Biology - B3 (Organism Level Systems) *GCSE OCR HIGHER*
1/115
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
116 Terms
ADH
A hormone secreted by the pituitary gland which increases water reabsorption in the kidney (making the kidney tubules more permeable to water)
Hormones - Adrenaline
- A hormone released by the adrenal gland which increases heart rate and breathing rate (involved in fight/flight)
- It raises blood sugar levels by increasing the conversion of glycogen into glucose
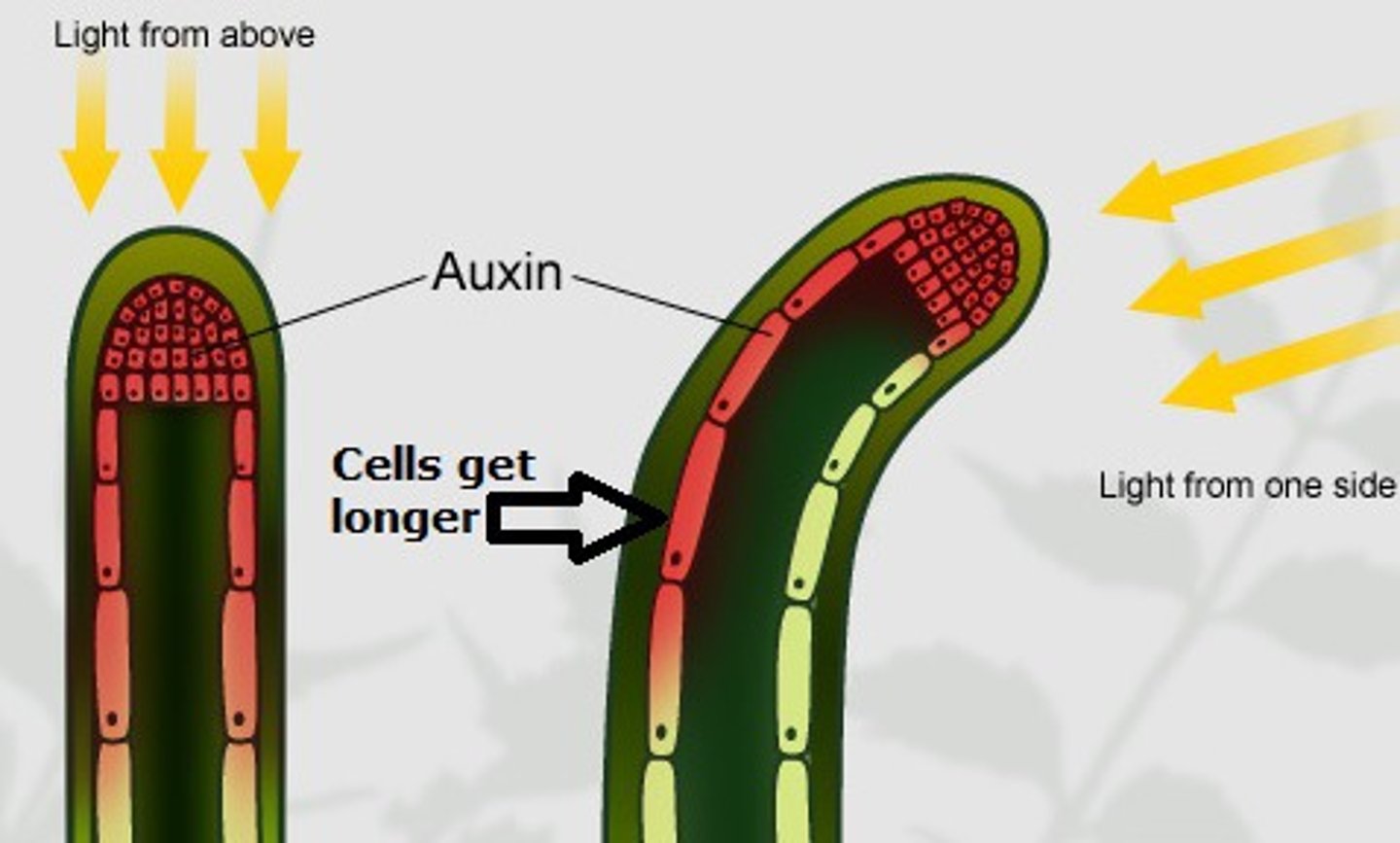
Plant Hormones - Auxin
A plant hormone that is responsible for cell elongation and regulation of fruit development
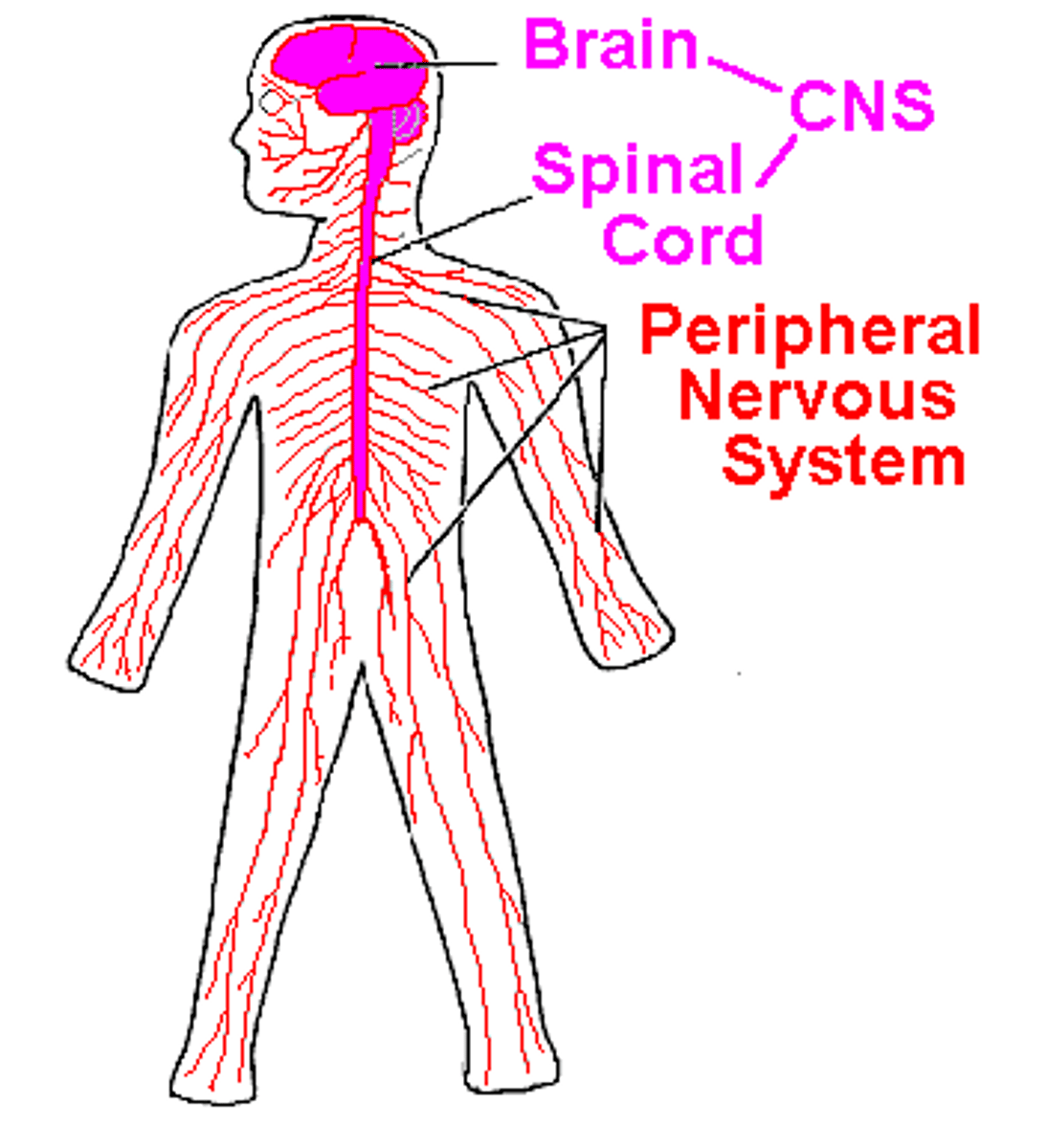
Central nervous system (CNS)
The brain and the spinal cord.
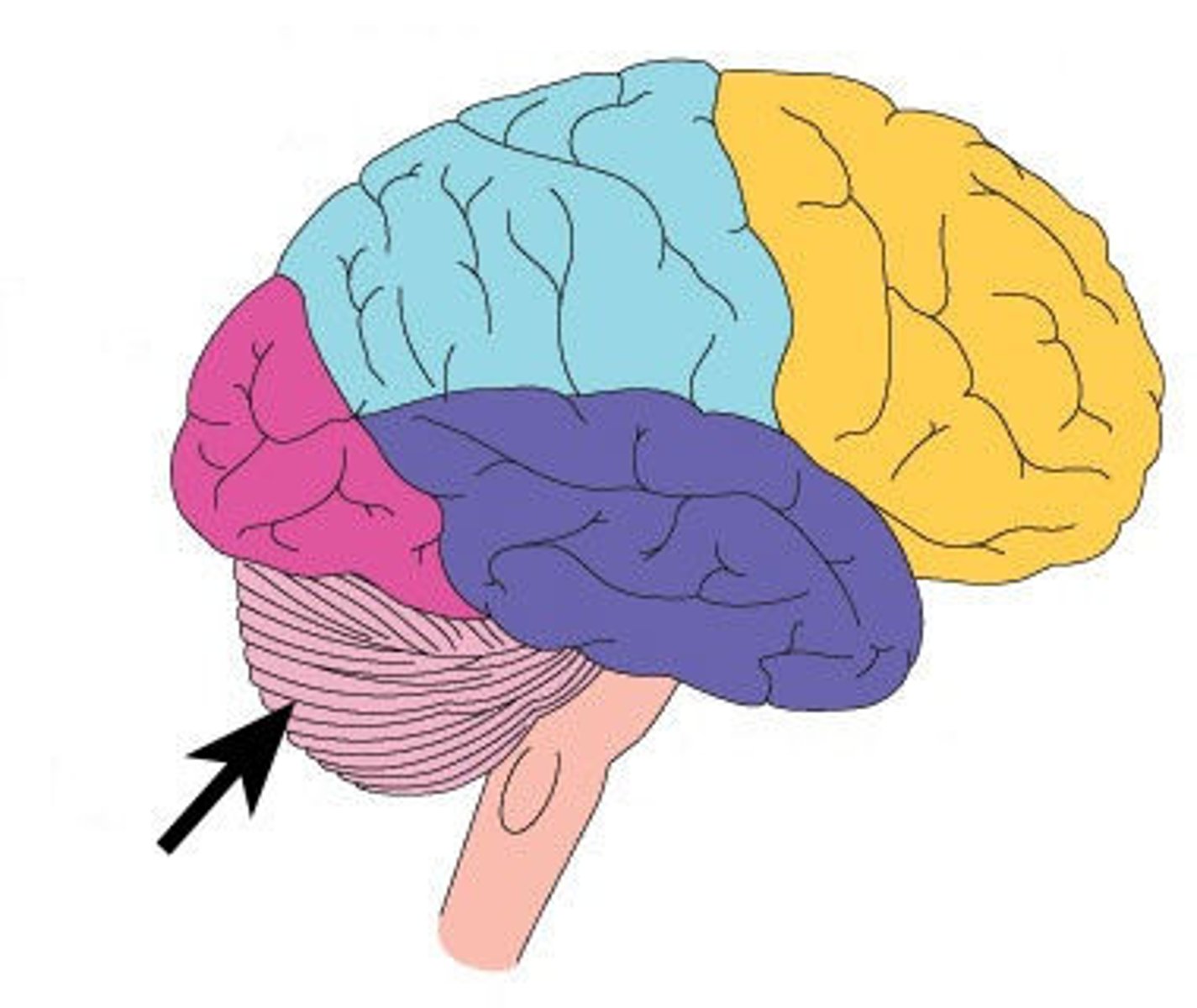
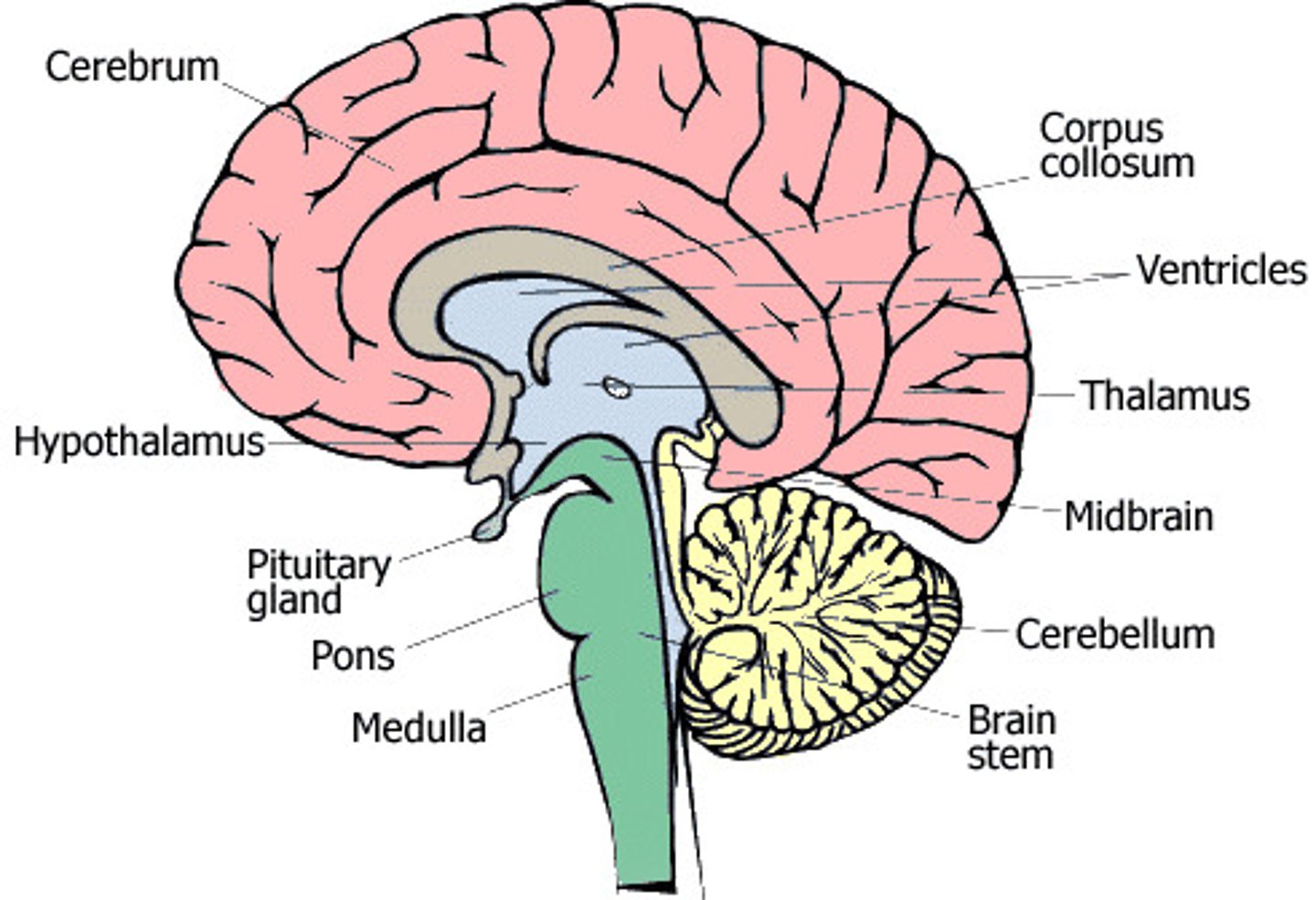
The Brain - Cerebellum
The region of the brain that controls unconscious functions such as posture, balance and muscular movement
The Brain - Cerebral Cortex
The outer layer of the cerebrum
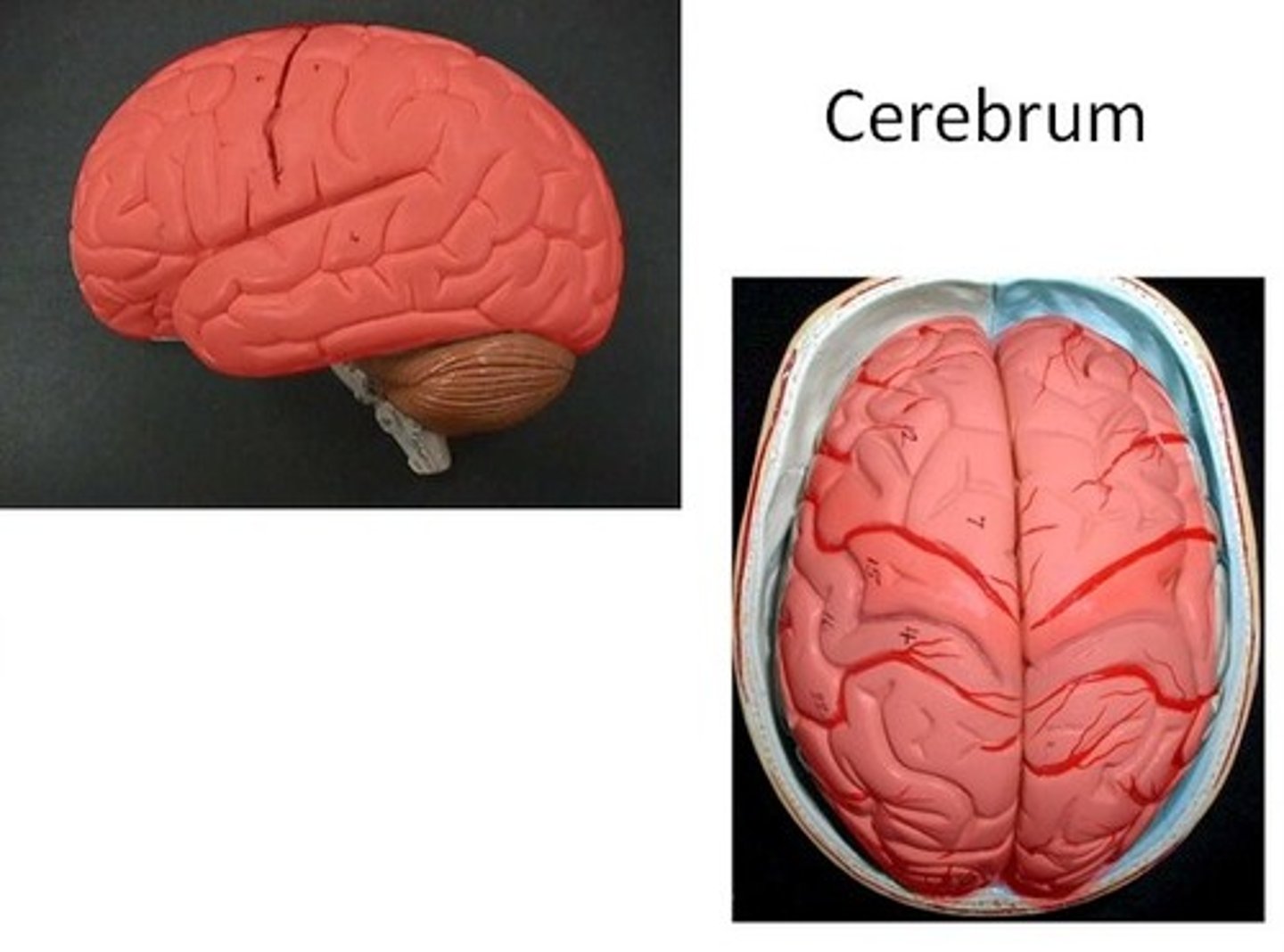
The Brain - Cerebrum
- The highly folded region of the brain that is responsible for controlling voluntary actions such as learning, personality and memory
- It is divided into the right and left hemispheres.
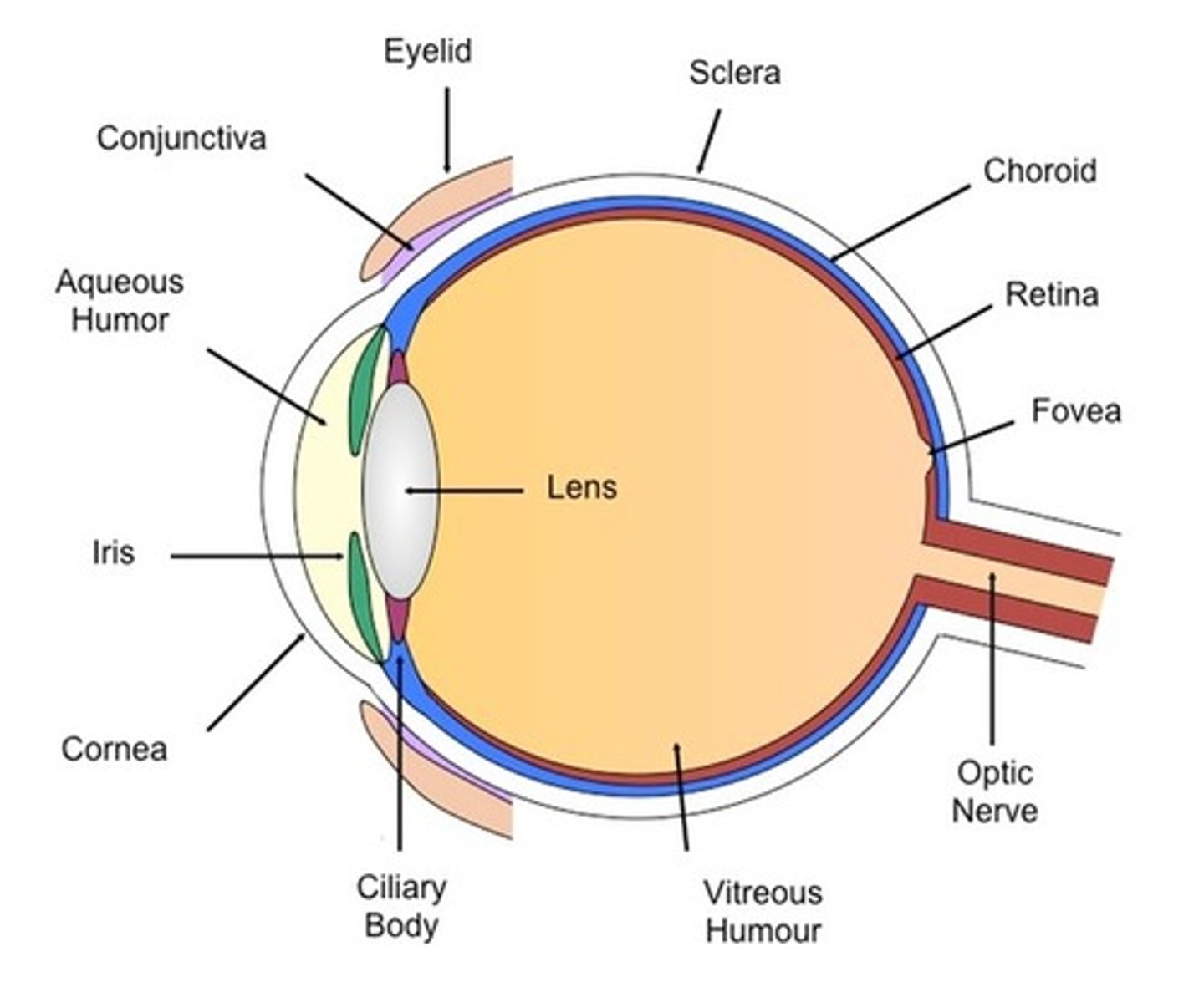
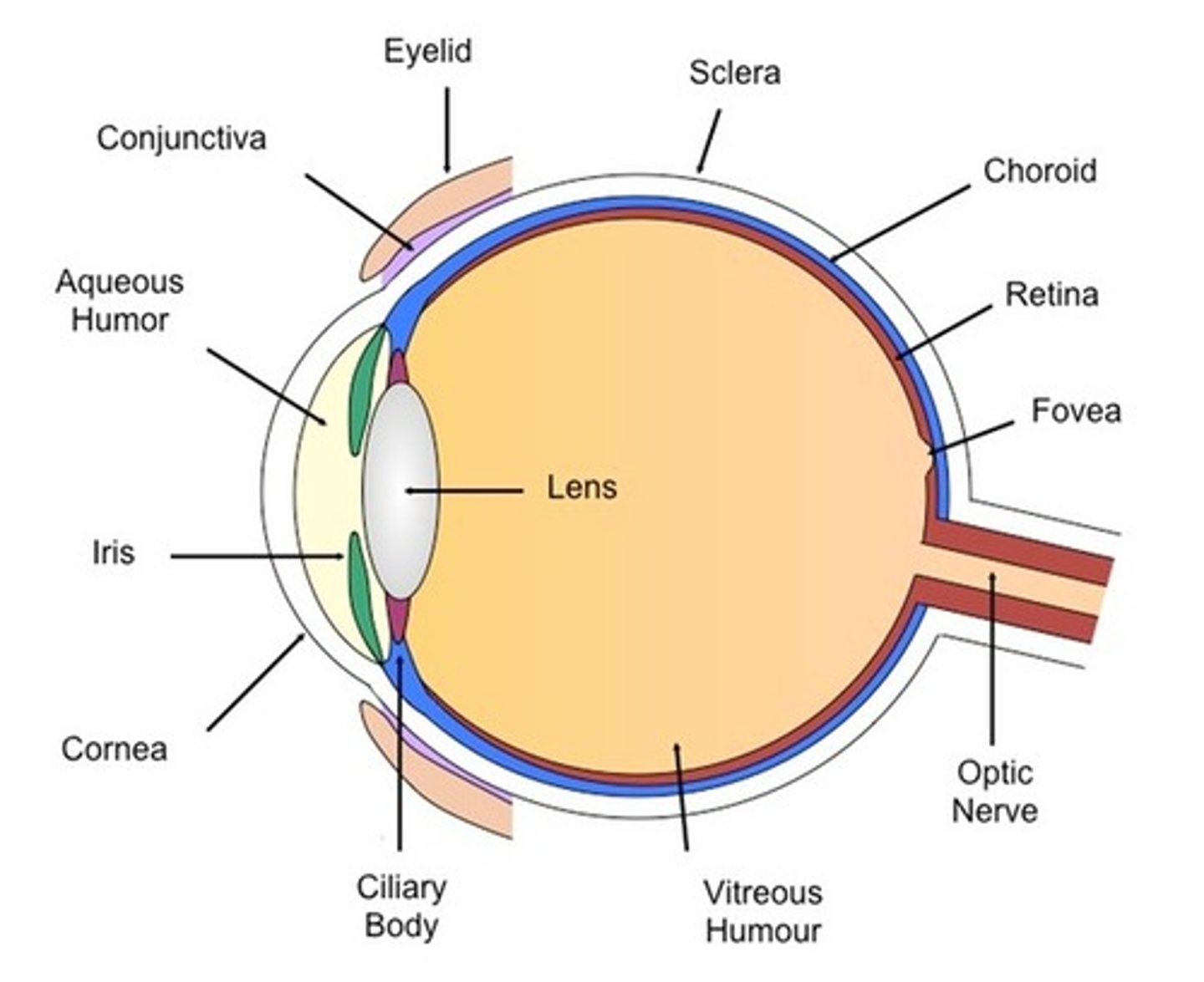
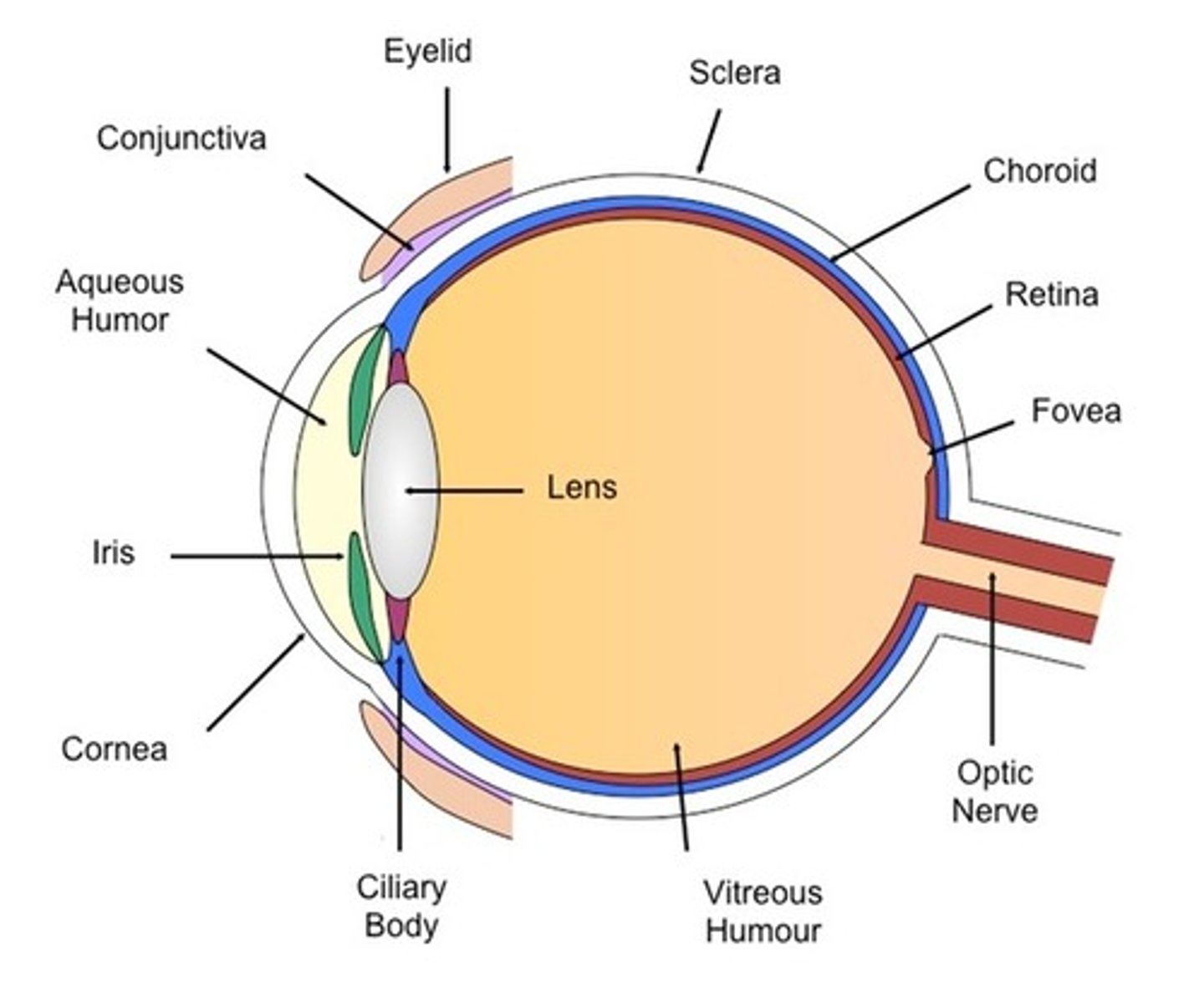
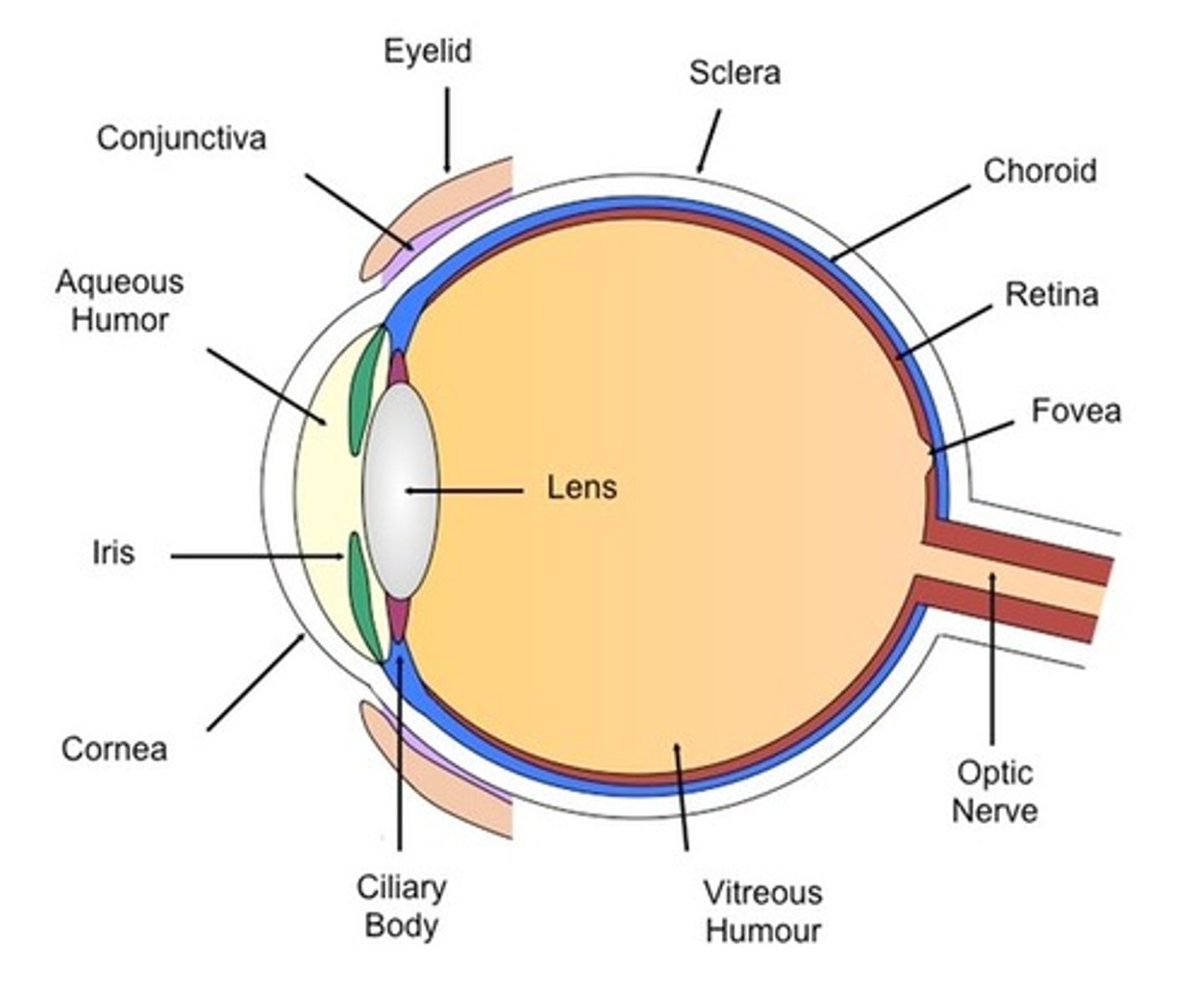
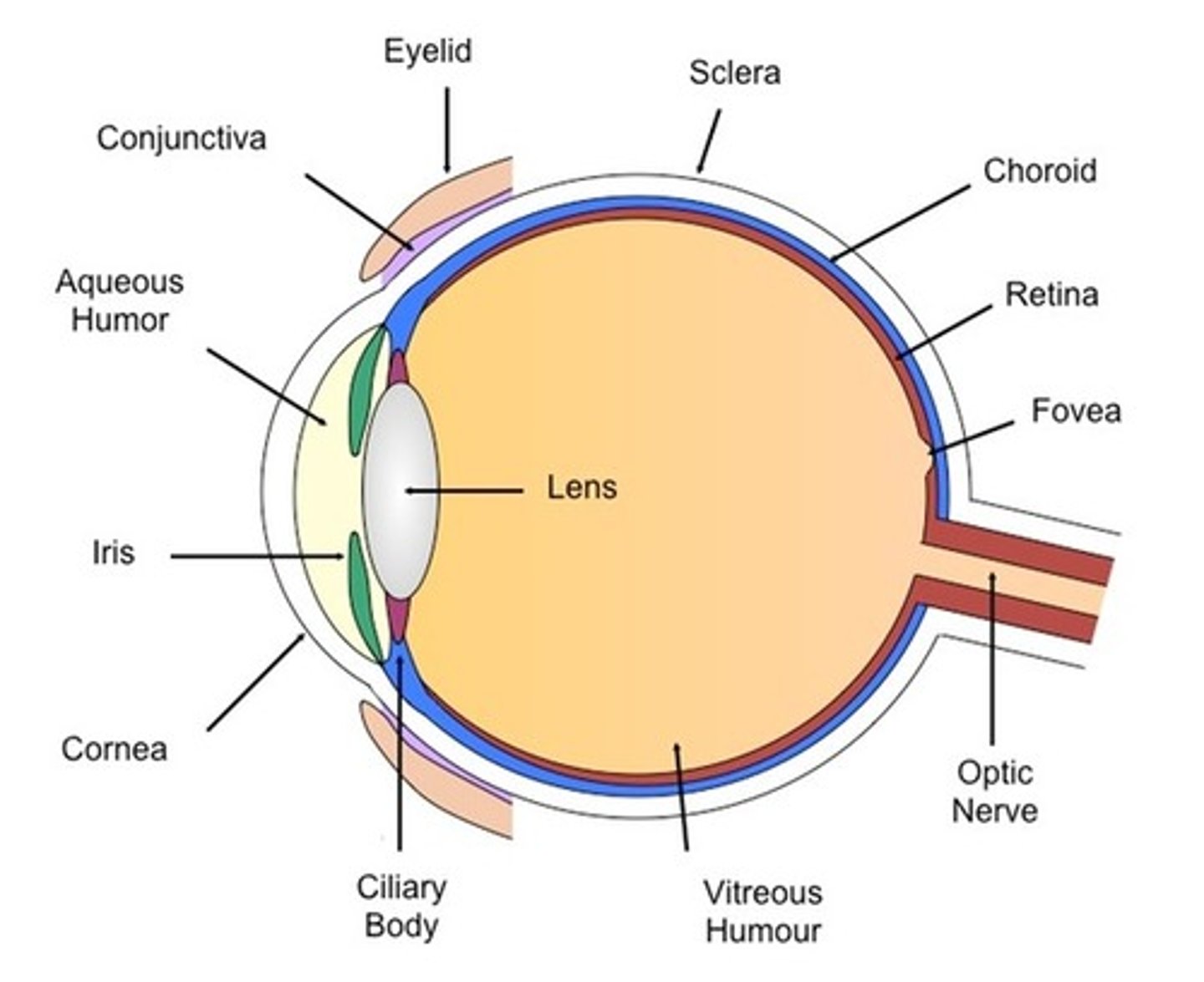
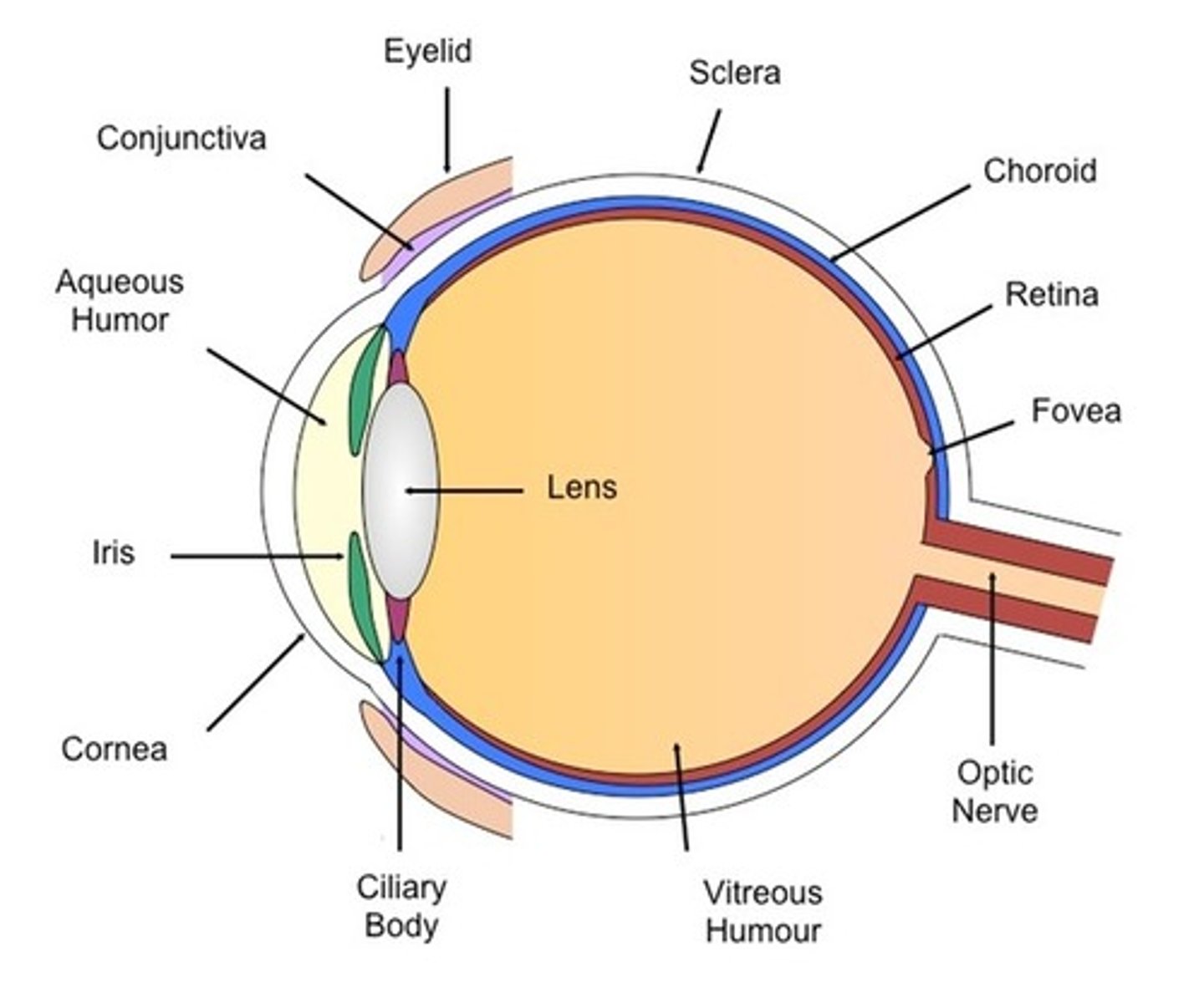
The Eye - Ciliary body
- An extension of the iris / ring of muscle tissue
- It alters the shape of the lens
The Eye - Colour Blindness
- A condition where a person has a defect in the receptors or a lack of receptors in the retina
- A person will have difficulty making out two different colours
Contraception
Methods that are used to prevent pregnancy
The Eye - Cornea
- Its the transparent coating on the front of the eye
- It protects they eye and refracts light as it enters, focusing it onto the retina
Dormancy
- A period of time in which seeds hibernate
- This stops when they germinate.
Effector
A gland or muscle that produces a response to the stimulus to restore optimum conditions.
Endocrine glands
A group of cells that are specialised in secreting chemicals (hormones) directly into the bloodstream
Endocrine system
A chemical messenger system that releases hormones directly into the bloodstream to control metabolism, development, growth and reproduction
Plant Hormones - Ethene
A plant hormone that promotes fruit ripening by stimulating the conversion of starch to sugars

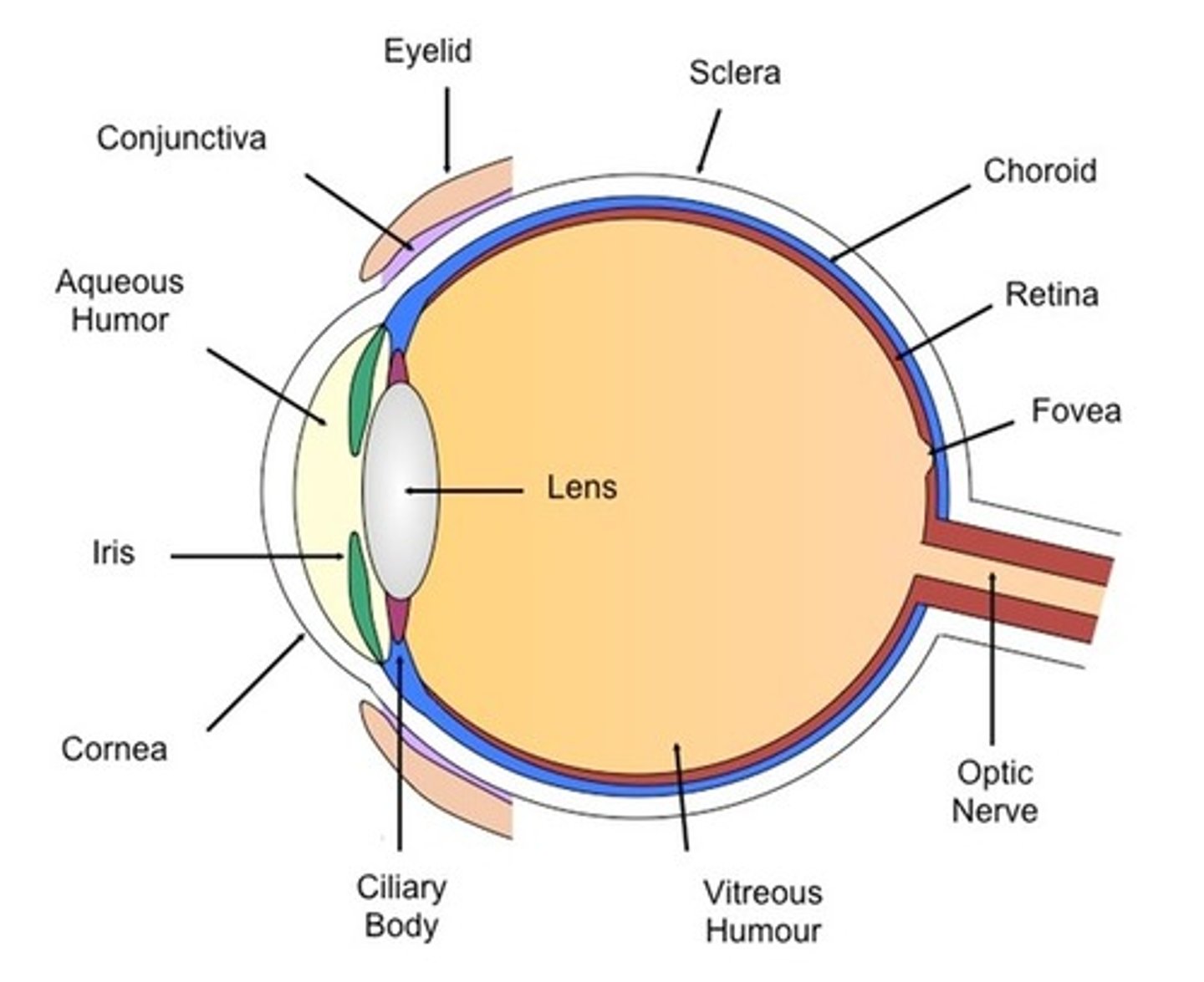
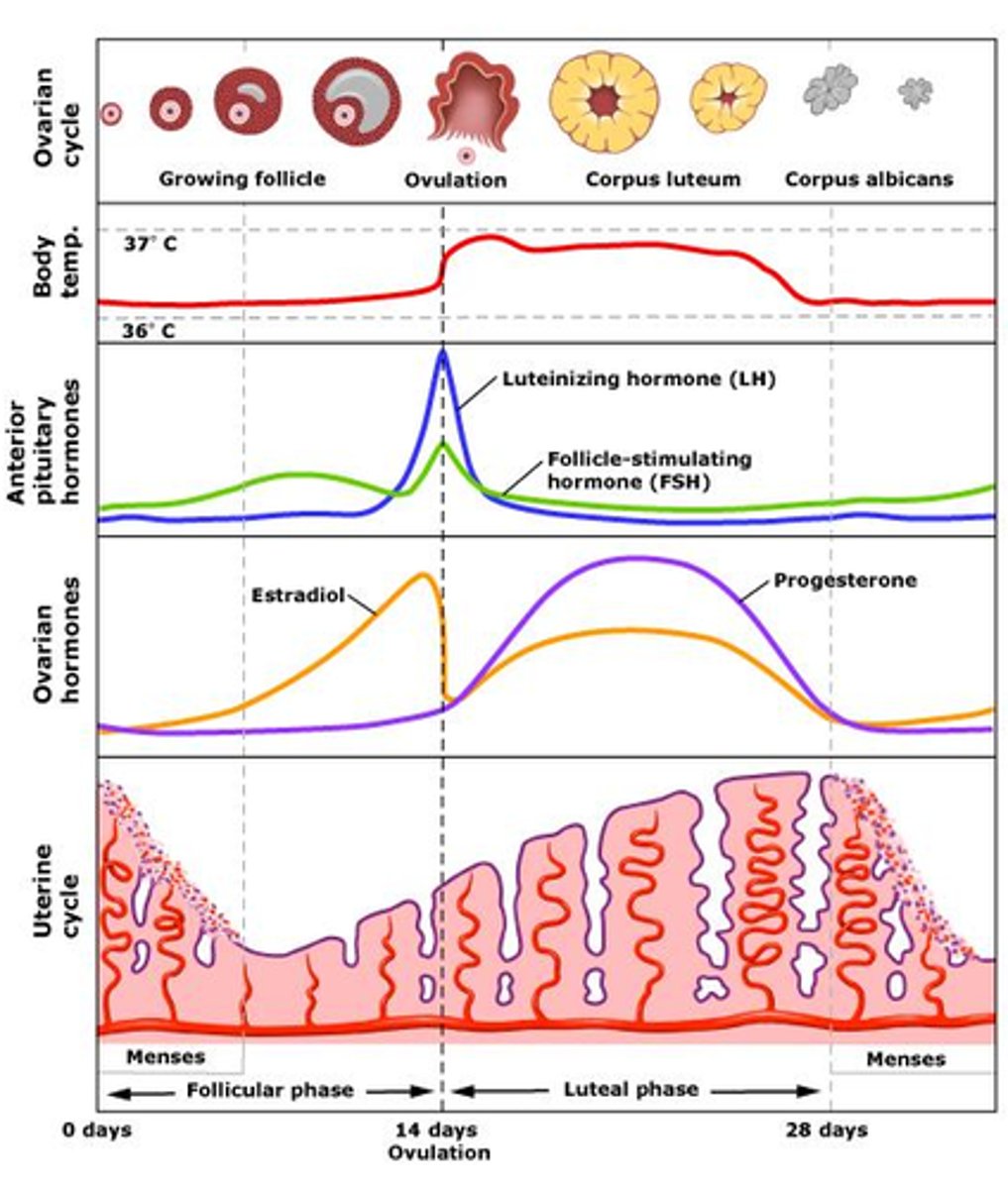
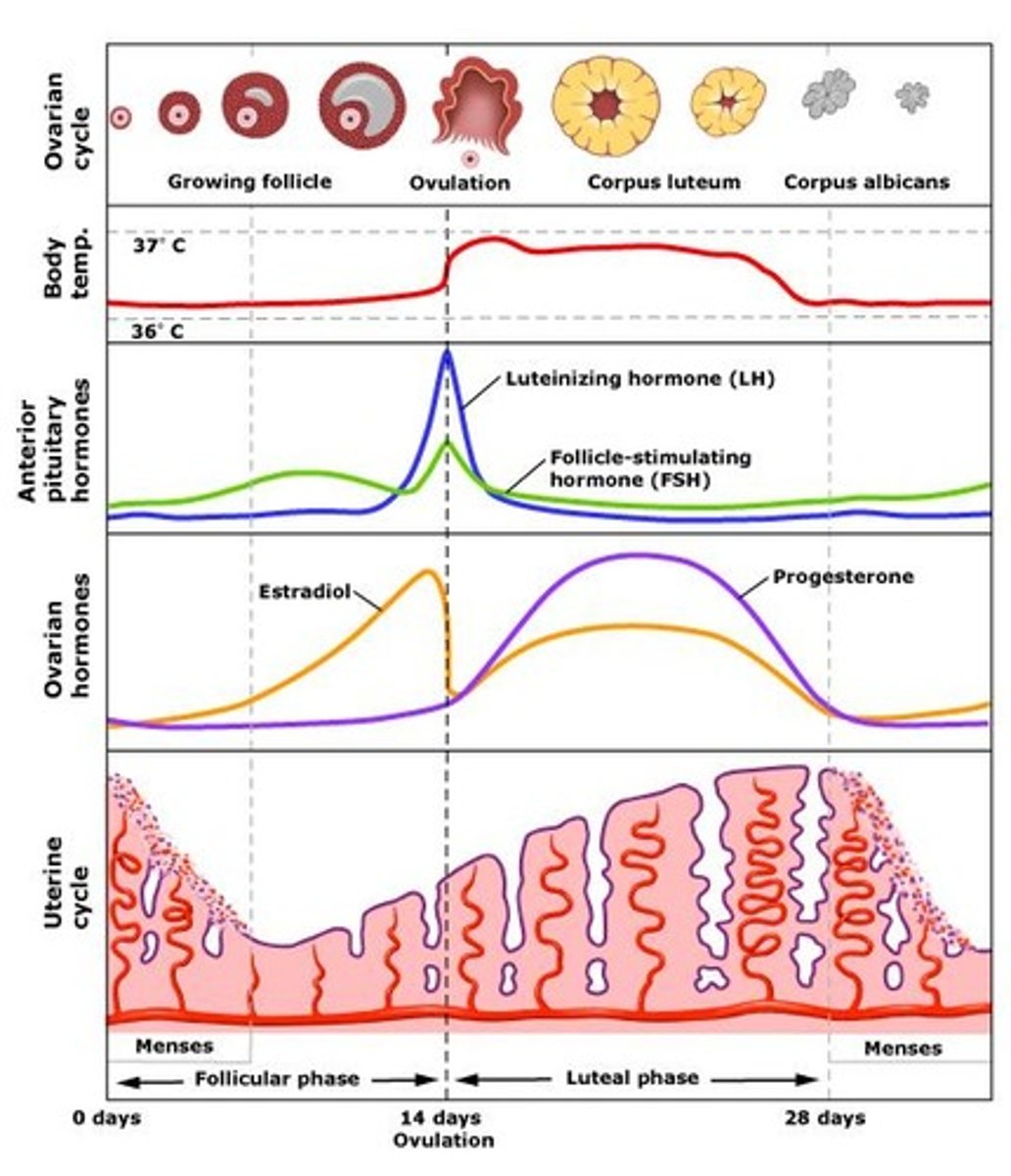
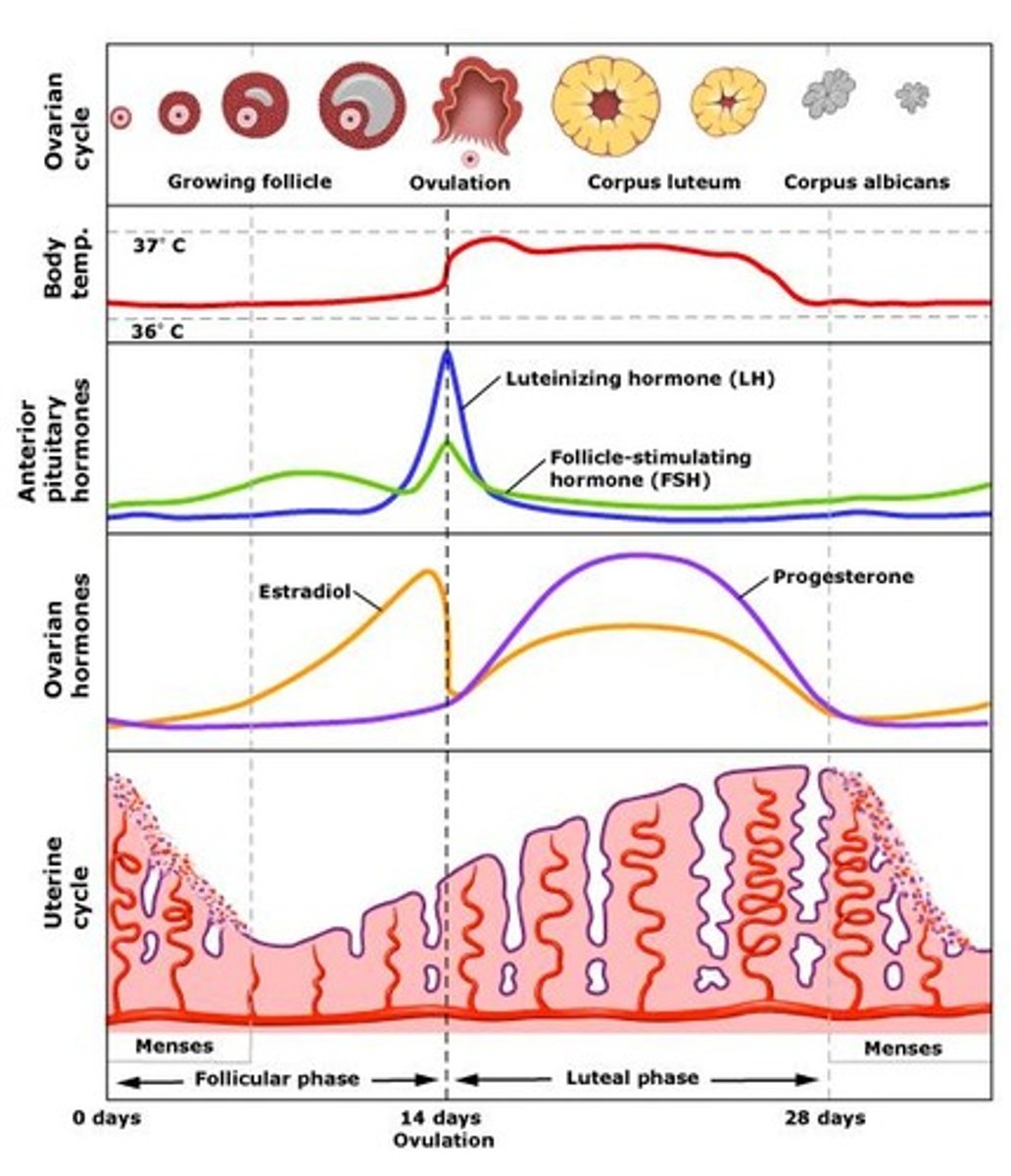
Menstrual Cycle - Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
- A female reproductive hormone that is released by the pituitary gland
- It is responsible for the maturation of an egg in the ovary
- It stimulates ovaries to produce oestrogen
Tropism - Geotropism
- The growth response of a plant to gravity
- Roots show positive geotropism as they grow down with gravity so the roots act as an anchor and are nearer to water
- The stem shows negative tropism as it grows up against gravity
Germination
The process by which seeds develop into plants
Plant Hormones - Gibberellins
Plant hormones that initiate germination and flowering as well as ending the dormancy period of seeds
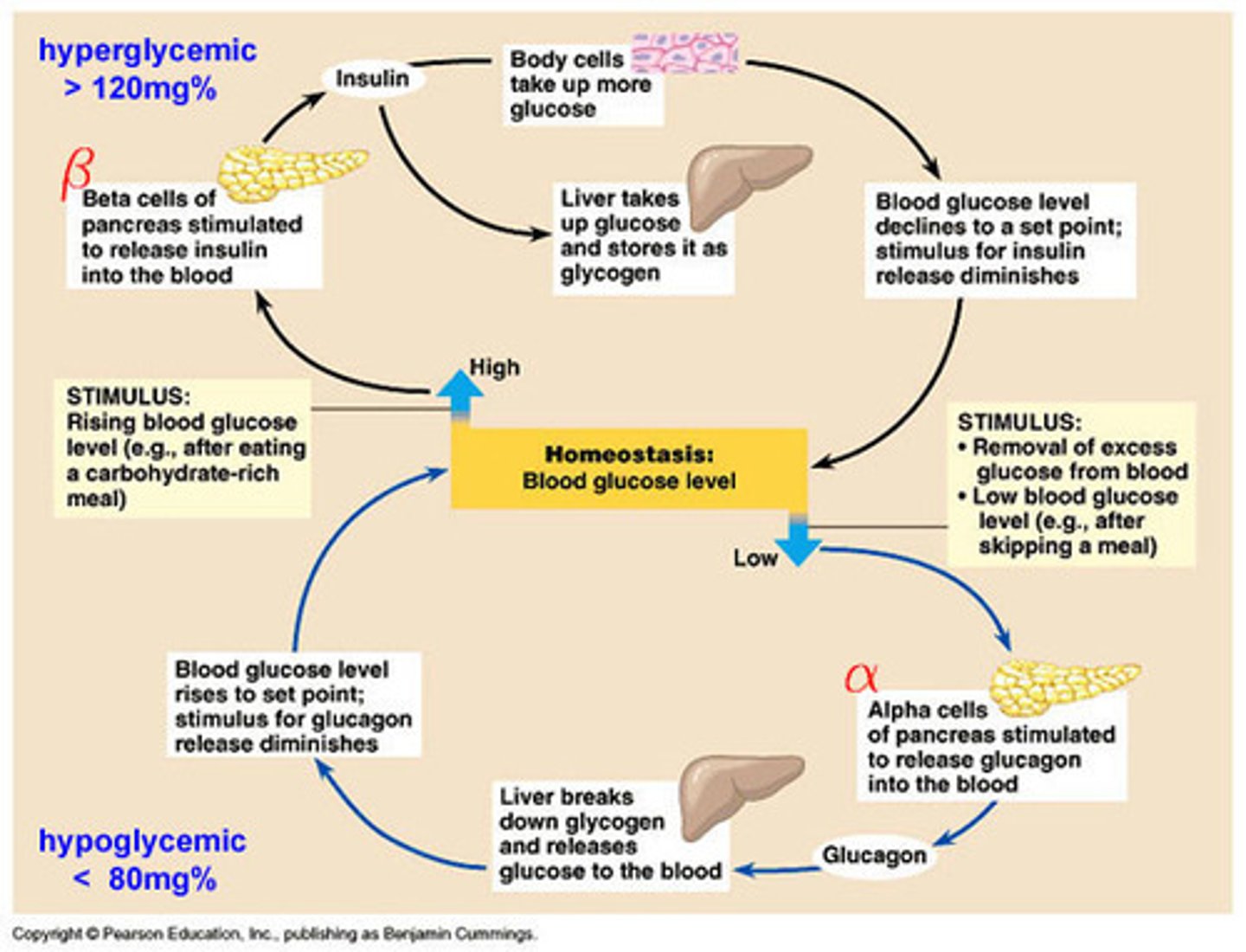
Glucagon
- A hormone produced by the pancreas which works with insulin to control blood sugar levels
- It increases blood glucose concentration by converting glycogen into glucose
Herbicide
A type of pesticide used to kill unwanted plants (weeds)
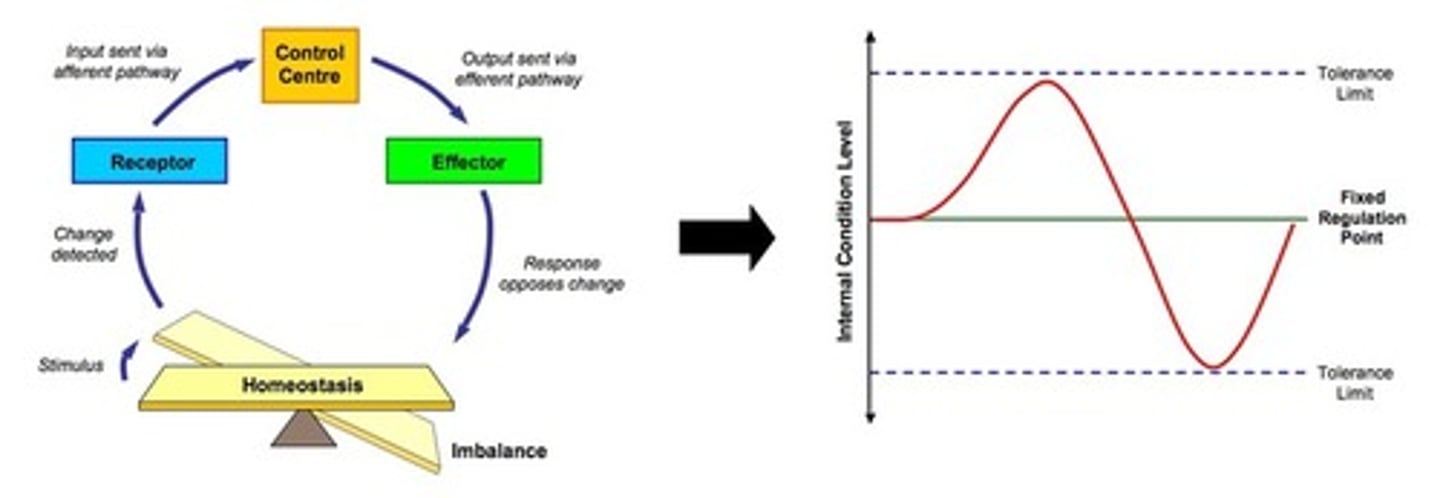
Homeostasis
The maintenance of a stable internal environment in the body despite fluctuations in internal and external conditions
Hormones
- A chemical messenger secreted by the ENDOCRINE GLANDS into the bloodstream and transported to receptors on TARGET ORGANS
- The can be slow and long lasting (oestrogen) or fast (adrenaline)
- They control the body processes that constantly need adjusting (body temperature)
Hypothalamus
- The part of the brain that is the regulation centre for temperature and water balance of the body
Infertility
The inability to reproduce after 12 months or more of unprotected sex
Insulin
- A hormone produced by the pancreas which controls the body's blood sugar levels
- It works to decrease glucose levels by turning glucose to glycogen which is stored in the liver
- If glucose levels are too low, the pancreas releases glucagon making the liver change glycogen back to glucose
Fertility Treatment - In vitro fertilisation (IVF)
- The fertilisation of an egg using sperm outside of the body
- IVF is used when a couple are having difficulty conceiving
- Doctors collect eggs from the mother and sperm from the father, fertilising them outside of the body
- They are collected in a petri dish and are placed back into the womb after the embryos start to develop
The Eye - Iris
- Its the coloured ring of muscle tissue
- It alters the pupil's size by contracting or relaxing to control the amount of light entering the eye
Kidney
The organ in the body that maintains water balance and produces urine.
The Eye - Lens
- It is a transparent biconcave lens
- It further refracts light to focus it onto the retina
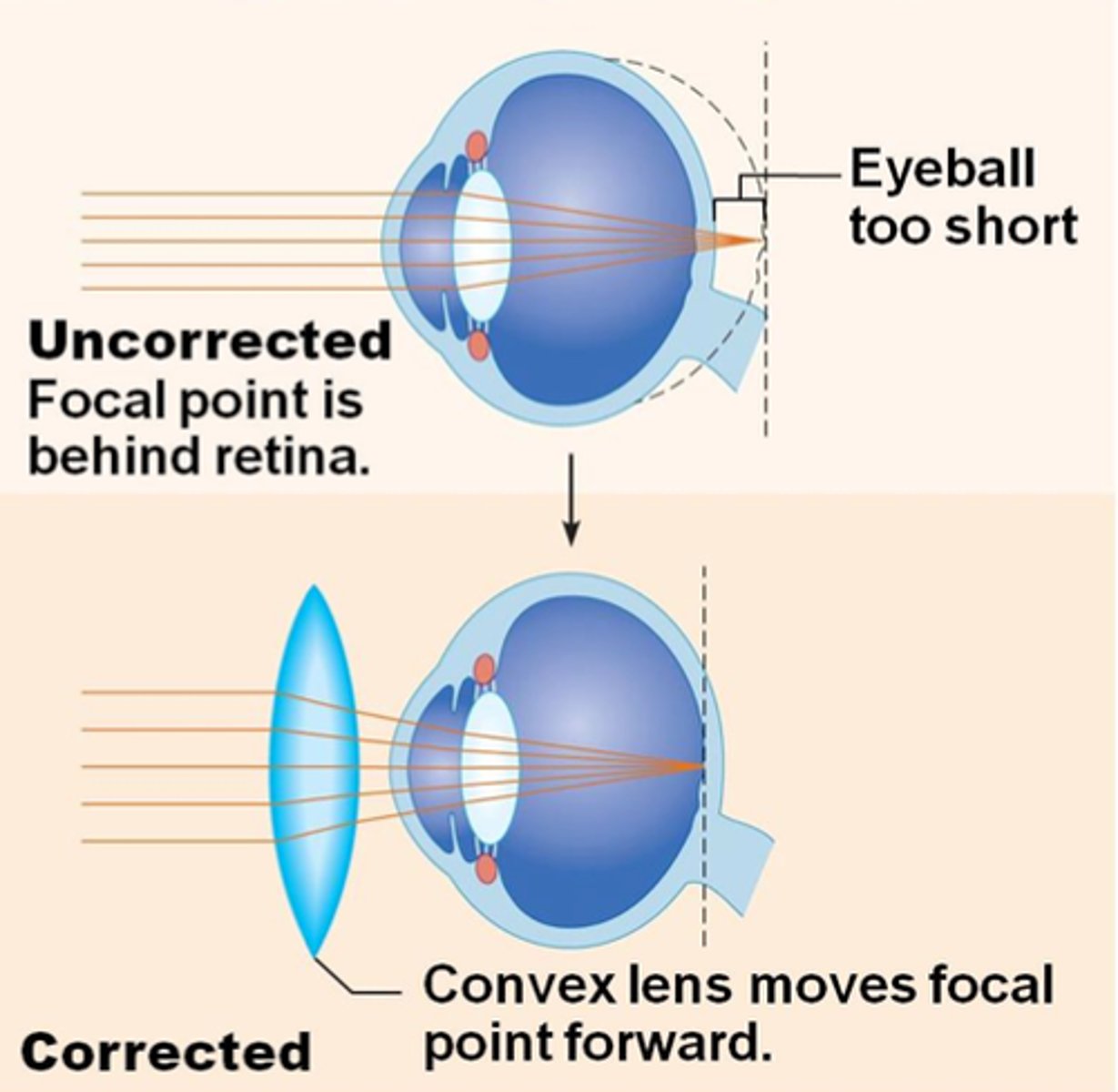
The Eye - Long Sightedness (Hyperopia)
- A defect of the eye where distant objects appear out of focus
- This is due to the convergence of light rays behind the retina
- Its when the person's lens is too weak or their eyeball is too short
Menstrual Cycle - Luteinising Hormone (LH)
- A female reproductive hormone released by the pituitary gland
- It stimulates the release of an egg (ovulation)
- It stimulates Progesterone
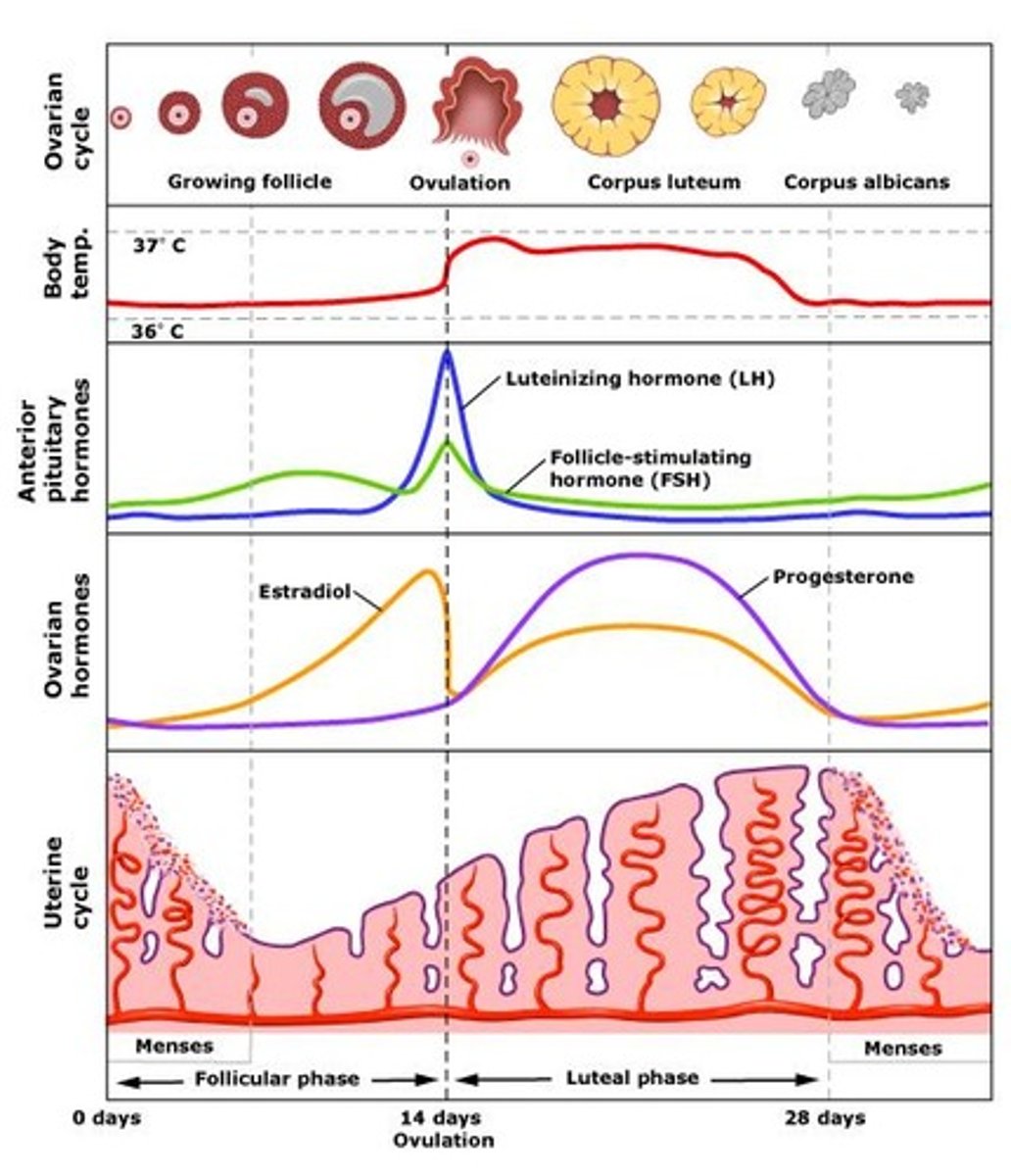
The Brain - Medulla
- The part of the brain responsible for non-voluntary movement such as breathing rate and heart rate
Menstrual Cycle
- The monthly cycle in women that involves the development of the uterus lining, ovulation, maintenance of the uterus lining and its shedding
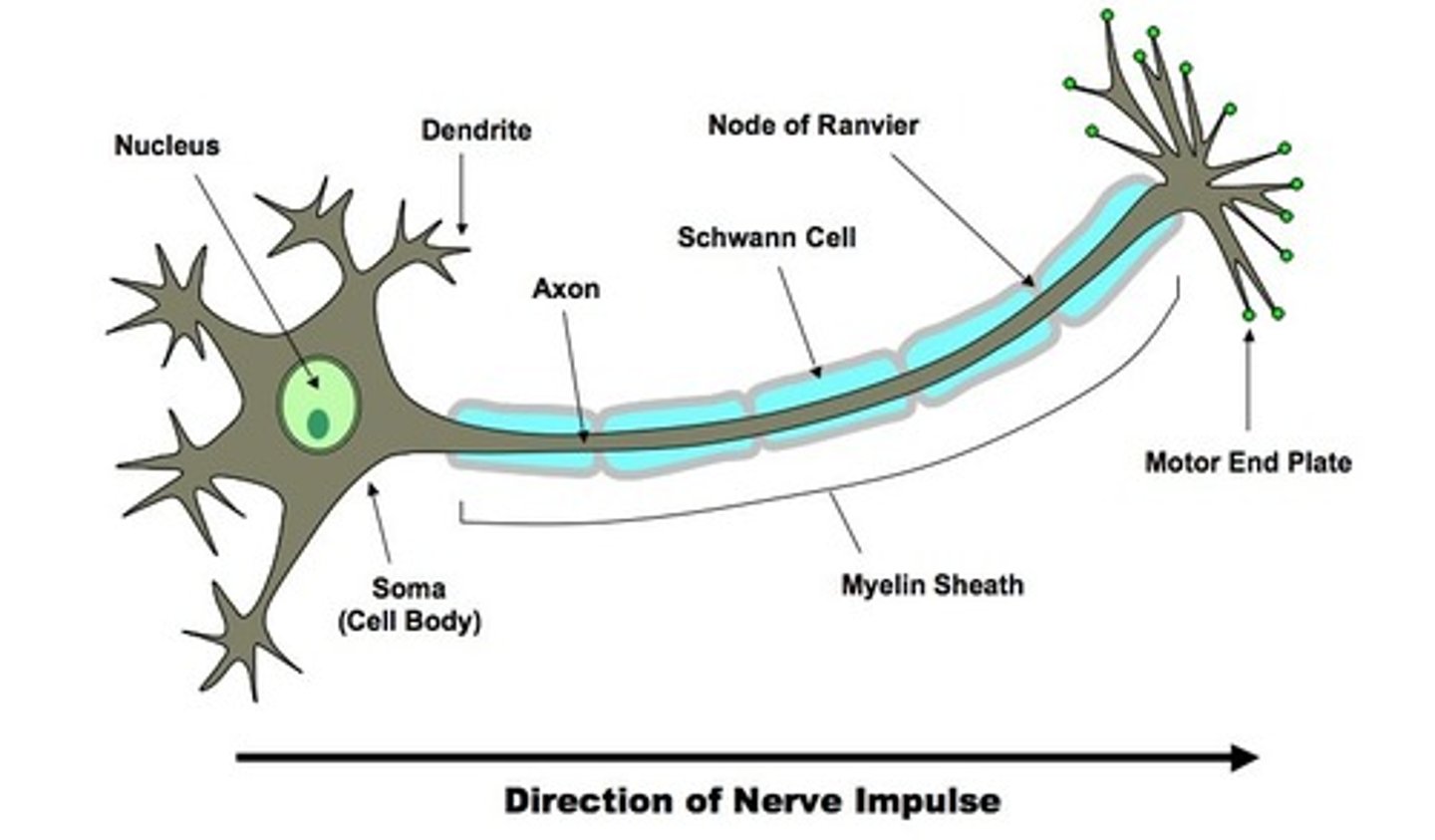
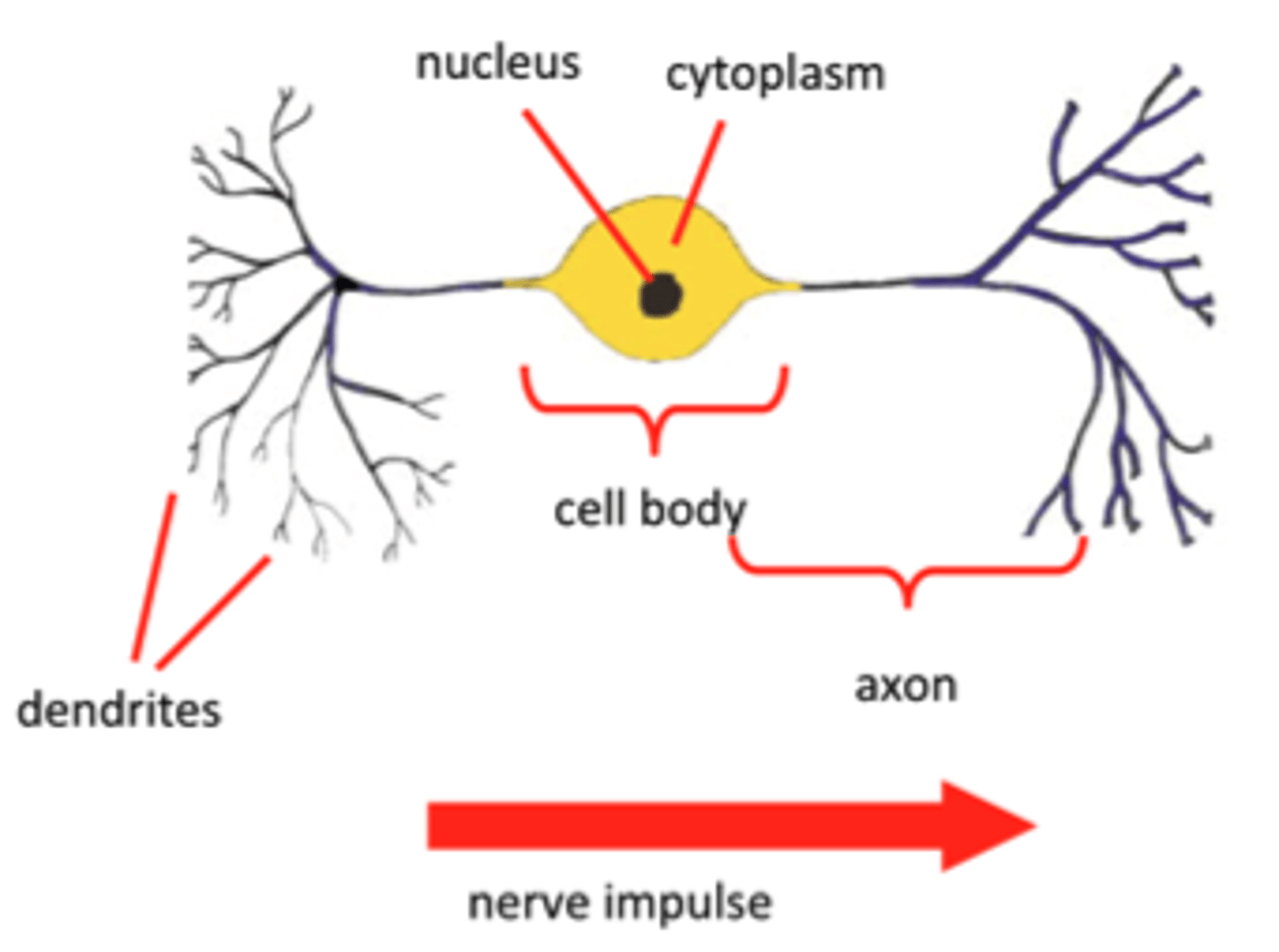
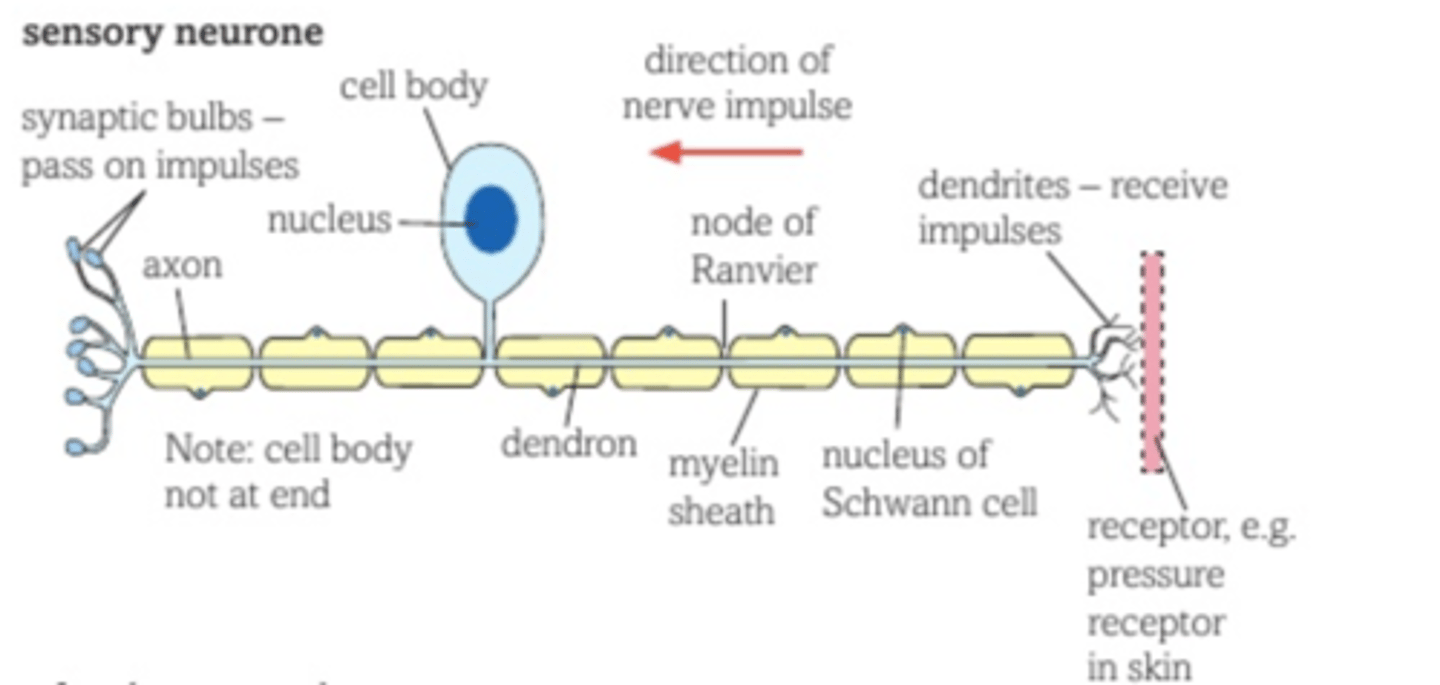
Motor neurone
The neurone that transmits impulses from the relay neurone to the effector to produce a response
Negative Feedback System
- A system which works to reverse the initial stimulus
- It is a type of control used in homeostasis
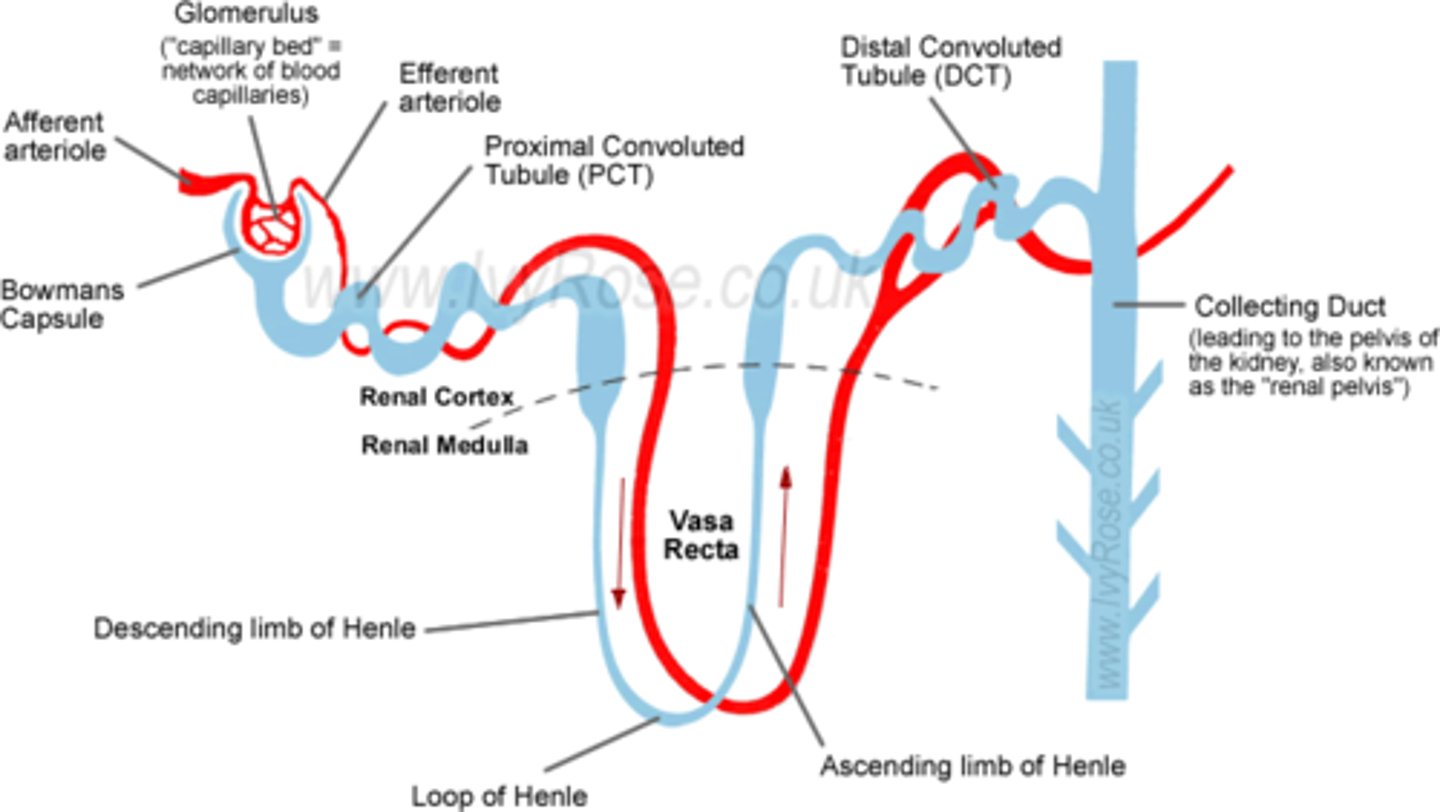
Nephron
- A kidney filtering unit
- Blood enters the kidney at high pressure from the renal artery which leads to the glomerulus which contains a knot of capillaries
- Blood vessels narrow, increasing blood pressure which forces small molecules out the capillary wall into the Bowman's capsule
- Selective reabsorption happens as the filtrate moves through the nephron tubule
- It moves through the loop of Henlé to the collecting duct where it regulates the amount of salt / water in the body by reabsorbing extra salts or water
- Excretion happens when waste solution collects in the the collecting duct and travels to the bladder before it is removed
Menstrual Cycle - Oestrogen
- A female sex hormone produced in the ovaries
- It regulates the menstrual cycle and causes the lining of the uterus to build up
- It inhibits FSH and stimulates the release of LH
The Eye - Optic nerve
- It is the nervous tissue
- It carries nerve impulses between the brain and the eye
Osmosis
The net movement of water molecules from a region of high water concentration to a region of low water concentration across a partially permeable membrane.
Osmotic lysis
When water moves into an animal cell causing it to burst.
Osmotic shrinking
When water moves out of an animal cell causing the cell to shrink.
Parthenocarpy fruit development
The development of seedless fruit.
Tropism - Phototropism
- The growth response of a plant to unilateral light
- The stem shows positive phototropism as it grown towards the light to photosynthesis more to increase its chance of survival
- Roots show negative phototropism as they grow away from the light, downwards into the soil
The Brain - Pituitary gland
- The gland that stores and releases hormones which regulate many bodily functions
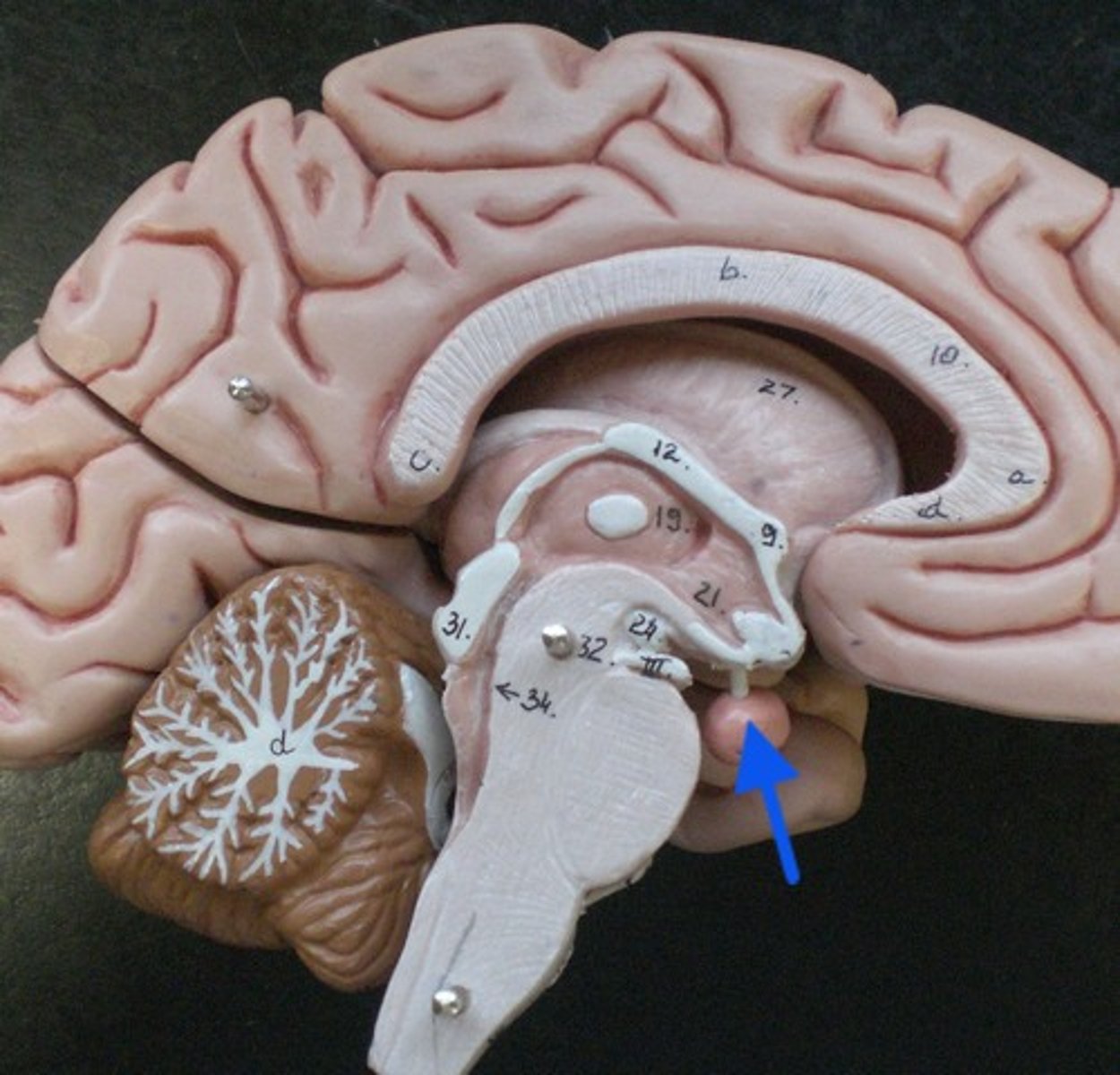
Menstrual Cycle - Progesterone
- The hormone that maintains the uterus lining during the later stages of the menstrual cycle and pregnancy
- It inhibits LH
The Eye - Pupil
- A hole in the centre of the iris
- It is controlled by the muscles of the iris and changes size depending on the brightness of the light
- It allows light to enter the eye
Cell Receptors
- A cell that recognises a specific the stimulus
- They are found in the sense organs
- They change the stimulus into an electrical impulse that travels to your central nervous system
Reflex arc
The pathway of neurones involved in a reflex action:
Relay neurone
The neurone that transmits electrical impulses from the sensory neurone to the motor neurone
Renal artery
The blood vessel that provides the kidney with blood.
Renal vein
The blood vessel that takes blood away from the kidney.
The Eye - Retina
The layer at the back of the eye that contains light receptors and is sensitive to light
Root cuttings
A method of cloning plants in which a root is cut from a parent plant and replanted in compost.
Rooting powder
A powder that contains auxins. The cut root is dipped into this before being replanted (during root cuttings).
Sensory neurone
The neurone that detects the stimulus and transmits the electrical impulse to the relay neurone located in the spinal cord
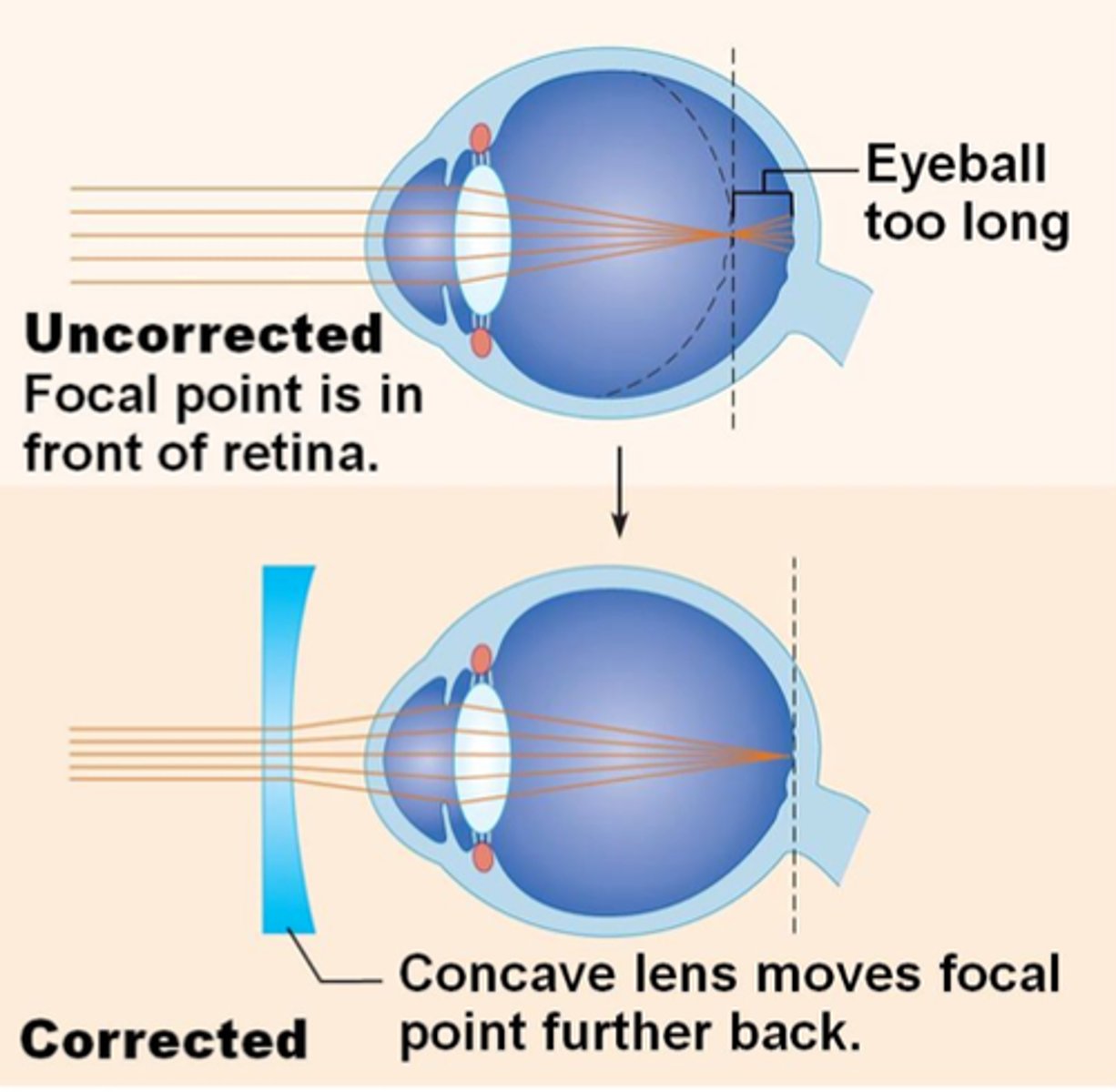
The Eye - Short Sightedness (Myopia)
- A defect of the eye where distant objects appear out of focus - This is due to the convergence of light rays in front of the retina
- The person's eyeball is too long or the lens is too strong
The Eye - Suspensory Ligaments
- It is ligament tissue
- It connects the lens to the ciliary muscle.
Synapse
The junction between two neurones (nerve cells).
Hormones - Testosterone
The male reproductive hormone that controls sperm production and the development of the secondary sexual characteristics.
Hormones - Thyroxine
- A hormone released by an endocrine gland (thyroid gland) that controls the metabolic rate (the speed that the body transfers energy from its chemical stores to perform functions)
- It controls the rate of glucose uptake during respiration and promotes growth
Tissue culture
A method of cloning plants where plants are grown in a growth medium containing many nutrients.
Type 1 Diabetes
- A condition in which the pancreas fails to produce insulin resulting in high blood sugar levels
- Their immune system has destroyed the pancreatic cells
- The condition occurs from childhood
- It can be controlled by injections of insulin or diet
Type 2 Diabetes
- A condition in which a person develops insulin resistance or doesn't produce enough insulin
- Occurs later in life and is linked to obesity
- Can be controlled by regulation of carbohydrate intake and exercise
Urine
- A liquid produced by the kidneys to help maintain water balance
- It contains mineral ions, water and urea which is toxic
- It is produced when small molecules pass into tubes inside the kidney which filters the small particles out
- It then puts the useful substances back into the blood (reabsorbtion)
Vasoconstriction
The constriction of blood vessels.
Vasodilation
The dilation of blood vessels.
Water potential
A measure for the tendency of water to move from one area to anotherarea. It is represented by the sign Ψ (Psi).
The Brain
- The mass of nerve tissue that is the main control centre of the nervous system
- It processes all information connected by receptor cells
- It receives and processes information from the hormonal system and provides a coordinated response
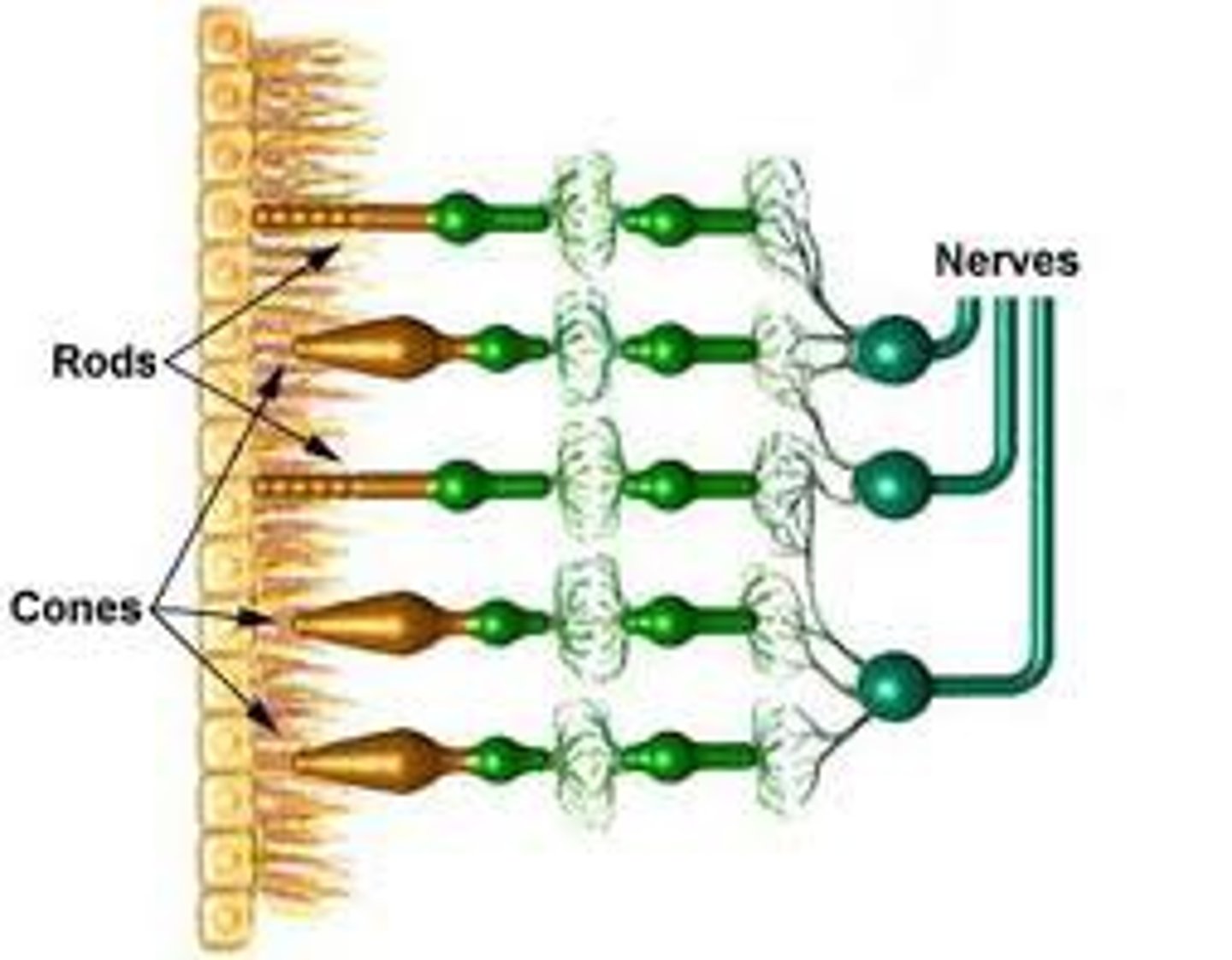
The Eye - Rods
The allow you to see in low level of lights
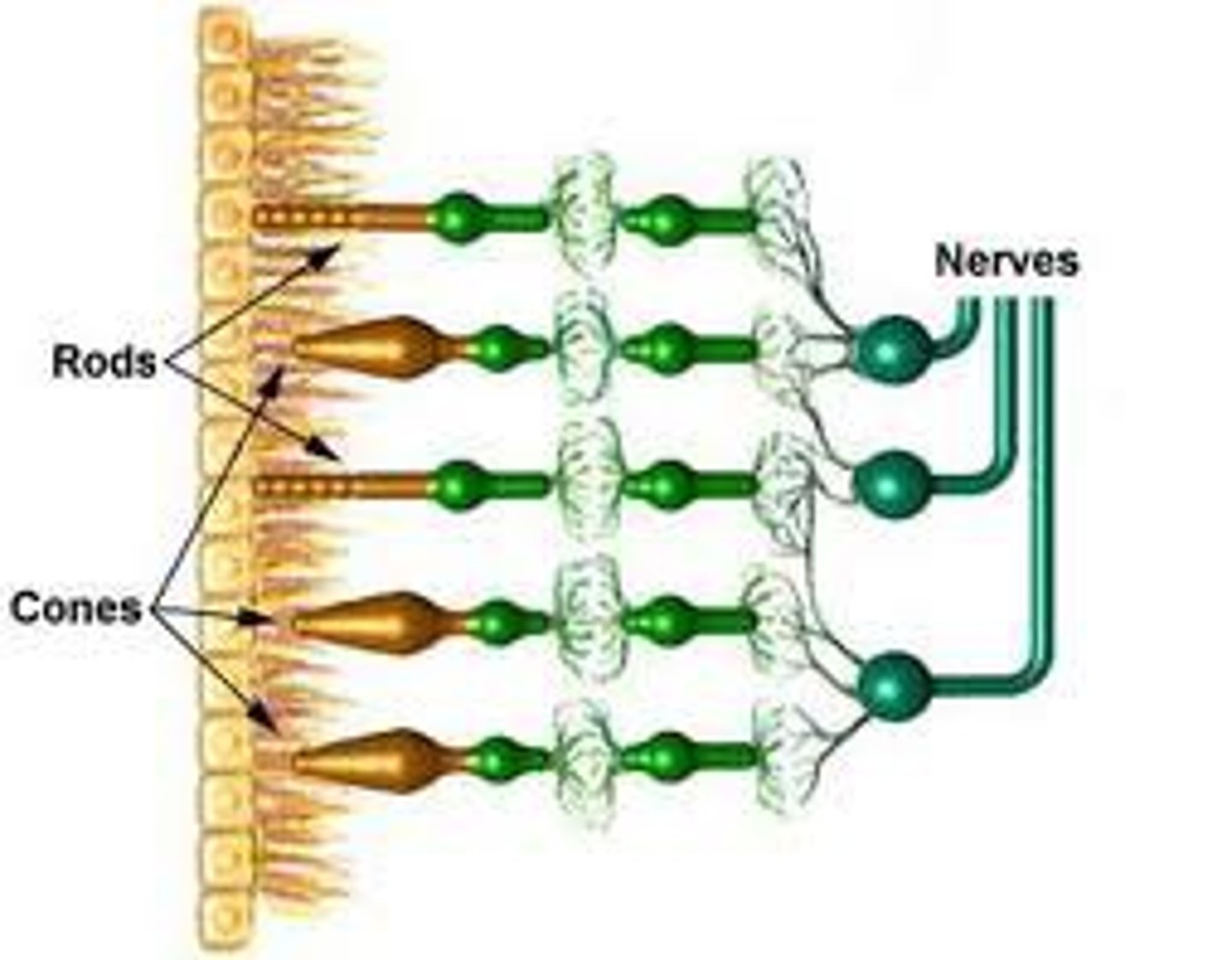
The Eye - Cones
Different cone cells respond to different light (red, blue, green)
Endocrine Glands - Thyroid Glands
It takes iodine (found in food) and coverts it to thyroxine by combining it with the amino acid tyrosine
Endocrine Glands - Adrenal Glands
- They are found near the kidney
- Adrenal glands produce hormones that help regulate your metabolism, immune system, blood pressure, response to stress and other essential functions
Target Cells / Organs
A tissue or organ on which a hormone exerts its action; generally, a tissue or organ with appropriate receptors for a hormone
- Hormones diffuse out the blood and bind to the target cells to produce a response
Contraception - Non Hormonal
- These are barriers preventing sperm from contacting the egg or physical devices that release chemical compounds
- These chemicals kill sperm cells (spermicides) or prevent the implantation of fertilised eggs
Contraception - Hormonal
- The use of hormones to disrupt the normal female reproductive system
Fertility Treatment - In vitro fertilisation (IVF) - Positives
- Allows parents to have children when they could not
- Enables older parents, meaning younger women can focus on their careers
Fertility Treatment - In vitro fertilisation (IVF) - Negatives
- Procedure could fail or women might have multiple births
- Its not a natural process
- It is expensive
Fertility Treatment
- Some people can't conceive as they have
= Blocked Fallopian tubes
= Not enough Sperm
= Lack of mature eggs
- The conditions above can be fixed using hormones like FSH which can be used as an artificial drug to trigger oestrogen and progesterone
Contraception - Condoms
- Type = Non hormonal
- Effectiveness = 95 - 98 %
- How it works = Placed over the penis or inside the virginal which prevents sperm entering the virginal
- Extra = Prevents the spread of STDs (sexually transmitted diseases)
Contraception - Diaphragm / Cervical Cap
- Type = Non hormonal
- Effectiveness = 92 - 96 %
- How it works = Inserted into virginal to cover the cervix to prevent sperm entering the uterus
- Extra = Not effectiveness unless used with spermicide and must be removed 6+ hours after sex
Contraception - Intrauterine Device (IOD / Coil)
- Type = Non hormonal
- Effectiveness = 99 %
- How it works = Inserted into uterus and releases copper, killing sperm to prevent implantation of fertilised egg
- Extra = Remains effective for 5 - 10 years
Contraception - Oestrogen Pills
- Type = Hormonal
- Effectiveness = 99 %
- How it works = Prevents ovulation
- Extra = Taken daily at the same time every day
Contraception - Progesterone Pills
- Type = Hormonal
- Effectiveness = 99 %
- How it works = Thickens mucus from cervix to stop sperm from entering
- Extra = Taken daily at the same time every day
Contraception - Intrauterine System (IUS)
- Type = Hormonal
- Effectiveness = 99 %
- How it works = Inserted into the uterus and thickens mucus from cervix to stop sperm from entering
- Extra = Remains effective for 3 - 5 years
Tropism
- A growth response of a plant toward or away from a stimulus
- If it grows towards the stimulus it is positive tropism
- If it grows away from the stimulus it is negative torpism
Body Temperature
- It works at 37°C which is it's optimum temperature for the enzymes to work at
- Small temperature changes means the body stops working efficiently
- The thermoregulatory centre in your brain is responsible for regulating your body temperature
- It relies on signal received by your skin cells and receptor cells
Body Temperature - Too Hot
- This causes enzymes to denature so body reactions cannot occur (40 - 42°C = death)
- Your brain triggers changes to make the body cool down
- Body hairs lower and lie flat, preventing the insulating layer of air
- Sweat glands produce sweat which uses energy by heating when it is evaporated
- Blood vessels supplying capillaries near the surface of the skin widen (vasodilation) cooling the blood
Body Temperature - Too Cold
- This causes enzymes to react too slowly, respiration doesn't release enough energy and cells begin to die (below 35°C = hypothermia and death)
- Your brain triggers changes to make the body warm up and prevent heat loss
- Body hairs rise, creating an insulating layer of air
- Sweat glands stop producing sweat
- Blood vessels supplying capillaries near the surface of the skin narrow (vasoconstriction)
- Shivering begins as your muscles contract and relax quickly making your cells respire more
Blood Sugar Levels
- Glucose is an energy store
- Chemical reactions transfer energy from glucose to ATP which is used by cells allowing them to perform normal body functions
- When exercising, more glucose is needed as the body transfers more energy causing your blood sugar levels to drop, preventing cells from respiring effectively
Water Balance
When your body regulates the amount of salts and water present which enter by consuming food and drinks
- Water and salts are lost by sweating, urine and breathing
- It stops lysis (too much water) and crenation (too much salts)
Water and the Body
- A person should drink about 2 litres of water a day
- If exercise is performed or you are exposed to high temperatures, then more water is needed
Lack of Water
- It triggers the thirst response
- An impulse is sent from your brain telling you to take on more fluids
- Kidneys produce less urine and the urine will be darker
- Not drinking water results in dehydration which can cause headaches, dizziness and lack of energy
- Dehydration can lead to permeant damage to the liver and kidneys
- It can be fatal
Excess Water
- It causes the water potential of your plasma to rise above the water potential of your cells
- Your kidneys produce more urine and the urine will be lighter
- Large amounts of water, if consumed rapidly can cause cells to burst
- It can lead to muscle cramping, confusion and seizure
- It can be fatal if water moves to brain cells
Hypertonic Sports Drinks
They contain high levels of sugar and salts
Hypotonic Sports Drinks
They contain low levels of sugar and salts
Isotonic Sports Drinks
They contain ion concentrations equal to those in blood
The Nervous System
- It detects changes in your external environment (stimulus) through a group of cells (sensory receptors)
- It sends this information to your brain where the brain decides on the appropriate response
- Then an impulse is sent to another part of your body like the muscles or glands (effectors)
Coordinated Response
Stimulus → Receptor Cells → Sensory Neurone → Spinal Chord → Brain → Spinal Chord → Motor Neurone → Effector → Response
- This whole process takes about 0.7 seconds
- It is a voluntary action