responsible for unidirectional transmission of nerve impulses
- can make contact with cell bodies, dendrites or other axons
- release neurotransmitters
- can make contact with cell bodies, dendrites or other axons
- release neurotransmitters
21
New cards
Excitatory
- type of synapse
- activity promotes impulses
- depolarizes the next cell membrane
- activity promotes impulses
- depolarizes the next cell membrane
22
New cards
Inhibitory
- type of synapse
- inhibits impulse transmission
- hyperpolarizes next cell membrane
- inhibits impulse transmission
- hyperpolarizes next cell membrane
23
New cards
Acetylcholine
- neurotransmitter that is released at all neuromuscular junctions
24
New cards
Multipolar Neuron
- has several dendrites
- one axon
- majority of the neurons in the CNS
- one axon
- majority of the neurons in the CNS
25
New cards
Unipolar Neuron
- one long axon with dendrites at the end
- touch and stretching
- touch and stretching
26
New cards
Bipolar Neurons
- one dendrite and one axon
- makes up many sensory nerves
- makes up many sensory nerves
27
New cards
Pyramid Neuron
- type of multipolar neuron
- triangular shaped bodies
- found in the cerebral cortex, hippocampus and amygdala
- linked to cognitive ability
- triangular shaped bodies
- found in the cerebral cortex, hippocampus and amygdala
- linked to cognitive ability
28
New cards
Neuroglia
- glial cells
- CNS and PNS
- physically protect and nourish the neuron
- higher amount compared to the amount of neurons
- CNS and PNS
- physically protect and nourish the neuron
- higher amount compared to the amount of neurons
29
New cards
Oligodendrocytes
- CNS axons only
- extensions of cytoplasm that wrap around the axon
- produce myelin to insulate the electrical activity and produce rapid nerve impulses
- extensions of cytoplasm that wrap around the axon
- produce myelin to insulate the electrical activity and produce rapid nerve impulses
30
New cards
Schwann Cells
- PNS only
- whole cell that wraps around an axon
- insulate electrical activity by myelinating the axons for rapid nerve impulses
- whole cell that wraps around an axon
- insulate electrical activity by myelinating the axons for rapid nerve impulses
31
New cards
Astrocytes
- most common glial cell
- regulation of the environment around axons and synapses
- repairs damage of neurons
- regulation of the environment around axons and synapses
- repairs damage of neurons
32
New cards
Microglia
- type of macrophage associated with the immune system
- clean-up cell
- clean-up cell
33
New cards
Multiple Sclerosis
- results from the destruction of the myelin sheath and axons
34
New cards
Meninges
- three layers of connective tissue that surround the spinal cord and brain
- protection
- protection
35
New cards
Pia Mater
- innermost layer of meninges
- adheres to surfaces
- highly vascular
- adheres to surfaces
- highly vascular
36
New cards
Arachnoid Mater
- middle layer of meninges
- weblike and avascular
- weblike and avascular
37
New cards
Dura Mater
- outer layer of meninges
- dense, irregular connective tissue
- 2 layers in the brain
- dense, irregular connective tissue
- 2 layers in the brain
38
New cards
Epidural Space
- area between the vertebral column/cranium and dura mater
- blood vessels, fat and connective tissue
- blood vessels, fat and connective tissue
39
New cards
Subdural Space
- area between the arachnoid and dura mater
- contains interstitial fluid
- contains interstitial fluid
40
New cards
Subarachnoid Space
- area between the pia and arachnoid mater
- contains cerebralspinal fluid
- contains cerebralspinal fluid
41
New cards
Severe Head Trauma Cases
- can create bleeding between the meninges
- cause pressure that can destroy neurons and glia cells
- cause pressure that can destroy neurons and glia cells
42
New cards
Epidural Block
- regional anesthesia that numbs the lower body
43
New cards
Spinal Tap
- needle inserted between the lumbar vertebrae into subarachnoid space
- withdraws cerebrospinal fluid and can introduce substances
- withdraws cerebrospinal fluid and can introduce substances
44
New cards
Cerebrospinal Fluid
- produced in the choroid plexuses of each of the four brain ventricles
- found in the subarachnoid space of the brain and spinal cord
- protection of the brain; brain floats in it and provides cushioning
- transports nutrients and removes wastes
- found in the subarachnoid space of the brain and spinal cord
- protection of the brain; brain floats in it and provides cushioning
- transports nutrients and removes wastes
45
New cards
Hydrocephalus
- cerebrospinal fluid accumulates in the brain ventricles
- babies heads with swell
- babies heads with swell
46
New cards
Blood-Brain Barrier
- barrier that strictly regulates which substances can enter the interstitial fluid in the brain
- capillaries in the brain are selectively permeable
- glial cells surround the capillaries to catch things that get through the barrier
- capillaries in the brain are selectively permeable
- glial cells surround the capillaries to catch things that get through the barrier
47
New cards
Bone
- most important physical defense for the CNS
- not applicable for the PNS
- not applicable for the PNS
48
New cards
Spinal Cord
- pathway for sensory and motor impulses to and from the brain
- responsible for the quickest reflex reactions to a stimulus
- responsible for the quickest reflex reactions to a stimulus
49
New cards
External Spinal Cord Anatomy
- from medulla oblongata to second lumbar vertebra
- cervical enlargement consists of nerves from the upper limbs
- lumbosacral enlargement consists of nerves from the lower limbs
- cervical enlargement consists of nerves from the upper limbs
- lumbosacral enlargement consists of nerves from the lower limbs
50
New cards
Internal Spinal Cord Anatomy
- grey matter consisting of unmyelinated axons and glial cells, butterfly shape
- white matter consisting of myelinated axons
- white matter consisting of myelinated axons
51
New cards
Anterior Horns
- grey matter in spinal cord
- contain cell bodies of somatic motor neurons which innervate skeletal muscle
- contain cell bodies of somatic motor neurons which innervate skeletal muscle
52
New cards
Posterior Horns
- grey matter in spinal cord
- contain axons of sensory neurons
- cell bodies of interneurons
- contain axons of sensory neurons
- cell bodies of interneurons
53
New cards
Lateral Horn
- grey matter in spinal cord
- found in T1-L2
- cell bodies of autonomic motor neurons
- innervate cardiac and smooth muscle and glands
- found in T1-L2
- cell bodies of autonomic motor neurons
- innervate cardiac and smooth muscle and glands
54
New cards
Grey Commissure
- grey matter in spinal cord
- unmyelinated axons
- communication route between the right and left side
- unmyelinated axons
- communication route between the right and left side
55
New cards
Spinal Nerves
- make up PNS
- connect the CNS to sensory receptors, muscles and glands
- connect the CNS to sensory receptors, muscles and glands
56
New cards
Meningeal Branch
- branch of spinal nerves
- returns through vertebral foramen to innervate meninges, vertebrae and ligaments
- returns through vertebral foramen to innervate meninges, vertebrae and ligaments
57
New cards
Rami Communications
- two branches in the spinal nerves that function within the autonomic nervous system
58
New cards
Dorsal Ramus
- branch of spinal nerves
- innervate deep muscles and skin of the back
- innervate deep muscles and skin of the back
59
New cards
Ventral Ramus
- branch of spinal nerves
- innervate superficial back muscles, lateral and ventral muscles and skins and muscles of upper and lower limbs
- do not go directly to body structures and form networks on both sides of the body
- innervate superficial back muscles, lateral and ventral muscles and skins and muscles of upper and lower limbs
- do not go directly to body structures and form networks on both sides of the body
60
New cards
Cervical Plexus
- portion of anterior rami of the C1-C4 and part of C5
- positioned laterally
- head, neck, upper shoulders and chest
- positioned laterally
- head, neck, upper shoulders and chest
61
New cards
Phrenic Nerve
- C3-C5
- innervate the diaphragm
- innervate the diaphragm
62
New cards
Brachial Plexus
- positioned lateral from C5-T1
- extends downward under the clavicle into axilla
- part of shoulders and all upper limbs
- 5 major nerves
- extends downward under the clavicle into axilla
- part of shoulders and all upper limbs
- 5 major nerves
63
New cards
Axillary Nerve
- from brachial plexus
- sensory from skin of shoulder
- motion to some shoulder muscles
- sensory from skin of shoulder
- motion to some shoulder muscles
64
New cards
Musculocutaneous Nerve
- from brachial plexus
- flexors of the arm
- flexors of the arm
65
New cards
Radial Nerve
- from brachial plexus
- extensors of the arm and forearm
- extensors of the arm and forearm
66
New cards
Median Nerve
- from brachial plexus
- anterior forearm and portion of the hand
- anterior forearm and portion of the hand
67
New cards
Ulnar Nerve
- from brachial plexus
- anterior/medial forearm and majority of the hand
- anterior/medial forearm and majority of the hand
68
New cards
Lumbar Plexus
- side of anterior rami of L1-L4
- anterolateral abdominal walls, external genitals and parts of lower limbs
- 2 major nerves
- anterolateral abdominal walls, external genitals and parts of lower limbs
- 2 major nerves
69
New cards
Femoral Nerve
- from lumbar plexus
- anterior muscles of the thigh
- anterior muscles of the thigh
70
New cards
Obturator Nerve
- from lumbar plexus
- medial (adductor) muscles of the thigh
- medial (adductor) muscles of the thigh
71
New cards
Sacral Plexus
- immediately caudal to lumbar plexus
- formed by L4-S5
- lower back, pelvis, posterior thigh, parts of the foot
- one main nerve
- formed by L4-S5
- lower back, pelvis, posterior thigh, parts of the foot
- one main nerve
72
New cards
Sciatic Nerves
- largest nerve extending the length of each leg
- irritation can cause crippling pain and discomfort, pinching of the nerve (sciatica), arthritic inflammation, bulging disk, vitamin deficiencies
- irritation can cause crippling pain and discomfort, pinching of the nerve (sciatica), arthritic inflammation, bulging disk, vitamin deficiencies
73
New cards
Dermatomes
- area of skin supplied by a single spinal nerve (all but C1 innervate single portion)
74
New cards
Reflexes
- rapide involuntary reactions to a stimulus
- required to initiate a response
- few neurons must be involved and synaptic delay must be minimal
- occurs the same way everytime
- required to initiate a response
- few neurons must be involved and synaptic delay must be minimal
- occurs the same way everytime
75
New cards
Reflex Arc
1. stimulus
2. sensory neuron activated
3. processed in the CNS
4. motor neuron activated
5. response by effector
2. sensory neuron activated
3. processed in the CNS
4. motor neuron activated
5. response by effector
76
New cards
Telencephalon
- the anterior division of the forebrain consisting of the cerebrum
77
New cards
Diencephalon
- the posterior division of the forebrain consisting of the thalamus, epithalamus and hypothalamus
78
New cards
Mesencephalon
- midbrain
79
New cards
Metencephalon
- the part of the hindbrain that develops into the pons and the cerebellum
80
New cards
Myelencephalon
- the posterior part of the hindbrain that forms the medulla oblongata
81
New cards
Medulla Oblongata
- last portion of the brain before the spinal cord
- contains sensory and motor tracts to and from the brain
- controls heart rate and breathing
- vomiting, coughing and sneezing reflexes
- contains sensory and motor tracts to and from the brain
- controls heart rate and breathing
- vomiting, coughing and sneezing reflexes
82
New cards
Pons
- contains sensory and motor tracts that connect the brain and spinal cord (bridge)
- helps to regulate the breathing rate
- involved in sound localization
- helps to regulate the breathing rate
- involved in sound localization
83
New cards
Cerebellum
- second largest part of the brain
- highly convoluted surfaced covered in folds
- coordinates and fine tunes skeletal muscle movement
- monitors position of joints and muscles
- highly convoluted surfaced covered in folds
- coordinates and fine tunes skeletal muscle movement
- monitors position of joints and muscles
84
New cards
Midbrain
- between pons and diencephalon
- controls various sub or unconscious movement of the eye
- contains elements of the auditory pathway
- controls various sub or unconscious movement of the eye
- contains elements of the auditory pathway
85
New cards
Diencephalon
- contains the thalamus, epithalamus and hypothalamus
- surrounds the third ventricle
- surrounds the third ventricle
86
New cards
Thalamus
- paired oval masses of grey matter, each consisting of a dozen thalamic nuclei
- division of the diencephalon
- all sensory signals pass through here (excluding smell)
- division of the diencephalon
- all sensory signals pass through here (excluding smell)
87
New cards
Hypothalamus
- division of the diencephalon
- involved in hormone production
- regulation of emotions, eating, drinking and body temperature
- involved in hormone production
- regulation of emotions, eating, drinking and body temperature
88
New cards
Epithalamus
- connects the limbic system to the rest of the brain
- division of the diencephalon
- main component is the pineal gland
- important for sleep regulation
- division of the diencephalon
- main component is the pineal gland
- important for sleep regulation
89
New cards
Cerebrum
- location of conscious thought processes and the origin of intellectual functions
- formed from the telencephalon
- surface folds into elevated ridges
- formed from the telencephalon
- surface folds into elevated ridges
90
New cards
Gyri
- adjacent gyri are separated by shallow grooves (sulci) or deeper grooves (fissures)
91
New cards
Cerebral Hemispheres
- 2 components of the cerebrum
- divided by a longitudinal fissure extends along the midsagittal plane
- memory and consciousness can not be assigned to particular regions
- divided by a longitudinal fissure extends along the midsagittal plane
- memory and consciousness can not be assigned to particular regions
92
New cards
Corpus Callosum
- main tract connecting the right and left cerebral hemispheres
93
New cards
Olfactory Nerve
- cranial nerve that carries impulses to the brain from the olfactory epithelium
- (I)
- sensory only
- only type of nervous tissue to regenerate
- anosmia is partial or total loss of smell
- (I)
- sensory only
- only type of nervous tissue to regenerate
- anosmia is partial or total loss of smell
94
New cards
Optic Nerve
- (II) cranial nerve that carries impulses from the retina
- sensory only
- left and right optic nerves unite at optic chiasma
- information passes through thalamus on way to occipital lobe of cerebrum
- anopsia is visual defects
- sensory only
- left and right optic nerves unite at optic chiasma
- information passes through thalamus on way to occipital lobe of cerebrum
- anopsia is visual defects
95
New cards
Oculomotor Nerve
- (III) cranial nerve that controls pupil size
- motor fibers to four extrinsic eye muscles and upper eyelid
- sensory fibers from proprioceptors
- damage causes upper eyelid droop, paralysis of eye muscles, double vision or difficulty focusing
- motor fibers to four extrinsic eye muscles and upper eyelid
- sensory fibers from proprioceptors
- damage causes upper eyelid droop, paralysis of eye muscles, double vision or difficulty focusing
96
New cards
Trochlear Nerve
- (IV) cranial nerve
- motor fibers to the fifth eye muscle
- sensory fibers from proprioceptors
- damage can cause paralysis of superior oblique muscle leading to visual issues
- motor fibers to the fifth eye muscle
- sensory fibers from proprioceptors
- damage can cause paralysis of superior oblique muscle leading to visual issues
97
New cards
Trigeminal Nerve
- (V) cranial nerve
- motor fibers innervate muscles of mastication
- motor sensory fibers from the face
- divides into three branches
- motor fibers innervate muscles of mastication
- motor sensory fibers from the face
- divides into three branches
98
New cards
Ophthalmic Branch
- part of the trigeminal nerve
- motor fibers to tear gland
- sensory fibers from cornea, nose, forehead and anterior scalp
- motor fibers to tear gland
- sensory fibers from cornea, nose, forehead and anterior scalp
99
New cards
Maxillary Branch
- part of the trigeminal nerve
- sensory fibers from nasal mucosa, gums and cheek
- sensory fibers from nasal mucosa, gums and cheek
100
New cards
Mandibular Branch
- part of the trigeminal nerve
- sensory fibers from the lower jaw and teeth and part of the tongue
- motor fibers to the temporalis, masseter and pterygoid muscles
- damage causes trigeminal neuralgia (inflammation of sensory components)
- sensory fibers from the lower jaw and teeth and part of the tongue
- motor fibers to the temporalis, masseter and pterygoid muscles
- damage causes trigeminal neuralgia (inflammation of sensory components)