physics 2
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
electricity
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
what is current
a flow of electric charge
what is potential difference
the driving force that pushes the charge round
what is resistance
anything that slows the flow down
what is the equation for charge flow
charge flow (Q)= current(I) x time(s)
what is the equation for potential difference
p.d(V) = current x resistance
what are 2 things the resistance can depend on
if it is in series or parallel
wire length
what does the ammeter measure and where must it be placed
measures current and must be placed in series with what you are measuring
what does the voltmeter measure and where must it be placed
measures potential difference and must be placed in parallel with what you are measuring
what can you say about the current and the potential difference in an ohmic conductor
they are directly proportional
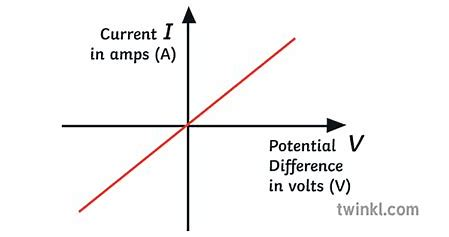
identify this graph
ohmic conductor
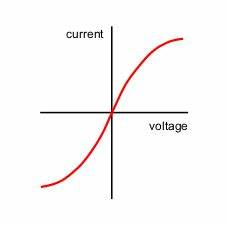
identify this graph
filament lamp
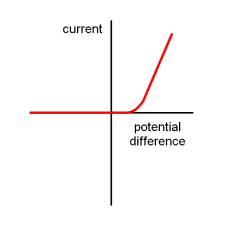
identify this graph
diode
what is an LDR
Light Dependent Resistor
in what condition is a thermistor at its highest resistance
cold
what are sensing circuits
can be used to turn on or increase power to components depending on the conditions they are in.
what is a series circuit
all the different components are connected in a line, end to end except for voltmeters which are always connected in parallel
in a series circuit what happens to the
potential difference
current
resistance
p.d is shared - the p.d always adds up to the source of p.d
current is the same everywhere
resistance adds up
what is a parallel circuit
each component is separately connected to the supply
in a parallel circuit what happens to the
potential difference
current
resistance
p.d is the same across all components
current is shared between branches
adding a resistor in parallel reduces the total resistance
what are the 2 types of electric supply
alternating
direct current
what are the 3 wires found in a cable called
neutral wire
live wire
earth wire
describe the neutral wire
BLUE
completes the circuit , current flows through the wire. it is around 0V
describe the live wire
BROWN
provides alternating potential difference (230V)
describe the earth wire
GREEN and YELLOW
stops the appliance casing from becoming live.
doesn’t usually carry a current - only when there is a fault
what’s the 2 equations for energy transferred
E.T = power x time
E.T = charge flow x P.D
whats the equation for power
Power = P.D x current
what is the national grid
a giant system of cables and transformers that covers the uk and connects power stations to consumers
what do transformers do
step-up transformer increases P.D