PSYCH1X03 - Instrumental Conditioning
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Unit/Week 3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Instrumental Conditioning (IC)
Training to learn contingency between voluntary behavior and its consequence (aka Operant conditioning)
IC
Thorndike’s Law of Effect
Behaviours with positive consequence are stamped, negative consequences are stamped out
IC
Thorndike’s Puzzle Box
Cat was placed in puzzle box that could be opened by pulling on rope. Cat would do random behaviour until rope was pulled & door opened.
Thorndike predicted that in subsequence trials, cat would escape immediately like a human would. In reality, escape time was linear.
Animals only followed simple stimulus-response type process, lack humans’ “ah-ha!” moment.
IC
Skinner’s Box/Operant Chamber
Apparatus to study instrumental conditioning by rewarding/punishing an animal for doing something
IC
Skinner’s Pigeon Box
Free food is periodically provided to pigeons, pigeons would repeat whatever behaviour that was being performed prior to food in a “superstitious” manner
IC
Reinforcer
Stimulus used after behaviour occurs to influence its frequency
Reward
Punishment
Escape
Omission
IC/Reinforcer
Reward Training
Presentation of positive reinforcer
(↑ frequency)
IC/Reinforcer
Punishment
Presentation of negative reinforcer
(↓ frequency)
Controversial, ethics of inflicting fear. Causes classical conditioning fear of authority figure
IC/Reinforcer
Escape
Removal of negative reinforcer
(↑ frequency)
IC/Reinforcer
Omission
Removal of positive reinforcer
(↓ frequency)
IC
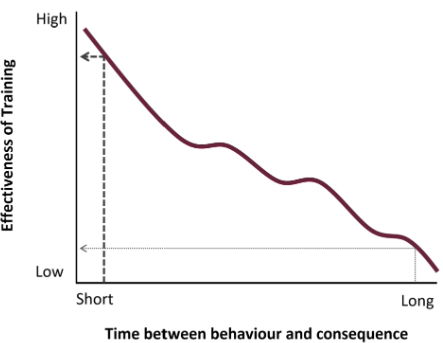
Reinforcer Timing
Correct timing of reinforcer is critical; more effective if minimized delay
IC
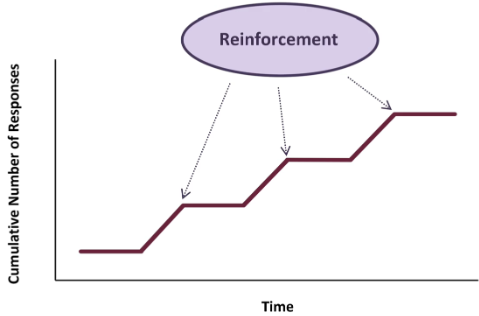
Acquisition of Conditioning
Visualized using a cumulative recorder
Flat horizonal = no response
Increase = response
Pattern depends on the participant, behaviour complexity, and reinforcer used
IC
Autoshaping
Learn contingency without guidance, can only be simple
IC
Shaping
Learn contingency with guidance through successive approximations, reinforce smaller behaviour to eventually build to wished behaviour
IC
Chaining
Learn to connect series of actions together, reinforced by providing opportunity to perform next sequential behaviour and given positive reinforcer after finishing
IC
Shaping vs Chaining
Shaping reinforces for improvement
Chaining reinforced for correct order
IC
Discriminative Stimulus
Signals validity of response-reinforcer contingency
IC/Discriminative Stimulus
SD/S+
Signals contingency is valid
i.e. being at parents house → eating vegetables = dessert
Can also be generalized
IC/Discriminative Stimulus
Sδ/S-
Signals contingency is invalid
i,e being at grandparents’ house → eating vegetables ≠ dessert
IC/Discriminative Stimulus
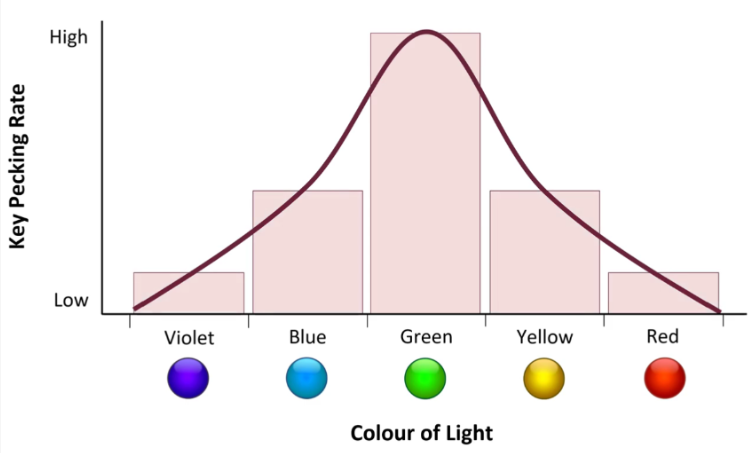
SD/S+ Generalization Gradient
SD/S+ can be generalized, stimuli similarity will affect rate of response. Must exist in same modality (existence)
i.e. pigeon will peck button when light is green SD/S+, but also sometimes at light with similar wavelength
IC/Discriminative Stimulus
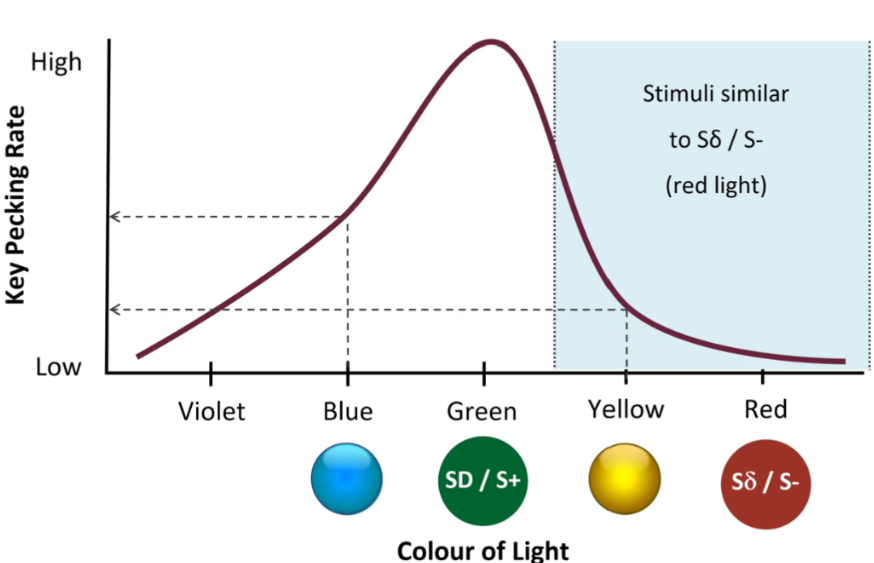
Sδ/S- Stimulus Discrimination
Sδ/S- will constrict range of generalization gradient. Training with Sδ/S- is better for fine tuning. Must exist in same modality (existence)
i.e. pigeon will not peck button when light is red Sδ/S- but also sometimes at light with similar wavelength
CC & IC
CS+ vs SD/S+
CS+ reflexive, involuntary
SD/S+ sets occasion for voluntary
CC & IC
CS- vs Sδ/S-
CS- predicts absence of US
Sδ/S- establishes no reinforcer
IC
Reinforcement Schedules
Rules that dictates when reinforcement will occur
Continuous reinforcement
Partial reinforcement
Partial is more robust compared to continuous, because its less obvious that reinforcement ceased
Same reason why VR-# is better than FR-#
IC/Reinforcement Schedules
Continuous Reinforcement (CRS)
Every response leads to reinforcement, very rare in real world
IC/Reinforcement Schedule
Partial Reinforcement Schedule (PRS)
Responses are only reinforced sometimes, based on
Ratio vs Interval
Fixed vs Variable
IC/Partial Reinforcement Schedule
Ratio (R)
Based on number of responses
FR-1 is rewarded every 1
FR-10 is rewarded every 10
IC/Partial Reinforcement Schedule
Interval (I)
Based on time since last reinforcement
FI-1 is rewarded every 1 minute
FI-10 is rewarded every 10 minutes
IC/Partial Reinforcement Schedule
Fixed (F)
Requirement for reinforcement is constant across trials
Fixed FI-10 is rewarded 10 pecks every trial
IC/Partial Reinforcement Schedule
Variable (V)
Requirement for reinforcement is random but averaged across trials
Variable VR-10 is rewarded an average 10 pecks across trials
Trial 1: 12 pecks
Trial 2: 8 pecks
Average: 10 pecks
IC/Partial Reinforcement Schedule
Basic Partial Reinforcement Schedules
Four basic reinforcement schedules based on Ratio vs Interval & Fixed vs Variable
FR-#
VR-#
FI-#
VI-#
IC/PRS/Basic Schedules
Fixed Ratio FR-#
Reward every # response(s)
Ratio Strain
Pause & Run Cumulative Pattern
IC/PRS/FR-#
Ratio Strain & Break Point
Limit to how stingy you can be with your required amount of responses before responses stop (reach break point)
i.e. FR-500, too many responses required and responder will stop
IC/PRS/FR-#
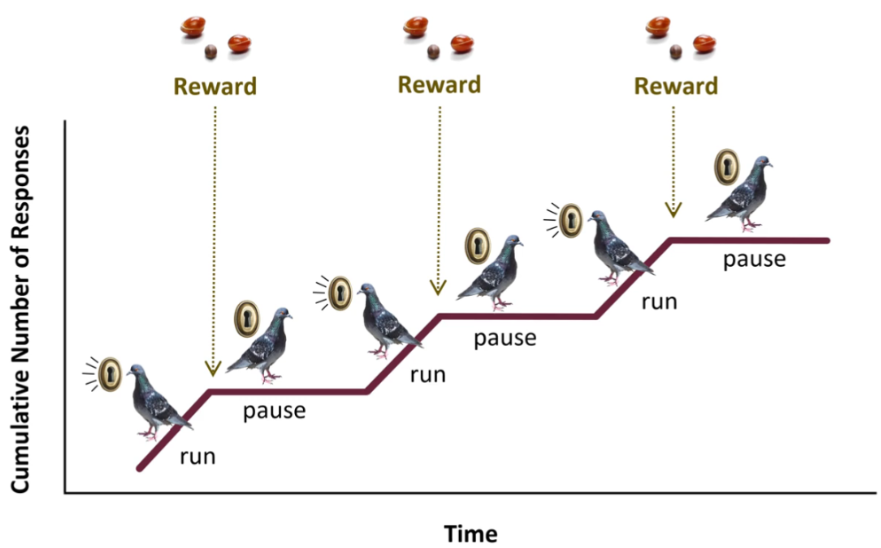
FR-# Cumulative Pattern
Pause & Run
After reinforcement, participant will pause before resuming next run
IC/PRS/Basic Schedules
Variable Ratio VR-#
Reward on average every # responses
Linear Cumulative Pattern
↓ ratio for reward = ↑ response rate
IC/PRS/VR-#
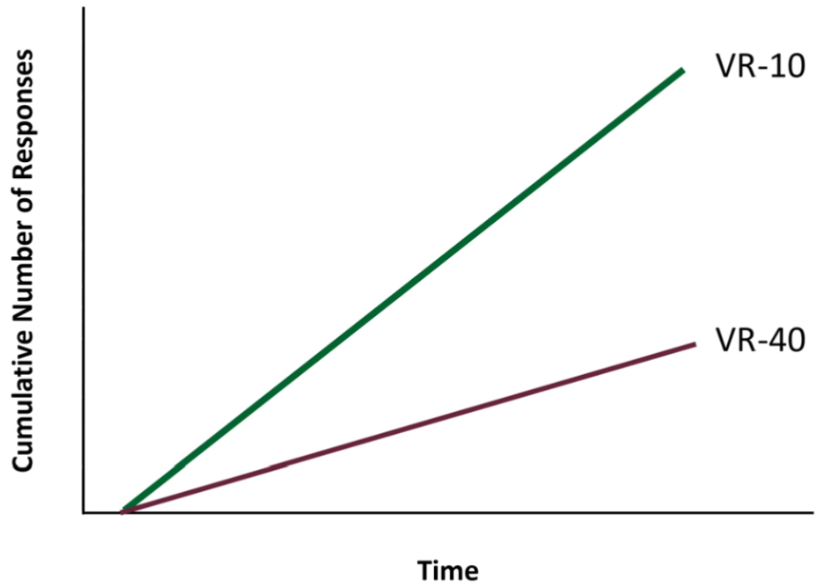
VR-# Cumulative Pattern
Linear
Slope is average number of responses before reinforcement. ↑ reinforcement frequency = ↑ response rate
VR-10 has steeper slope than VR-40
IC/PRS/Basic Schedules
Fixed Interval FI-#
Reward on every # time
Very rarely seen in real world
Scallop Cumulative Pattern
i.e. Weekly quizzes: start of week = less stress, stress ramps up, after quiz = no stress
IC/PRS/FI-#
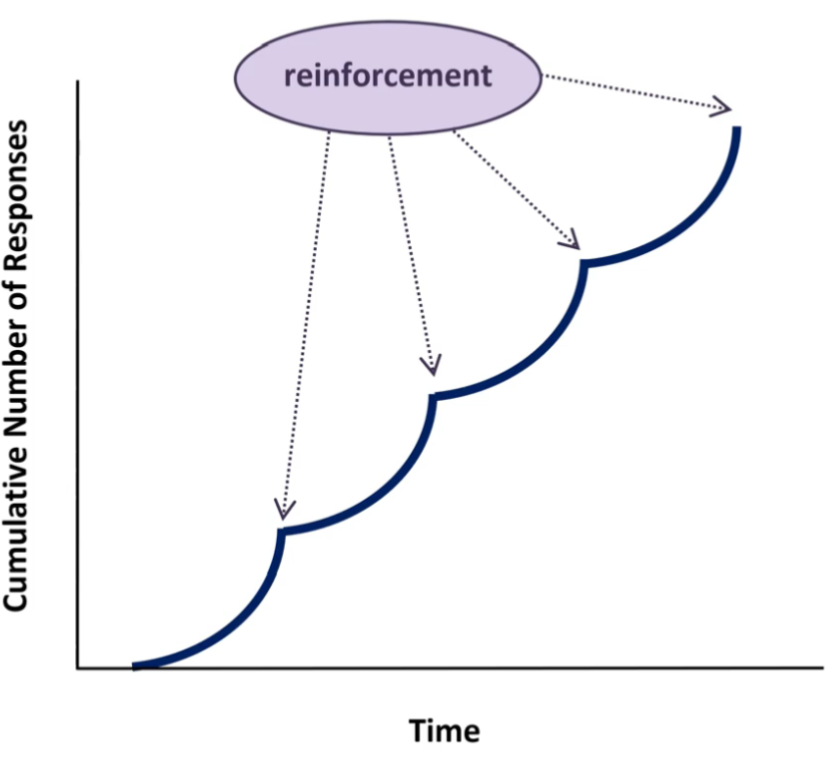
FI-# Cumulative Pattern
Scallop
After reinforcement, there is period where responses drop & slowly ramps up, peaking before next reinforcement
Does not want to miss reinforcement
No early reward if respond early
IC/PRS/Basic Schedules
Variable Interval VI-#
Reward on average every # time
Reinforcement can come anytime but have an idea of when, so respond at average rate to ensure they will not miss reinforcement
Dashed Linear Cumulative Pattern
↑ average reinforcers = ↑ response rate
IC/PRS/VI-#
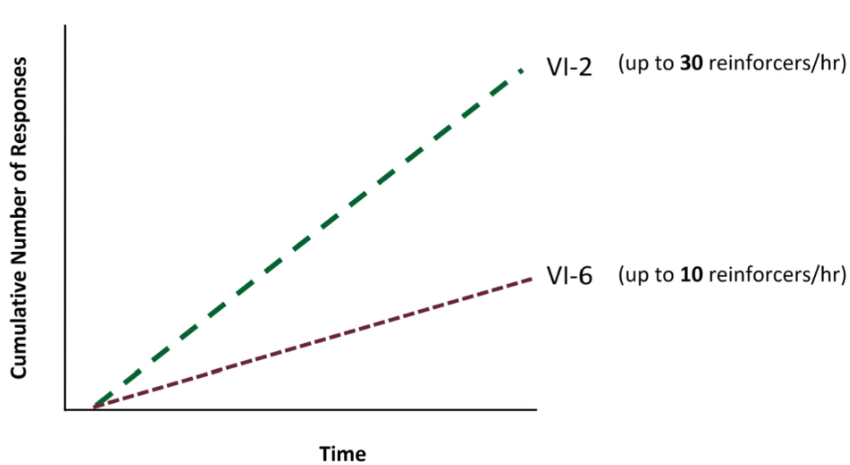
VI-# Cumulative Pattern
Dashed Linear
Usually respond in steady rate to ensure that they don’t miss reinforcement
IC/Textbook
Primary Reinforcer
Reinforcer that satisfies biological need; unconditioned
IC/Textbook
Secondary Reinforcer
Reinforcer that gains value through association with primary reinforcer; conditioned
IC/Textbook
Delay of Gratification
Ability to tolerate delay between reinforcement, increases as humans age
IC/Textbook
Contrast Effect
Change in reward value → change in response rate
IC/Textbook/Contrast Effect
Positive Contrast
↑ reward value = ↑ response rate
IC/Textbook/Contrast Effect
Negative Contrast
↓ reward value = ↓ response rate
IC/Textbook
Overjustification
Reward for a previously unrewarded task alters perception of that task. Remove reward = response rate drops below that of unrewarded response rate
IC/Textbook
Observational Learning
Children learn through imitating observed behaviour
IC/Textbook
Mirror Neurons
Neurons that activate the same way when performing, observing, or imagining action
IC
Watson
Behaviourist: nurture over nature, children’s environment is more important
IC/Behaviourism
Biological
Predisposition to learn by imitating (i.e. baby learns to stick tongue out)
IC/Behaviourism
Cultural Transmission
Socially transmit/imitate behaviour (i.e. macaque learns to wash sweet potato by watching another)