SJSU SP24 BIOL-65 Chapter 9 - The Skeletal System IV: Joints
1/115
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
116 Terms
Joint (articulation)
point where two bones meet
Arthrology
study of joint structure, function, and dysfunction
Biomechanics
study of movements and mechanics in body
Kinesiology
study of musculoskeletal movement
Synostosis (bony) joints
immovable; two bones ossified together
Synarthrosis (fibrous) joints
collagen fibers bind adjacent bones; little to kno movement
Three types of Synarthrosis (fibrous) joints
Sutures, Gomphoses, Syndesmoses
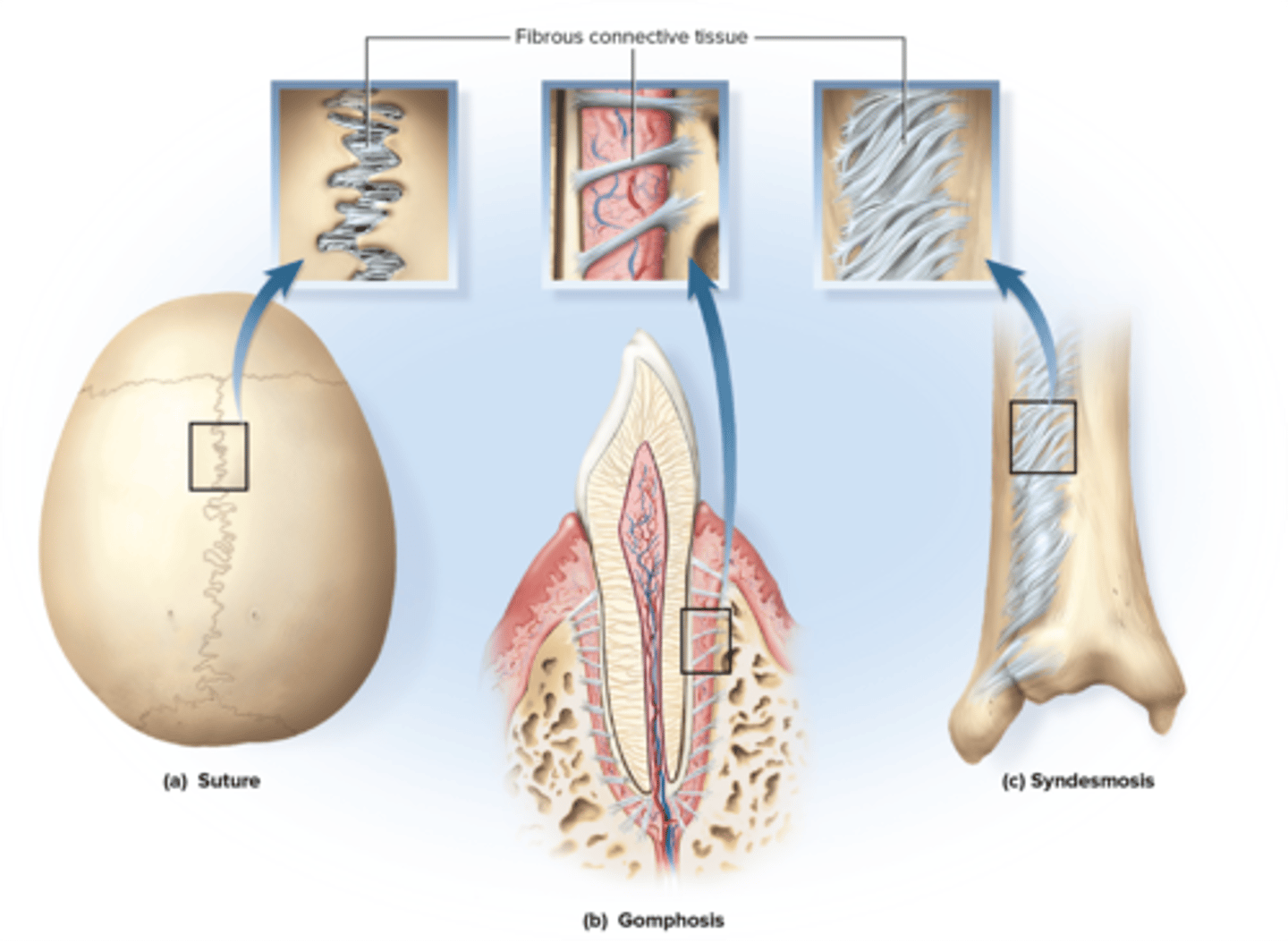
Sutures
A line along which any two bones of the skull are immovably joined; Immobile or slightly movable.
Three Classifications of Sutures
Serrate, Lap (squamous), Plane (butt)
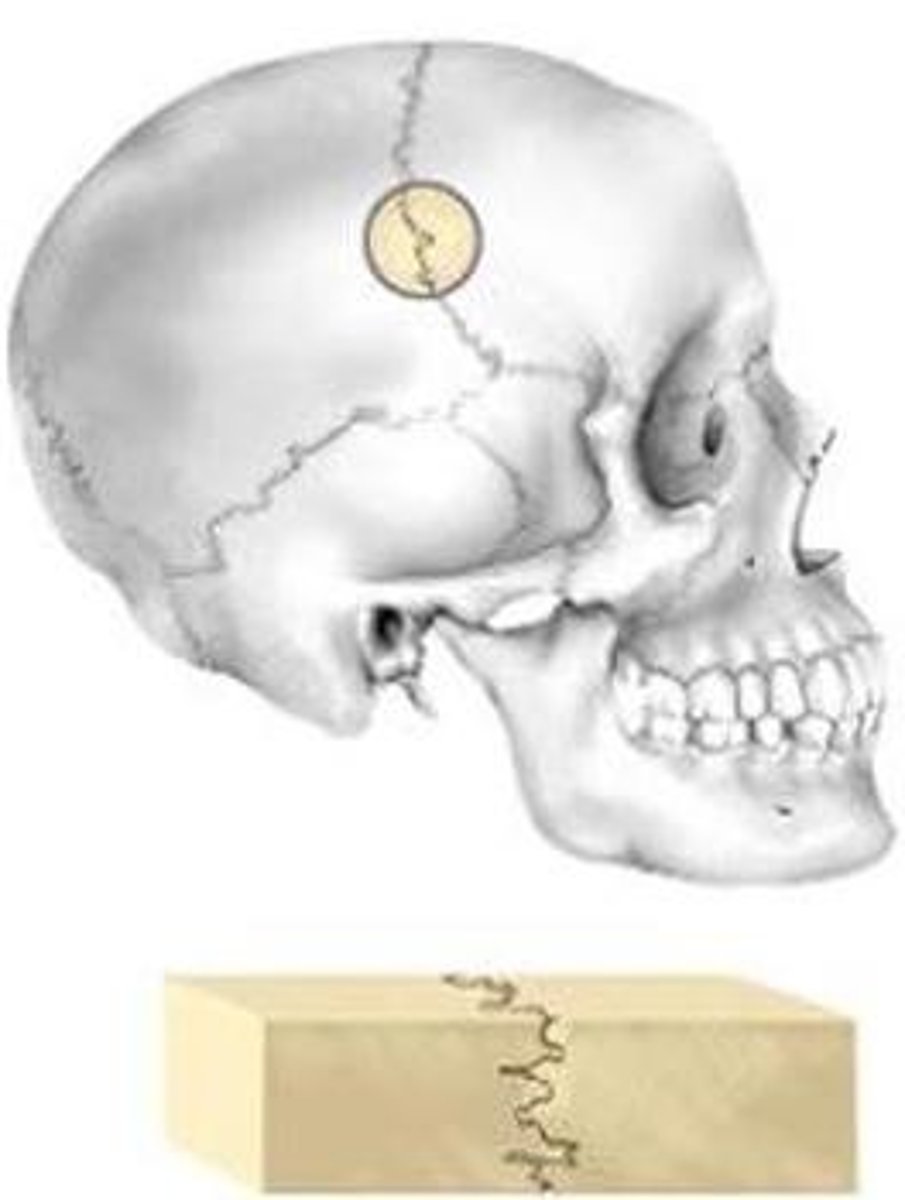
Serrate suture
interlocked
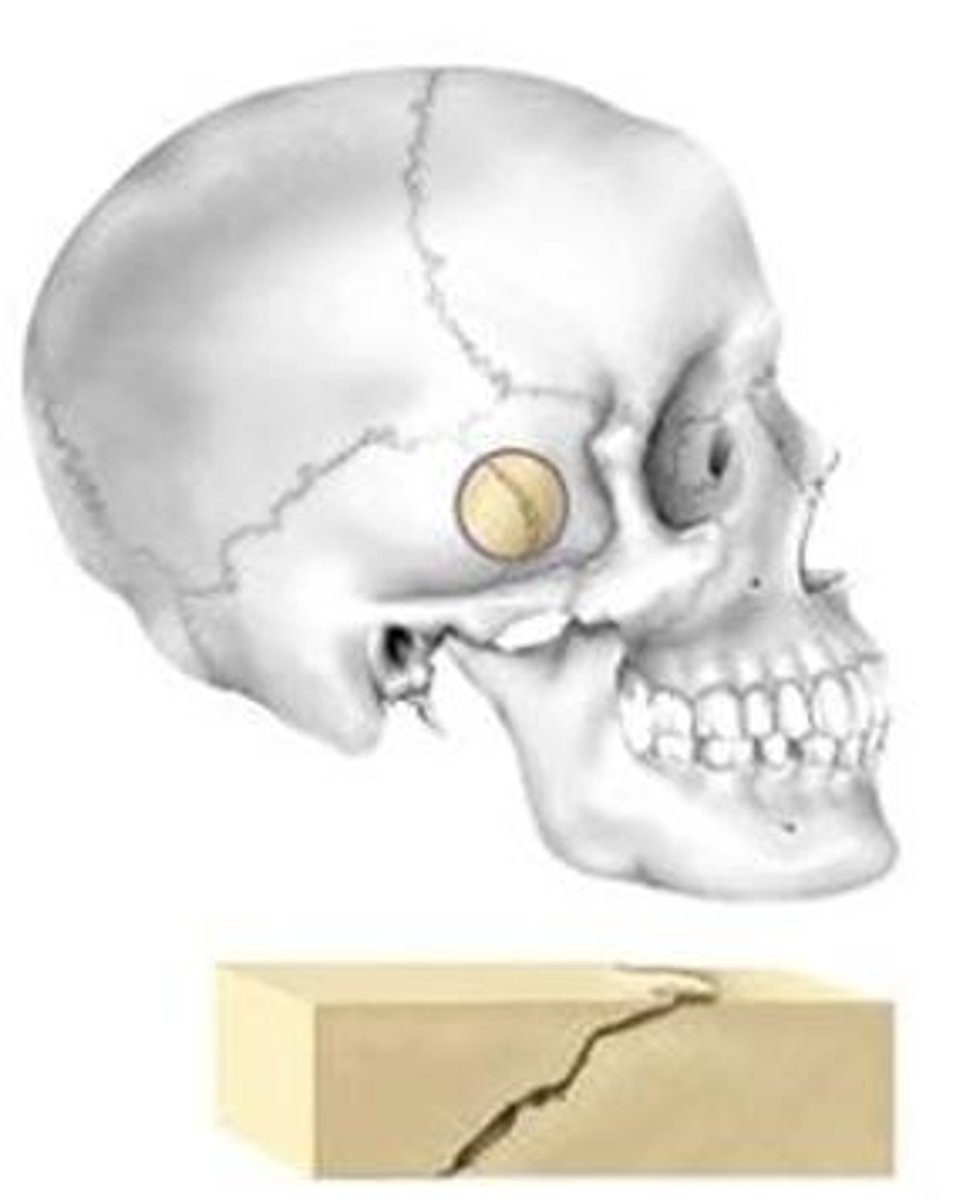
Lap (squamous) suture
overlapped
Plane (butt) suture
straight, nonoverlapped
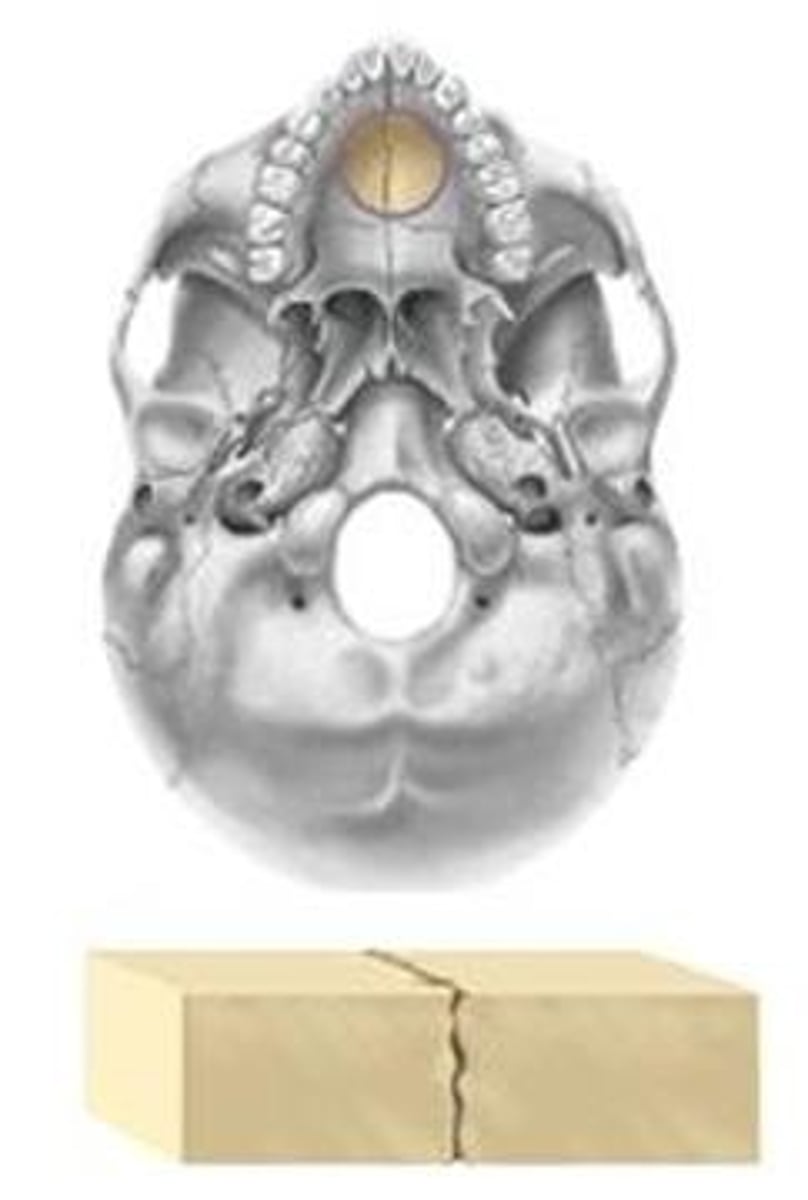
Gomphoses
held in place by periodontal ligaments; slight movement under stress
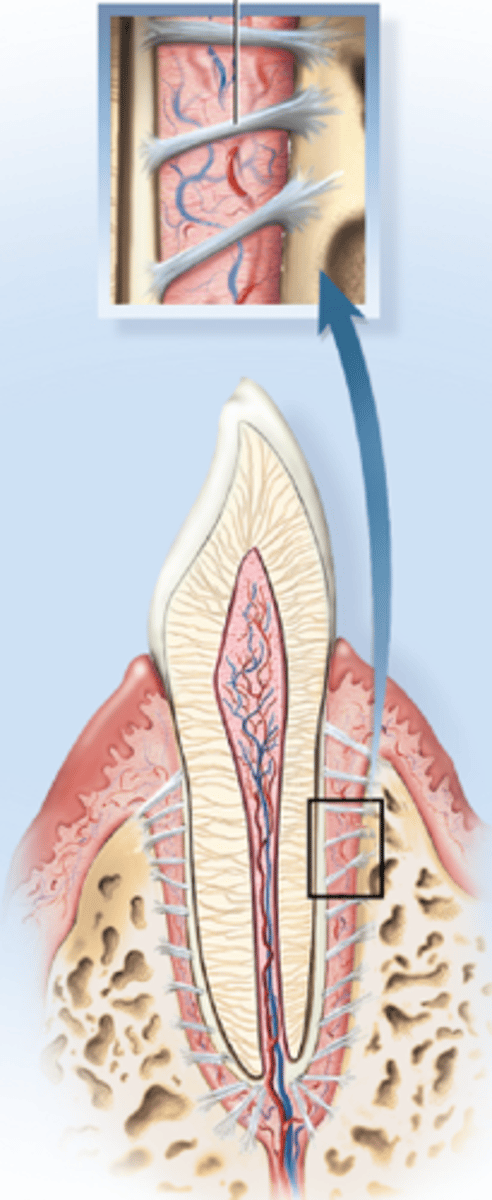
Syndesmoses
Long collagen fibers
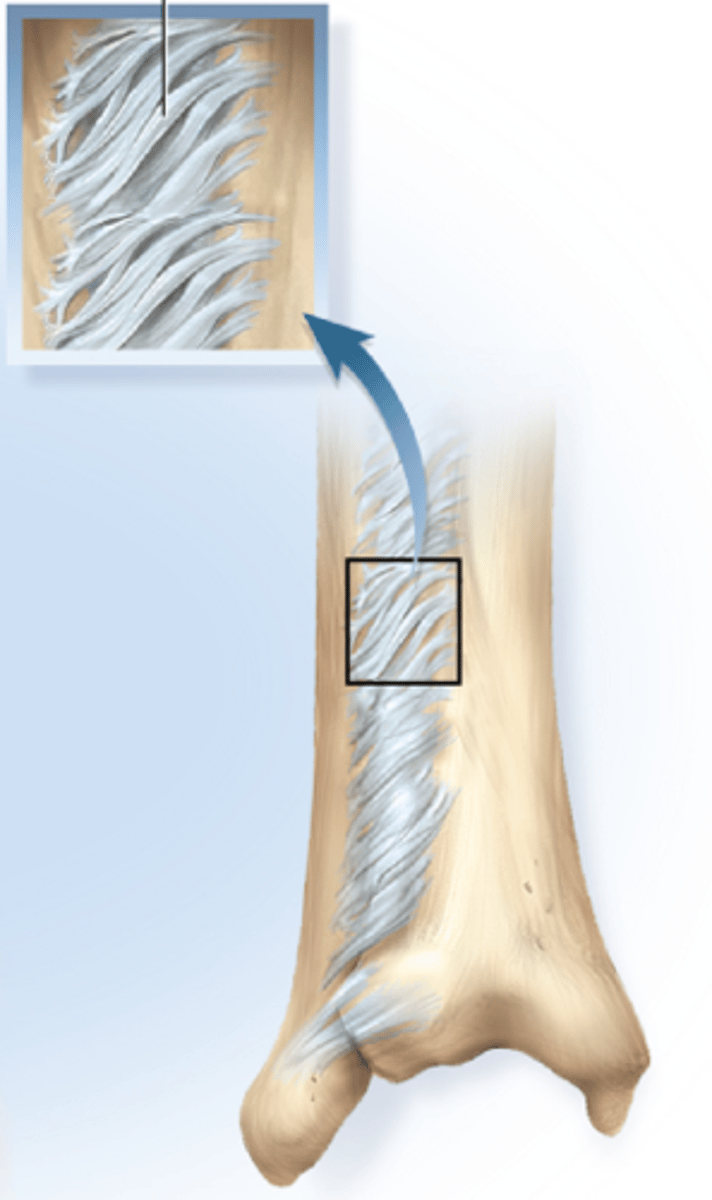
Amphiarthrosis (Cartilaginous) joints
Interlinked by cartilage
Two types of Amphiarthrosis (Cartilaginous) joints
Synchondroses, Symphyses
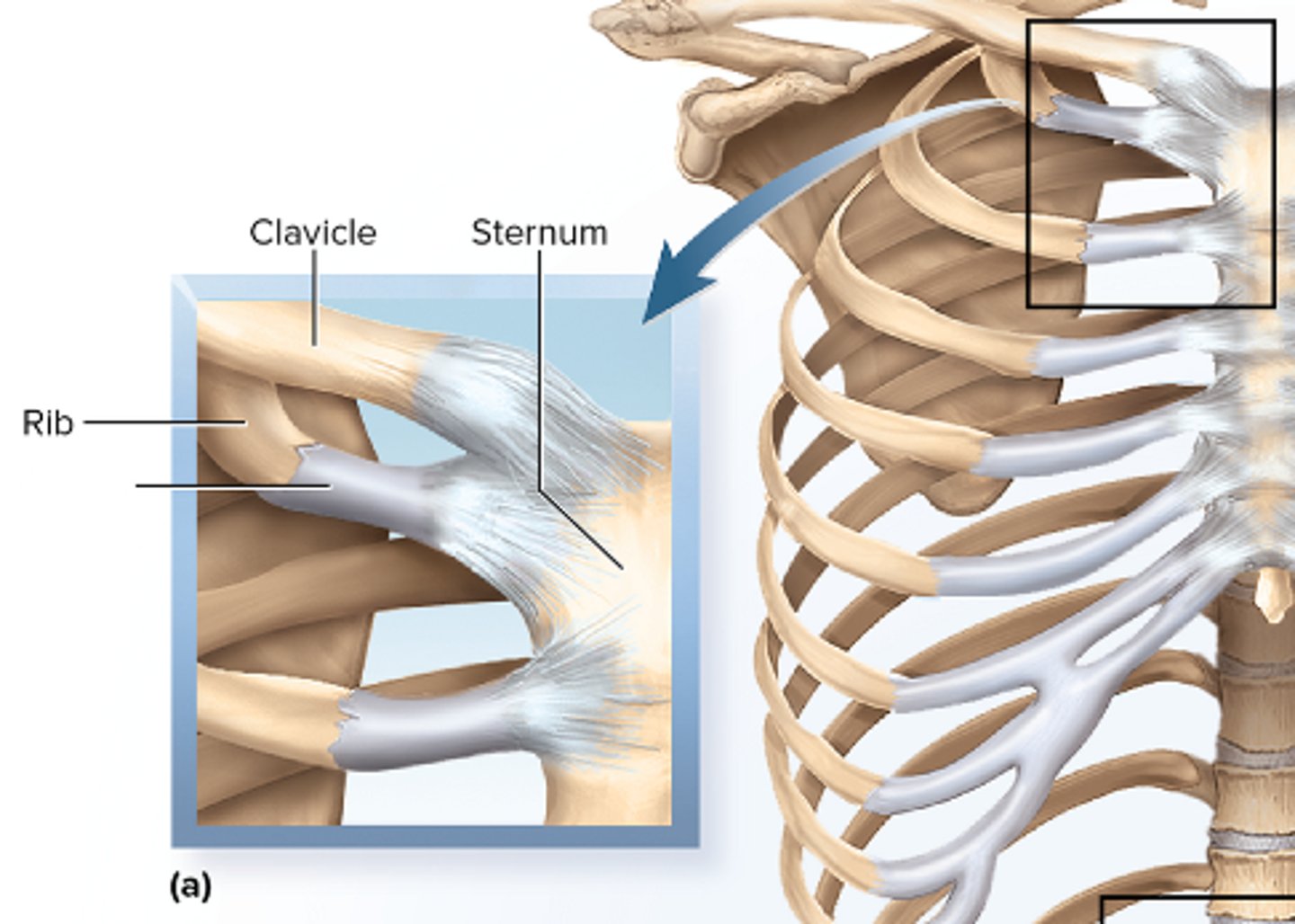
Synchondroses
bones bound by hyaline cartilage; i.e. epiphyseal plate, attachment of the first rib to the sternum
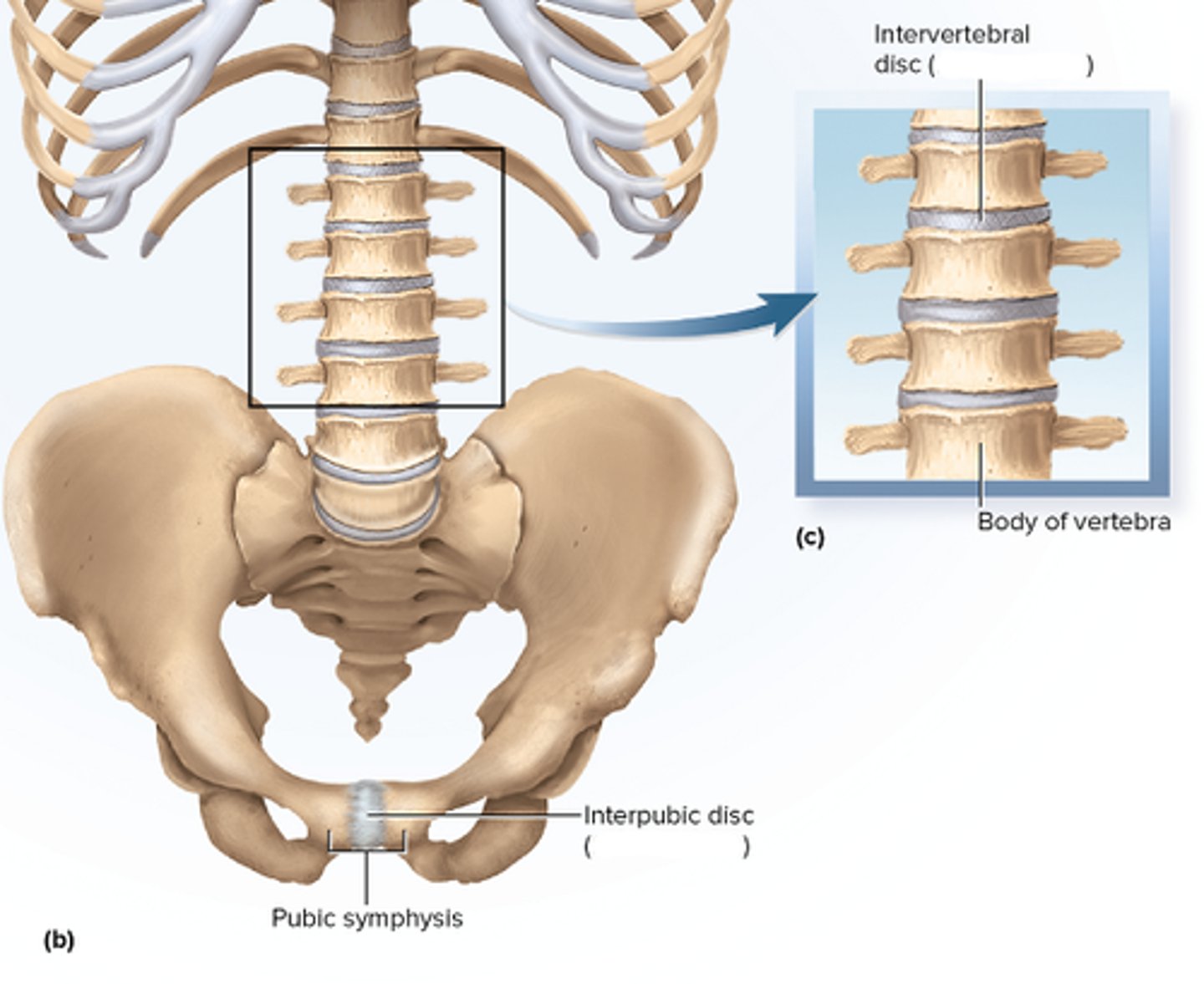
Symphyses
bones joined by fibrocartilage; i.e. pubic symphysis, intervertebral discs
Diarthrosis (Synovial) joints
points where two bones are separated by a narrow, encapsulated space filled with lubricating synovial fluid; varied mobility, freely movable to limited
General Anatomy of Synovial Joints
Articular cartilage; joint (articular) cavity, synovial fluid, joint (articular) capsule, outer fibrous capsule, inner synovial membrane
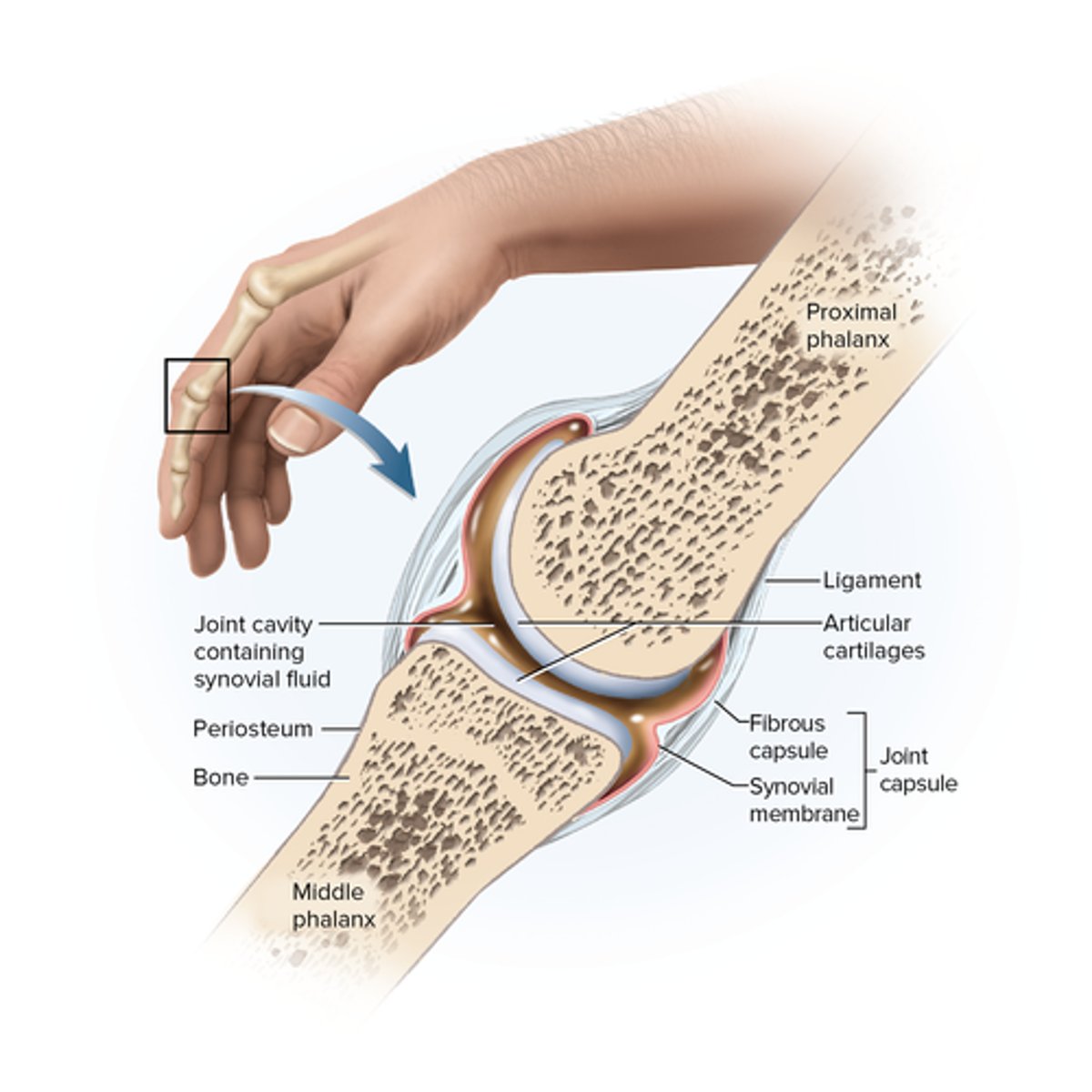
Accessory structures associated with synovial joints
tendons, ligaments, and bursae
Articular cartilage
a thin layer of hyaline cartilage covering the articular surface of a bone at a synovial joint, serving to reduce friction and ease joint movement
Joint capsule
Encloses joint cavity -- narrow fluid-filled space
Inner synovial membrane
Produces synovial fluid
Synovial fluid
lubricant consisting of fibroblast-like cells
Tendons
muscle to bone
Ligaments
bone to bone
Bursa
sac of synovial fluid
Tendon sheath
elongated bursa
Classes of Synovial Joints
Ball-and-socket, Condylar, Saddle, Plane, Hinge, Pivot
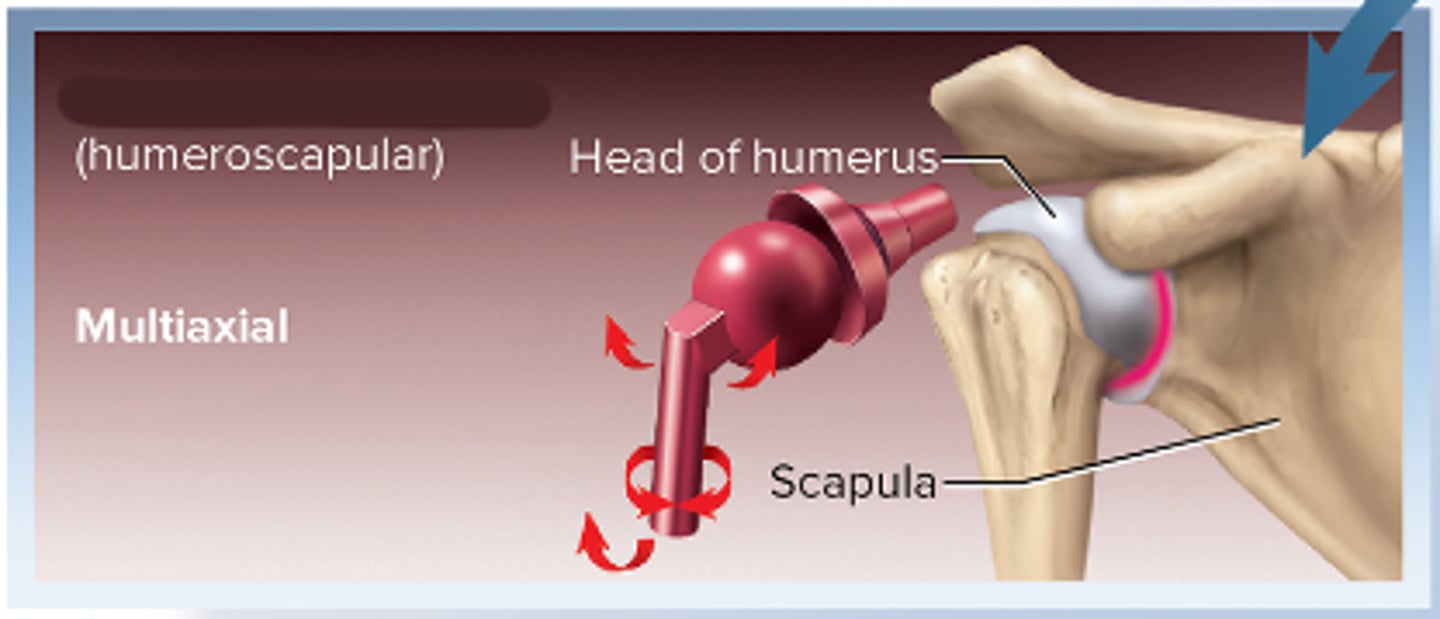
Ball-and-socket joint
Multiaxial(>2)
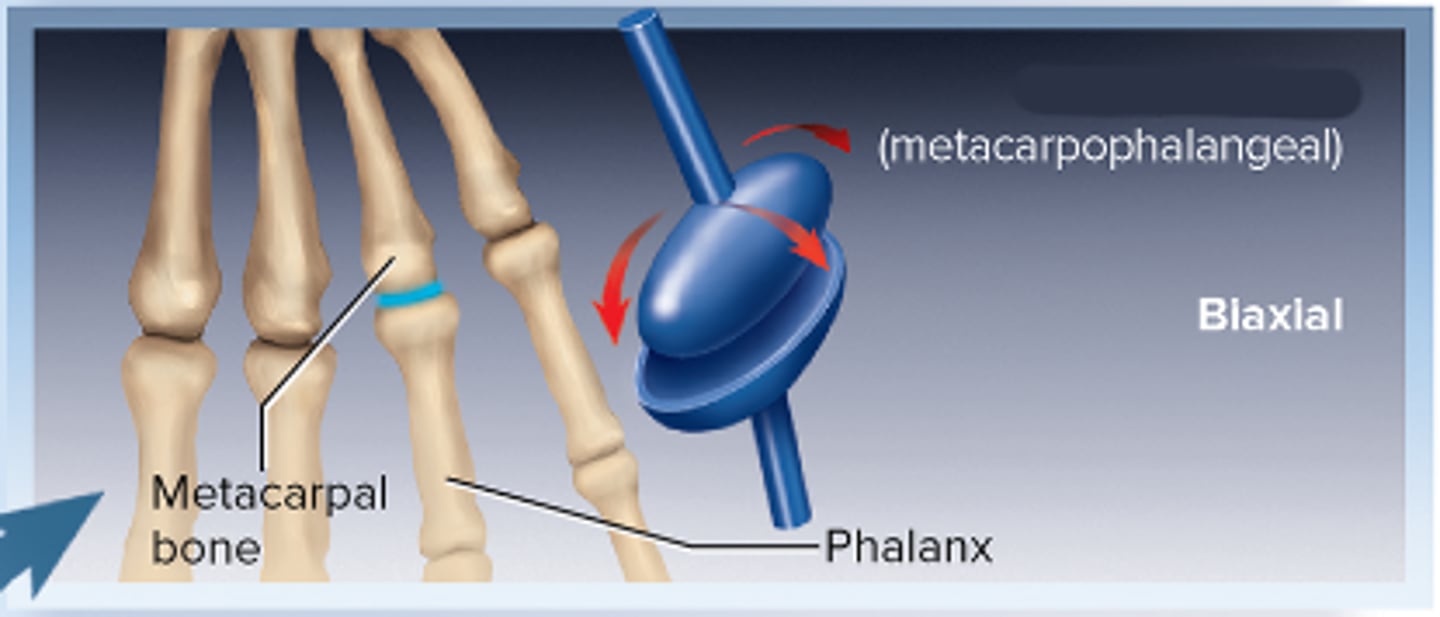
Condylar (ellipsoid) joint
Biaxial(2)
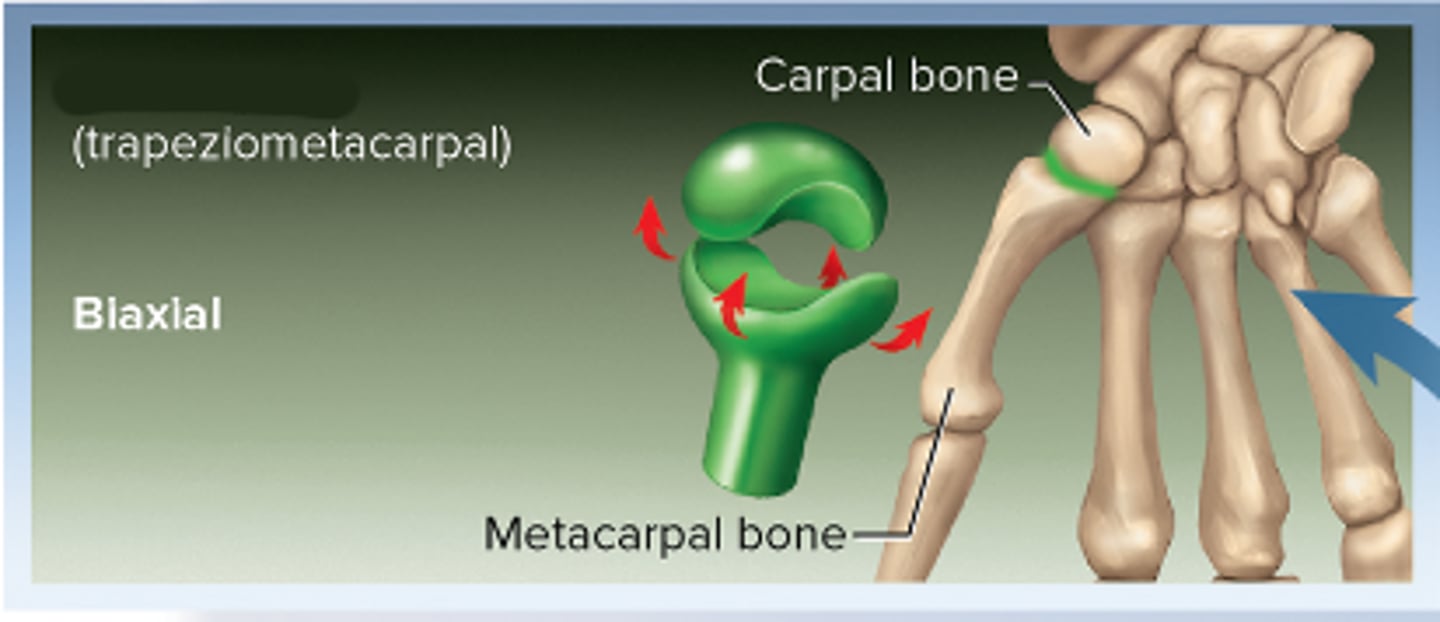
Saddle joint
Biaxial(2)
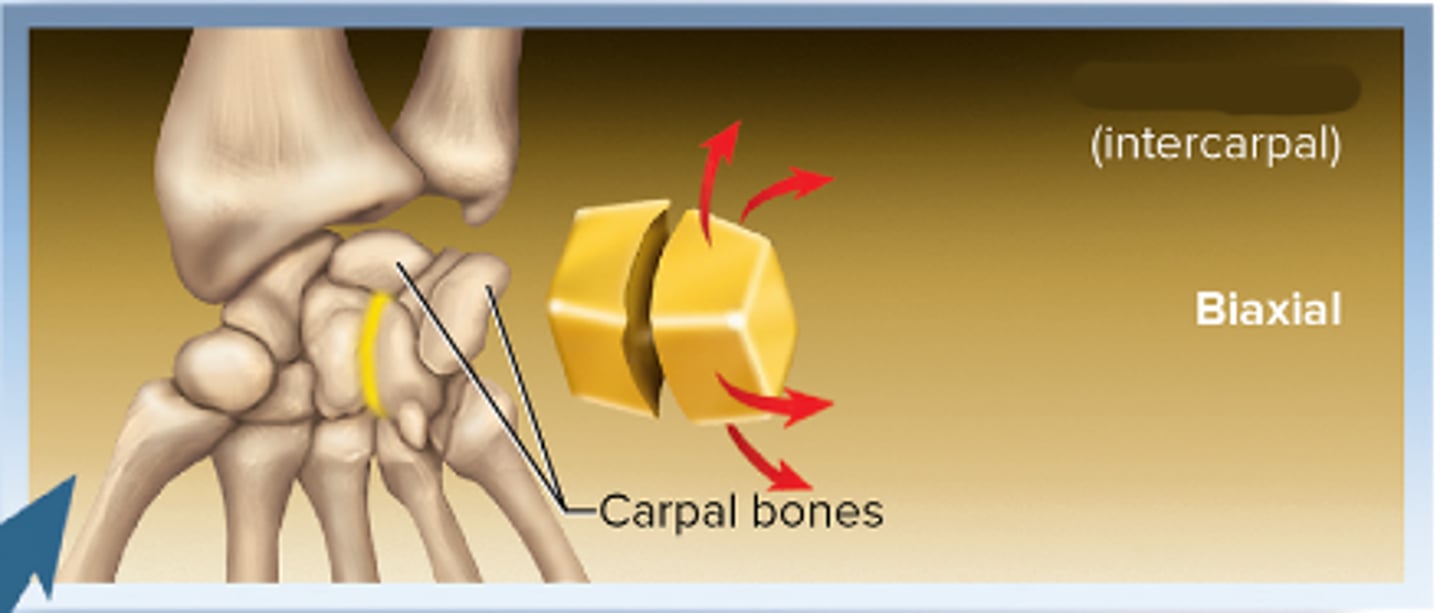
Plane (gliding) joint
Biaxial(2)
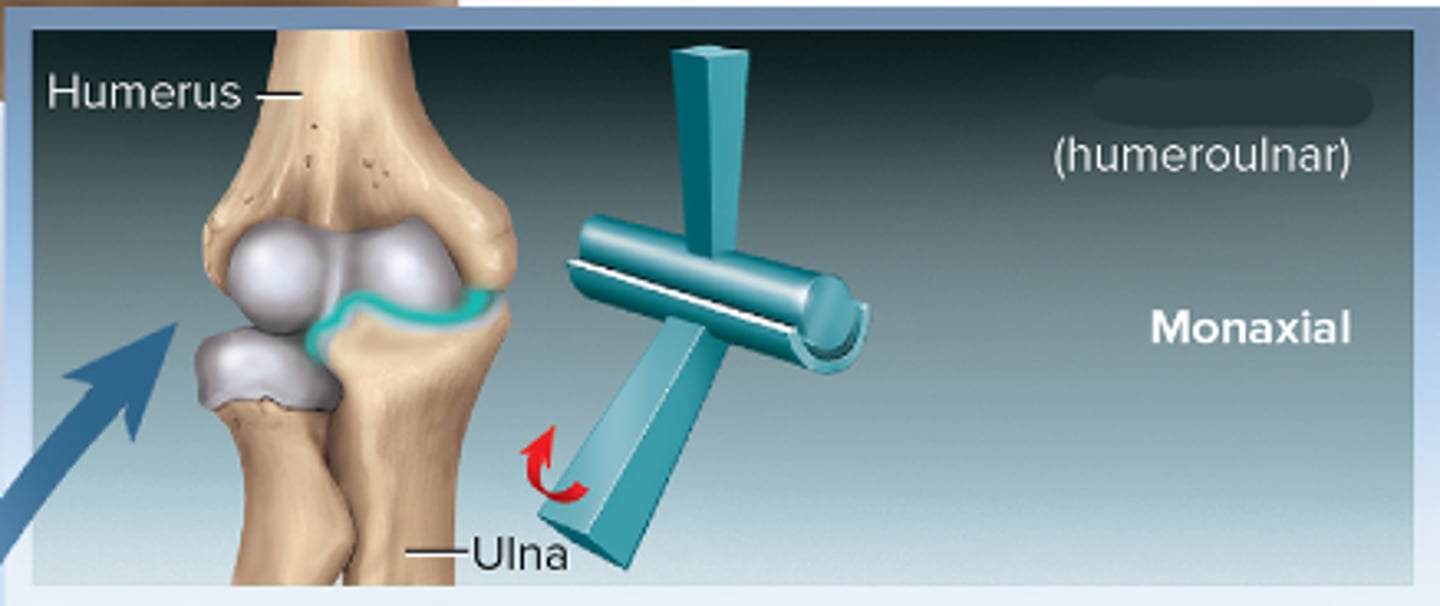
Hinge joint
monoaxial
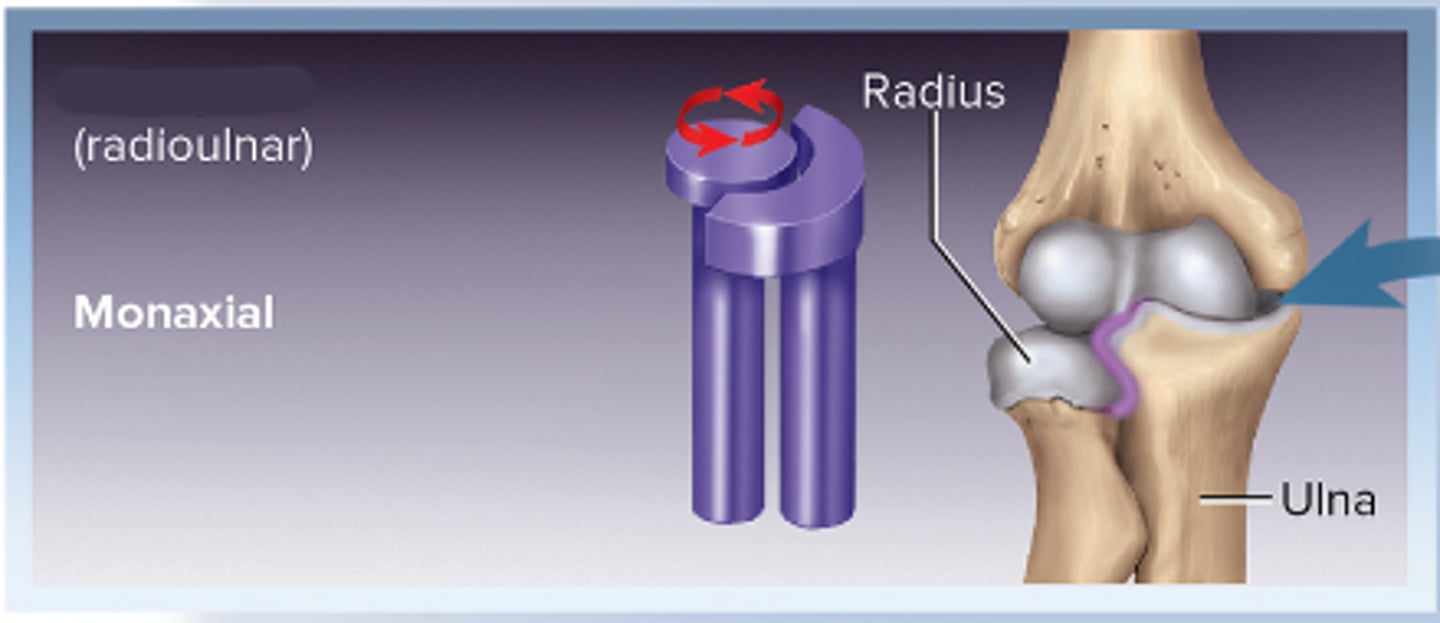
Pivot joint
Monoaxial(1)
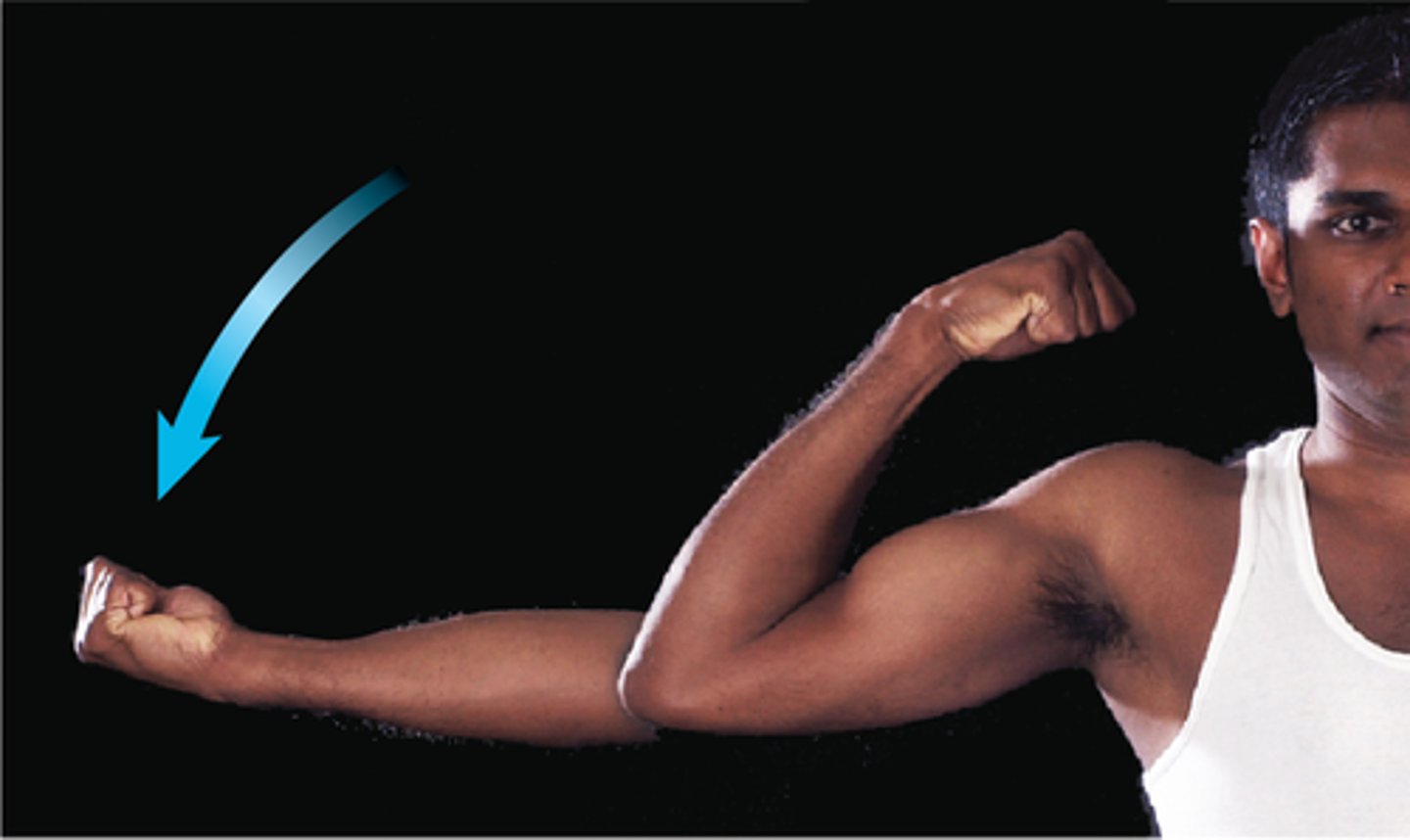
Flexion
decreases angle joint
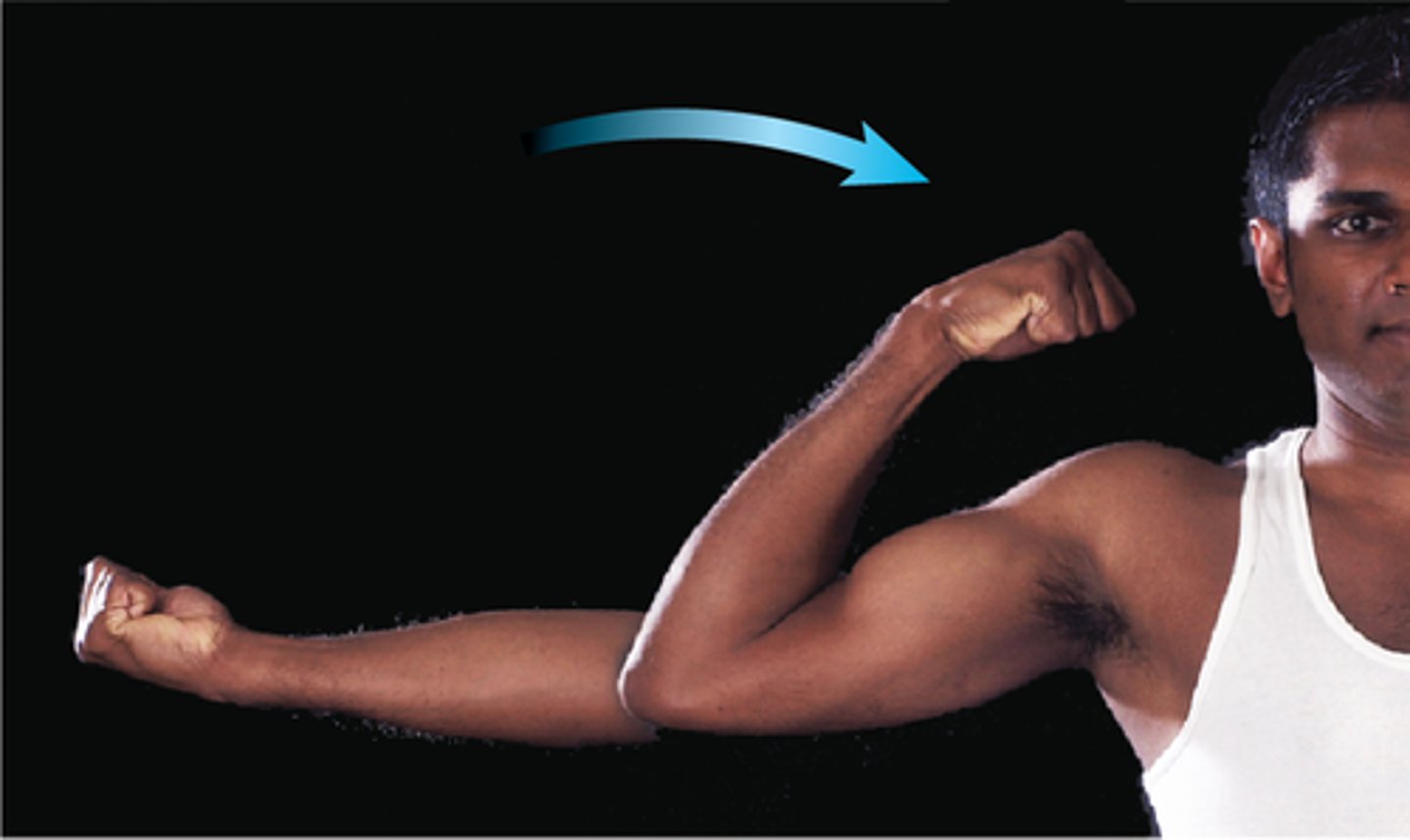
Extension
straightens joint angle

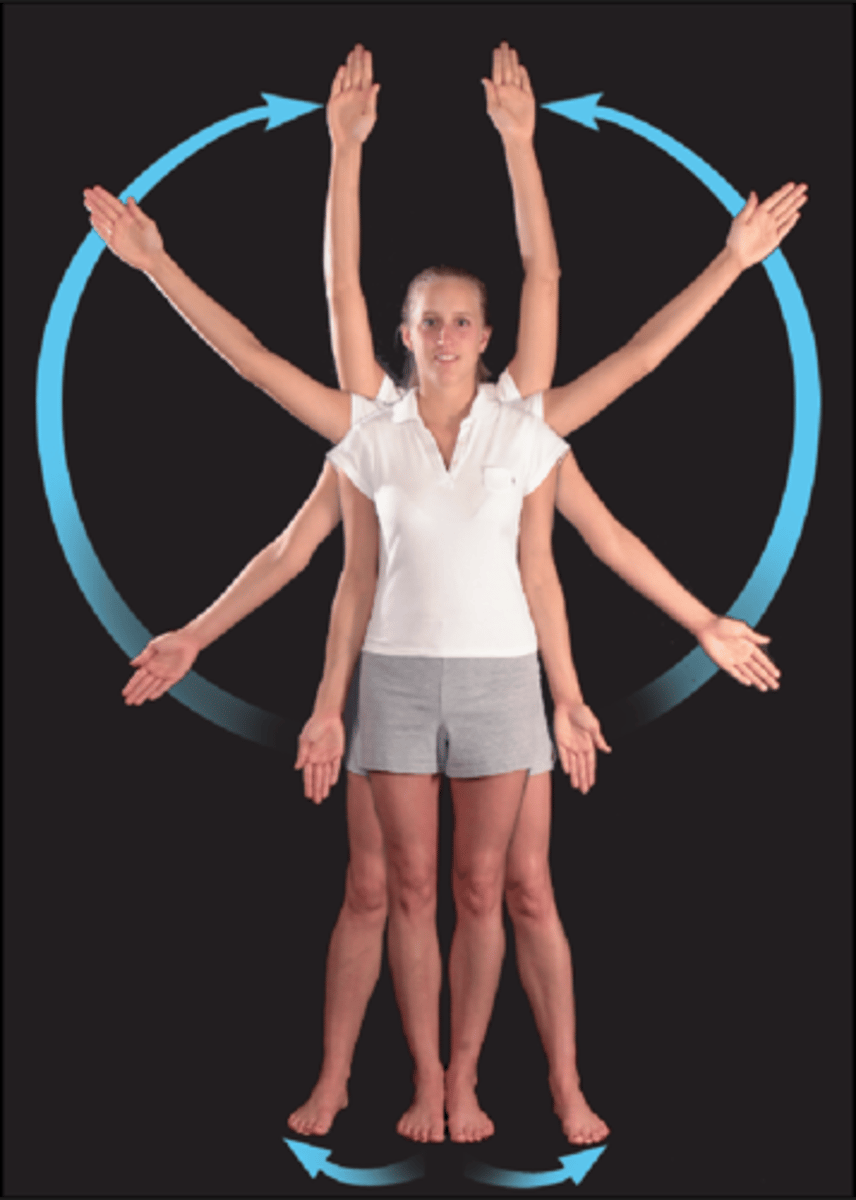
Abduction
moves away from midline

Adduction
moves toward midline
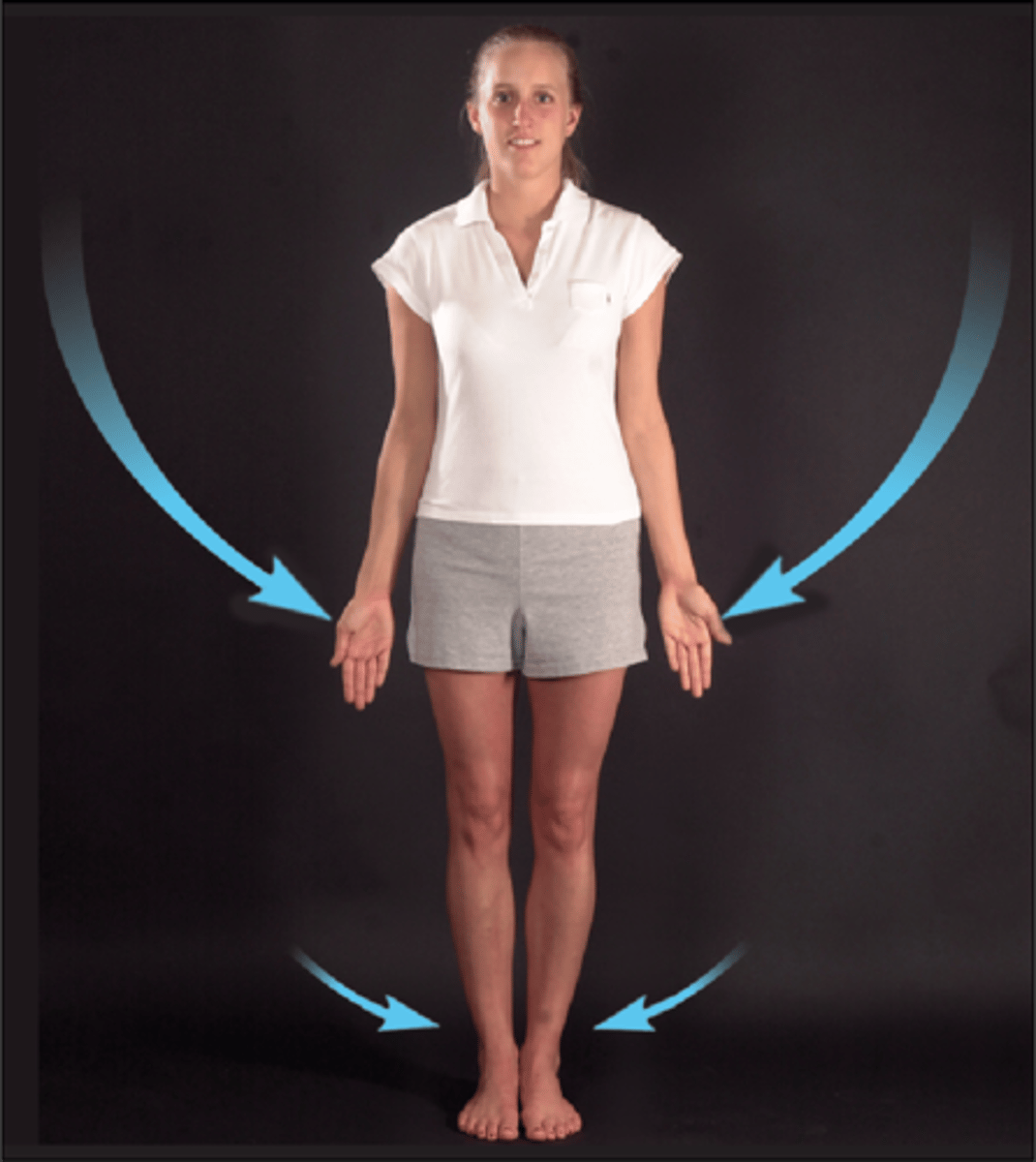
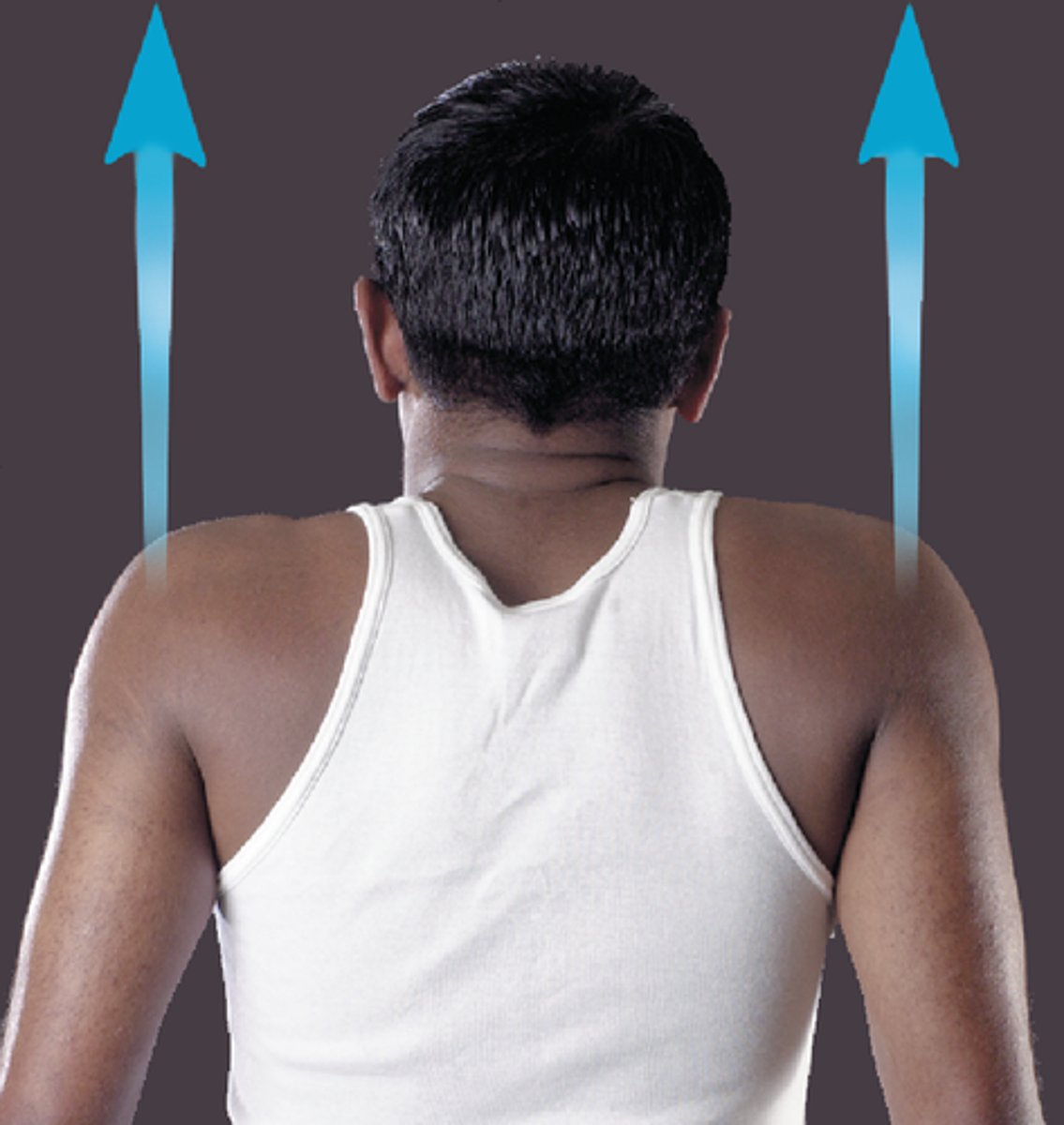
Elevation
raises body part
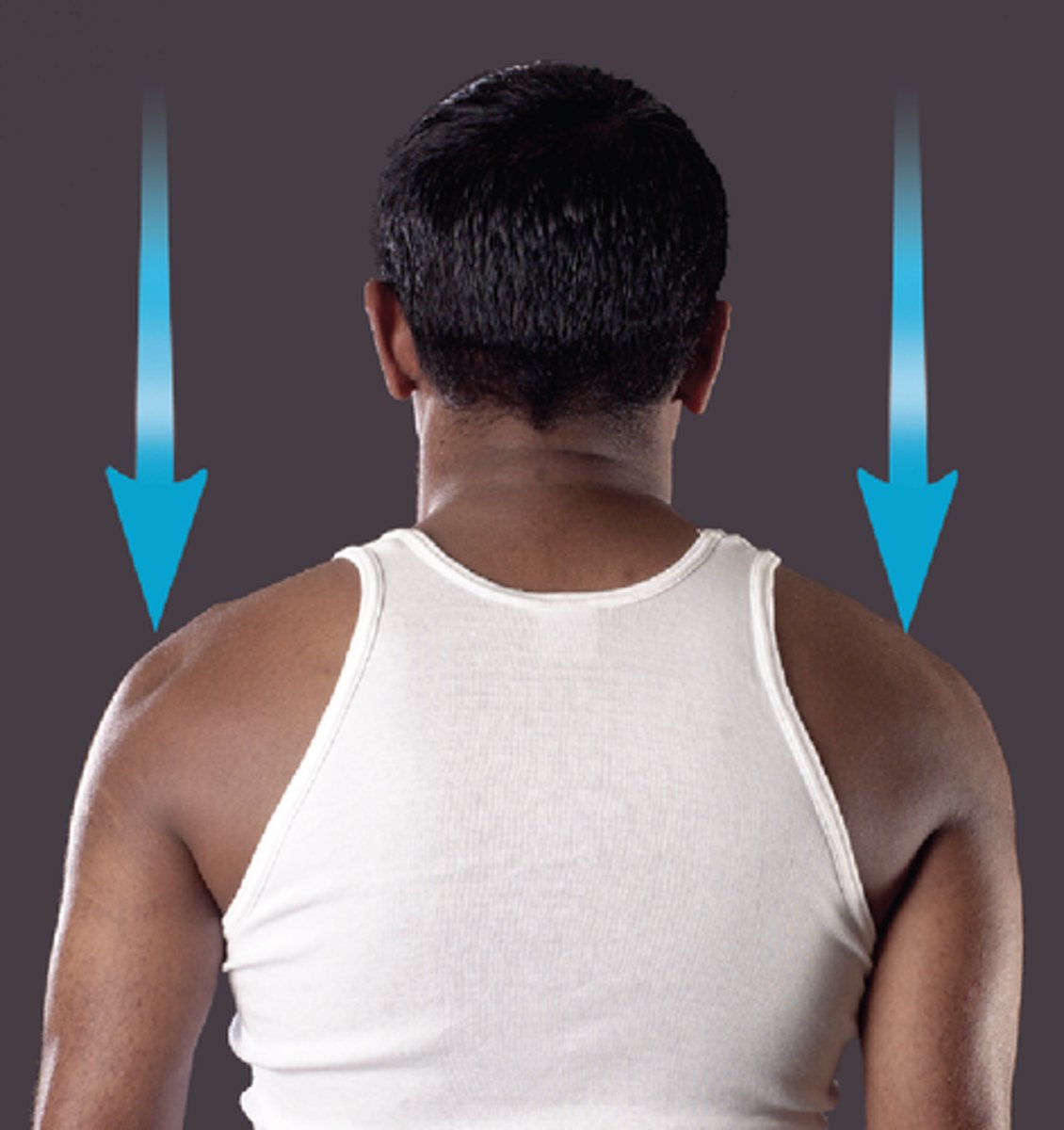
Depression
lowers body part
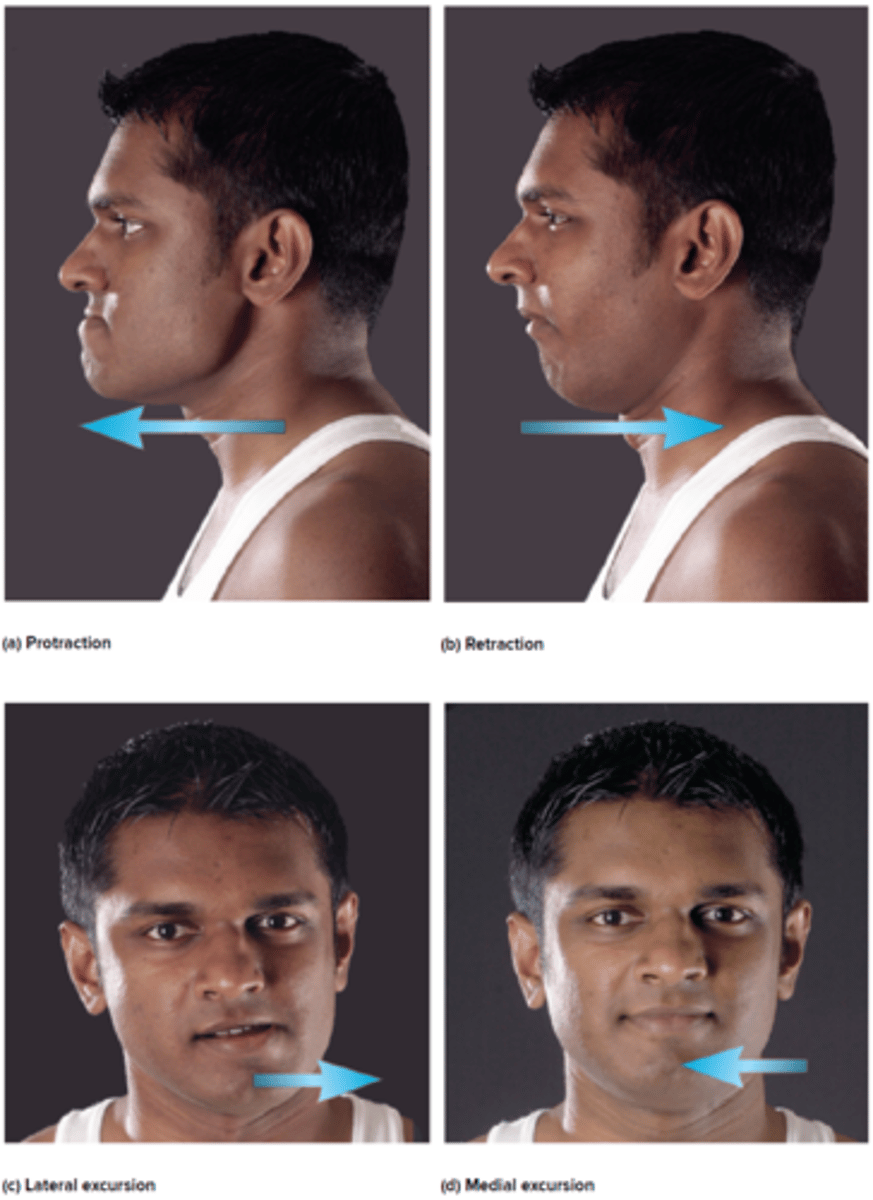
Protraction
anterior movement
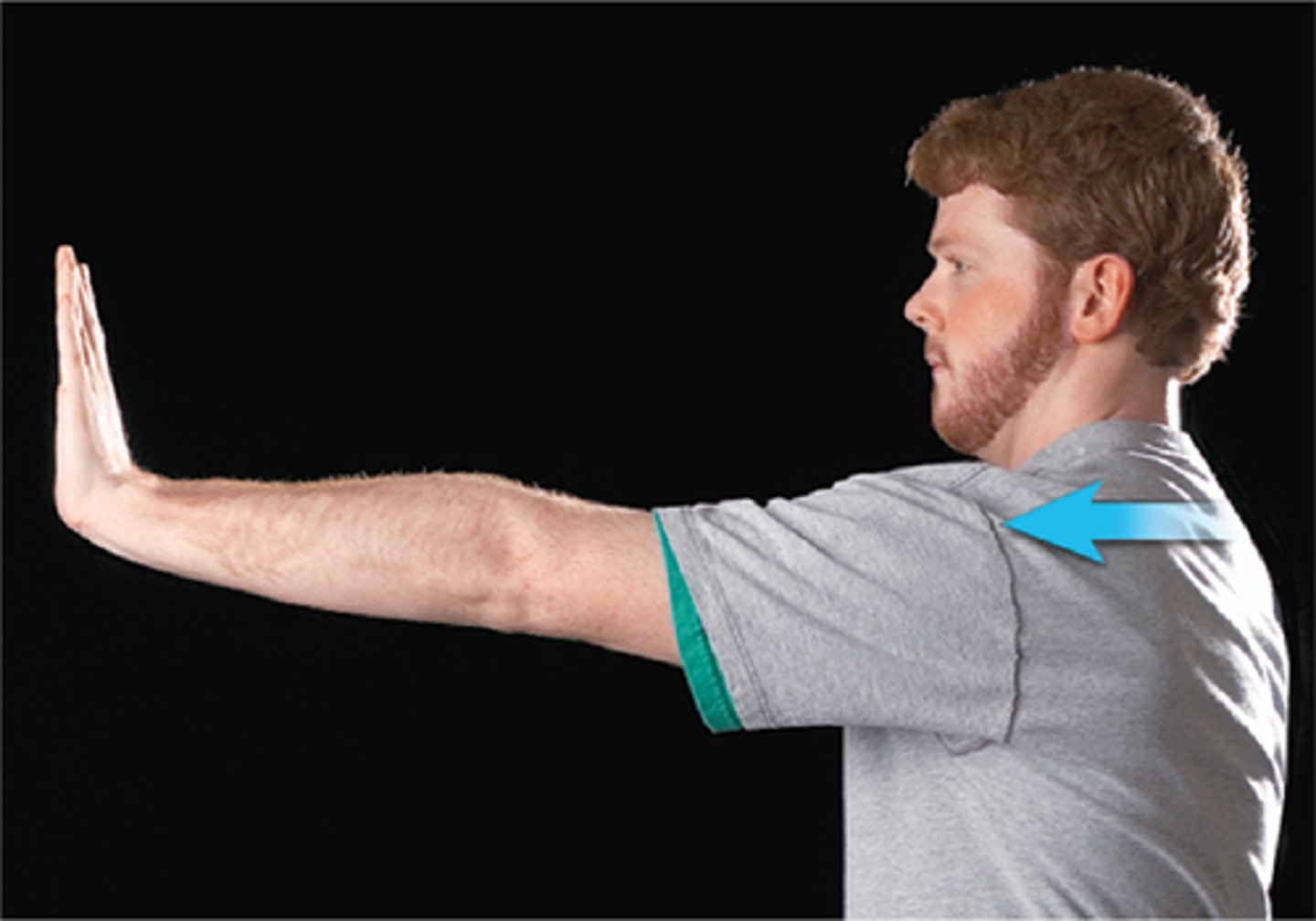
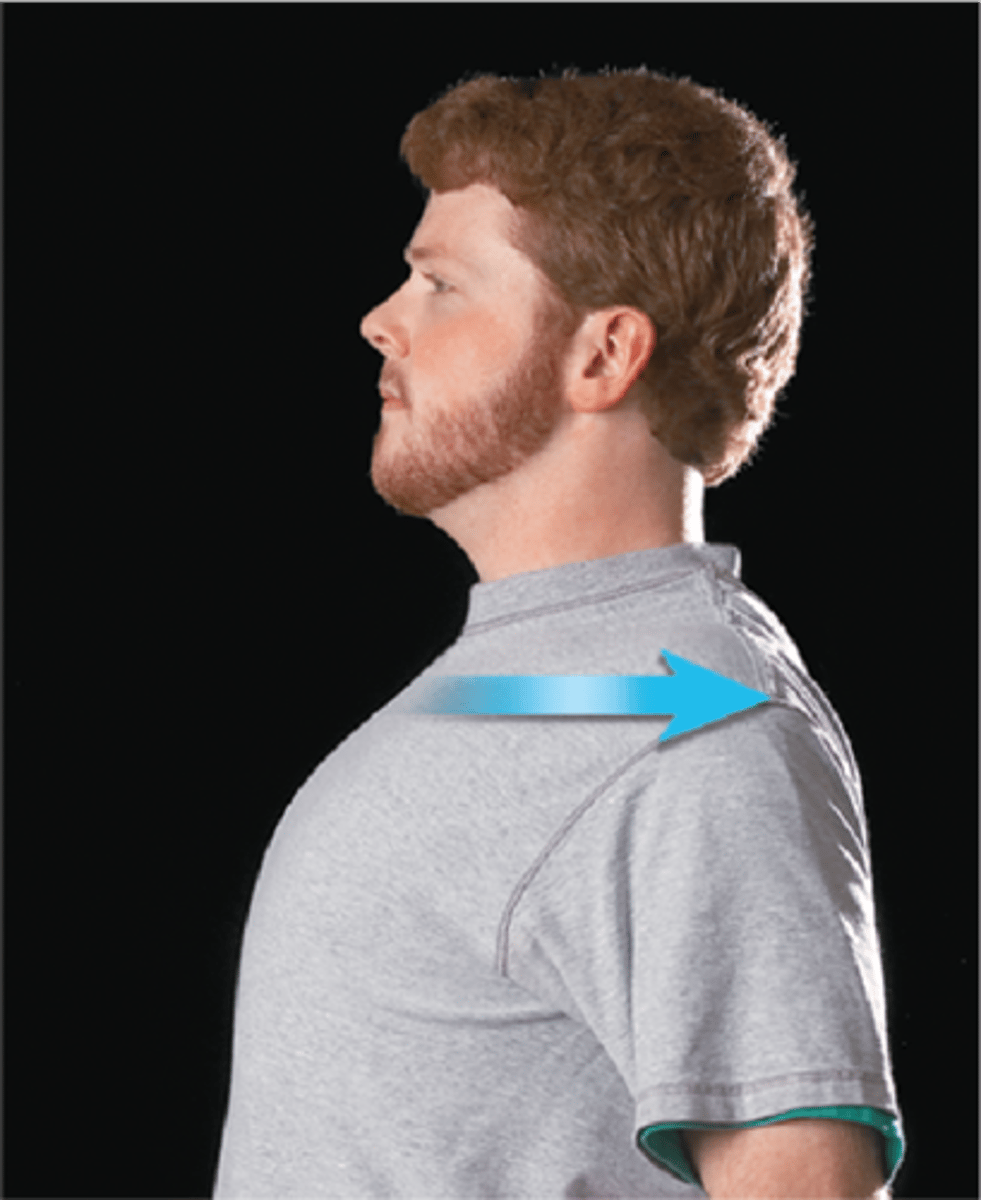
Retraction
posterior movement

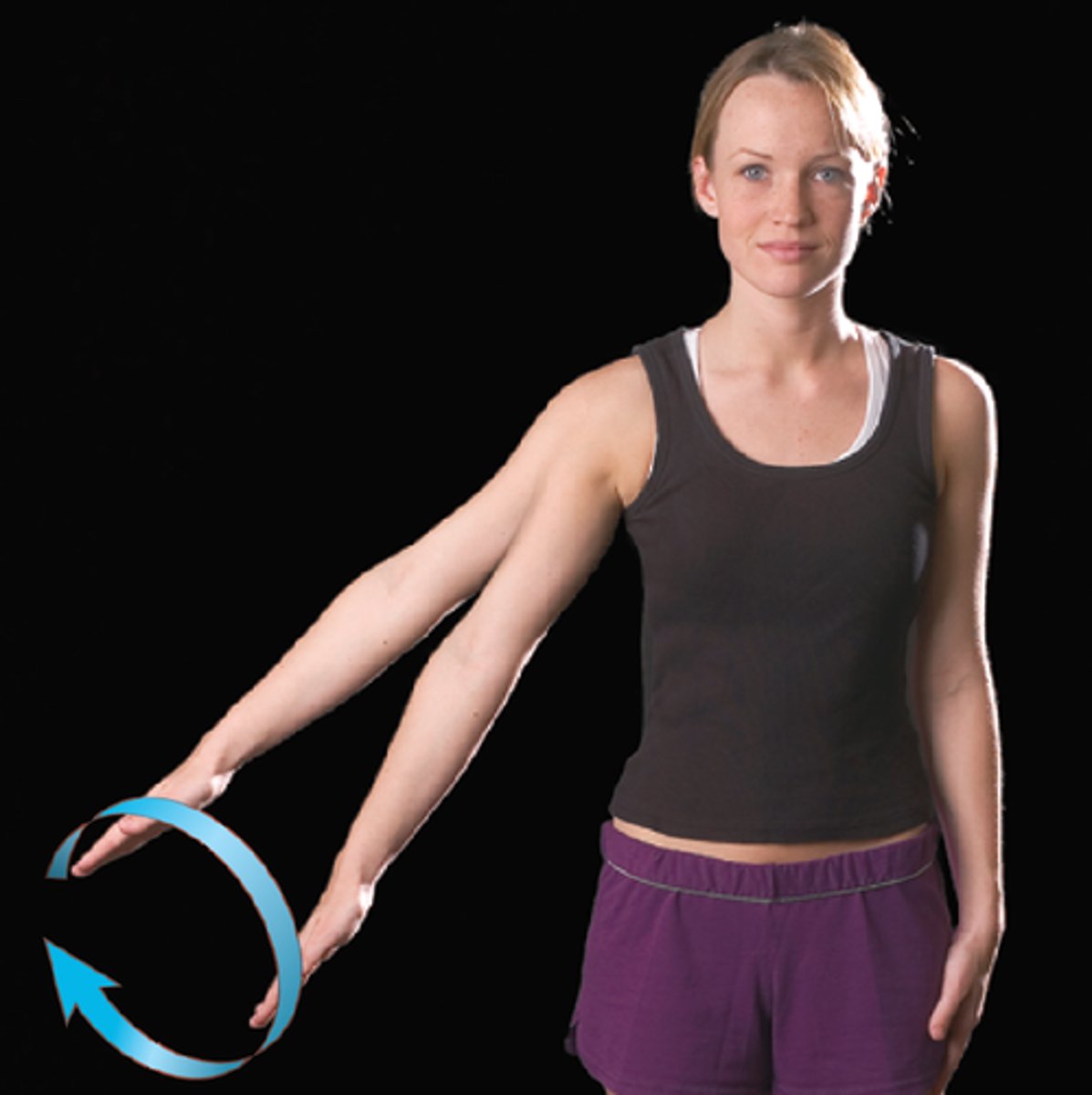
Circumduction
distal end of limb makes circle while proximal end is stationary

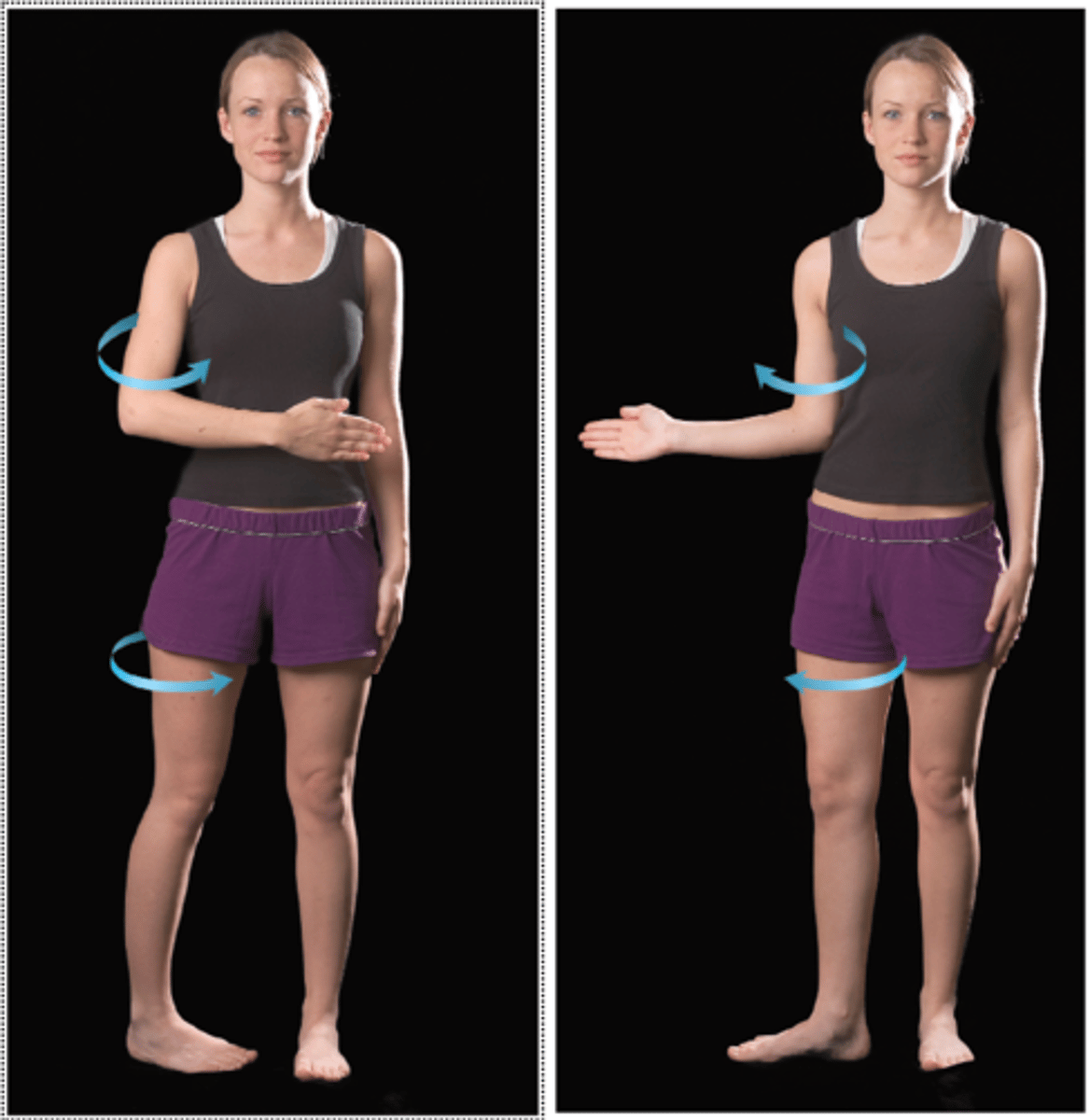
Rotation
bone spins on its long axis

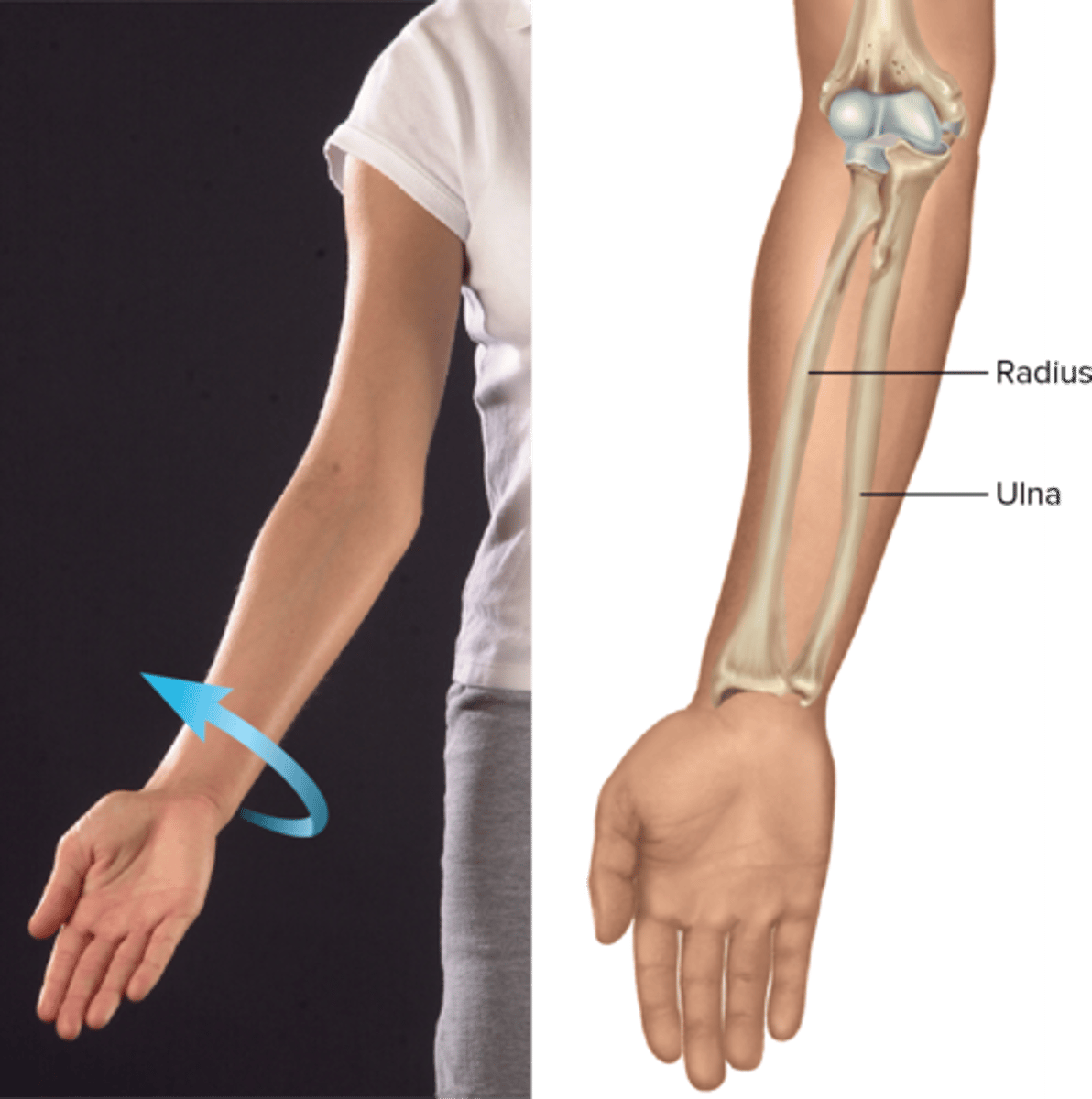
Supination
moves palm to face anteriorly
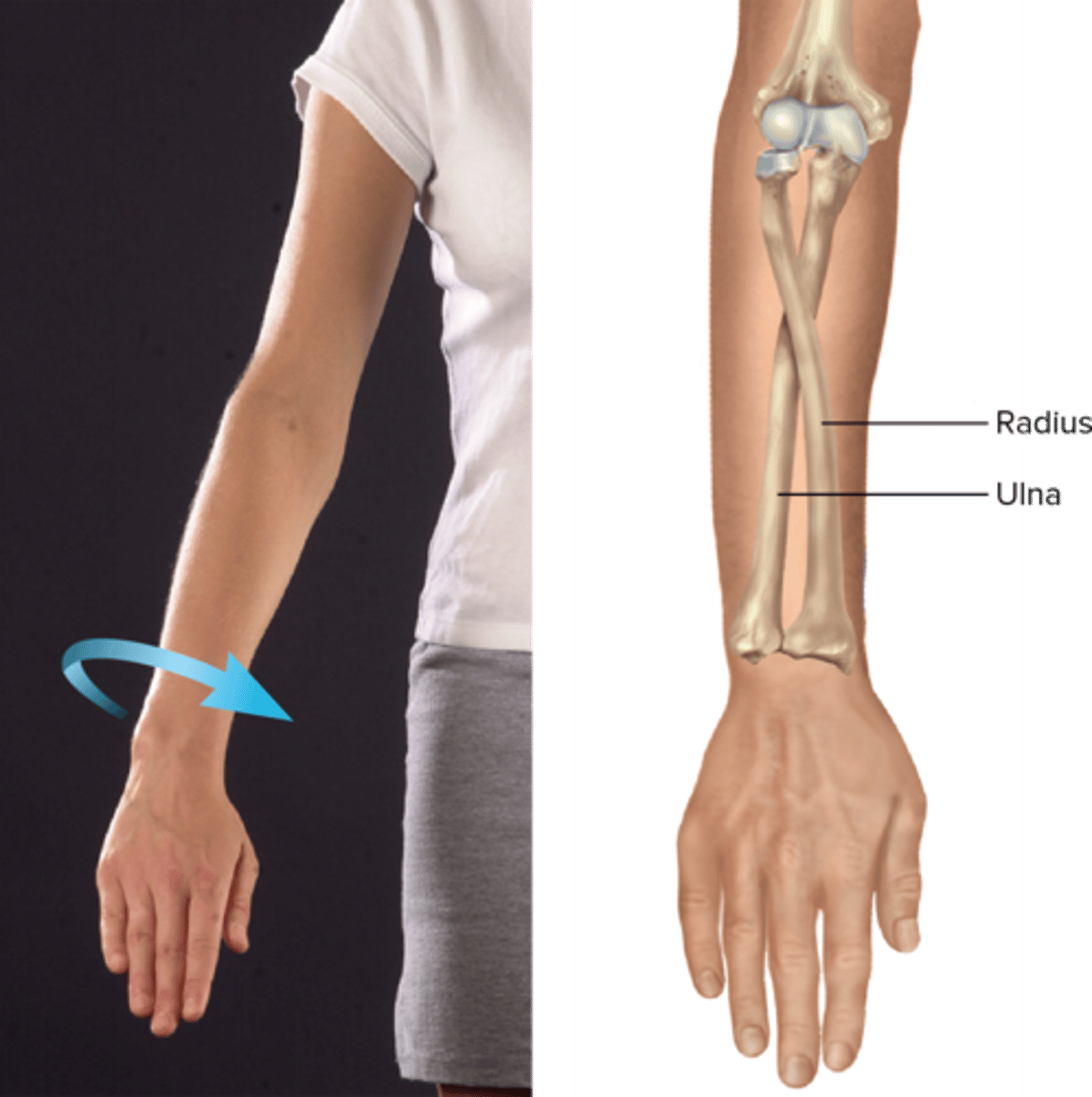
Pronation
moves palm to face posteriorly
Special Movements of the Head and Trunk

Special Movements of the Mandible
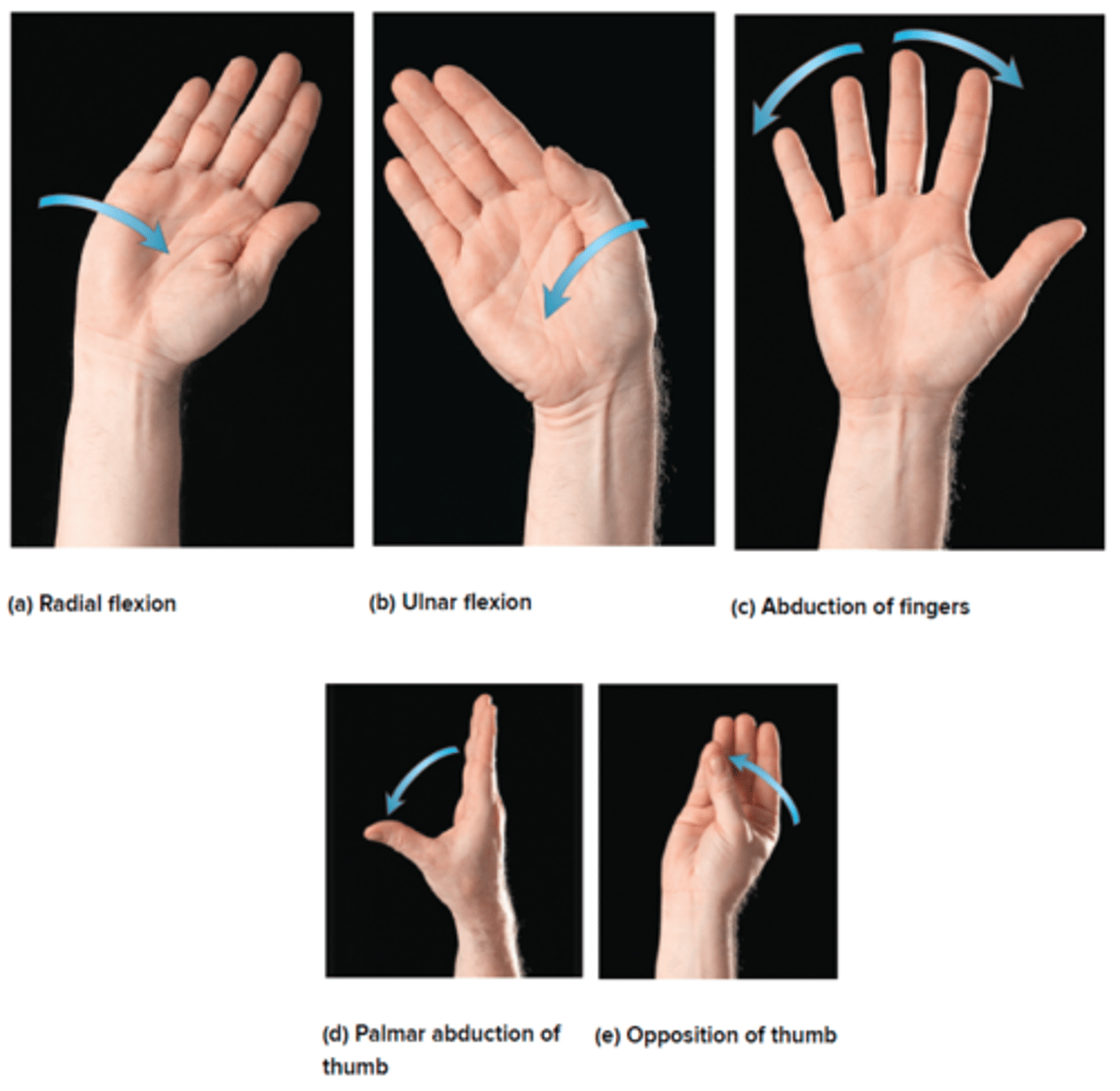
Special Movements of the Hand and Fingers
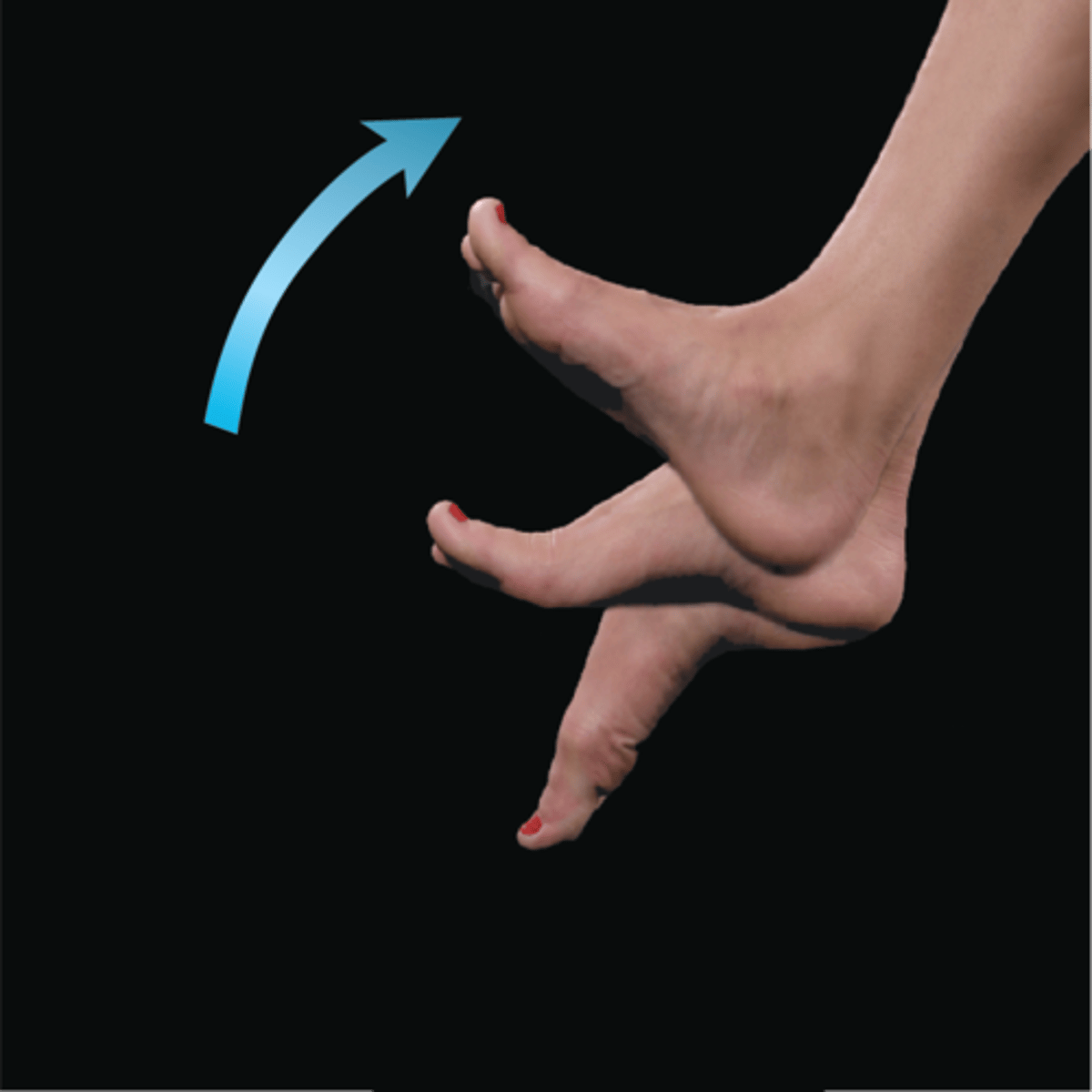
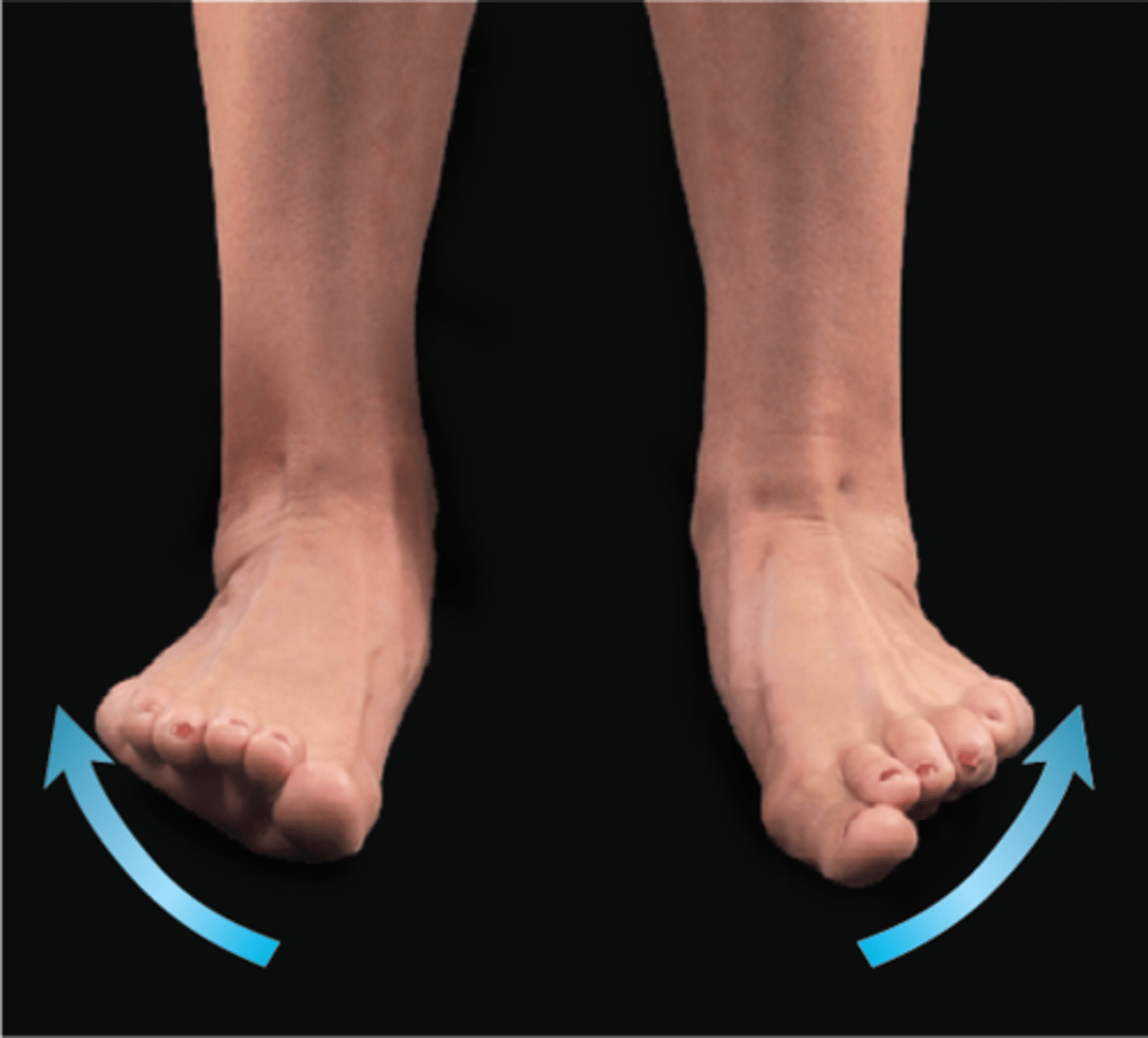
Dorsiflexion
foot elevates at ankle
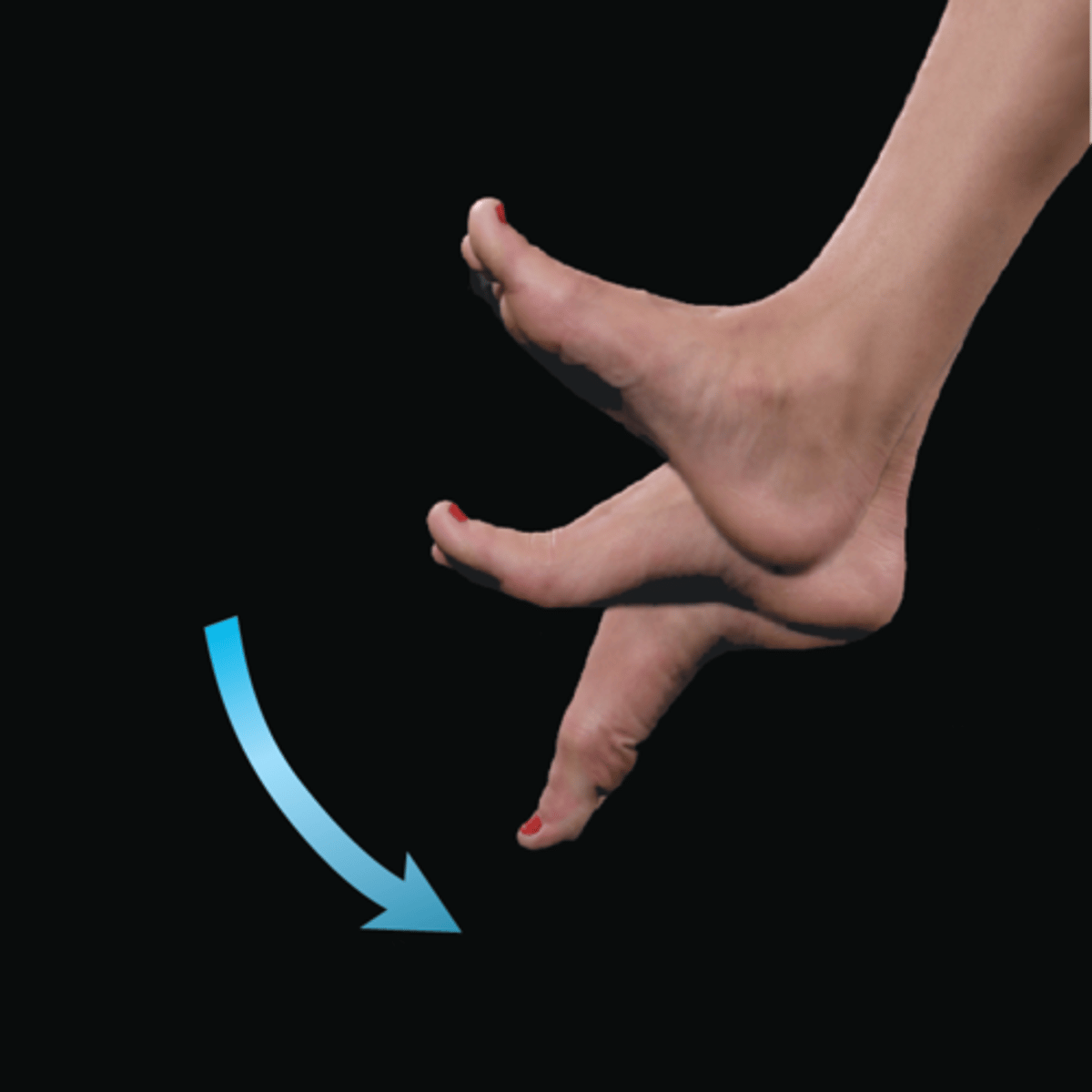
Plantar flexion
foot points down at ankle
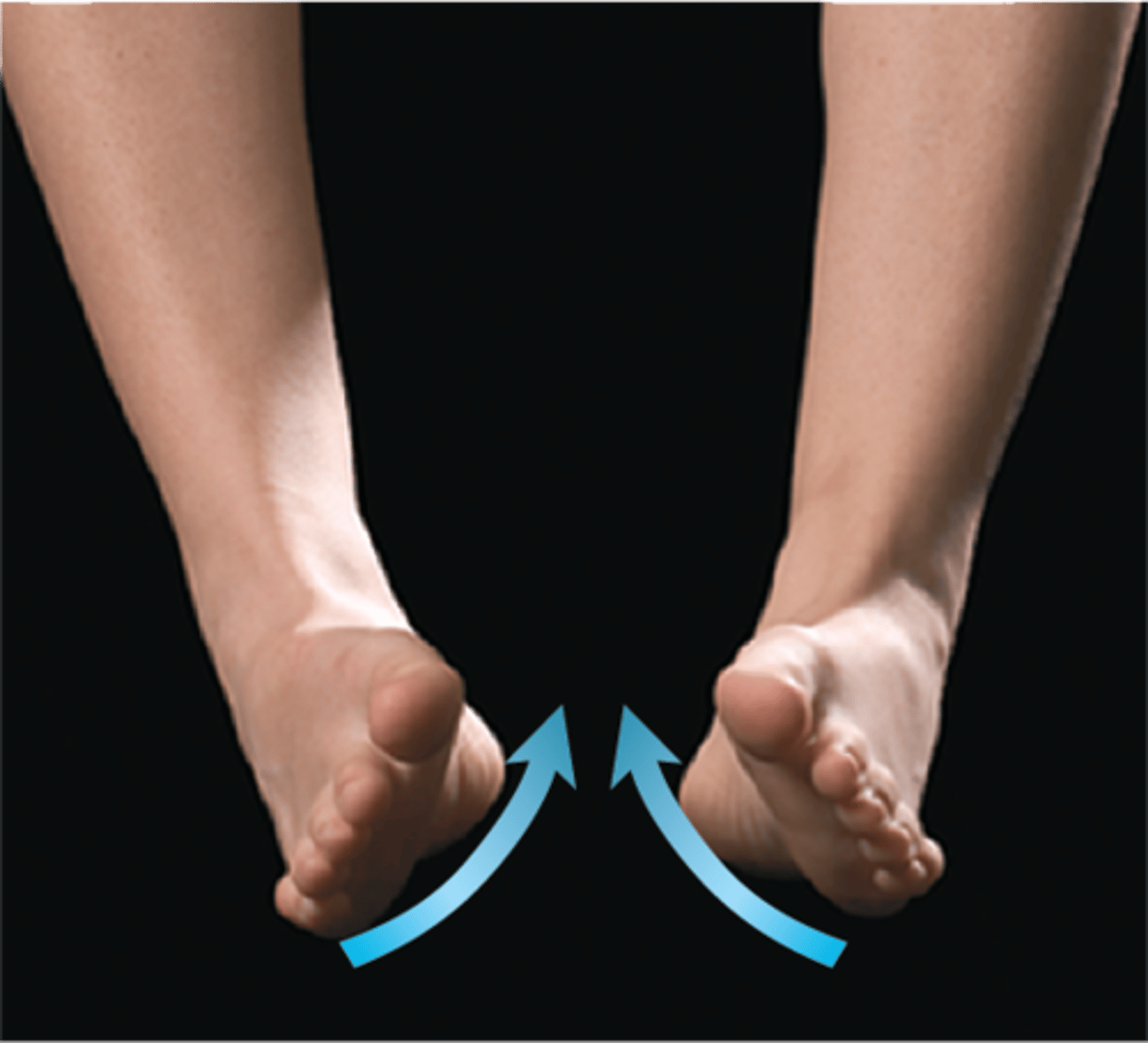
Inversion
soles face medially
Eversion
soles face laterally
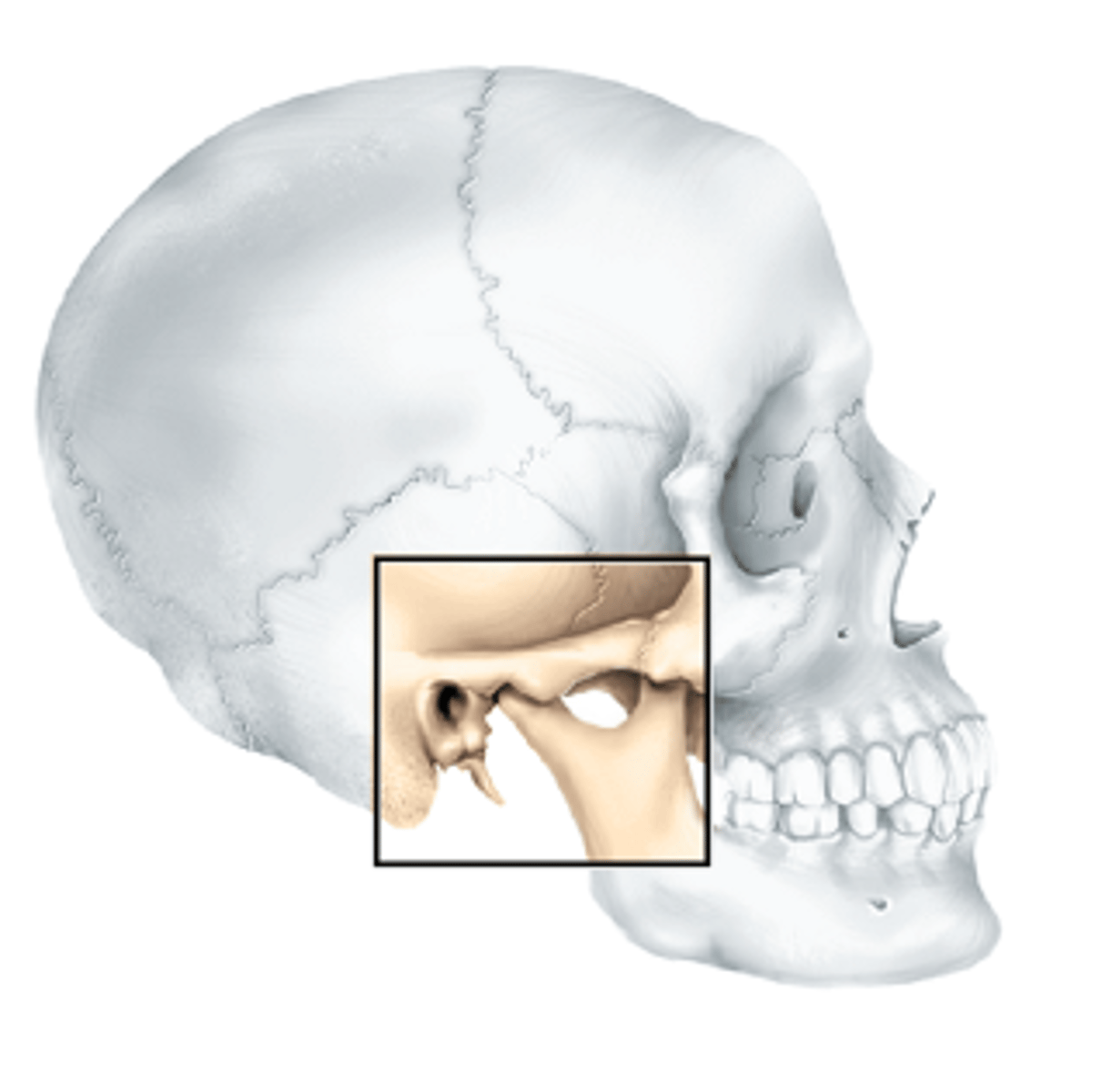
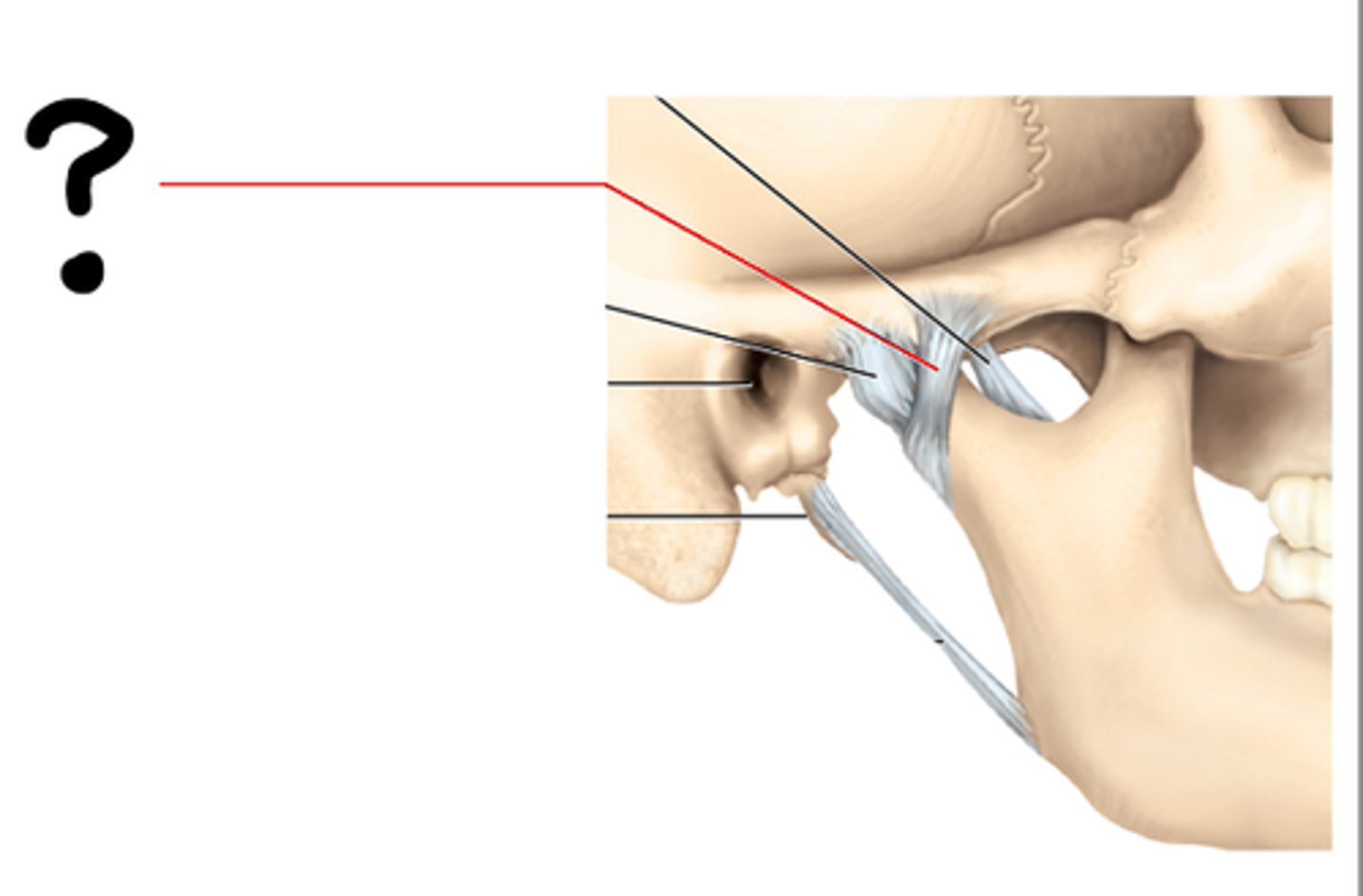
Temporomandibular joint (TMJ) -- jaw joint
the articulation of the condyle of the mandible with the mandibular fossa of the temporal bone.
Jaw joint classification
condylar, hinge, and plane
Jaw joint movements
elevation, depression, protraction, retraction, lateral and medial excursion
Jaw joint ligaments
lateral and sphenomandibular
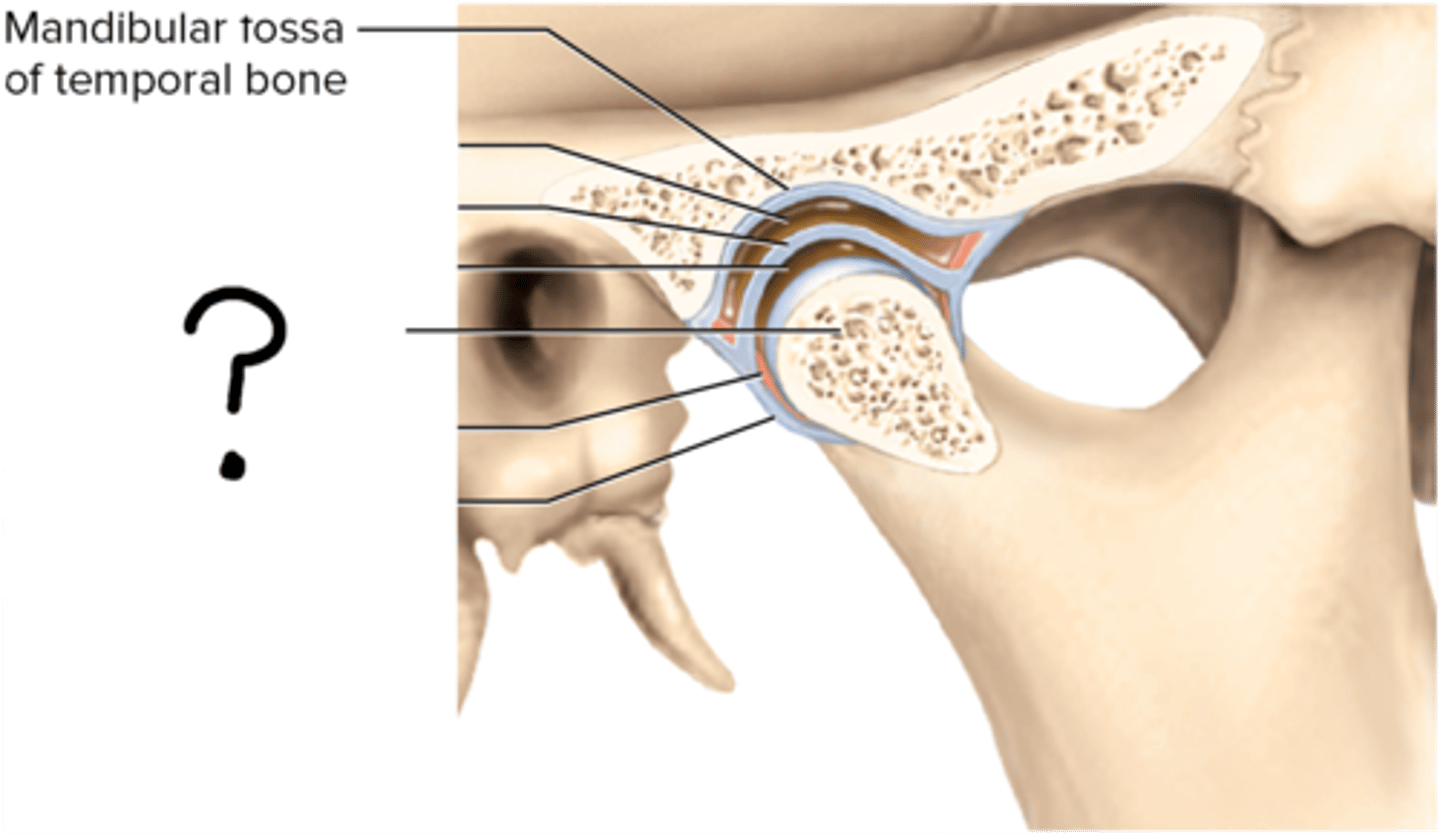
Jaw joint bone articulation
condyle of mandible and mandibular fossa of temporal bone
Mandibular fossa of temporal bone
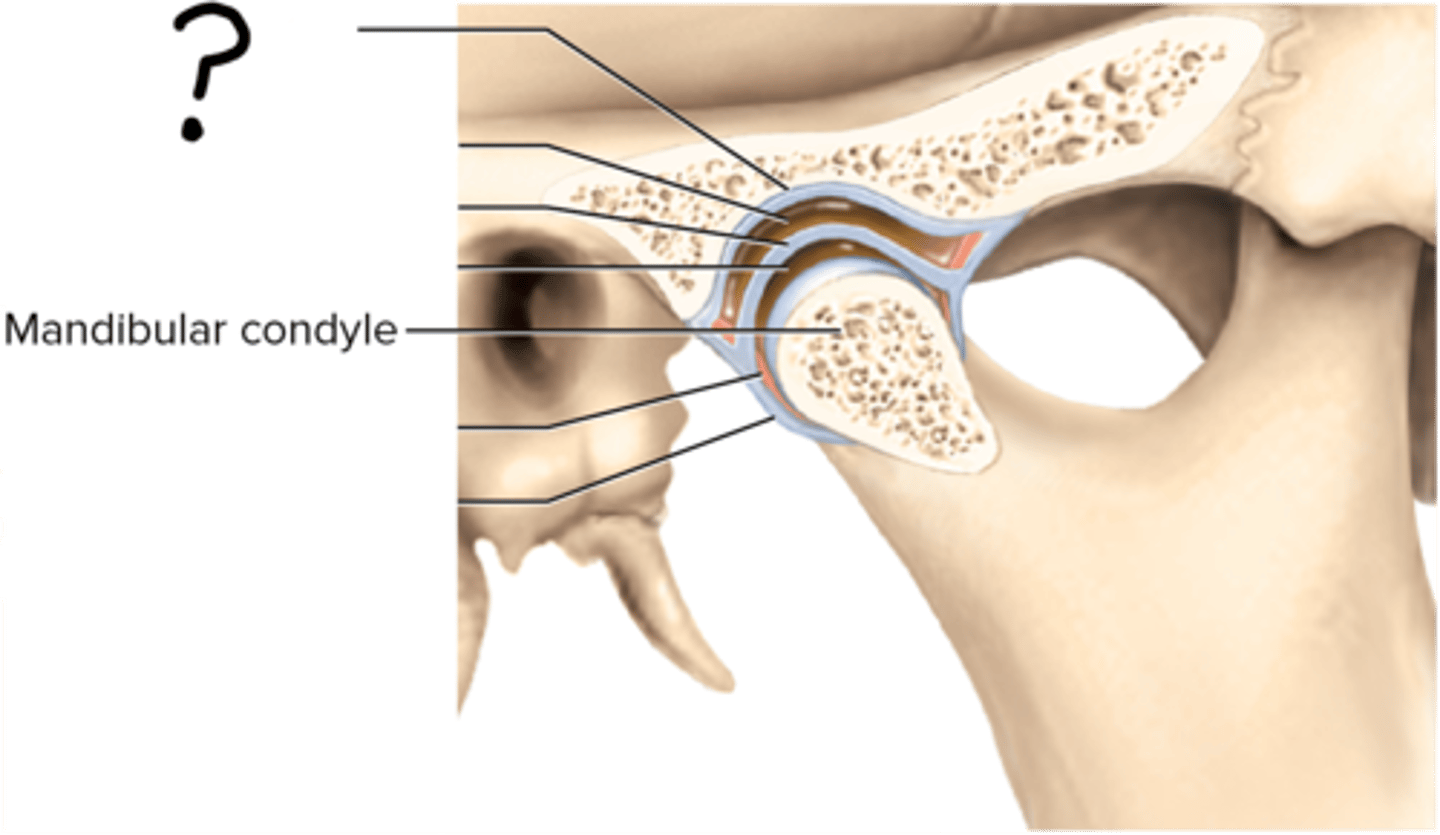
Mandibular condyle
Lateral ligament
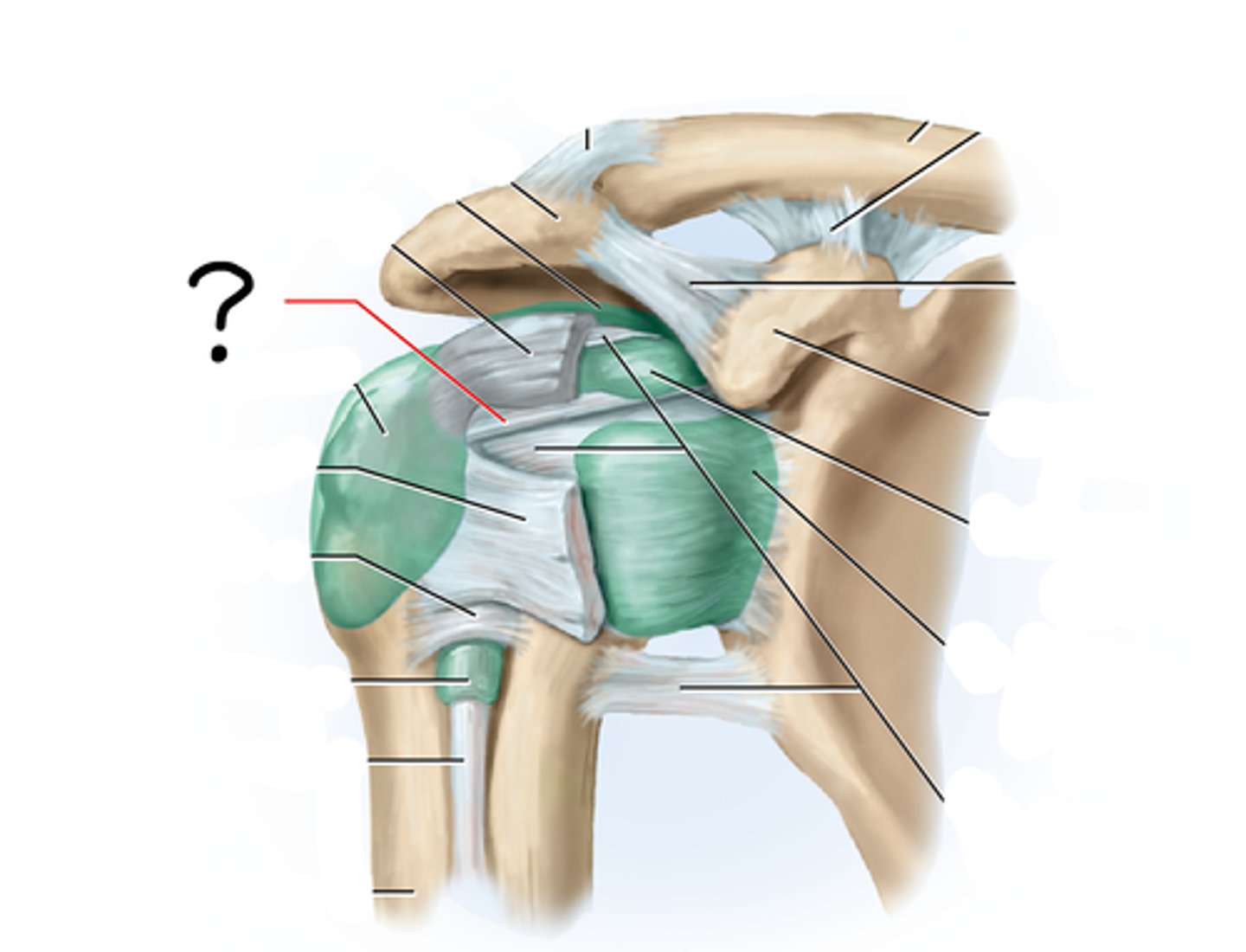
Glenohumeral (humeroscapular) joint/shoulder joint
where the hemispherical head of the humerus articulates with the glenoid cavity of the scapula
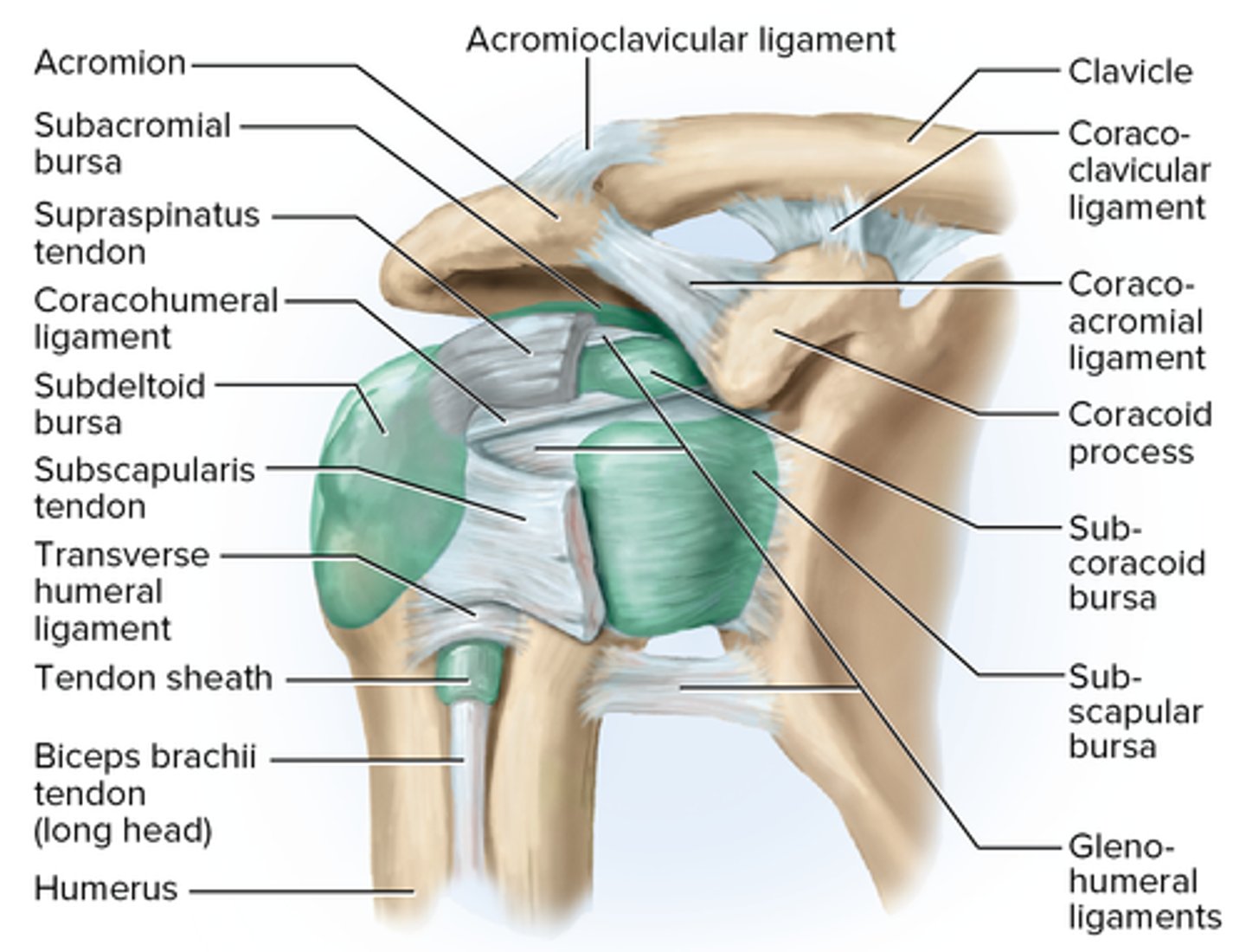
Shoulder joint classification
ball-and-socket
Shoulder joint bone articulation
head of humerus and glenoid fossa of scapula
Shoulder joint movements
adduction, abduction, flexion, extension, circumduction, medial and lateral rotation
Shoulder joint ligaments
coracohumeral, transverse humeral, three glenohumerals
Glenoid labrum
ring of fibrocartilage that deepens socket
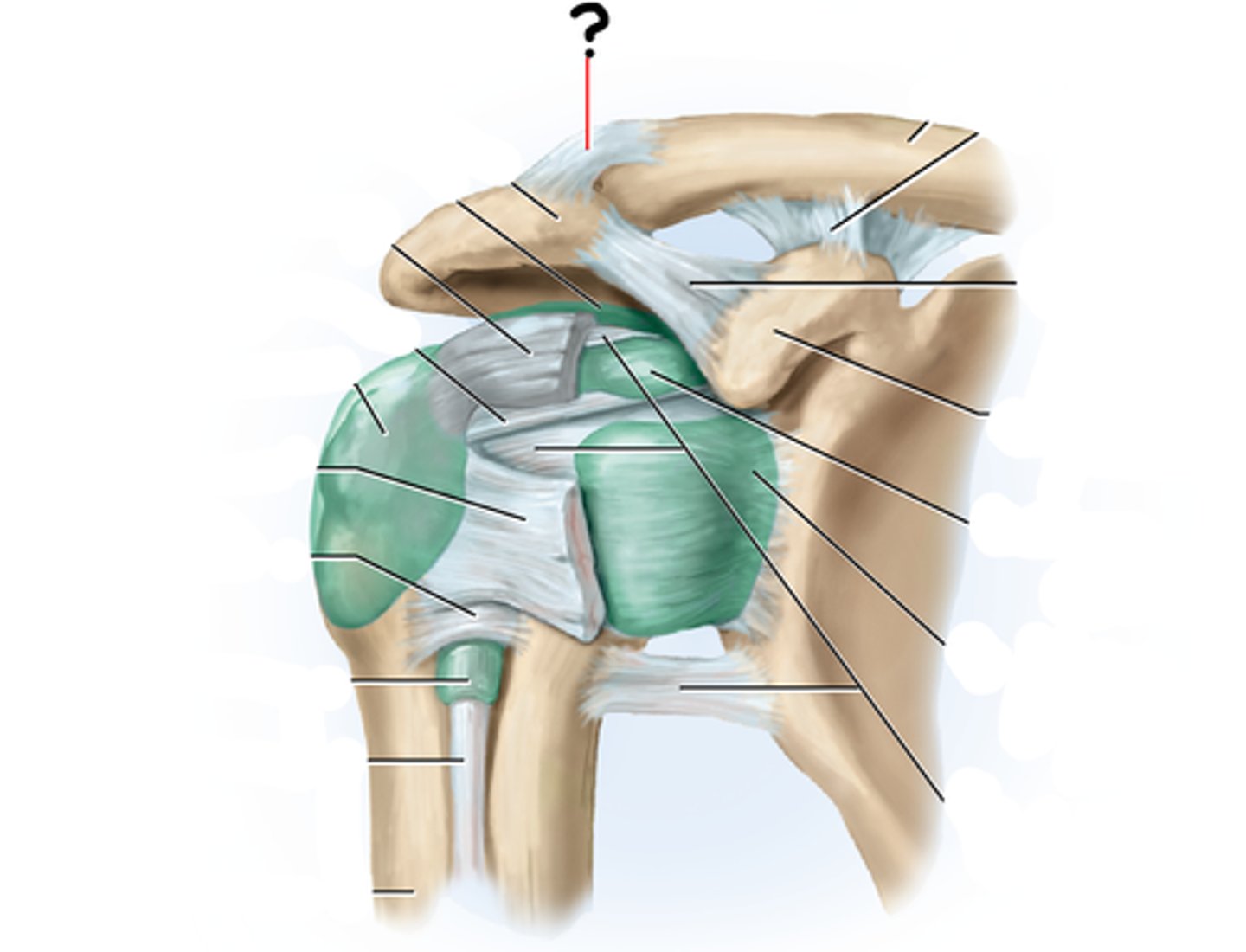
Acromioclavicular ligament
Coracoacromial ligament
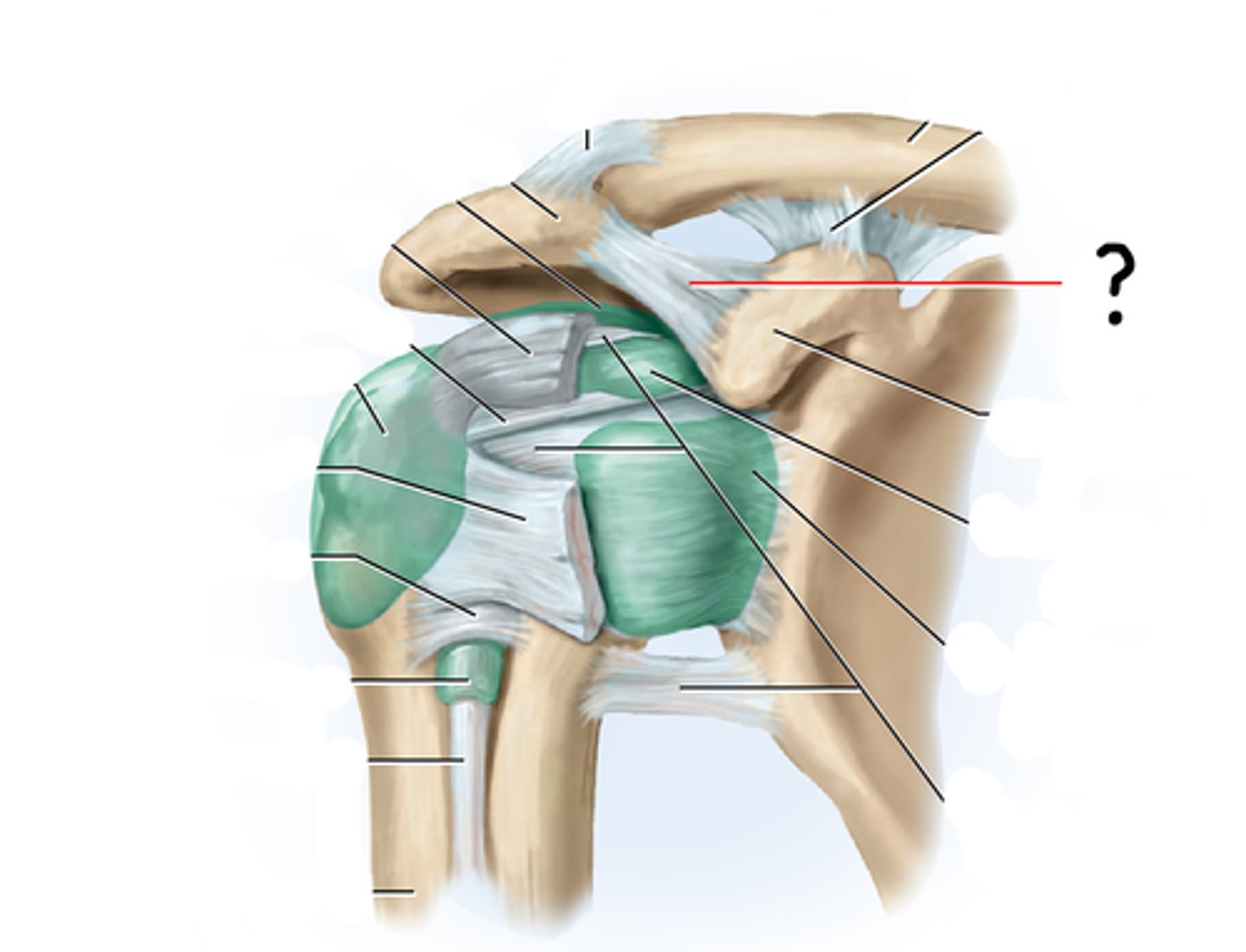
Coracoclavicular ligament
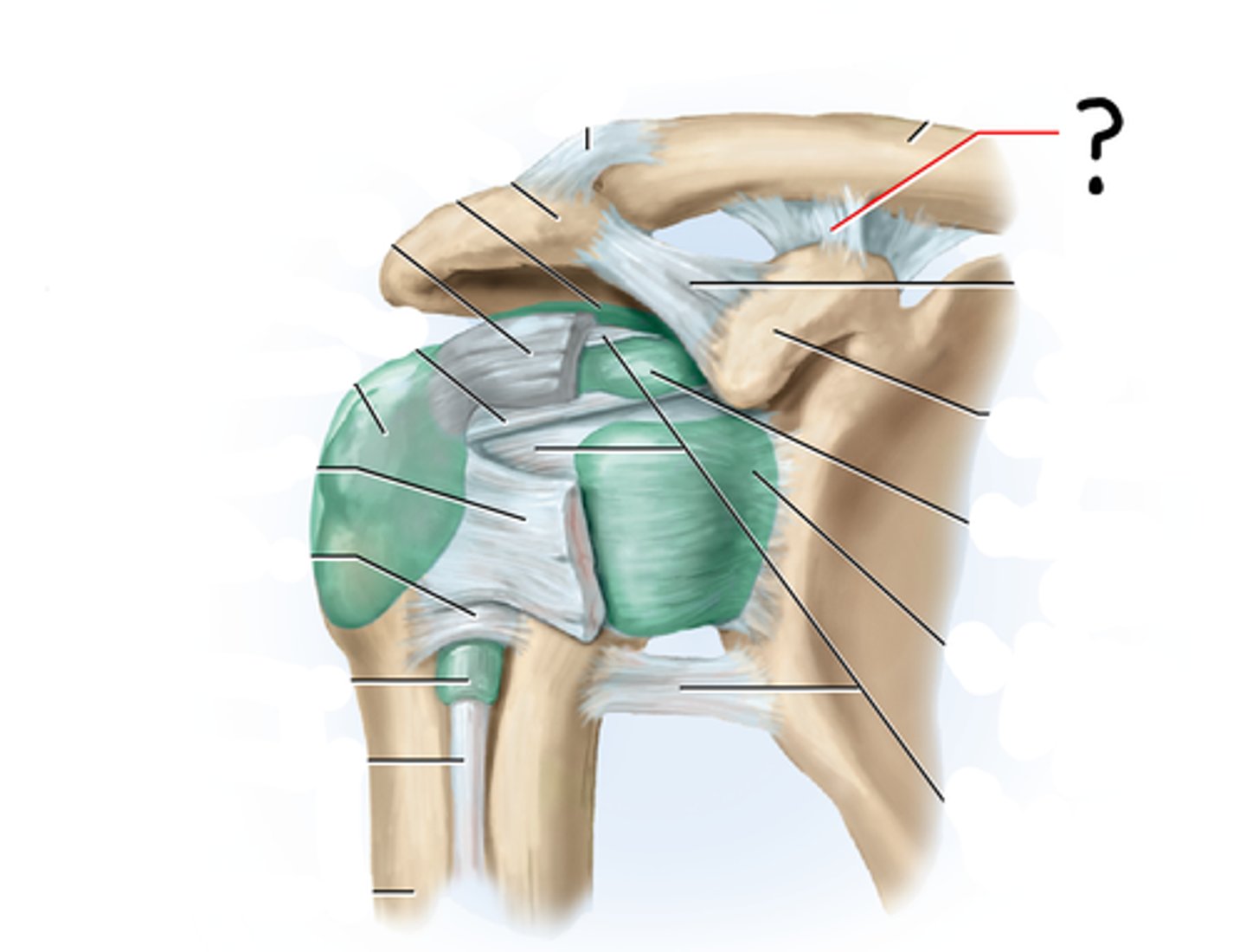
Coracohumeral ligament
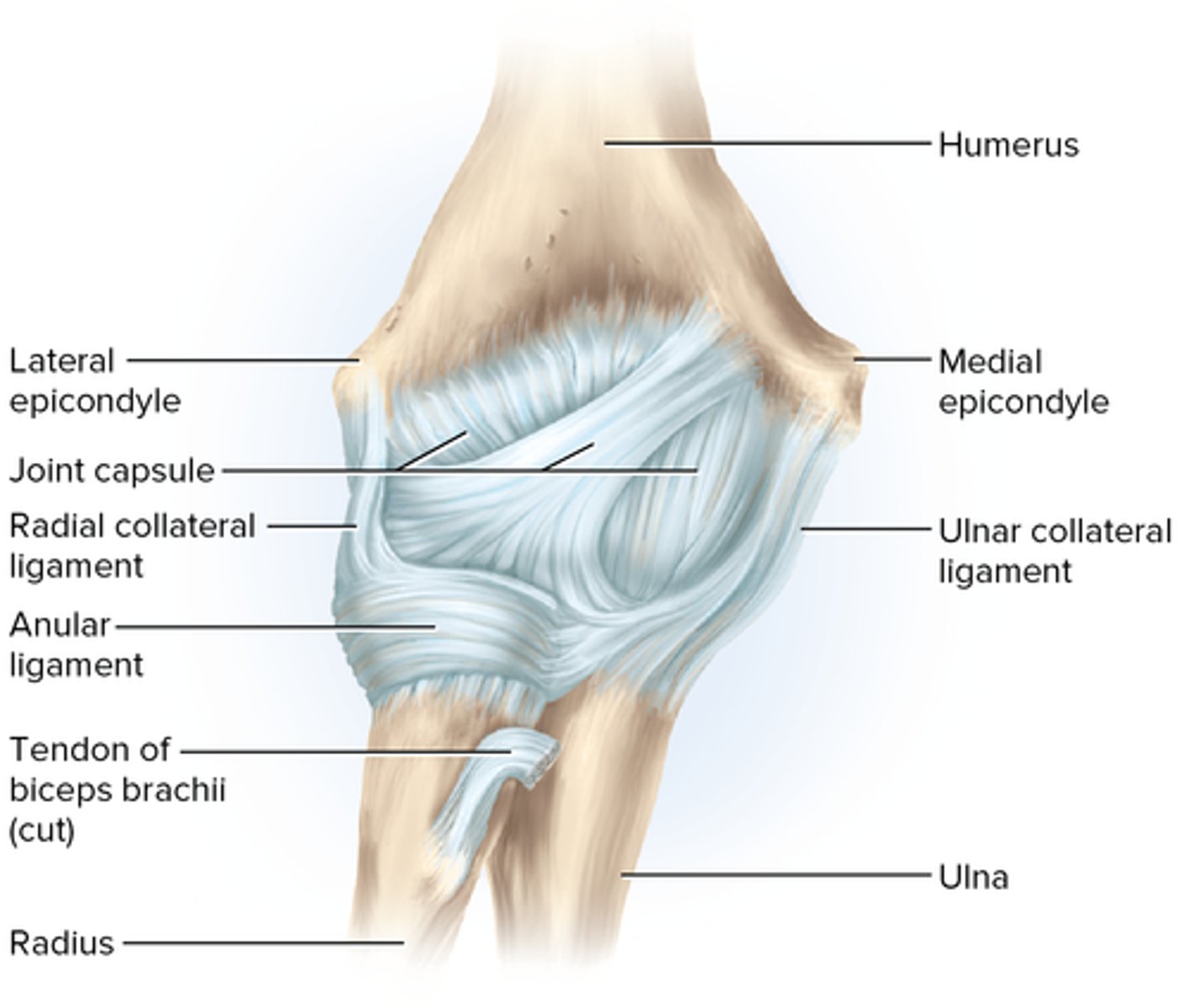
Elbow (humeroulnar and humeroradial) Joint
composed of two articulations--the humeroulnar joint and the humeroradial joint; stabilized by radial collateral and ulnar collateral ligaments
Elbow joint classification
hinge and pivot
Elbow joint movements
flexion, extension, pronation, supination, rotation
Elbow joint articulations
humeroulnar, trochlea of humerus, trochlear notch of ulna
Elbow joint ligaments
radial collateral, ulnar collateral, anular
humeroulnar joint
where the trochlea of the humerus joins the trochlear notch of the ulna
humeroradial joint
where the capitulum of the humerus meets the head of the radius
radial collateral ligament
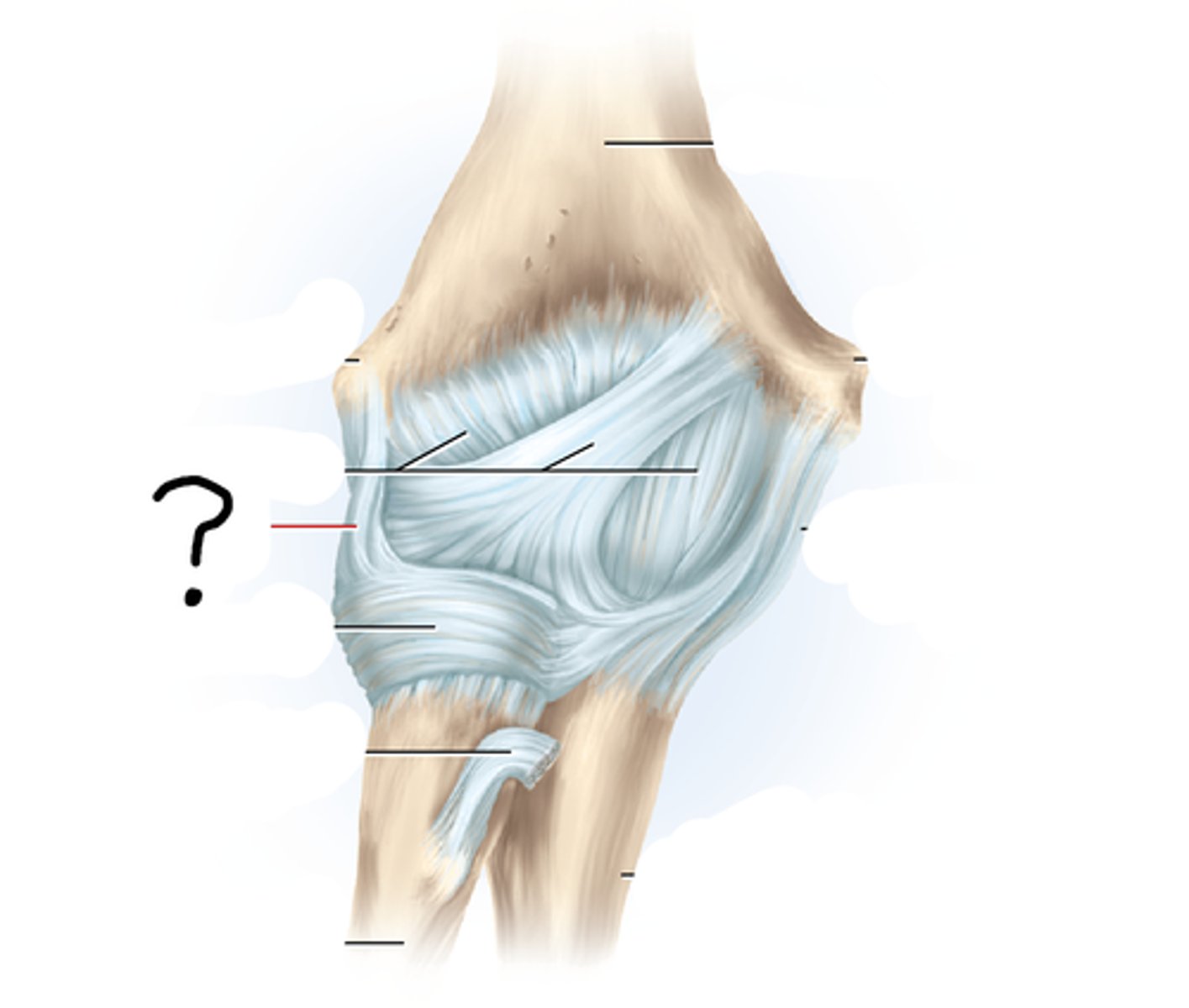
ulnar collateral ligament
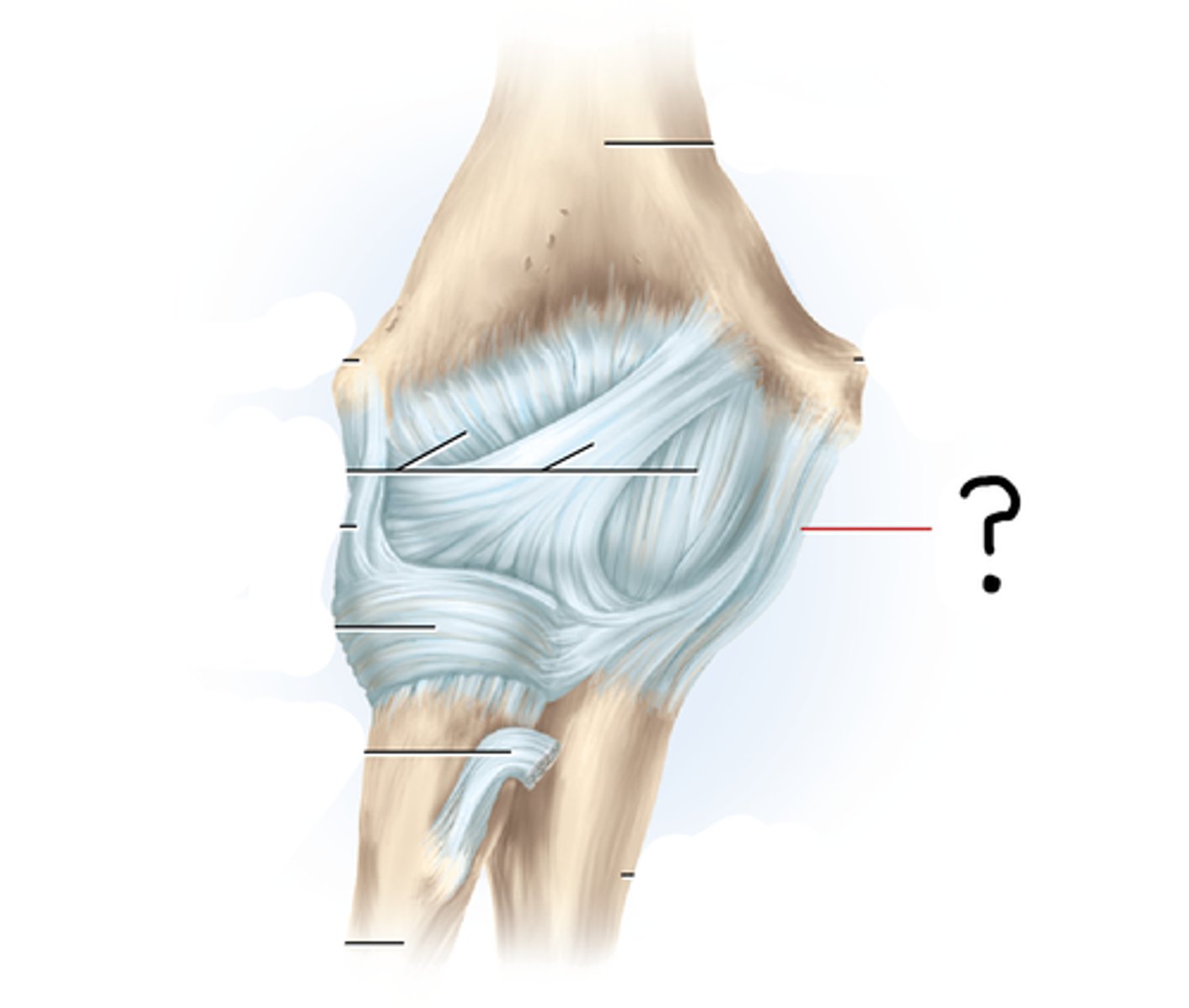
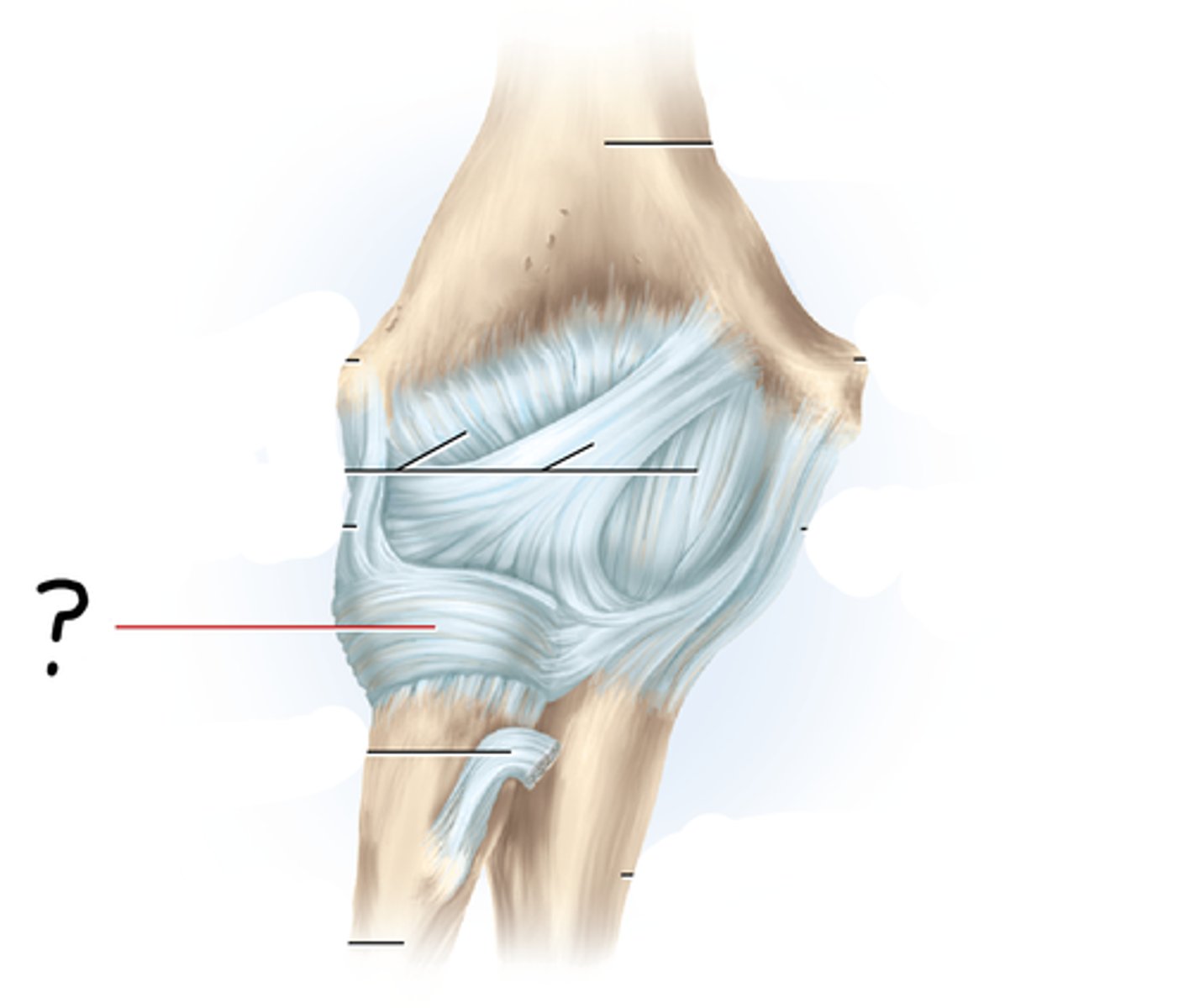
anular ligament
encircles the head of the radius and attaches at each end to the ulna
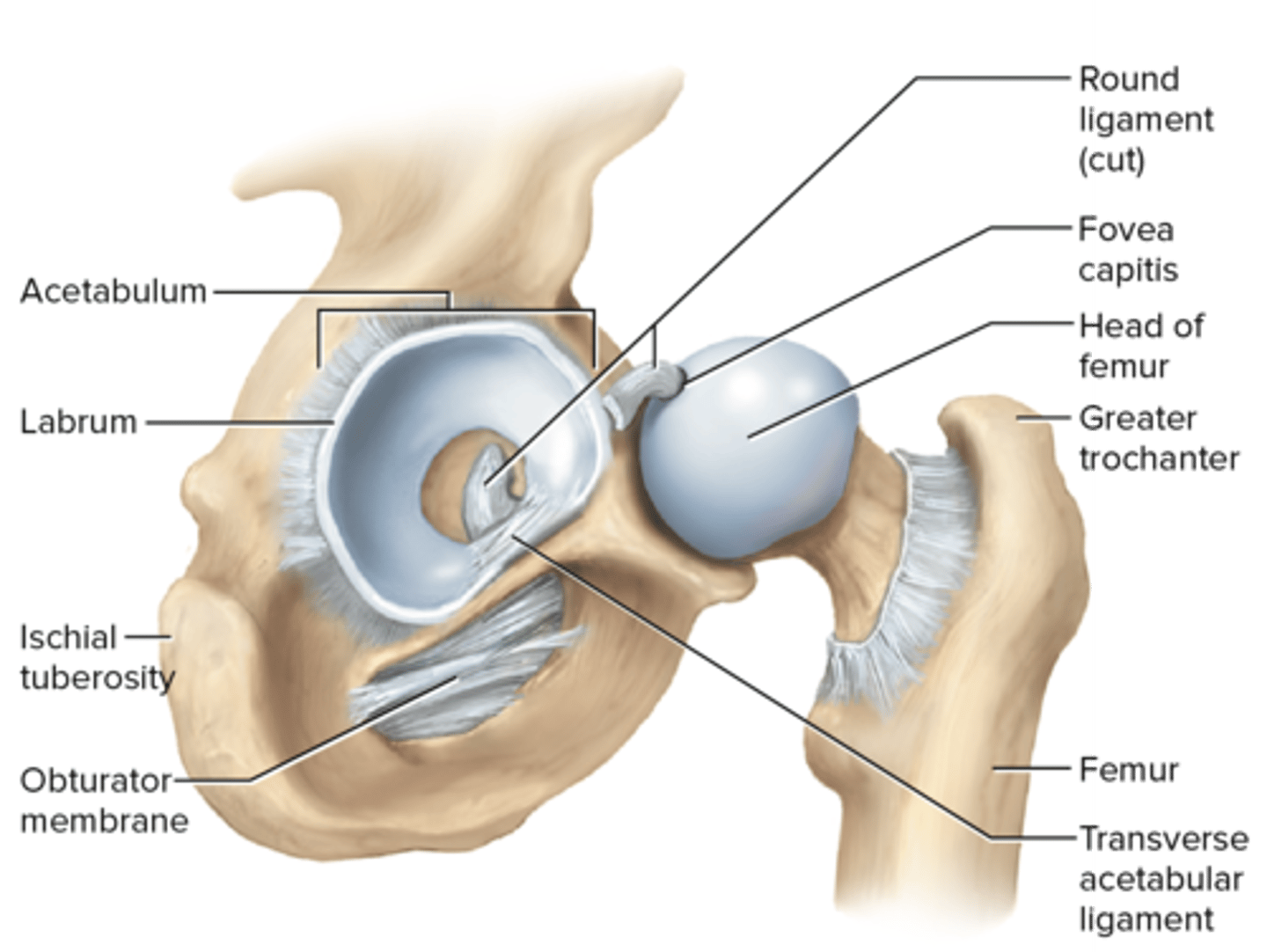
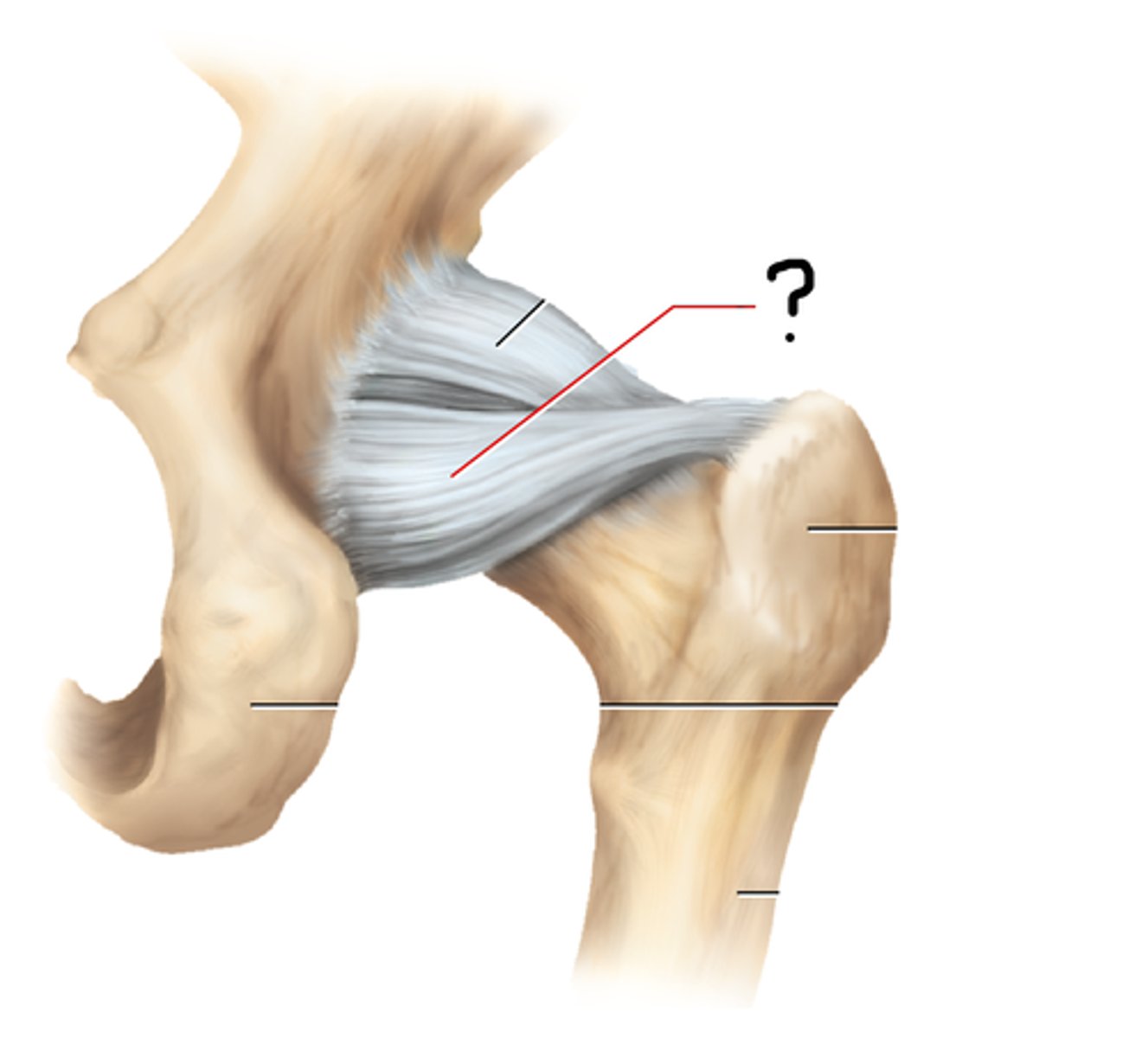
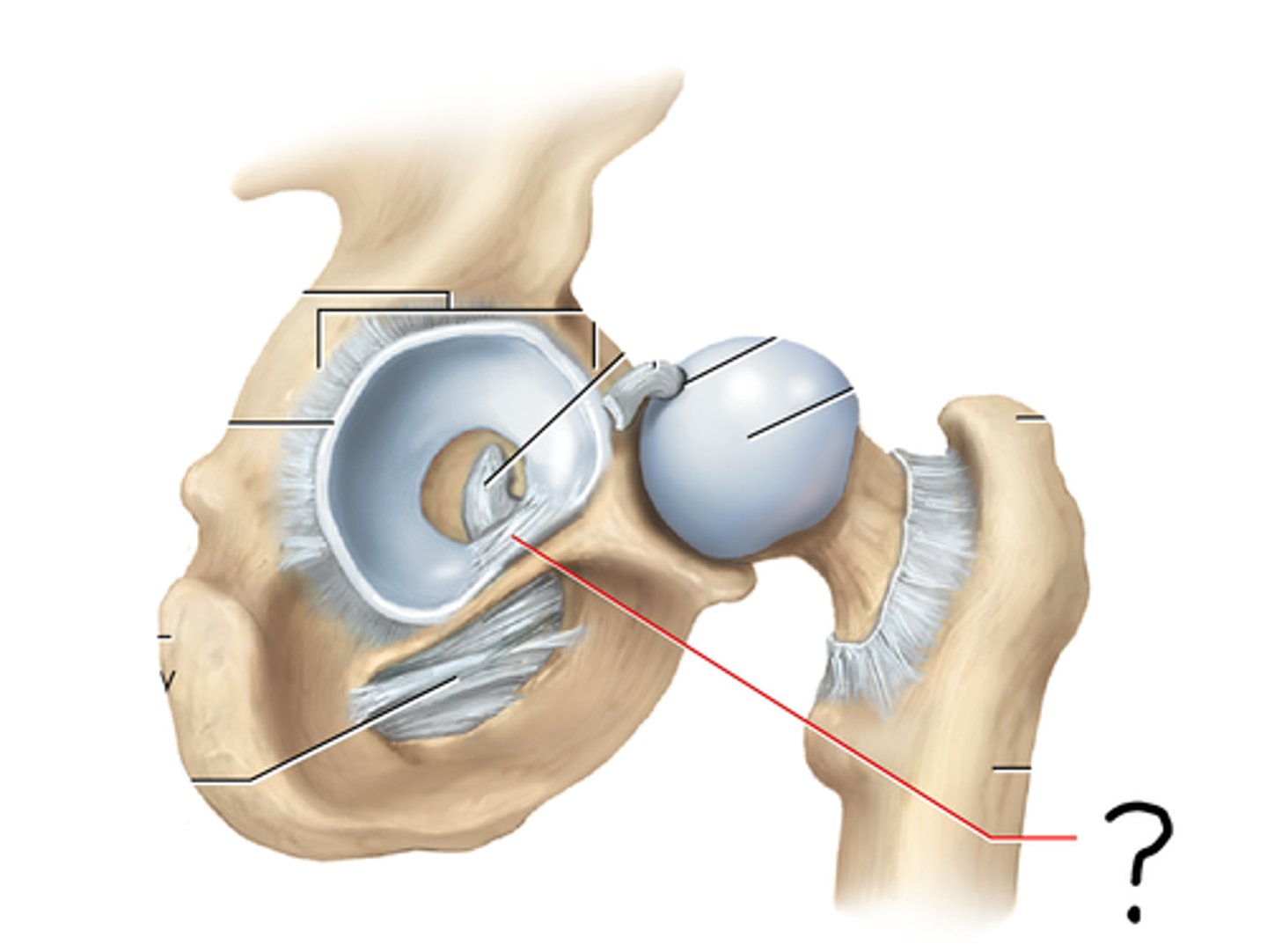
coxal (hip) joint
coxal joint; acetabular labrum; round ligament attaches to fovea capitis; iliofemoral, pubofemoral, and ischiofemoral ligaments
hip joint classification
ball-and-socket
hip joint movements
adduction, abduction, flexion, extension, circumduction, medial and lateral rotation
hip joint articulation
head of femur, acetabulum of hip bone
hip joint ligaments
iliofemoral, pubofemoral, ischiofemoral, ligamentum teres, transverse acetabular
iliofemoral ligament
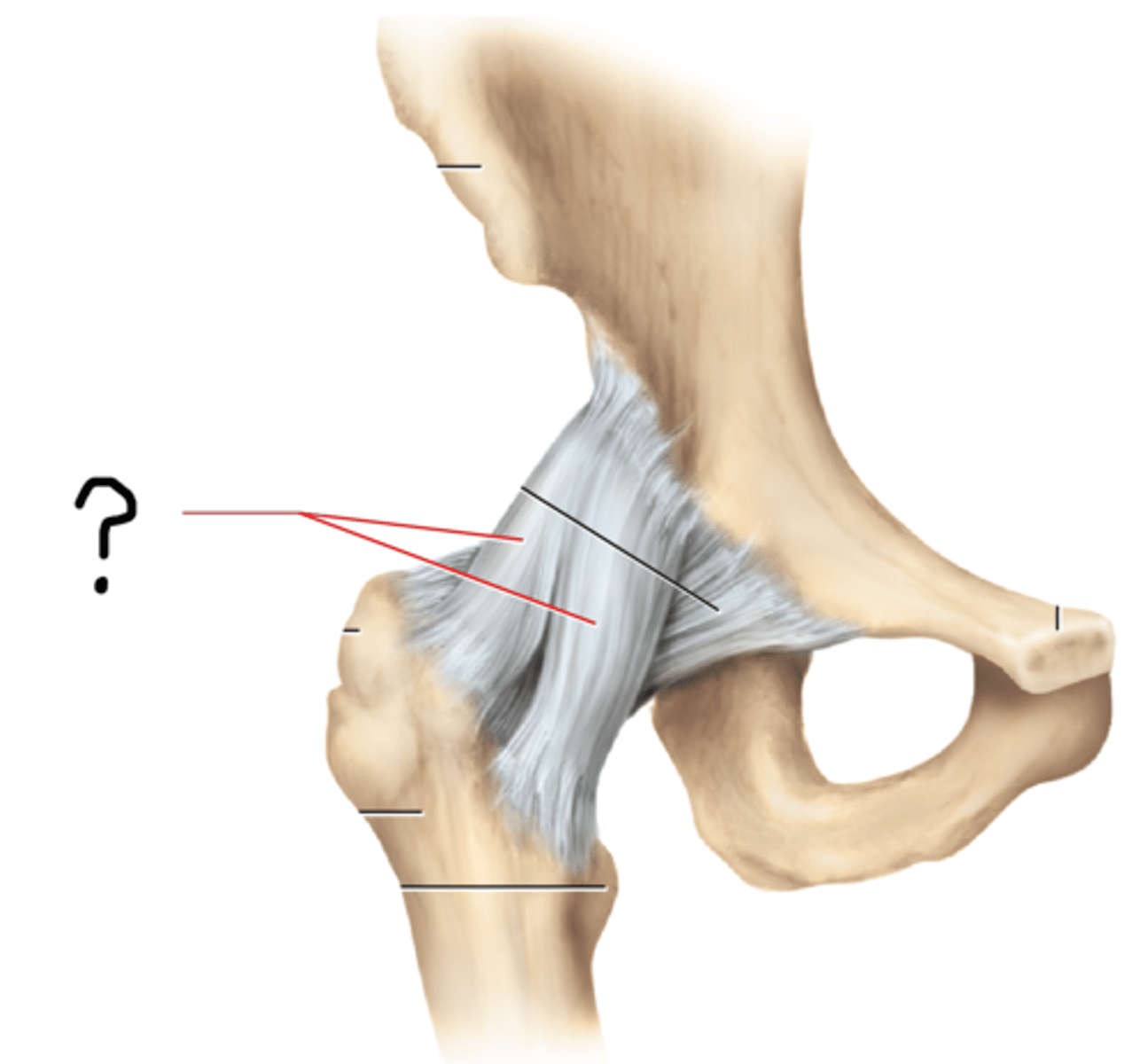
pubofemoral ligament
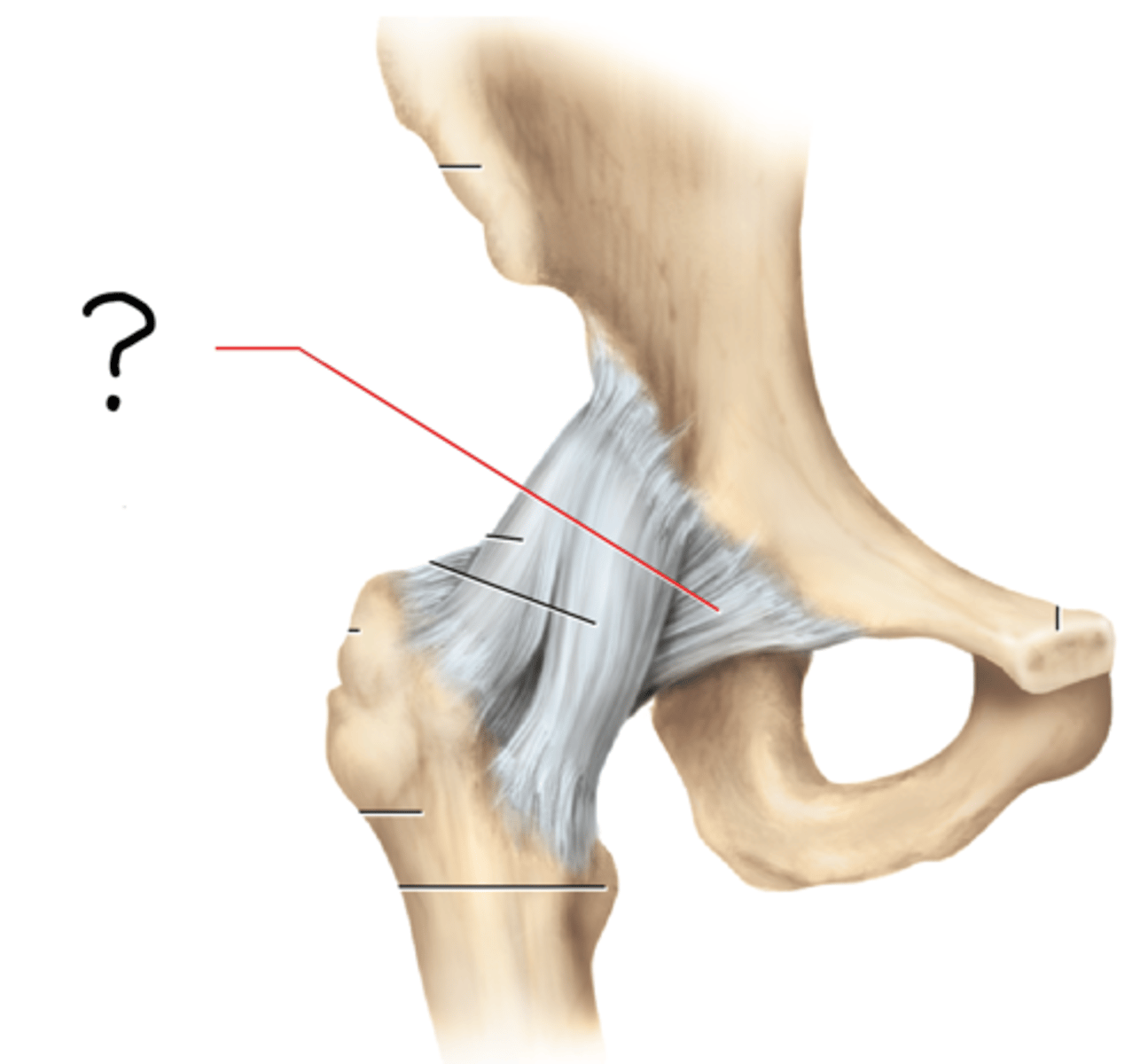
ischiofemoral ligament
round ligament
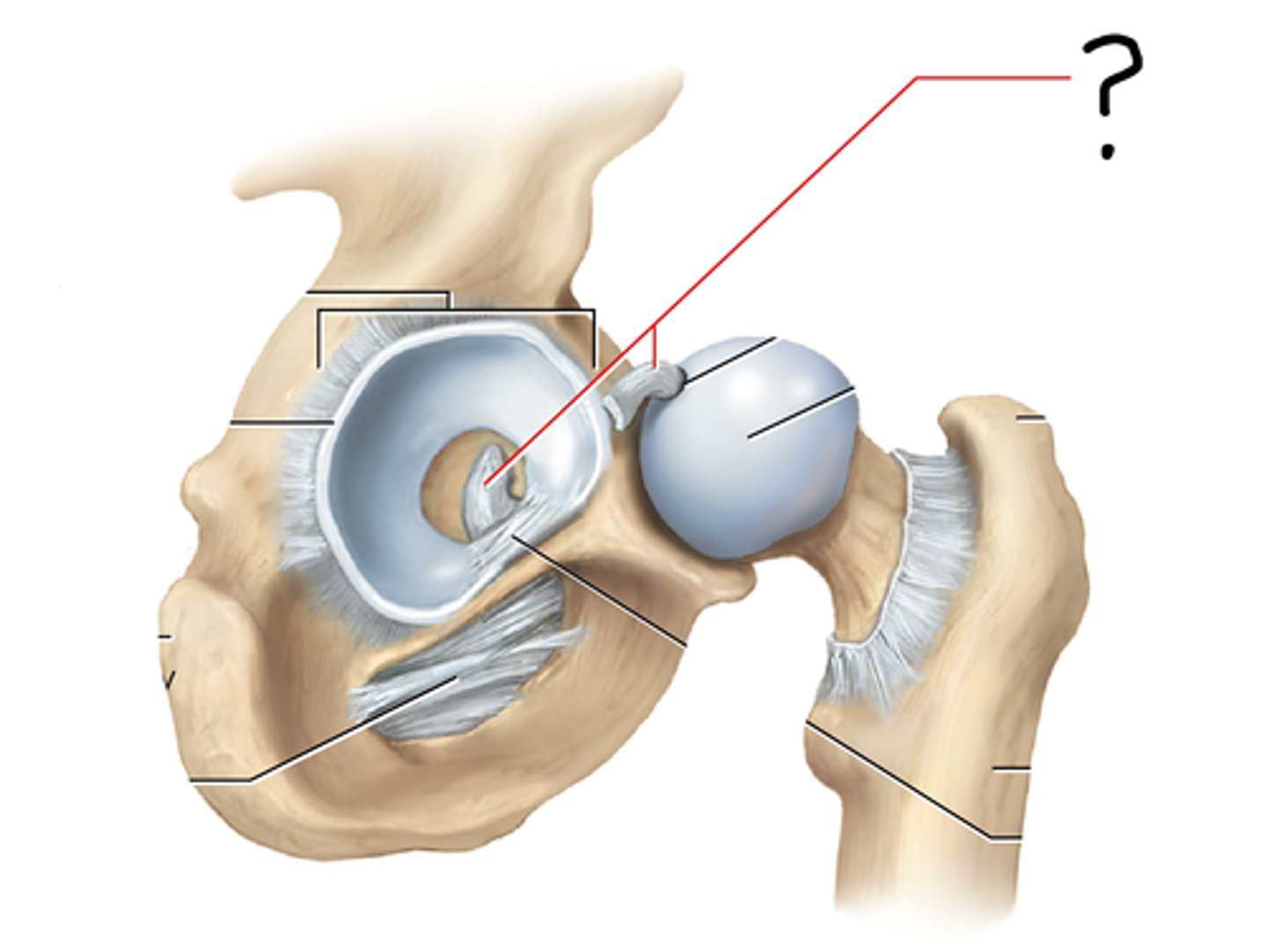
transverse acetabular ligament
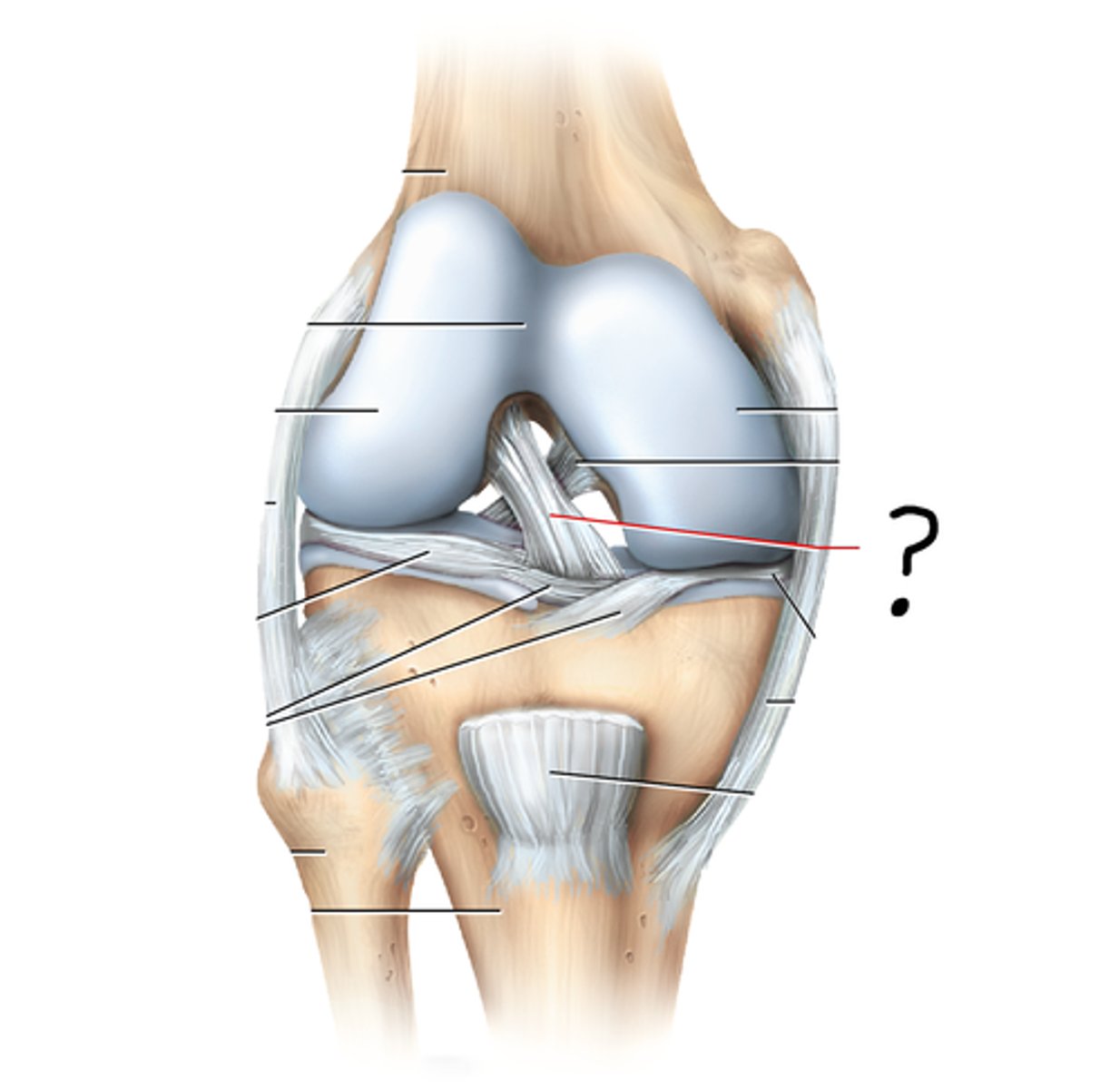
tibiofemoral (knee) joint
femorotibial joint, the largest and most complex diarthrosis of the body; functions as a hinge joint; has lateral and medial menisci; fibular collateral, tibial collateral, anterior cruciate, posterior cruciate ligaments
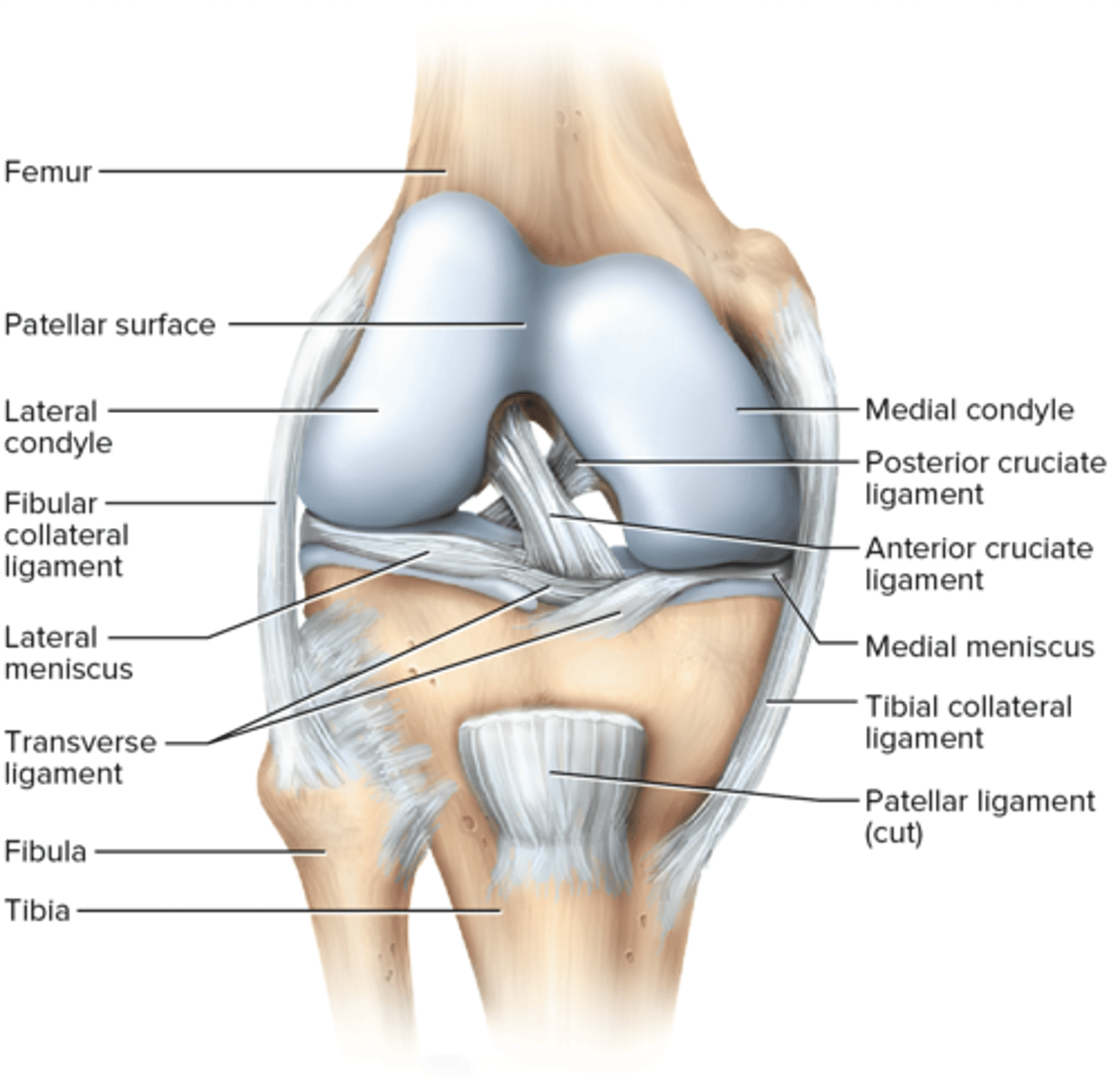
knee joint classification
primarily hinge
knee joint movements
flexion, extension, slight rotation
knee joint articulation
tibiofemoral, patellofemoral
fibular collateral ligament
tibial collateral ligament
anterior cruciate ligament