Foundational Serology Techniques
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
ELISA
Primary binding assay, Enzyme Linked ImmunoSorbent Assay. Detects Ags or Abs. Very sensitive
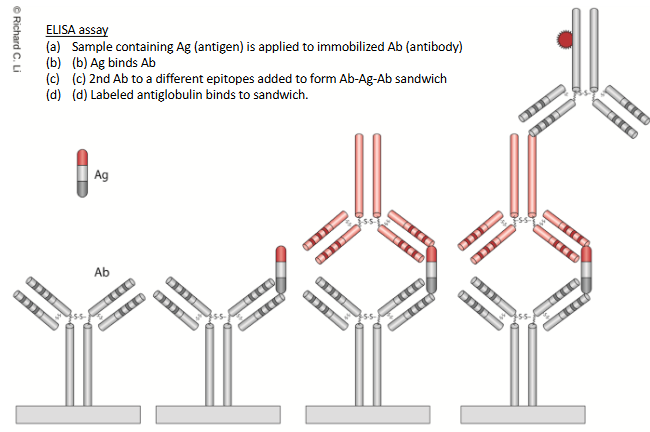
ELISA Assay Process
Sample containing Ag is applied to immobilized Ab
Ag binds Ab
2nd Ab to a different epitope added to form Ab-Ag sandwich
Labeled antiglobulin binds to sandwich
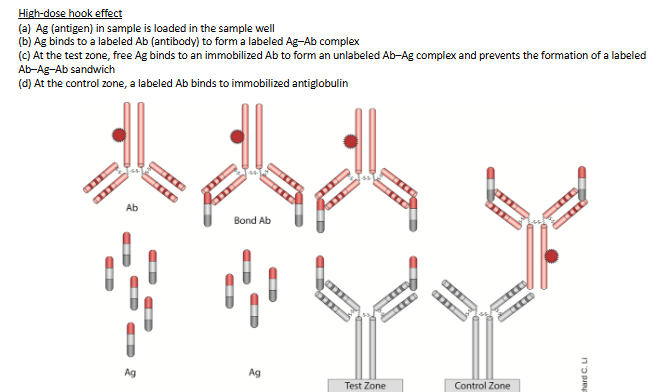
High-dose Hook Effect
False negative if sample is too concentrated of antigen to saturate dye-labelled antibody. Unbound antigen competes with complex for immobilized antibody. Prevent by applying a smaller volume or diluting sampe
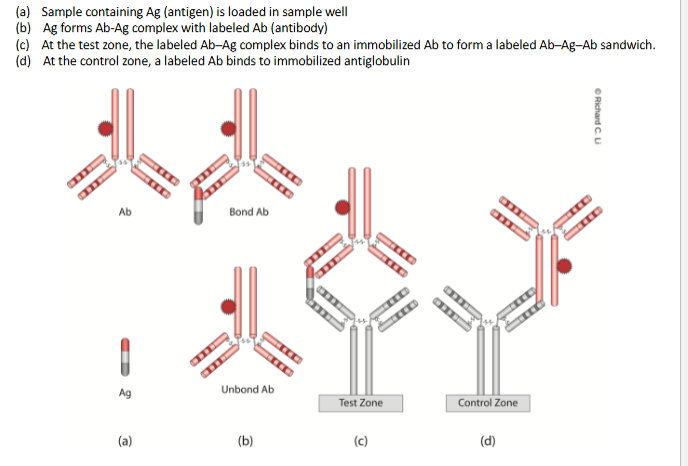
Immunochromatographic Assays
Simple and rapid, often used for screening tests. Consists of a dye labelled monoclonal antibody in a sample well and a polyclonal antibody immobilized on a nitrocellulose membrane. When sample is loaded into the well, antigen forms Ag-Ab complex with the antibody. The complex diffuses to reach the test zone where immobilized antibody traps complex to form antibody-antigen-antibody sandwich.
Immunodiffusion
Passive method, Antigen or Antibody allowed to diffuse to create a gradient. Precipitation occurs from interaction of Ab and Ag
Single/Radial Immunodiffusion
Concentration gradient is established for Ab or Ag. Antibody is uniformly distributed in gel matrix, precipitate forms ring around well. Area within ring is proportional to amount of antigen
Double immunodiffusion
Ab and Ag diffuse into matrix and migrate towards one another. If they’re specific to one another, a band forms.
Ring test
Antigen solution is layered onto antibody solution. Antigen and antibody diffuse toward each other. Positive = ring of precipitate
Ouchterlony Test
Antibody is loaded into central well, questioned samples and control loaded in surrounding wells. Double diffusion of antigen and antibody. Positive = precipitate line between wells. Can be stained to aid observation
Immunoelectrophoresis (IEP)
Antigens in sample are separated by aragose gel. Antibody is loaded parallel and incubated for double diffusion. Positive = arc shaped precipitate line.
Crossed IEP
Two dimensional IEP. Antigens in sample are separated by gel electrophoresis. Strip of gel containing separated antigens is cut and turned 90 for 2nd dimension electrophoresis. Positive = arc shaped precipitate line. More sensitive than IEP.
Rocket IEP
Antigen loaded in well of gel. Electrophoresis drives antigen into gel. Psoitive reaction = rocket shaped precipitate line. Height of rocket is proportional to the amount of antigen. Can be quantified by comparison of known standard on the same gel.
Agglutination Based Assays
Qualitative, but semi-quantitative with titration. Can be used for blood group typing and menstrual blood ID
Direct Agglutination
Antibody reacts with antigens originally located on cell surfaces
Agglutination Inhibition
Indirect detection. Known antigen added to mixture of antigen containing cells and antibodies, known antigen will compete with cell surface antigens for antibodies
Passive Agglutination
Carrier cells are incubated with antigen samples. Forms a coating of antigen on carrier cell surface. Antigen-coated carrier cells are agglutinated with specific antibody.