StemUp: AQA A level Biology 3.3.4.2 Mass transport in Plants
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What is the function of the xylem vessels? (3)
- Transports water and minerals through the plant
- From roots to leaves
- Supports the plant
Describe the structure of the xylem vessels? (5)
- Xylem tissue is dead and has no cells
- This leaves it as a hollow tube
- So there is minimal resistance to the flow of water and ions
- Cell wall has been strengthened by lignin
- This makes their cell walls more rigid and provides strength
Draw and label the apparatus for a potometer (6)
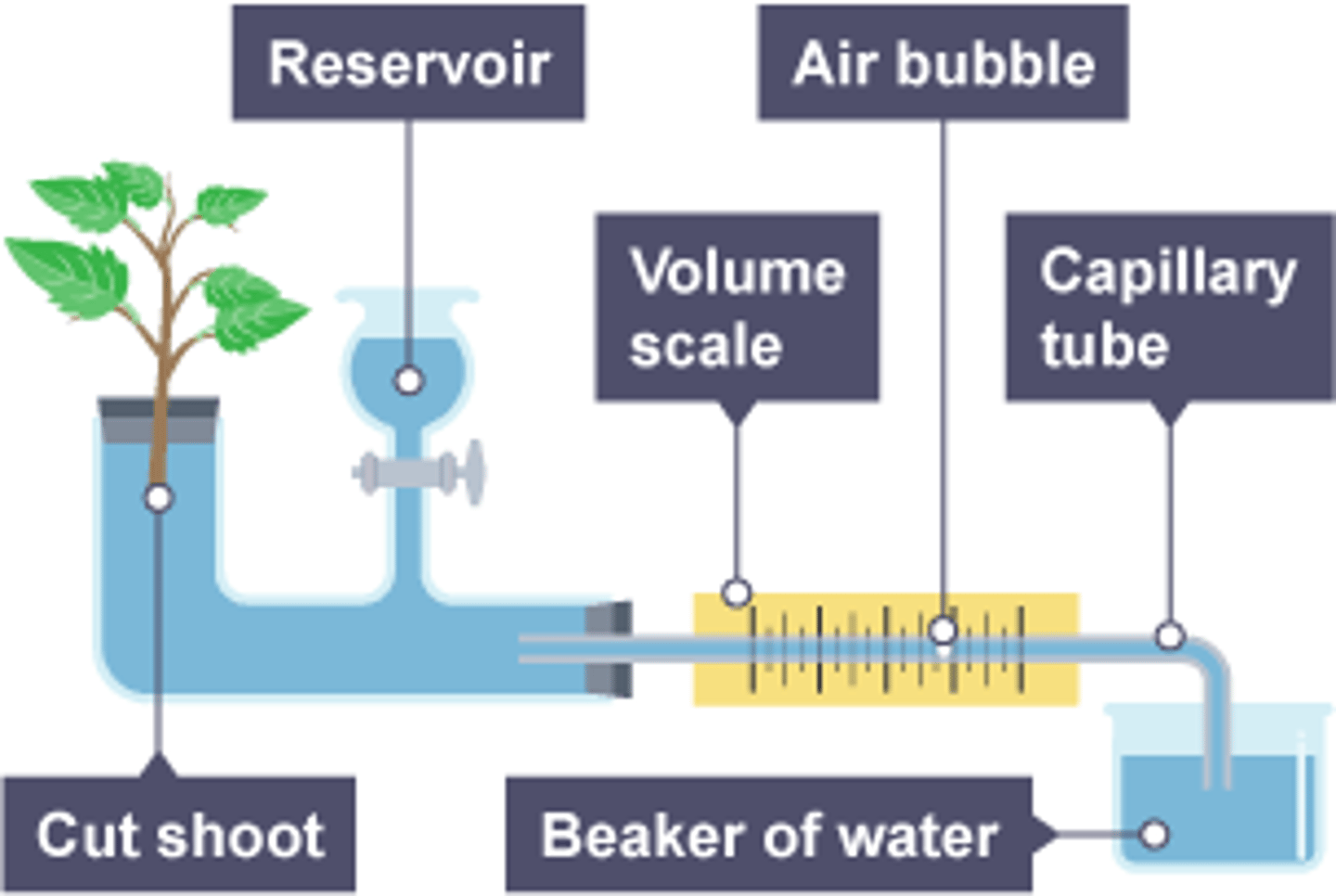
How can a potometer be used to measure the rate of transpiration? (1)
Measures the rate of water uptake by recording the distance the air bubble moves
How do you calculate the volume of water taken up using a potometer? (1)
Uses the formula: πr²d
How is the rate of water uptake determined from the potometer measurements? (2)
- Divide the volume of water taken up
- By the time
What assumption does the potometer method make about water uptake? (1)
The rate of water uptake is equal to the rate of transpiration
Why might the potometer method not always accurately reflect the rate of transpiration? (2)
- Some is used to maintain turgidity
- Small percentage is used in photosynthesis.
Describe the cohesion-tension theory for transpiration of water (5)
1. Transpiration of water molecules through the stomata occurs
2. This lowers the water potential of the mesophyll (leave) cells
3. Water is pulled up from the xylem creating tension (negative pressure)
4. Water molecules cohere - stick together by hydrogen bonds
5. Adhesive forces attract the water molecules to xylem wall forming a water column
What is the function of the phloem tissues? (3)
- Transport organic substances from the leaves leaves
- To the rest of the plant
- By the process of translocation
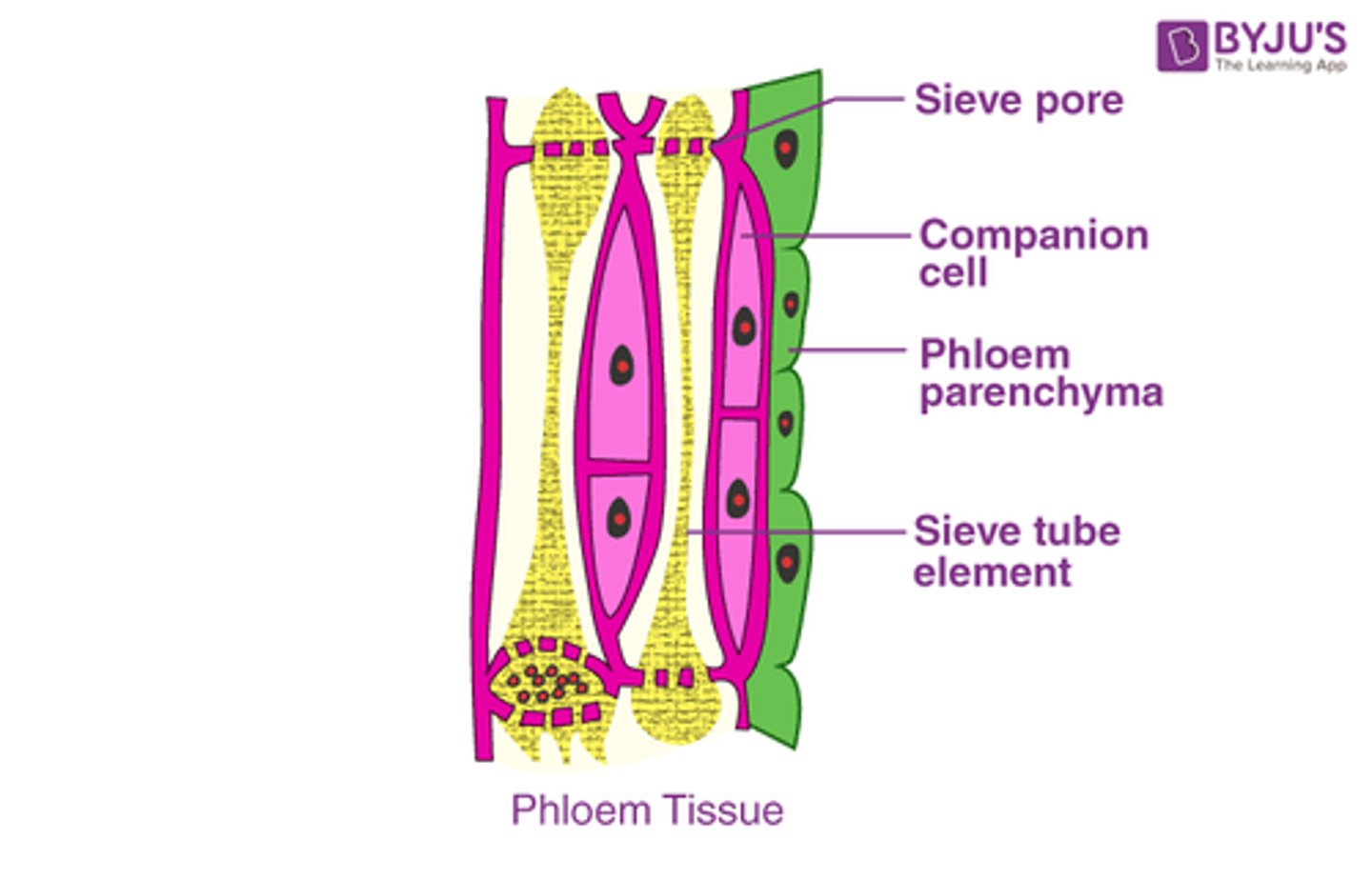
Describe the structure of the phloem tissues (3)
- Consists of sieve elements and companion cells
- Sieve elements are joined end to end to form sieve tubes
- Next to each sieve element is a companion cell with dense cytoplasm and many mitochondria
What is the source in translocation? (1)
The leaves
What is the sink in translocation? (1)
The roots
Describe the mass flow hypothesis for translocation (7)
1. In the source, sugars are actively transported into phloem
2. By companion cells
3. This lowers the water potential of the sieve tube
4. Water enters by osmosis
5. This creates a high turgor pressure which causes mass movement towards roots
6. In the sink, sugars are being used up in respiration
7. Which lowers the turgor pressure and the cycle continues
What is the ringing experiment used for? (1)
Shows the transport in plants via the phloem
Describe the use of ringing experiment to show transport in plants via the phloem (2)
1. Involves removing a complete ring of phloem around the stem
2. Preventing transport through the phloem at this point
What does swelling in the ringing experiment indicate? (3)
- A build up of photosynthetic products from the leaf
- Which were prevented from being transported past the ring
- Due to the removal of the phloem
Describe how you would use tracers to show the transport in plants via both the phloem and xylem
- Radioactive substances are supplied to the leaf of a plant
- After a while, you can use autoradiography to detect where the radioactive substances have moved
What radioactive substance is used to show transport in plants via xylem vessels? (1)
Mineral ions e.g. Na+
What radioactive substance is used to show transport in plants via phloem? (1)
Carbon dioxide, CO2
What does autoradiography reveal about the action of phloem in plants? (2)
- Photosynthetic products are present in growing regions
- Which indicates translocation through the phloem
What are some evidences that support the mass flow hypothesis? (4)
- Cutting the stem of a plant results in phloem sap being released
- Indicating hydrostatic pressure in the sieve tubes
- Lowering the temperature or the use of respiratory inhibitors reduces the rate of translocation
- Indicating an active transport mechanism is involved
What are some evidences that are against the mass flow hypothesis? (4)
- Not all solutes move at the same speed
- They should do if it is mass flow
- In young phloem tissue, substances have been observed moving in opposite directions
- In the same sieve tube