STRUCTURES 1 - LECTURE 03 FORCES IN EQUILIBRIUM
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
mechanics
branch of science that deals with the study of forces and their effects on the objects they act upon
the three branches of mechanics
statics, dynamics, and the mechanics of materials
statics
deals with forces in equilibrium or things staying in balance (newton's first law)
- bodies are assumed to be rigid with no noticeable deformation under a load
- bodies that do deform showcase a material's strength
dynamics
deals with unbalanced systems of forces involving acceleration (newton's second law)
the mechanics of materials
deals with deformation and the internal effects that applied forces have on bodies
newton’s 1st law
a body at rest will stay at rest and a body in motion will move in a straight line unless a force acts on it
- a body is in equilibrium when the net effect of all the forces acting on it is 0
newton’s 2nd law
the time rate of change of momentum is equal to the force producing it, and change takes place in the direction the force is acting on (F=ma)
newton’s 3rd law
every force of actions has a reaction that is equal in magnitude and opposite in direction with the same line of action
force
the action of one object exerted on another.
- typically a vector characterized by magnitude and direction.
- a force's line of action extends infinitely through both sides of the force.
- magnitude of a force is expressed in pounds (lbs) or kips (k), or sometimes newtons (kN).
- point of application can be anywhere on a line of action and the effect on the external force will still be the same.
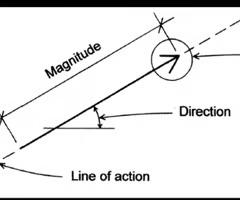
how is the direction of a force characterized
it is indicated by a line of action and the angle it forms with an axis
1k (1 kip) = ?
1000 lbs
the point of application
the point where the force is applied.
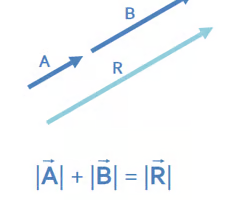
when can vectors be added?
when their line of actions and directions are the same/ parallel.
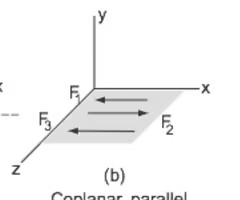
coplanar forces
forces that act on lines in the same plane.
- "2D" arrangement.
- tend to translate the object they act on.
non-coplanar forces
forces that don't lie on the same plane.
- "3D" arrangement.
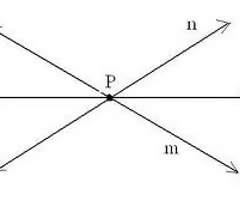
concurrent forces
forces that either meet at or pass through the same point.
- "2D" arrangement
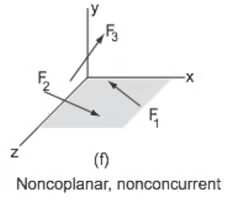
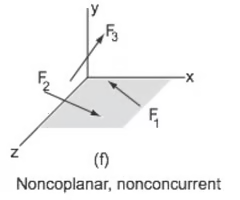
nonconcurrent forces
forces that don't pass through the same point or interract.
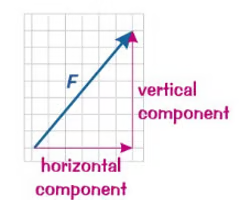
components of a force
two or more forces that replace another force by producing the same effect as it.
- substituting/replacing the force is called resolving the force into its components.
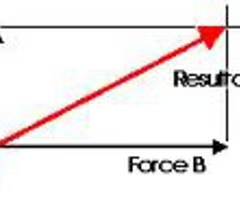
resultant force
a single force that replaces a system of concurrent forces by producing the same effect.
the two equations for equilibrium conditions of coplanar, concurrent forces:
∑Fₓ = 0
∑Fᵧ = 0
reaction force
internal equal and opposing forces that resist another applied force.
- in a building, they are developed in the supporting elements.
three types of structural connections:
roller/rocket support, pin/hinge support, fixed support
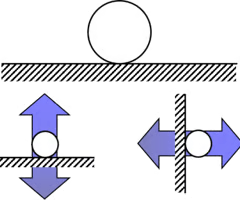
roller/rocket support
resists translation of a member in a direction perpendicular to the contact surface.
- reaction of a roller force represents one unknown force component.
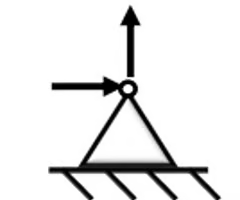
pin/hinge support
resists translation of a member in both horizontal and vertical directions.
- reaction of a pin support represents two unknown force components.
fixed support
resists translation of a member in both horizontal and vertical directions.
- reaction of a pin support represents two unknown force components.
free body diagram
a simplified and conceptual diagram that investigates the applied and reaction forces of a structural member with their correct directions.