Urban Planning Theories, Laws, and Processes for Architecture Students
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
Theories
Provide conceptual frameworks for understanding the city
5 Elements of City Image
According to Kevin Lynch, these elements form the alphabet of how we read cities
Legibility
Orientation, safety, belonging in urban design
Jane Jacobs
Critic of modernist planning; advocated for mixed-use, walkable neighborhoods
Eyes on the Street
Promoted by Jane Jacobs as a concept for vibrant communities
Christopher Alexander
Introduced 'patterns' at multiple scales: buildings to cities
Pattern Language
A practical design 'toolbox' adaptable to context
New Urbanism
Advocated for compact, walkable, mixed-use communities
Landscape Urbanism
Prioritizes ecological processes and green infrastructure
Resilience and Adaptation
Focus on climate change in urban design
Central Place Theory
Explains the spacing and function of settlement patterns
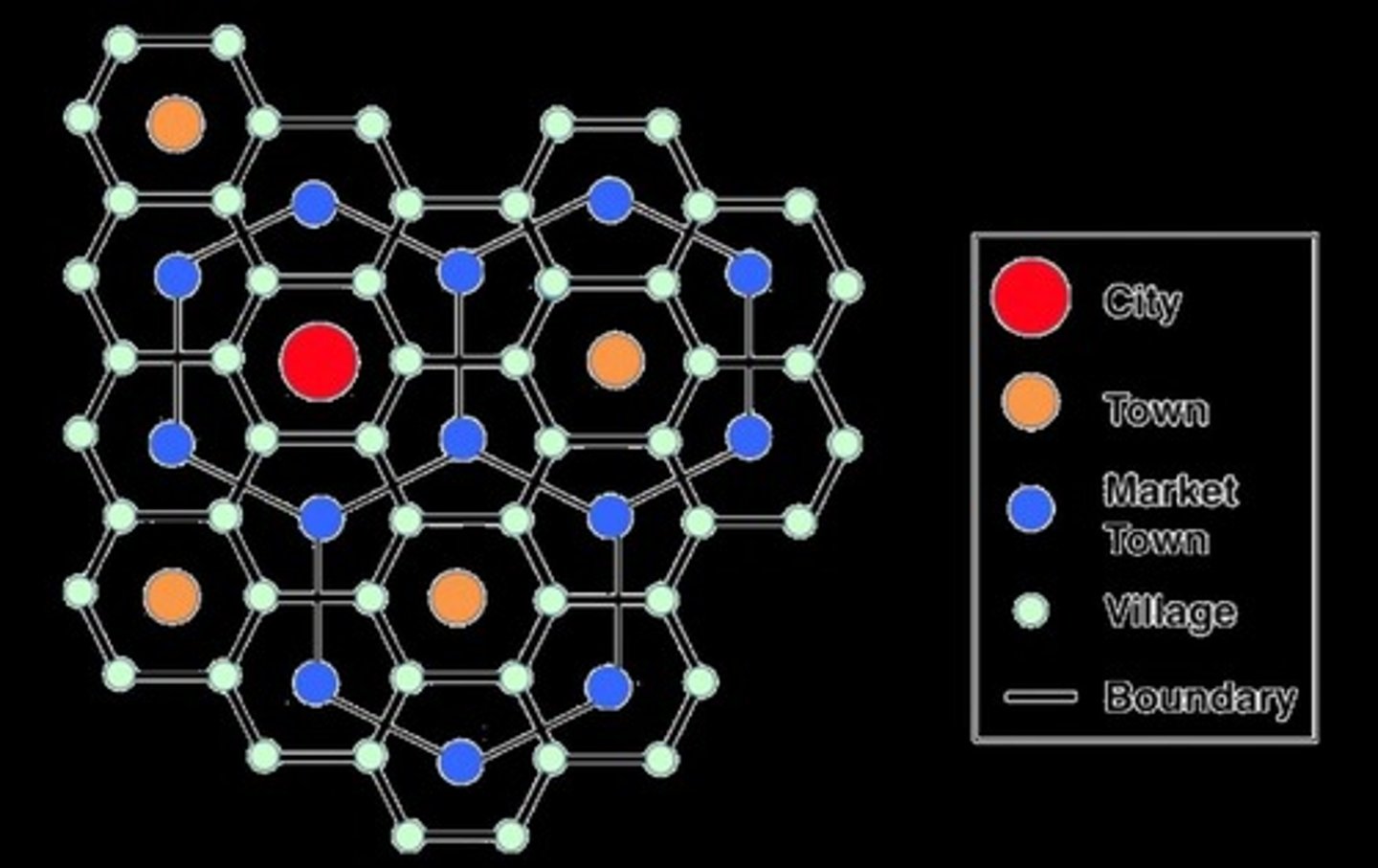
Central Place
A settlement providing services for the population of its periphery
Threshold Population
The minimum population necessary to support the service activity
Modernism
Zoning, towers-in-the-park, functional city design
Postmodern Urbanism
Context, symbolism, pluralism in design
Everyday Urbanism
Informal spaces, bottom-up practices as discussed by Margaret Crawford
Smart Growth
Compact, mixed-use, sustainable development
Transit-Oriented Development
Linking land use & public transport as proposed by Peter Calthorpe
Just City
Justice and equity as central to planning according to Susan Fainstein
Urban Acupuncture
Small-scale interventions with large impact as proposed by Jaime Lerner
Walter Christaller
A German geographer whose principal contribution to the discipline is a set of ideas and principles to explain the spacing and function of settlement patterns.
Market Range of a Service Activity
The distance which people are willing to travel to reach the service.
Nesting Pattern
The infiltration of a lower-order center within a high-order center.
Lower Order Places
Provide only low order goods to low order tributary areas and require frequent purchasing with little consumer travel.
Basic Function of a City
To be a central place providing goods and services for a surrounding tributary area.
Centrality of a City
The degree of it being a service center, where the greater the centrality of a place, the higher is its 'order'.
Higher Order Places
Offer goods with more establishments and business types, larger population, tributary areas and population, do greater volume of business and are more widely spaced than lower order places.
Static and Descriptive Approach
Fails to account for the evolutionary process; this is not fixed and is subject to change.
Shadow Effect
Possible distortion of the hierarchy by the domination of large centers, which could be discouraging for small centers.
Problems of Actual Ranking of Central Places
Actual identification which may be confused by the problem of sprawl.
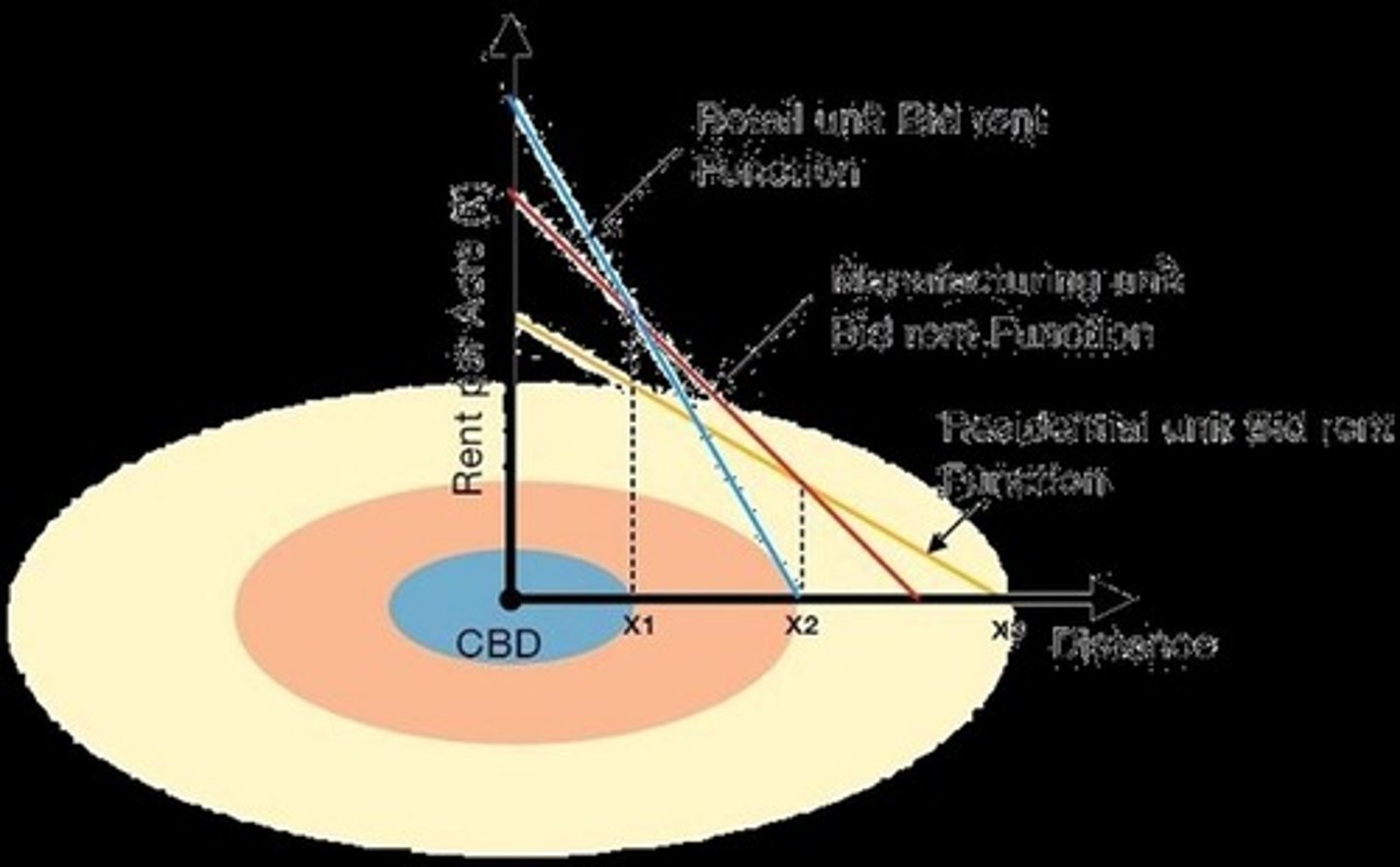
Bid Rent Theory
A geographical economic theory that refers to the changes of real estate price and demand based on its location from the Central Business District (CBD).
William Alonso
An American planner and economist who created the Bid Rent Theory.
Rents Diminish Outward from the CBD
A principle of Bid Rent Theory indicating that real estate prices decrease as one moves away from the Central Business District.
Willingness to Pay
The willingness to pay to acquire a central location versus accepting distant locations for lower 'rental' cost responds to the 'bid' gradient.
Bid Rent Curve
The gradient is related to the marginal cost of distance for each activity, where distance influences its bidding rent.
Friction of Distance
An important impact on the rent gradient; no friction would mean all locations would be perfect locations.
Central Business District (CBD)
The commercial and business center of a city, often characterized by high land values and dense development.
Activity with highest bid rent
The activity that is theoretically expected to occupy a location based on its willingness to pay the highest rent.
Transport costs
Expenses associated with the movement of goods or services, which can influence location decisions in real estate.
Utility/Profits
The level of satisfaction or financial gain that a household or firm seeks to achieve through their location choice.
Offset
To balance both lower revenue and higher operating costs, including transport costs.
Bid Gradient
The willingness to pay to acquire a central location versus accepting distant locations for lower rental costs.
Laws of the Indies
Spanish colonial planning codes shaping towns in the Philippines and Latin America.
Grid Layout
A design structure featuring a central plaza, church, and civic buildings.
Zoning Regulations
Modern urban law controlling land uses, densities, and building forms.
Universal Design
Design that is equitable, accessible, and inclusive for all abilities.
Equitable Use
One of the seven principles of Universal Design.
Flexibility
One of the seven principles of Universal Design.
Simple Intuitive Use
One of the seven principles of Universal Design.
Perceptible Information
One of the seven principles of Universal Design.
Tolerance for Error
One of the seven principles of Universal Design.
Low Physical Effort
One of the seven principles of Universal Design.
Size and Space for Approach and Use
One of the seven principles of Universal Design.
Garden City Principles
Principles by Ebenezer Howard promoting greenbelts and self-contained communities.
City Beautiful Movement
A movement focused on monumental planning for civic pride.
Form-Based Codes
Codes that focus on physical form over use categories.
Urban Growth Boundaries
Boundaries designed to contain sprawl and preserve open land.
Compact City Principles
Principles emphasizing density, proximity, and sustainable mobility.
Resilient City Principles
Principles focusing on flexibility, climate adaptation, and redundancy.
Urban Design Steps
A classic workflow consisting of Survey, Analysis, Synthesis, Implementation, and Feedback.
Rational Comprehensive Planning
A systematic research-driven approach that is logical and comprehensive.
Advocacy Planning
Planning that represents marginalized groups and creates alternatives or opposition to planning proposals.
Participatory Planning
A process where the community is actively involved in design and decision-making.
Incrementalism
A decision-making process characterized by small, pragmatic step-by-step decisions.
Placemaking
A people-centered design approach involving small-scale interventions to strengthen community identity.
Central Place Theory (Christaller)
Hierarchy of settlements.
Arnstein's Ladder
Diagnostic tool that highlights power dynamics in participatory planning.
Strategic Spatial Planning
Vision-driven, multi-stakeholder process.
Design Thinking in Urbanism
Iterative problem-solving and prototyping approach.
Sustainable Urbanism Process
Integrating ecological, social, and economic goals.