Biblical Studies
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Questions to determine a worldview:
Purpose of life
Biggest problem in the world
How do you determine right and wrong
When did Hinduism begin?
It began over 5000 years ago.
What type of religion is it?
Polytheistic - 330 million gods and pantheistic - God is in everything
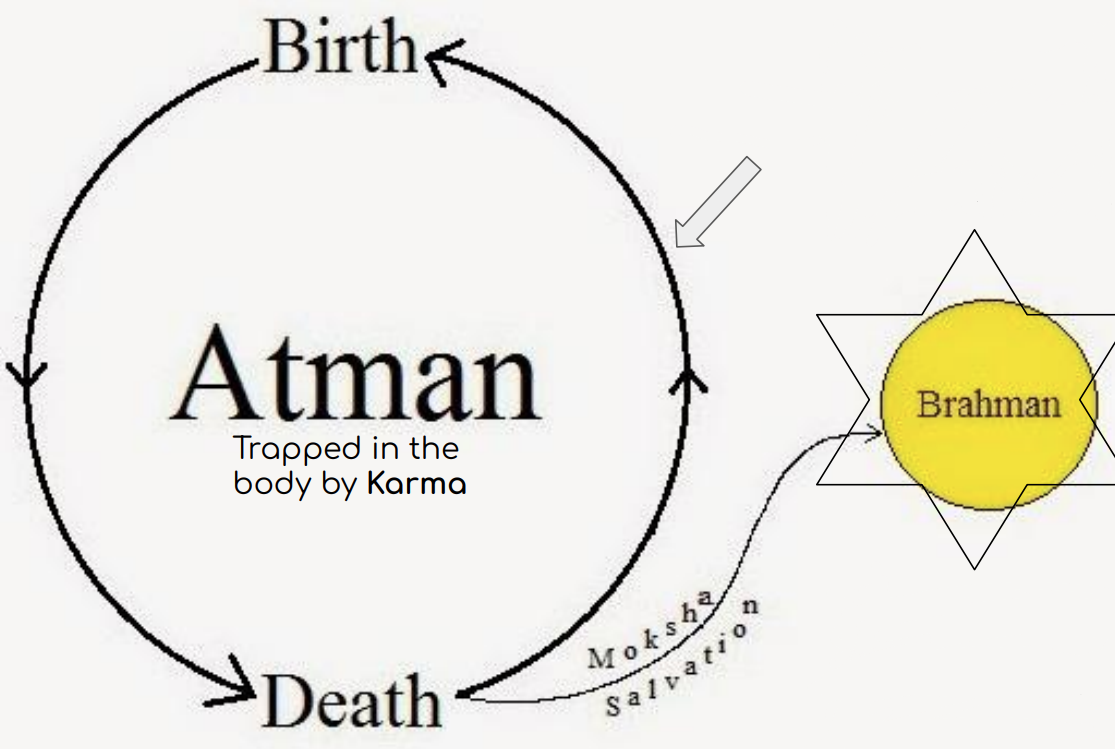
Brahman
The life force of the universe. The creative force behind the universe. From Brahman, everything in the universe came and everything will return
Atman
The life force that exists in every living creature. A part of Brahman living inside of you which gives you life
Dharma
duty. The goal of Hindu life is to complete one’s dharma. Note: Your dharma is informed by your class and therefore different people have different dharma
Karma:
Karma is a force that balances the universe. It is the Hindu understanding of the consequences of our actions. The karma you create in life by acting in line with your dharma will determine whether you reincarnate and what it looks like (good or bad)
Reincarnation
Reincarnation is a core belief of Hinduism. Reincarnation is the cycle of being reborn to live another life
Samsara
The cycle of being trapped in birth, rebirth and death. The ultimate goal of Hinduism is to escape Samsara
Vedas
Hindu holy texts. This is a collection of writings that spans hundreds of years
Bhagavad Gita
A 700 verse Hindu scripture written in Sanskrit. It is about Prince Arjuna fulfilling his destiny (dharma) as a warrior. The god Krishna informs him that he must follow this path because it is his destiny.
How do Hindu’s follow their Dharma?
The path of duties: following your caste duties
The path of knowledge: meditation and priestly knowledge.
The path of devotion: devoting oneself to a God
The path of Duties
One’s dharma is decided by which caste you belong to.
Accumulate good karma by living according to one’s caste.
Perform these actions with a sense of “detachment”
The path of Knowledge
Devoting oneself to living a life of contemplation.
Becoming a ‘Sadhu’.
Meditation and contemplation to achieve mythical states of mind.
Denial of all pleasures and bodily comforts.
Perform these actions with a sense of “detachment”
The path of Devotion
Devoting oneself to worship of a particular god.
Paying homage to your god in temple worship such as offering food or money to the deity.
Setting up a shrine in your home
Brahma - GOD
The Trimurti - hindu trinity
The creator
4 heads, 4 arms, reddish complexion
Not commonly worshipped
Vishnu
The Trimurti - hindu trinity
The preserver
Garuda - bird; as vehicle
4 arms, blue complexion, sits on snake
Was reincarnated 9 times, still one more time to come
Shiva
The Trimurti - hindu trinity
The destroyer/transformer
Bull - Vehicle
Matted hair, third eye, trident, blue throat
Main god of Salvism
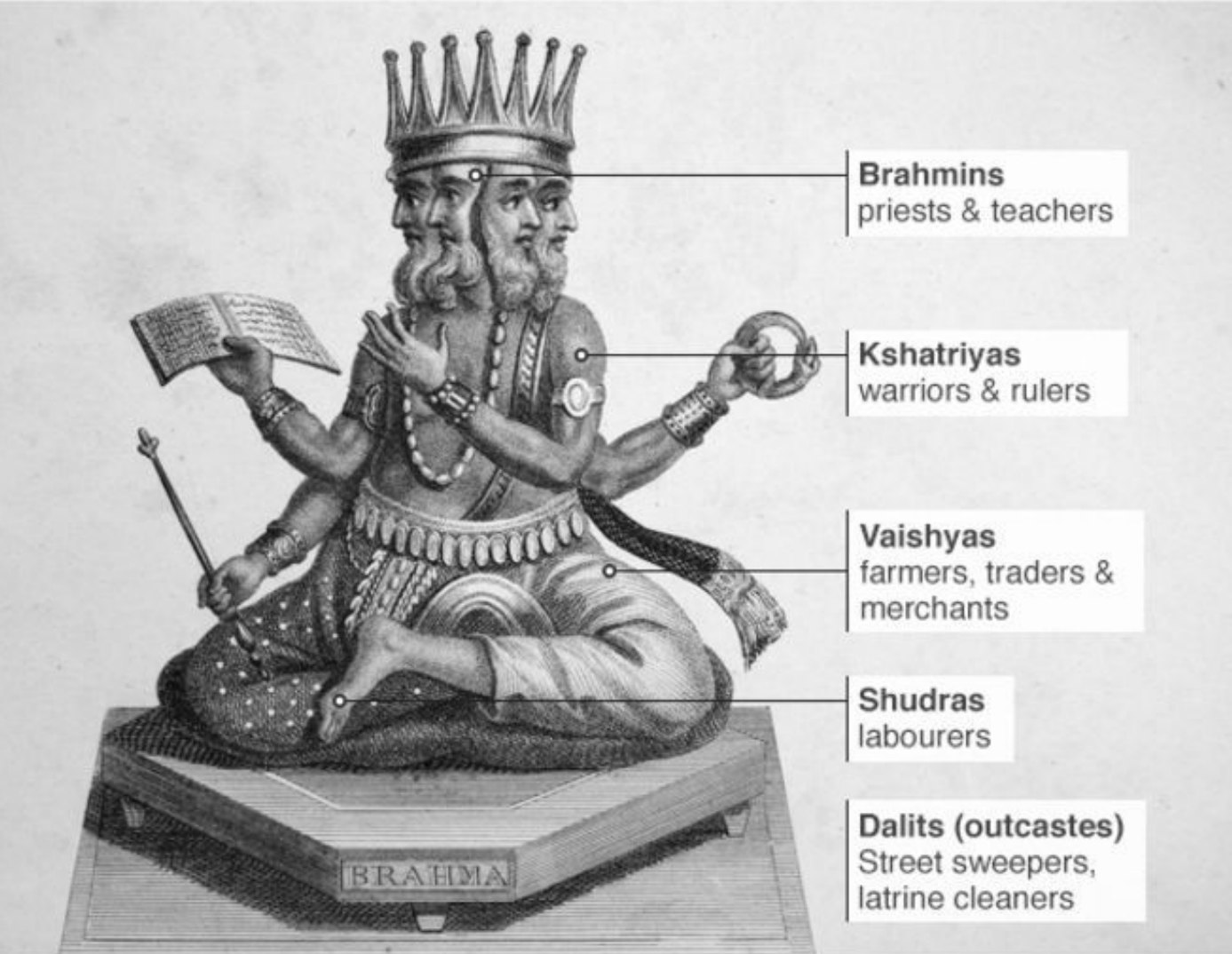
Caste System
Founding of Buddhism
Buddhism was founded by Siddhartha Gautama, a Hindu prince. He was born in around 500 BC. When he was a child, it was prophesied that Siddhartha would become either a powerful ruler or a holy man. His father, wanting to ensure he became a king, sheltered Siddhartha in the palace, hiding him from any suffering. He distracted Siddhartha with beautiful things so that he would not want to leave.
However, one day at age 29 he snuck out of the palace and saw 3 different kinds of suffering:
An old man,
A sick man
A dead man
Siddhartha was so troubled by the problem of suffering that he was overcome with grief. However, lastly he then encountered a Hindu ascetic, a guru who had given up everything in life to meditate and reach enlightenment. Siddhartha was so impressed by the ‘look of peace’ on the guru’s face that he decided to immediately give up his life of luxury and set out to discover for himself the secret to serenity in a world of pain. He wanted to achieve enlightenment.
He decided to give up his lavish lifestyle and endure poverty. So, he began his journey to becoming a holy man, just as the prophecy had predicted. He left his palace, wife and newborn son and set out to find and answer to the problem of suffering. This journey involved fasting, meditating, being homeless and travelling all in the quest to find spiritual knowledge. Siddhartha's journey also included a rejection of Hinduism as he began searching for a way to escape from suffering.
One day, sitting under this tree in Nepal, he had a profound realisation. Buddhists believe this is the moment he reached ENLIGHTENMENT. This is also the moment he became BUDDHA. From here, Buddha would go on to establish his 4 noble truths and the 8 fold path
Enlightenment
Deep spiritual knowledge. An awakening to the answers about big questions about life and existence. A way to solve the problem of suffering Freeing oneself from being attached to the world.
Goal of Buddhism
Escape samsara and enter Nirvana
Nirvana
Nirvana means the extinguishing of desire. Those who reach nirvana will escape the cycle of Samsara and cease to exist.
Karma
In Buddhism, accumulating any form of Karma is bad. Karma traps one in the cycle of samsara (which is bad)
Bodhisattva
Someone who has been enlightened, but has delayed reaching Nirvana in order to show others the way
4 noble truths
Suffering Exists - DUKKHA
Everything is temporary, nothing exists forever, therefore it is all suffering.
Suffering is caused by attachment and desire for things.
Suffering comes from desire, wanting things. These can be good or bad things.
Eg. If you crave riches, poverty will feel painful to you. If you desire comfort, discomfort will trouble you. Even wanting to exist causes suffering. As does wanting not to exist. Any action causes karma which will trap a person in Samsara (the cycle of birth and rebirth.)
Suffering ceases when attachment ceases.
Suffering comes from desire, wanting things. These can be good or bad things. Therefore, we end suffering if we end desire.
This is how you reach NIRVANA. Nirvana means ‘to extinguish’. It is the blowing out of any desires
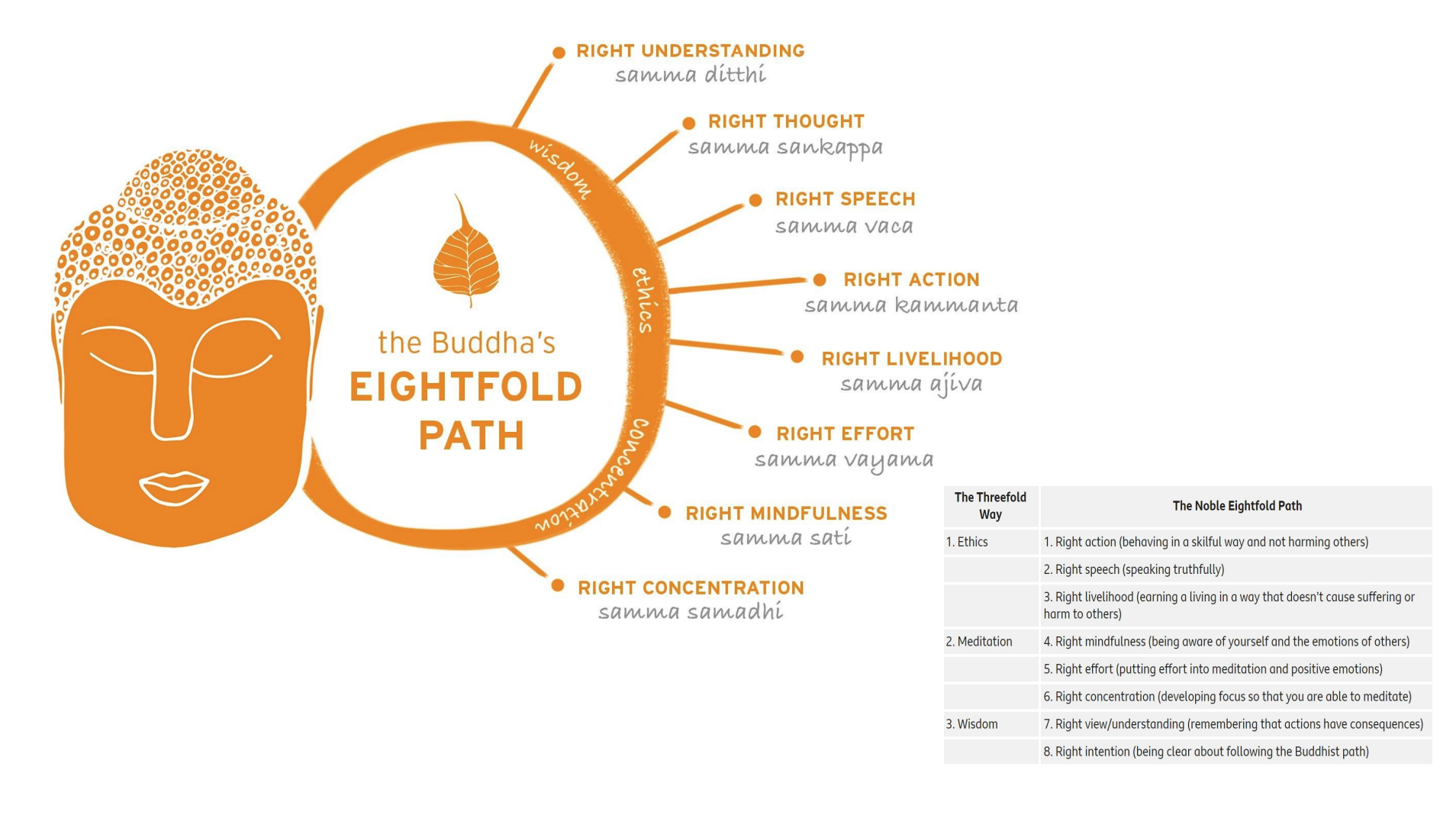
Freedom from Attachment (and therefore suffering) is possible through practising the 8 Fold Path.
In order to reach Nirvana, a Buddhist must follow the 8 fold path
8-fold Path
4 Critiques of Hinduism - from Buddhism
Enlightenment for the Buddha involved the rejection of Hinduism. He rejected it because of 4 main critiques:
The Middle Path
Indulging in all of the pleasurable things in the world will not bring you satisfaction. But depriving yourself and only fasting and meditating will not achieve this either. Actually neither path leads to enlightenment.
The Caste System
Buddha taught that there is no distinction between members of the human race. Anyone can reach enlightenment.
The role of Brahmans
In Hinduism, Brahman’s are seen as the most wise and keepers of knowledge, as they are the closest to reaching Moksha. Buddha rejected this idea; Everyone is ignorant about the truth regardless of caste.
God, the soul and the self
God does not exist. You do not actually exist. We are just guessing about these ideas. There is no point asking these questions on the path to wisdom.
Types of Buddhism
Theraveda Buddhism
Oldest form of Buddhism
More common in India, Thailand, Sri Lanka, Cambodia
Goal is to become an arhat or fully awakened being
Big focus on meditation and denial of self/self control
Atheistic religion
Mahayana Buddhism
Mainly practised in East Asia (China, South Korea, Japan)
The most commonly practiced form of Buddhism
Aim is to become a bodhisattva or enlightened being
Involves dedication towards Buddha statues
Believes people don’t exist
Founding of Islam
Islam was founded by Muhammed. He is known as ‘the Prophet’.
Muhammed was born in 570AD.
He began Islam when in 610 AD when an angel spoke to him in a cave.
The angel told him to speak the words from Allah. - QURAN
The Holy Book: means ‘Recitation’
Muhammad received messages via angels, committing them to memory or writing.
The Quran is treated with reverence – Muslims do not place it on the ground, and wash hands their before handling it
Islam
Way of peace and submission
A muslim
Someone who practises Islam. Muslim means: one who submits to Allah.
Allah:
Arabic word for God
Sharia
A central concept of Muslim life is submission to Allah’s law. This is known as Sharia. Sharia means ‘path to the watering hole’.
Sira (Life)
Biography of Muhammad, written 125 years after his death by Muslim scholar Ibn Ishaq
Hadiths (Reports)
Collection of individual reports about Muhammad, not regarded as divine, 2-3 centuries after his death
Jihad
Struggle or striving – to be a faithful Muslim:
By the heart - refers to the inner, spiritual battle of the heart against vice, passion, and ignorance.
By the tongue - means speaking the truth and spreading the word of Islam with one's tongue.
By the hand - involves choosing to do what is right and to combat injustice and what is wrong with action, or one's hand.
By the sword - refers to defending Islam and waging war against its enemies with the sword.
Military Jihad
Military jihad helped the success of early Islam. 3 options when in contact with military expansion:
Conversion – to Islam
Protection – keep way of life but pay a tax
Battle – military jihad
Many Muslims consider the Greater Jihad to be the internal struggle to be pure and submit to Allah. Military Jihad is considered the Lesser Jihad
Principal of Islam:
The articles of faith explained in the Aqida (creed) are:
Tawhid (Existence and unity of God)
Angels (Mala’ika)
Books of Allah (Katubullah)
Rasul (Prophets)
Akhira (Resurrection for an afterlife)
Fate/predestination (al-Qudar)
5 Pillars of Islam
Declaration of Faith
Daily Prayer
Tax for the poor
Fast of Ramadan
Pilgrimage to Mecca - Hajj
Declaration of Faith

Daily prayer

Tax for the poor

Fast of Ramadan

Pilgrimage to Mecca

Mecca pilgrimage steps and customs

Sunni and shia
There are two major forms of Islam practiced today. Sunni Islam accounts for approximately 90% of Muslims whilst Shia Islam accounts for approximately 10%. This divide occurred shortly after the death of Muhammad and was centred on who should lead the Muslim nation after Muhammad.
Similarities:
Believes in Quran
Prophets
Fasting in Ramadan
5 pillars
Speaks Arabic
Differences:
5 daily prayers, but prayed 3 times a day; prayers are paired up
Brick that they prey on, head on brick: SHIA Head on floor: SUNNI
Hand by sides: SHIA Crossed: SUNNI
Ramadan is on different days
Ali vs Abu Baker
Sunni Muslims believe that the Prophet did not explicitly declare a successor. Shia Muslims believe that the Prophet publicly designated his cousin and son-in-law, Hazrat Ali (peace be upon him), as the first in a line of hereditary Imams from the Prophet's family to lead the community after him
Differences between Sunni and Shia
#1: Questions of Hereditary Succession
Shiites believe the Prophet Mohammed should have been succeeded by his son-in-law, Imam Ali, and leadership of the Muslim world should pass through the prophet’s descendants. Sunnis don’t believe the leadership of the Muslim world should necessarily pass through hereditary succession.
#2: Reverence of Imam Ali and His Family
Shiites continue to observe what they consider to be Imam Ali and his descendants’ persecution and to revere his family, making annual pilgrimages to shrines to the Imam and his 11 descendants.
#3: The Sunni Majority
Sunnis greatly outnumber Shiites, constituting nearly 90% of the global community of Muslims. The governments of some Persian Gulf countries—including Saudi Arabia, Bahrain and the United Arab Emirates—are Sunni, while Iran and Iraq are ruled by Shiites. Syria’s regime is Alawite, a Shiite offshoot.
#4: Styles of Prayer
Shiites and Sunnis pray differently: Sunnis cross their arms, while Shiites keep their arms by their sides. Sunnis observe five daily prayer sessions; Shiites condense the five prayers into three sessions.
#5: Governance
Shiites are governed by more hierarchical structures, following living religious leaders. But Sunnis typically follow scholarly texts penned by past religious leaders.