A&P - 4.3 Connective Tissue Supports and Protects
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
overview of connective tissue
serves to hold in place, connect, and integrate the body’s organs and systems
most abundant tissue in the body
highly variable in structure and function
never exposed to the outside environment
functions of connective tissues
binding of organs - tendons and ligaments
support - bones and cartilage
physical protection - cranium, ribs, sternum
immune protection - white blood cells attack foreign invaders
movement - bones provide lever system
storage - fat, calcium, phosphorus, energy
heat production - metabolism of brown fat in infants
transport - blood, fluid, dissolved materials
main types of connective tissue
fibrous tissue
adipose tissue
cartilage
bone
blood
characteristics of connective tissue
all types of connective tissue originate from mesenchyme
connective tissues vary widely in appearance and function but all forms share 3 basic components:
specialized cells
extracellular protein fibers
ground substance
the function of the connective tissue comes from there fibers
mesenchyme
loose embryonic tissue from which connective tissue cells derive
contains mesenchymal cells which are undifferentiated stem cells that give rise to various adult connective tissues
specialized cells
the cells present in each type of connective tissue helps to distinguish the various types from one another
a few of the cells are listed here:
fibroblast cells = produce connective tissue proper
chondrocytes = produce cartilage
osteocytes = produce bone
hemocytoblast cells = produce blood
extracellular protein fibers
three primary fibers are produced in connective tissues
elastic fibers = slender, straight, and very stretchy
contains a high percentage of the protein elastin that allows the fibers to stretch and return to original size
collagen fibers = thick, straight or wavy, and often forms bundles
very strong and resist stretching
reticular fibers = strong fibers that form a branching network or scaffolding
cross-link to form supporting “nets”
ground substance
fluid or semi-fluid material that fills the space between cells and surrounds the extracellular fibers
matrix
extracellular material which is produced by the cells embedded in it
ground substance and extracellular fibers make up the matrix of connective tissues
connective tissue proper
connective tissue containing a viscous matrix, fibers, and cells
includes connective tissues with many types of cells and extracellular fibers in a gel-like substance
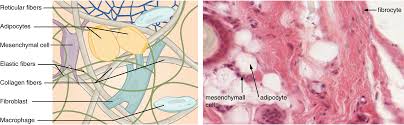
reticular fibers, adipocytes, mesenchymal cell, elastic fibers, collagen fibers, fibroblast, macrophage
types of connective tissues
loose connective tissues (areolar tissue, adipose tissue, reticular tissue)
dense connective tissues (dense regular, dense irregular, elastic)
fibers of fibrous connective tissue
collagenous fibers
reticular fibers
elastic fibers
collagenous fibers
collagen is most abundant of the body’s proteins - 25%
tough, flexible, and stretch-resistant
tendons, ligaments, and deep layer of the skin are mostly collagen
less visible in matrix of cartilage and bone
common in dense irregular connective tissue, prevents hyperextension
reticular fibers
thin collagen fibers coated with glycoprotein
form framework of spleen and lymph nodes
elastic fibers
thinner than collagenous fibers
branch and rejoin each other
made of protein called elastin
allows stretch and recoil
found in elastic tissue which is found in ear, the more elastin we have the more the tissue can stretch
types of fibrous connective tissue
loose connective tissue
dense connective tissue
loose connective tissue
fibers created a loose, open framework
much gel-like ground substance between cells
types:
areolar tissue!!
adipose tissue
reticular tissue
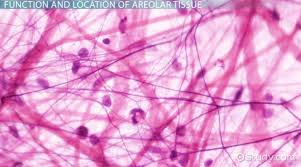
areolar tissue
DESCRIPTION: loosely organized fibers, abundant blood vessels, and a lot of seemingly empty space
possess all six cell types
fibers fun in random directions
mostly collagenous, but elastic and reticular are also present
LOCATION: fills the spaces between muscle fibers, surrounds blood and lymph vessels, and supports organs in the abdominal cavity
FUNCTION: nearly every epithelium rests on a layer of areolar tissue
blood vessels provide nutrition to epithelium and waste removal
vascular - direct blood supply
ready supply of infection-fighting leukocytes (white blood cells) that move about freely
attaches skin to underlying body parts
lamina propria
areolar connective tissue underlying a mucous membrane
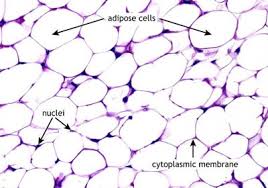
adipose tissue
DESCRIPTION: loose connective tissue that consists of fat cells with little extracellular matrix
adipocytes - fat cells
FUNCTION: stores fat for energy and provides insulation
LOCATION: found deep to the skin, especially at the sides of waste, buttocks, and breasts
reticular tissue
DESCRIPTION: loose connective tissue made up of a network of reticular fibers
FUNCTION: provides a supportive framework for soft organs and resists distortion
LOCATION: found in liver, kidney, spleen, lymph nodes, and bone marrow
reticular fibers create a complex supporting network known as a stroma (framework)
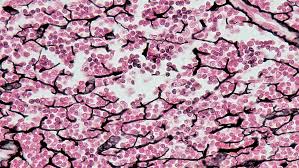
mucous connective tissue
specialized loose connective tissue present in the umbilical cord
dense connective tissue
fibers are densely packed together
fibers fill spaces between cells
fibers provide both elasticity and protection
types vary in fiber orientation:
dense regular!!
dense irregular!!
elastic
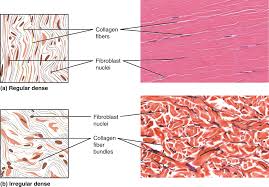
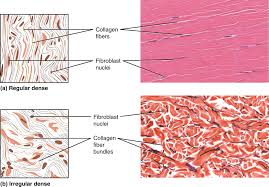
dense regular connective tissue
DESCRIPTION: consists of collagenous fibers packed into parallel bundles
densely packed, parallel collagen fibers
compressed fibroblast nuclei
FUNCTION: provides strength along the axis of the collagen fibers
LOCATION: found in cords (such as tendons) or sheets (ligaments)
difference between tendons and ligaments
tendons connect muscle to bones
ligaments connect bones to bones
dense irregular connective tissue
DESCRIPTION: consists of collagenous fibers interwoven into a mesh-like network
densely packed, randomly arranged (non-parallel), collagen fibers and few visible cells
FUNCTION: provide strength in many directions and are particularly important in areas subjected to stress from many directions such as the dermis of the skin
withstands unpredictable stress
LOCATION: deeper layer of skin (dermis); capsules around organs
elastic tissue
DESCRIPTION: when elastic fibers outnumber collagen fibers, the tissue has a springy, resilient nature
FUNCTION: elasticity allows it to tolerate cycles of extension and recoil
LOCATION: bound between vertebrae of the spinal column and the erectile tissues of the penis
fluid connective tissue
specialized cells that circulate in a watery matrix that contains salts, nutrients, and dissolved proteins
types:
blood
lymph
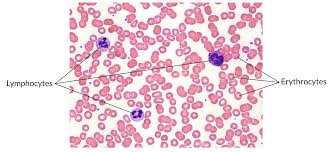
blood
DESCRIPTION: fluid connective tissue containing erythrocytes and various types of leukocytes that circulate in a liquid extracellular matrix
LOCATION: flows within the cardiovascular system
FUNCTION: hemocytoblasts (specialized cell) gives rise to three formed elements suspended in plasma:
erythrocytes; red blood cells - transport oxygen and carbon dioxide
leukocytes; white blood cells - help defend the body from infection and disease
thrombocytes; platelets - cell fragments that are involved in the clotting response that seals broken blood vessels
lymph
DESCRIPTION: forms as interstitial fluid enters a lymphatic vessel
FUNCTION: lymph passes through lymph nodes where it is cleaned and filtered
LOCATION: flows within the lymphatic system
supporting connective tissue
type of connective tissue that provides strength to the body (supports the weight of the body) and protects soft tissue
less diverse cell population and a matric containing much more densely packed fibers
types:
cartilage
bone
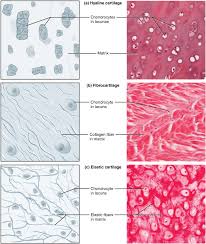
cartilage
connective tissue consisting of collagenous fibers embedded in a firm, solid, rubbery matric containing chondrocytes; stiff connective tissue with flexible matrix
no (rarely) blood vessels
diffusion brings nutrients and removes wastes
heals slowly (because it doesn’t have the supply of nutrients since its avascular)
types of cartilage vary with fiber composition:
hyaline cartilage
elastic cartilage
fibrous cartilage
chondroblasts
cartilage cells that produce the matrix that will trap them
chondrocytes
cartilage cells that are trapped in lacunae (cavities) - chondroblast is sealed off in a lacunae within the matrix
contains a reserve population of chondroblasts that contribute to cartilage growth throughout life
lacunae
(singular = lacuna) small spaces in bone or cartilage tissue that cells occupy
hyaline cartilage
DESCRIPTION: most common type of cartilage, smooth and made of short collagen fibers
FUNCTION: provides support with some flexibility and reduces friction between bony surfaces
LOCATION: found connecting the ribs to the sternum, covering the articular surface of long bones, supporting the respiratory passageways such as the trachea, and forming the tip of the nose and part of the nasal septum
trachea (rings) and the part of the bone in joints is covered in hyaline
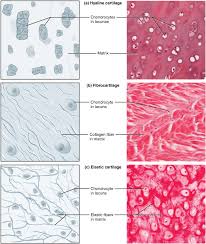
fibrocartilage
DESCRIPTION: tough form of cartilage, made of thick bundles of collagen fibers
FUNCTION: provides some compressibility and can absorb pressure
LOCATION: found within the intervertebral discs, the meniscus of the knee, and pubic symphysis
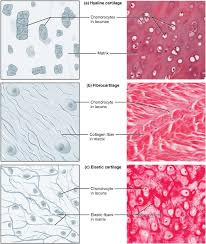
elastic cartilage
DESCRIPTION: type of cartilage, with elastin as the major protein
FUNCTION: provides firm but elastic support; characterized by rigid support as well as elasticity
LOCATION: found in the ear and epiglottis