Co-ordination and response
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
2025
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
What is a stimulus?
A change in the environment that can be detected by an organism
What detect stimuli and where are they found in humans and plants?
Receptors.
Humans: sense organs
Plants: specialised cells that detect stimuli like light, gravity or water
What are examples of responses to stimuli
Moving away or towards something
Secreting chemicals
Adjusting body processes
What is homeostasis?
The maintenance of a constant internal environment, ensuring optimal conditions for enzyme activity and cell function.
Give two examples of homeostasis
Control of body temperature
Control of body water content
Give two examples of an effector organ
Muscle or gland
What structures do all neurones have and what are their functions?
Dendrites - receive impulses from receptors or axon nerve endings of other neurones
Cell body - Contains nucleus
Axon - Transmits nerve impulses over large distances
Myelin sheath - Fatty coat that surrounds axons; increases speed to nerve impulse and insulates axon
Nerve ending - releases neurotransmitters across synapses to muscle cells of other neurones
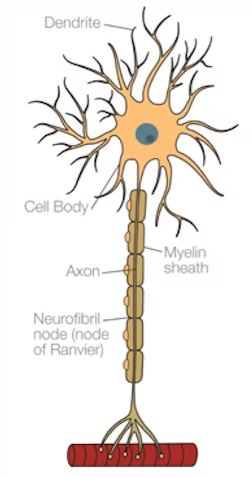
What does a sensory neurone do and what does it look like
Transmits nerve impulses from receptors to CNS; long dendrites and long axon with cell body located centrally
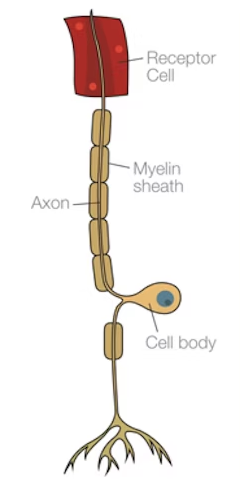
What does a relay neurone do and what does it looks like
Transmits nerve impulses from sensory neurones to motor neurones; numerous, short processes; only in CNS
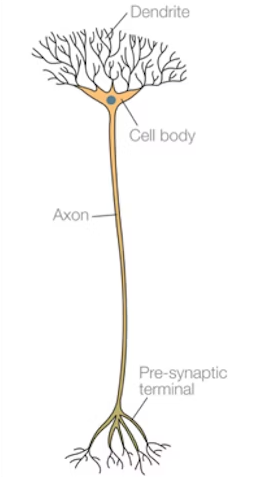
What does a motor neurone do and what does it look like
Transmits nerve impulses from CNS to muscles or glands; short dendrites but long axons
Describe the reflex arc when touching something hot
Receptors in skin detect a stimulus, sending it through the sensory neurone
The sensory neurones send it to the relay neurone
Information is sent to the relay neuron located in the CNS which transmits nerve impulses to motor neurones
The relay neuron sends impulses to muscles (or glands)
The muscles contract and you pull your finger away
What is a synpase?
The junction between two neurons or between a neuron and muscle cells
What is a synaptic cleft?
The gap between an axon and dendrite
What are neurotransmitters?
A chemical substance released across a synapse to communicate a nerve impulse
How does vasodilation help regulate body temperature?
Blood vessels dilate so more blood gets near to surface to increase heat loss by radiation when it is hot.
How does hair help regulate body temperature?
Hair erector muscles contract and make hairs stand upright on skin, trapping warm still air close to the surface of the skin so less heat is lost by radiation when it is cold
How does sweat help regulate body temperature?
Swear evaporates from the skin surface, taking away heat with it