Cell and Tissue quiz
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
nucleus
control center
nucleolus
cluster of ribosomes within the nucleus
smooth er
lipid synthesis
rough er
protein assembly
golgi apparatus
packages and exports proteins
mitochondria
active transport synthesis
cell membrane
double layer of phospholipid molecules, protects the cell.
cytoplasm
fluid inside the cell.
lysosome
digestion
chromatin/chromasomes
DNA
ribosomes
dots - protein synthesis
centrioles
cell division
phosphoid bilayer
what makes up the cell membrane
hydrophillic
loves water
hydrophobic
hates water
blood cell
skin cell
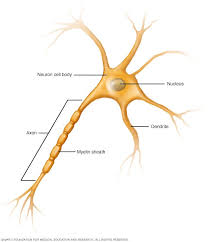
nervous cell
sperm cell
egg cell
isotonic
solute is equal inside and outside the cell
hypertonic
solute is greater outside the cell than inside the cell. water flows out.
hypotonic
solute is greater inside the cell than outside the cell. water flows in.
active transport
transports using cellular energy - atp
passive transport
requires no energy, from high concentration to low concentration (diffusion)
osmosis
the flow of water from high to low.
exocytosis
ejection of substances from cell. ex: Mucos, hormones
endocytosis
large particles enter the cell. ex: white blood cells
filtration
high pressure to low pressure without energy
epithelial tissue
tightly packed, found in sheets. lines, protects, absorbs, and secretes.outer layer of skin, inner cheeks, endocrine glands.
connective tissue
support, connects. bone, cartilidge, fat, blood.fibers, minerals, few cells.
muscle tissue
movement, skeletal, cardiac, smooth. long and stringy cells, capable of shortening.
nervous tissues
communication and coordination - brain, spinal cord, nerves. irregular shapes, neurons and supporting cells.
solute pumping
substance through membrane against concentration gradient.