unit 8: energy production
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
non-renewable energy sources
ones which cannot be produced again
can be used up and become depleted.
primary energy
energy found in nature such as raw fuels and other forms of energy received as input to a system
secondary energy
energy transformed from primary energy sources through energy conservation processes
degraded energy
thermal energy that is released into the surrounding environment after any process
specific energy
the amount of energy which can be extracted per unit mass of fuel
measured in J Kg^-1
equal to energy/mass
energy density
the amount of energy which can be extracted per unit volume of a fuel
measured in J m^-3
equal to energy/volume
relationship between energy density and specific energy
Es/ED = 1/density of the fuel
useful energy
primary and secondary energy
not degraded energy
do gases have higher specific energy or energy density?
gases tend to have higher specific energy than energy density → makes gaseous fuels harder to transport as a greater volume is needed
examples of primary fuels
fossil fuels
sunlight
flowing water
examples of secondary fuels
hydrogen (as it has to be extracted)
electricity
biofuel (has been processed)
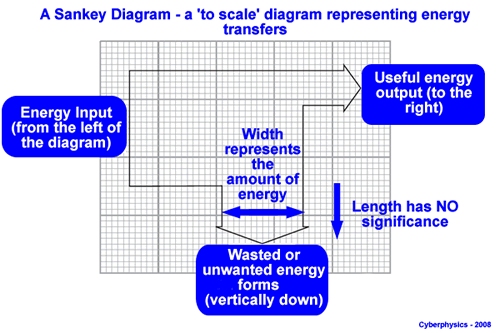
Sankey diagrams
definition
direction
meaning of width
meaning of length
a type of energy diagram where the width of each arrow is proportional to the amount of energy in that section.
what are primary sources of energy used for?
to generate electricity, a secondary form of energy
efficiency
useful energy/power / input power/energy
0<e<1 or 0%<e<100%
renewable energy source examples
Solar power
Wind power
Hydroelectric power
Tidal power
Geothermal
Biomass
non-renewable energy source examples
Coal
Oil
Natural gas
Nuclear power
renewable energy sources
ones which cannot be depleted
purpose of a moderator in nuclear power plants
to slow down neutrons so that fission reactions can occur
increases reactivity
purpose of control rods in nuclear power plants
absorb neutrons which stops fission
fission requires a nucleus to absorb a neutron
decreases reactivity so increases safety
purpose of fuel rods in nuclear power plants
to hold the fuel
what is a nuclear reactor filled with?
water to serve as a moderator, slowing down neutrons enabling fission
advantages of wind power
renewable
no harmful waste product
cost effective in the long run
disadvantages of wind power
expensive to build
requires a large, windy area
low power output
conduction
the transfer of heat through matter by transferring kinetic energy from particle to particle with no net movement of the particles
convection
the transfer of thermal energy by the movement of a fluid
hot fluids rise because it is less dense, the fluid then cools becomes more dense and sinks
this creates a convection current
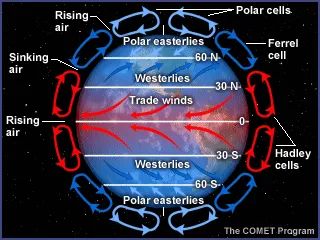
convection current in the atmosphere
heat driven cycles
warm air rises and cold air sinks
due to points having different proximities to heat sources (the sun)
radiation
the transfer of energy by electromagnetic waves / photons
how the sun provides heat energy to Earth
can happen in a vacuum
why can thermal energy sometimes not be seen?
photons are emitted from everything that has a temperature
this is only visible in infrared light
something that appears less hot can have heat energy inside, kept there by an insulator
when can thermal energy be seen?
if heated to a high enough temperate objects will give of visible light
knowing that T∝λ^-1 and T∝f so λ∝f^-1
what is a black body radiation? what are thermal photons?
the “glow” coming from an object due to its temperature
what are thermal photons?
photons coming out of a black body
all due to the temperature of the black body
what is a black body?
A black body which absorbs all incident electromagnetic radiation is both the perfect absorber and the perfect emitter of radiation.
The radiation emitted by such a body at constant temperature is called black-body radiation.
what is emissivity (e)?
power per unit area radiated by the object / power per unit area radiated by a black body at the same temperature
when e=1 it is perfect emissivity
for black bodies e is closer to 1
varies with surface material
which law shows the power emitted from a black body?
Stephan-Boltzmann Law
P=eσAT^4
σ = Stephan-Boltzmann constant
T must be in Kelvins
Wien’s displacement law
the energy radiated by a body is electromagnetic radiation and distributed over an infinite range of wavelengths
most energy is radiated at a specific wavelength λmax
λmax = 2.9×10^-3/T (Kelvin)
earth’s energy balance
Earth’s energy balance describes how the incoming energy from the sun is used and returned to space. If incoming and outgoing energy are in balance, the Earth’s temperature remains constant.
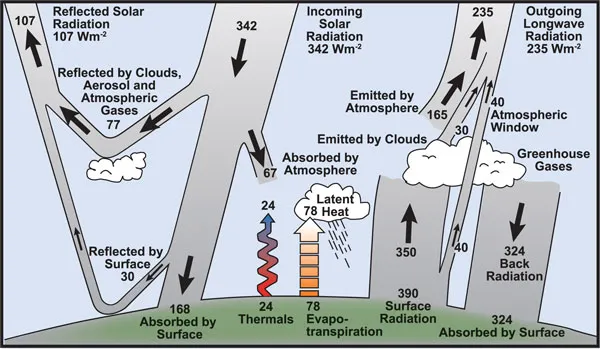
albedo
The Albedo (α) of a planet is defined as the ratio between the total scattered (reflected) radiation and the total incident radiation of that planet.
solar constant
The solar constant is the amount of energy that normally falls on a unit area (1m^2) of the Earth’s atmosphere per second when the Earth is at its mean distance from the sun.
The solar constant is approximately 1366 W/m^2.
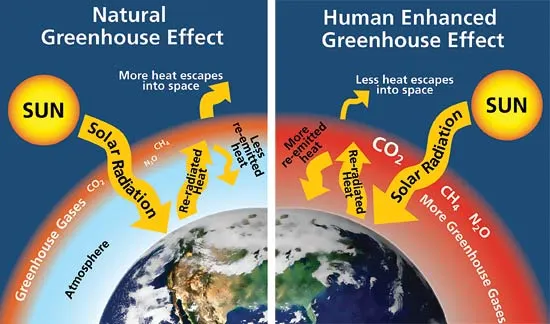
greenhouse gases
Greenhouse gases absorb infrared radiation because its molecules have natural frequencies in the infrared region and readily absorb infrared radiation due to resonance.
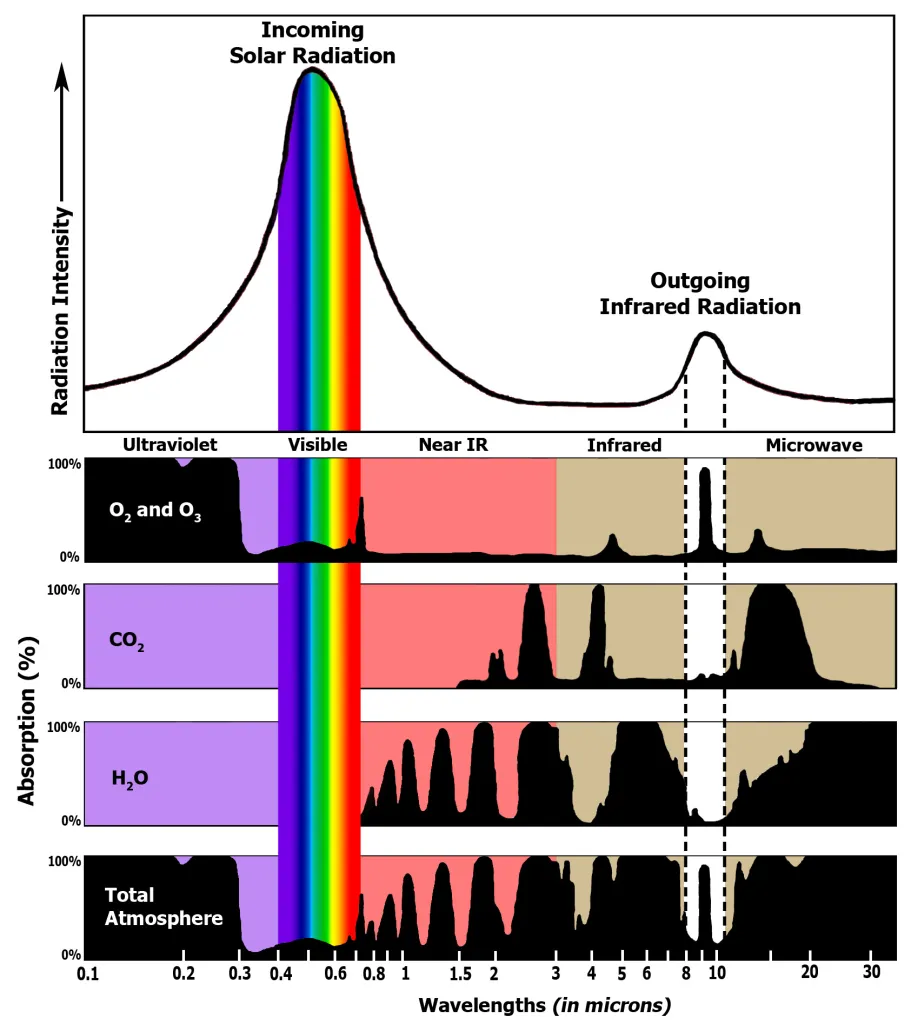
greenhouse gas effect
The greenhouse gases present in the atmosphere absorb infrared radiation and reflect it back towards the Earth’s surface.
Thus, heat energy becomes trapped inside Earth’s atmosphere and accumulates, leading to the greenhouse effect and an increase in average mean temperatures on Earth.