Biology Unit 8 study guide, DNA replication, Scientists (s/r-strain) and (Rosalind Franklin + other scientists)
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
Who was Fredrick Griffith?
Scientist from 1928 who wanted to learn more about pneumonia and the flu
Fredrick Griffiths time-line/year of EXP
1928
Fredrick Griffiths experiment
R-strain - injected into mouse = living mouse
S-strain - injected into mouse = dead mouse
Boiled S-strain + living R-strain = dead mouse
Fredrick Griffiths conclusion
Something in the dead S-strain was transferred into the living R-strain when mixed together that killed the mouse
Who was Oswald Avery?
Scientist form 1944 who wanted to learn more about Griffiths EXP and “transforming vairable”
Oswald Avery’s time-line/year of EXP
1944
Oswald Avery’s experiment
Boiled S-strain + living R-strain + Carboxylase = dead mouse
Boiled S-strain + living R-strain + Protease = dead mouse
Boiled S-strain + living R-strain + Lipase = dead mouse
Boiled S-strain + living R-strain + RNAse = dead mouse
Boiled S-strain + living R-strain + DNAse = living mouse
Oswald Avery’s conclusion
DNA is the transforming variable, but did not know how DNA was the transforming variable
Who were Hershey and Chase?
Scientists from the 1952 who wanted to prove that DNA was the genetic material
Hershey and Chase time-line/year of EXP
1952
Hershey and Chase experiment
Radioactive PRO → Allow bacteria to infect cell = cell is not radioactive, then, radioactive sulfur (35s) → Centrifuge to separate → Radioactive supernatant (pellet at the bottom of flask) = PRO is not the genetic material
Radioactive DNA → Allow bacteria to infect cell = cell is radioactive, then, radioactive phosphorus (32p) → Centrifuge to separate → Radioactive pellet (pellet at top of flask, supernatant at the bottom) = DNA is the genetic material
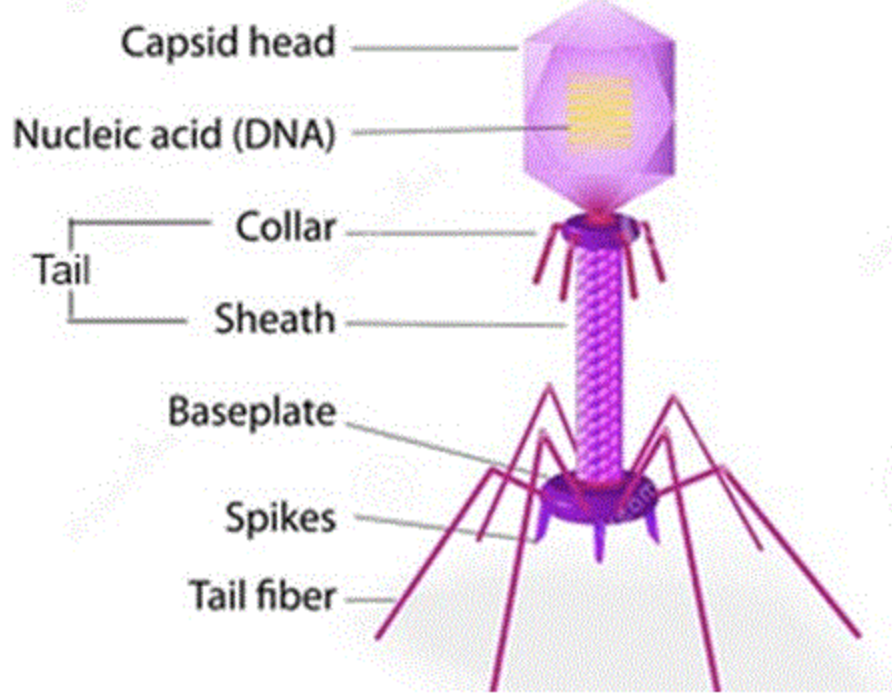
Bacteria used in Hershey and Chase’s EXP
T2 Bacteriophage
Hershey and Chase conclusion
DNA is the genetic material
Sulfur is found in what
PRO
Phosphorus is found in what
DNA
What does a virus (bacteriophage) look like when drawn
Full name of DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid
Nucleotide
Monomers for nucleic acid
How many strands does DNA have
2, it is double stranded
How many strands does RNA have?
One
Strands of DNA are not parallel, they are __________.
Antiparallel
Why is DNA antiparallel?
Because the strands would look like this:
3’ ——————- 5’
5’ ——————- 3’
Phosphate group chemical formula

Deoxyribose chemical formula (CHO)
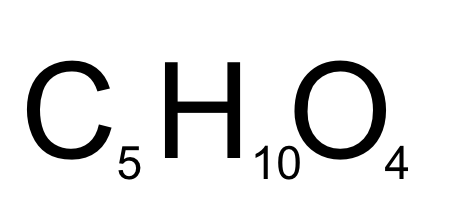
What type of process is DNA replication?
Semi-conservative
What is the top strand called?
Leading strand
What is the bottom strand called?
lagging strand
What’s Helicase?
An enzyme that unwinds DNA and breaks the hydrogen bonds.
What is topoisomerase?
ENZ that Goes at the top of DNA and makes sure that the DNA does not overwind
What does SSB stand for?
Single stranded binding protein
What does DNA polymerase do?
Finds a primer, builds a new molecule(I and III), and it also checks for errors(III)
What are Okazaki fragments?
Pieces made on the lagging strand
Which way does the DNA polymerase work to create the new DNA
3’ → 5’
What does lygase do?
Glues the okazaki fragments together
Where does DNA replication occur?
Nucleus (sometimes)
When does DNA replication occur?
During interphase (s-phase)
Helicase
Unzips the strand
Primase
Adds RNA primers
lygase
gluer of Okazaki fragments
Where does DNA Polymerase I work?
On bottom/lagging strand
Where does DNA polymerase III work?
Top/leading strand
Where does DNA polymerase work on specifically? *hint: what does it replace
Where there are RNA primers and replaces them with correct nucleotides
Order of enzymes in DNA replication
Helicase - Flattens out DNA + breaks H+ bonds
SSB - Placed to make sure DNA would not attach again
Topoisomerase - Placed at top of DNA to prevent overcoiling
Primase - Places RNA primers
DNA polymerase:
III - Works on building leading strand
I- replaces RNA primers w/ right nucleotides, and builds lagging strand
Ligase - Glues together Okazaki fragments
DNA polymerase III - checks for errors and fixes them
DNA polymerase I vs III
III - adds new DNA strand and checks for errors in the end
I - replaces RNA primers and replaces with correct nucleotides
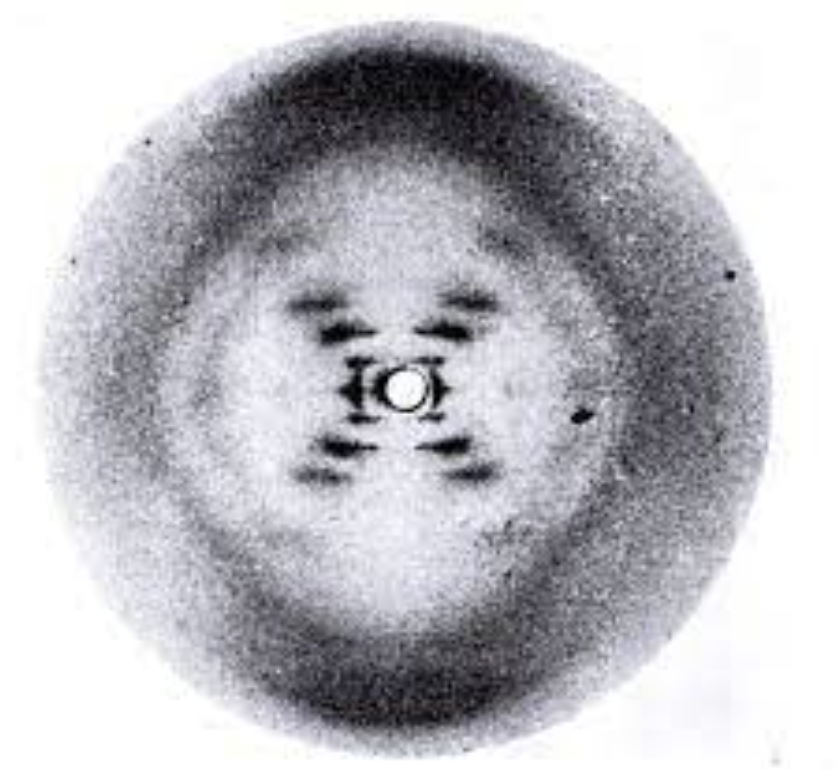
Who actually discovered that DNA was double stranded?
Rosalind Franklin
Who took credit for discovering that DNA was double stranded?
Watson and Crick
Who were the men who made Rosalind Franklin feel low to their superiorness, and later stole her work?
Watson and Crick
What impact did Wilkins have to Rosalind Franklin?
Wilkins hired her, but was also really mean and discriminatory to her for being a woman
Some studies and experiments of Rosalind Franklin?
X-ray crystallography studies on DNA (finding that DNA is made up of 2 strands)
Working on figuring out the complex structure of a virus
More too!
What was Rosalind Franklins photo of DNA called?
Photo 51