Cells as the basis of life
1/27
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Prokaryotic
simple cell
unicellular organisms
little organisation
not membrane-bound nucleus or organelles
DNA in the cytoplasm
circular DNA
small (6.5-10 micromillimeters)
Bacteria and Achaea
Eukaryotic
Complex cells
unicellular to multicellular organisms
membrane-bound nucleus and organelles
DNA in the nucleus
linear DNA
larger (30-150 micromillimeters)
Animalia, plantae, fungi, protists
Autotrophs
organisms that make food from CO2 and an energy source. They produce food for themselves snd others as well as storing food.
Producers
Heterotrophs
Organisms that are unable to make their own food and must take food from other organims.
Consumers
Nucleus
Control center of the cell
contains genetic materials
produces ribsomes + RNA
Essential in cell division
Mitochondria
rod-shaped
thin membrane
site of cellular respiration
powerhouse of the cell
generate ATP through the conversion of energy from nutrients
Rough + Smoother Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
Extension of the outer nuclear membrane,
involved in protein and lipid synthesis.
Forms a transport network through out the cell.
large surface area for chemical reactions
Rough ER has ribosomes attached
Smooth ER is involved in detoxification and metabolism. and produces lipids and steriods.
Glogi Apparatus
Membrane bound sacs
produces glycoproteins and secretory enzymes
Secrets carbohydrates which are used in cell wall production
Transports and stores lipids
forms lysosomes
Lysosomes
Contains + releases digestive enzymes
helps destroy unwanted or worn-our cell organelles
digestion of material within cell
complete digestion of cell after death
Vacuoles
Fluid-filled saces surrounded by membrane
Stores sugar and amino acids
Chloroplasts
Helps with photosythesis
double strandard DNA molecules
In plants and proteins
3 membranes which allows for compartments that contain the enzymes used in photosythesis
Chlorophyll absorbs light and converts it into chemical energy.
Unicellular Organisms
one cell
preform all functions and activities of life within a single cell
cell feeds, respires, excretes, is sensitive to internal and external conditions, may move and eventually divides or reproduces
Examples; Amoeba, Paramecium, etc
Multicellular organisms
made up of a mass of cells fused together
cells become specialised to preform special functions
all have speciliased cells
allowed by only some genes being expressed - the genes are different for different functions
Examples; Most living things, including humans
Digestive System
Nutrients:
Breaks down food and allows movement through the intestines
Ciculatory System
Nutrients
delivers nutrients to the extracellular fluids and therefore all cells
Gas
Blood vessels transfer oxygen to the cells and remove CO2
Waste
Wastes will move around the bloodstream to be removed from the body
Respiratory System
Gas
lungs allow oxygen to be absorbed from the air and CO2 to be removed from the body.
Waste
lungs allow CO2 to be removed from the body.
Extretory System
Waste
Kidneys filter blood to remove waste (via the bladder)
Fluid Mosaic Phospholid Bilayer structure
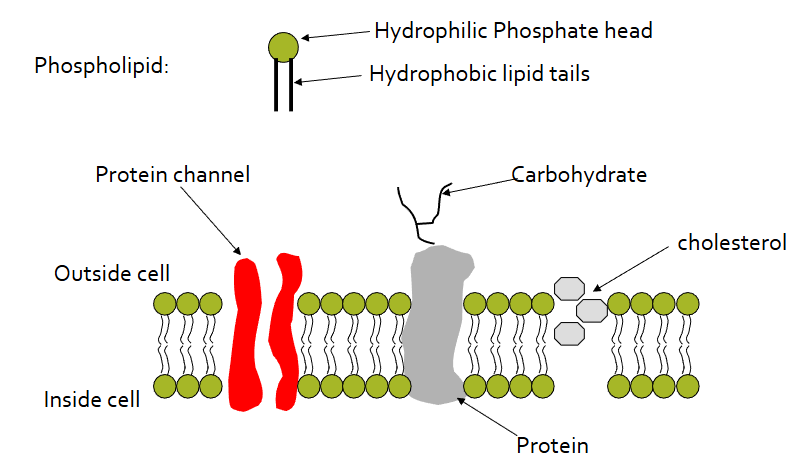
Phospholipids
main componenet of membranes
2 layers
phosphate hydrophilic head
lipid hydrophobic tails
Protein Channels
integral protein
transmembrane proteins
involved in transport, enzymatic action and signla transduction
Cholesterol
stabilises the membrane
reduces permeability to small watersoluable molecule
buffer against changing temperature
Glycoproteins
carbohydrate attached to a protein
on the outer surface
recognition between cells and of antibodies, hormones and virus
Osmosis
the movement of water from an area of high water concerntraion to an area of low water concerntration
Passive
simple and facilitated diffusion
Simple
the movement of molecules from an area of high concerntration to an area of low concerntraion
Passive
examples; oxygen and carbon dioxide
Facilitated
For larger molecultes
passive
examples; amino acids, glucose, calcium and sodium ions
Active transport
molecules moving from an area of low concerntraion to an area of high concerntration.
moves through proteins channels
Requires energy in the form on ATP
moves against the concerntration gradient
examples; glucose, amino acids, sodium and potassium ions.
endocytosis
transports substances into the cell
requires energy
Phagocytosis and Pinocytosis
bacteria and cell debris
Exocytosis
Transport substances out of the cell
requires energy
transports waste and digestive enzymes
Passive and Active Transport
Passive: when a system (like osmosis) doesn’t require energy to be able to take place/ transport what’s being moved.
Active: when a system needs energy to take place/transport what needs to be moved.