Mandibular Anesthesia Part 2
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
114 Terms
what are the 3 techniques that can be used to administer inferior alveolar nerve blocks?
Standard “classic” technique
Gow-Gates Mandibular technique
Akinosi “closed mouth” technique
what are 4 technique/reasons inferior alveolar nerve block might fail?
deposited too low (below mandibular foramen)
deposited too anteriorly to ramus
deposited too posteriorly on ramus
accessory innervation (mylohyoid n.)
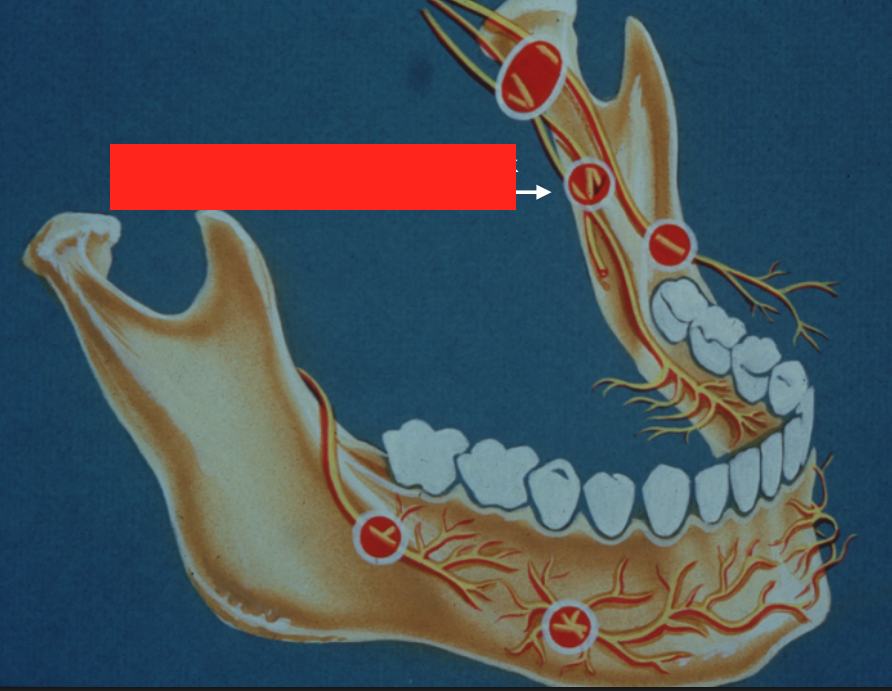
target site for which injection?
standard inferior alveolar nerve block AND lingual nerve block (can anesthetize both nerves using single injection at this site)
during inferior alveolar nerve block, if anesthetic is deposited too low (below mandibular foramen), you can correct it by reinjecting ____ mm above the previous site.
5-10 mm
what are some anatomical reasons an inferior alveolar nerve block might fail?
Bifid inferior alveolar nerve/canal (A second mandibular foramen may exist)
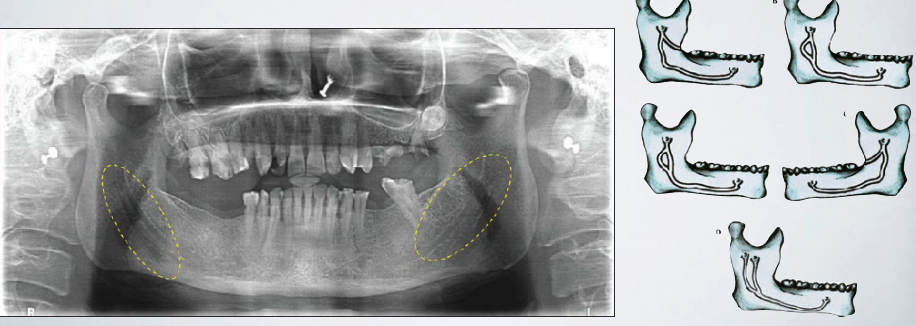
if a patient has a bifid inferior alveolar nerve/canal, the nerve block might fail. how can you correct this?
second injection inferior to the normal anatomical landmark
what nerve block is indicated when lingual soft tissue anesthesia is required?
lingual nerve block
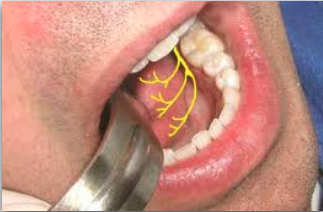
what nerve is indicated here?
lingual n.
lingual nerve block
what contraindications occur for lingual nerve block?
infection/acute inflammation in area of injection
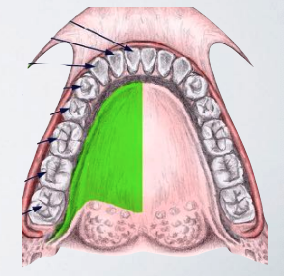
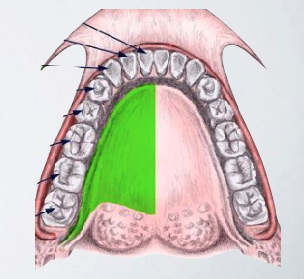
what areas are anesthetized with ›lingual nerve block?
Lingual soft tissue
Floor of the mouth
Anterior two thirds of the tongue to midline
is a separate injection usually necessary for lingual nerve block?
no (it is part of inferior alveolar nerve block)
if lingual nerve block is administered as a separate injection from IAN block, what is the proper technique?
may use a long needle but only need to advance half way
what is the proper injection/needle target site for lingual nerve block?
Same for inferior alveolar nerve block
Withdraw needle halfway after inferior alveolar nerve block and deposit local anesthetic solution
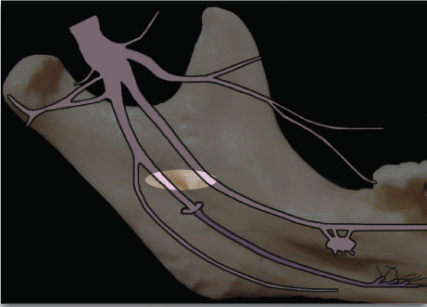
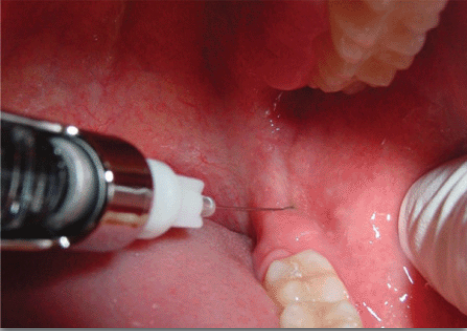
what is the proper depth of penetration for lingual nerve?
about 1/3-1/2 the length of a long needle
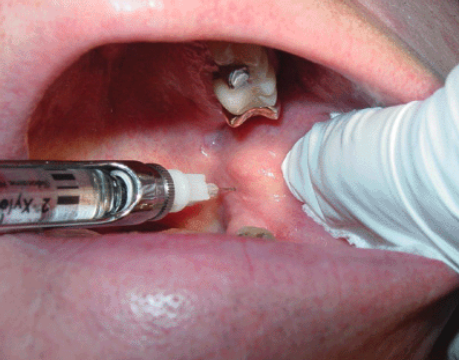
what is the proper depth of penetration for inferior alveolar nerve?
2/3-3/4 the length of a long needle
what is the proper operator position for lingual nerve block technique?
7 o’clock right side, 11 o’clock left
what is the proper needle size for lingual nerve block technique?
25 or 27 gauge long
what is the proper needle target for lingual nerve block technique?
Same as inferior alveolar nerve block
what is the proper bevel orientation for lingual nerve block technique?
not significant
what is the proper insertion point for lingual nerve block technique?
Same as inferior alveolar nerve block
what is the proper insertion pathj for lingual nerve block technique?
Through the mucosa and buccinator muscle, from the opposite premolars, parallel to occlusal plane and towards the mandibular sulcus
what is the proper insertion depth for lingual nerve block technique?
10-13 mm (1/3- 1/2 of a long needle)
what is the proper anesthetic volume for lingual nerve block technique?
0.3 to 0.5 mL
what nerve block is indicated when mandibular posterior buccal soft tissue is required for dental procedure?
long buccal nerve block
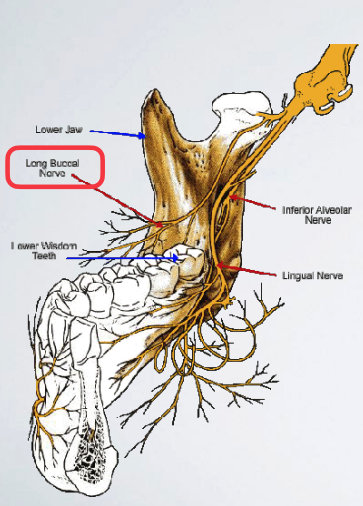
what is a contraindication for long buccal nerve block?
infection/acute inflammation
what areas are anesthetized with long buccal nerve block?
Soft tissue and periosteum buccal to the mandibular molar teeth
long buccal nerve block
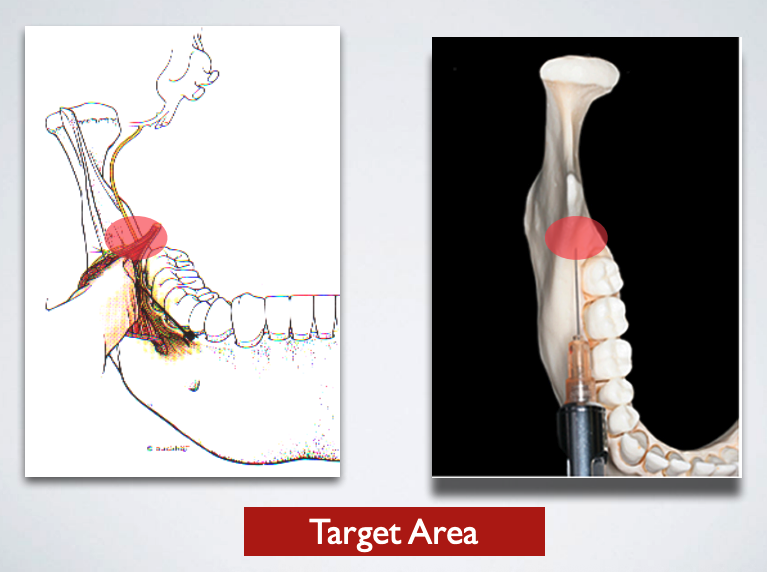
target area of which nerve block?
long buccal nerve block
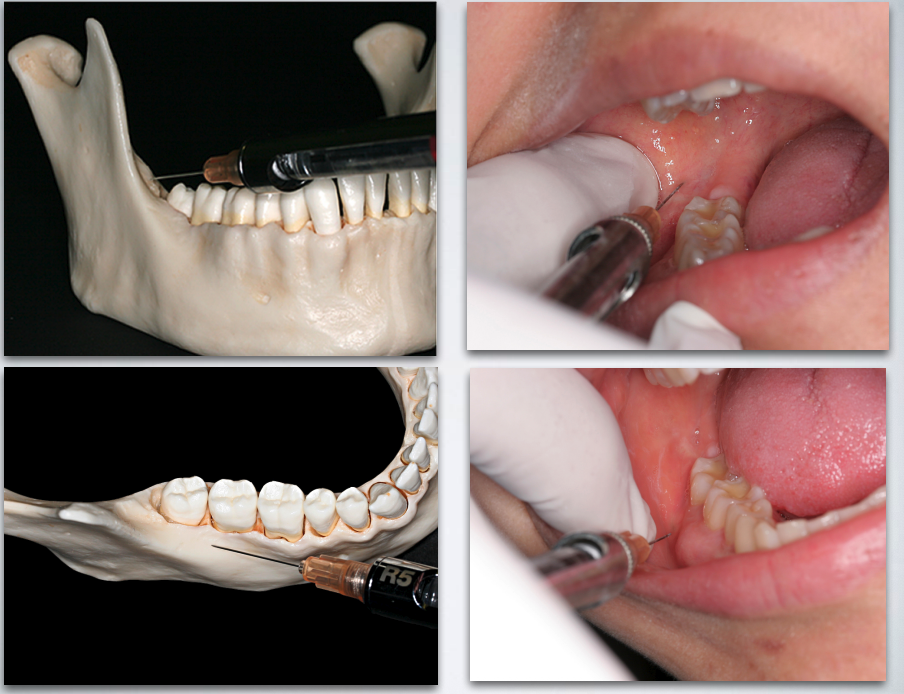
long buccal nerve block
what is the proper injection site for long buccal nerve block?
buccal side of 2nd or 3rd molar (injection depth is very shallow)
what is the proper operator position for long buccal nerve block?
7 o’clock right side, 11 o’clock left
what is the proper needle size for long buccal nerve block?
25 or 27 gauge long (usually administered together with IANB)
what is the proper needle target for long buccal nerve block?
Buccal nerve as it crosses the anterior border of the ramus at the level of the occlusal plane
what is the proper bevel orientation for long buccal nerve block?
toward bone
what is the proper insertion point for long buccal nerve block?
Just medial to the external oblique ridge at the level of the occlusal plane
what is the proper insertion path for long buccal nerve block?
Through the mucosa and buccinator muscle until bone in gently contacted on the anterior ramus
what is the proper insertion depth for long buccal nerve block?
2 – 3 mm (very superficial)
what is the proper anesthetic volume for long buccal nerve block?
0.3-0.5 mL
what is the proper area of anesthesia for long buccal nerve block?
Buccal mucosa and cheek adjacent to the mandibular molars; variable extent of effect
mylohyoid nerve can provide portion of pulpal innervation to which mandibular teeth?
most commonly in the mesial portion of the mandibular 1st molar or premolars
______ nerve block can be a useful supplement to inferior alveolar block when it appears to be inadequate
Mylohyoid
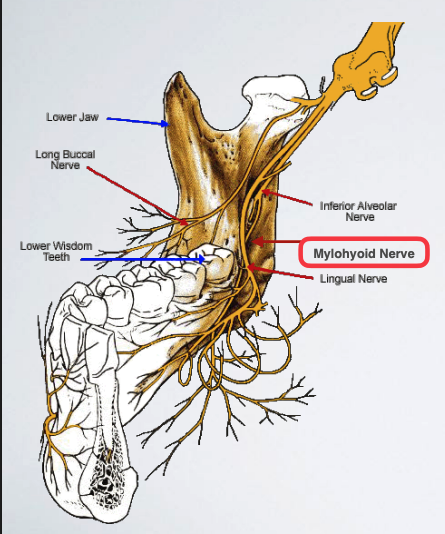
what is the proper technique for mylohyoid nerve block?
Use 25 gauge long needle
Retract the tongue
Direct the syringe from the opposite side
Direct needle tip to the apical region of the tooth immediately posterior to the tooth in question, until bone is contacted
Aspirate and deposit ~0.6 ml of solution
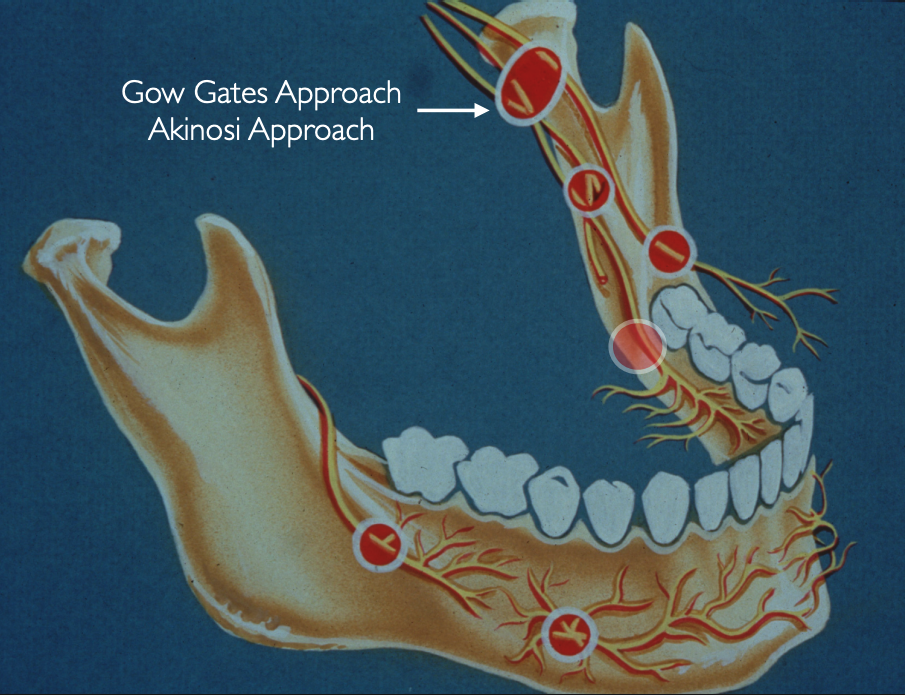
Gow Gates Approach and Akinosi Approach
what nerves are anesthetized with gow gates technique?
Inferior alveolar nerve
Mental/incisive nerve
Lingual nerve
Mylohyoid nerve
Auriculotemporal nerve
Buccal nerve (in most cases)
why is gow gates technique considered a “true” manidbular nerve block?
because the injection site is a lot higher up on the mandibular nerve, it is able to anesthetize more branches/more of the mandibular nerve than your standard with a singular injection
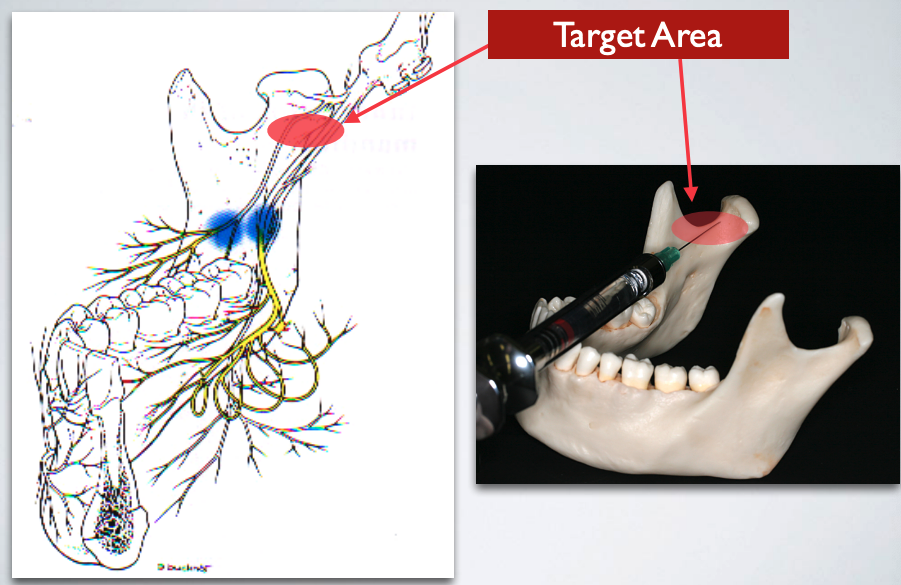
target area of which technique?
gow gates technique
gow gates technique (IAN)
the following areas are anesthetized with which nerve block?
All mandibular teeth on the side of injection
Surrounding periodontium and alveolar
Buccal and lingual soft tissue
Anterior two thirds of the tongue and floor of oral cavity
Floor of the mouth
Body of the mandible, inferior portion of the ramus
Skin over the zygoma, posterior portion of cheek, and the temporal regions
gow gates mandibular nerve block
which nerve block is inidcated for multiple procedures on mandibular teeth?
GOW-GATES MANDIBULAR NERVE BLOCK
which nerve block is inidcated when buccal and lingual soft tissue anesthesia is required?
GOW-GATES MANDIBULAR NERVE BLOCK
which nerve block is inidcated when a classic IAN block is unsuccessful?
GOW-GATES MANDIBULAR NERVE BLOCK
what are some contraindications for GOW-GATES MANDIBULAR NERVE BLOCK?
infection/acute inflammation of injection area (rare)
pts who might bite/lacerate lip/tongue
pts unable to open mouth wide (trismus)
what are some advantages to GOW-GATES MANDIBULAR NERVE BLOCK?
singular injection for total mandibular anesthesia
higher success rate than standard
less positive aspiration than standard
fewer post-injection complications
no problems with accessory innervation
bony contact
what is the success rate with GOW-GATES MANDIBULAR NERVE BLOCK?
>95%
what are some disadvantages to GOW-GATES MANDIBULAR NERVE BLOCK?
lingual/lower lip anesthesia uncomfortblae
onset time is longer (5 min)
learning curve for high success
what is the proper insertion point for GOW-GATES MANDIBULAR NERVE BLOCK?
At the height of the ML cusp of maxillary 2nd molar, penetrate just distal to the maxillary 2nd molar
what is the target point for GOW-GATES MANDIBULAR NERVE BLOCK?
Lateral aspect of condylar neck
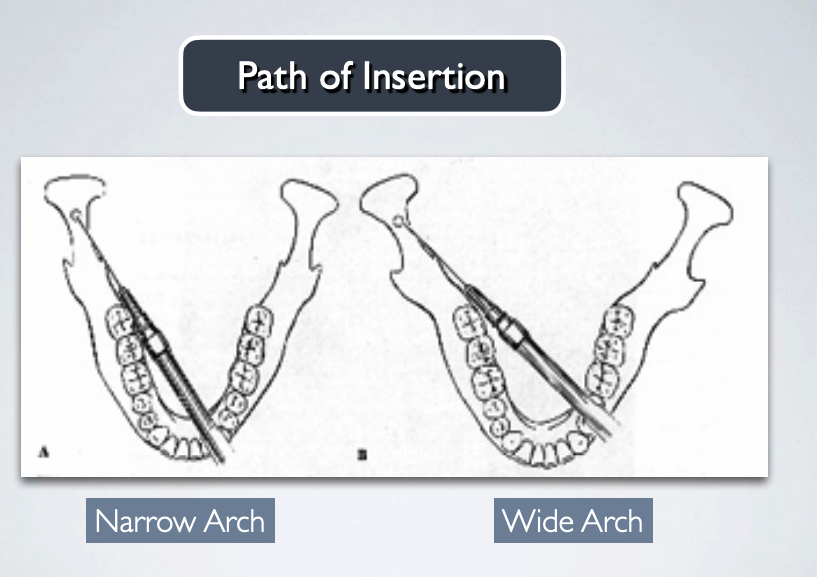
Use both intra-oral and extra-oral landmarks to establish the path of insertion
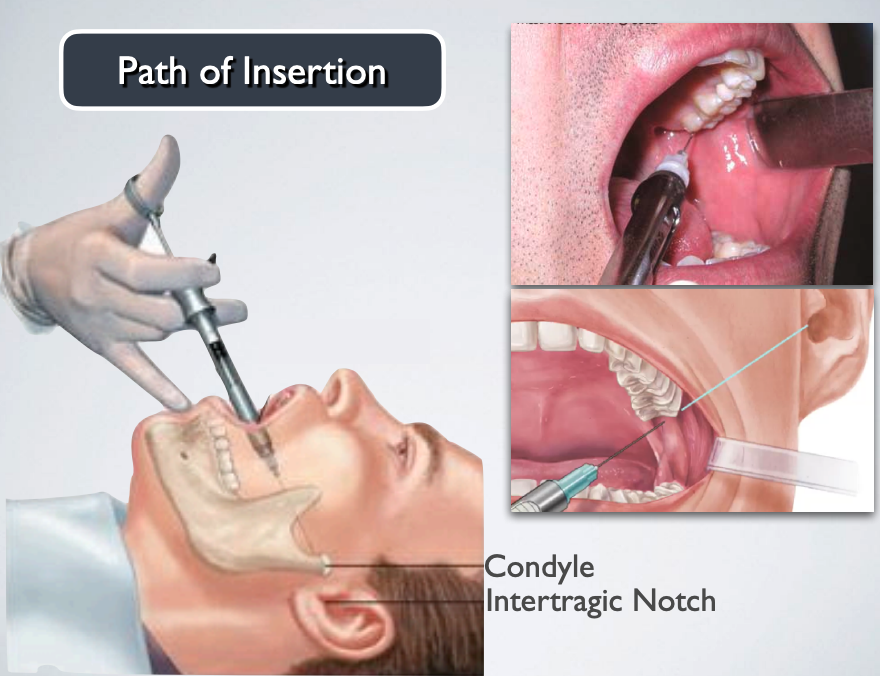
what extra oral landmarks are used for GOW-GATES MANDIBULAR NERVE BLOCK?
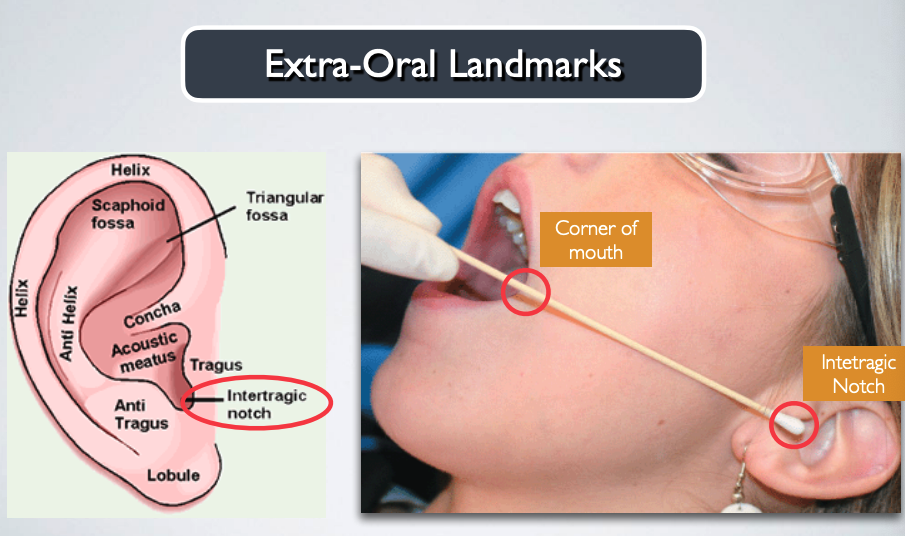
what intra oral landmarks are used for GOW-GATES MANDIBULAR NERVE BLOCK?
barrel of syringe in corner of mouth on opposite side
height of insertion = maxillary occlusal plane
needle tip just below ML cusp of maxillary 2nd molar + just distal to maxillary 2nd molar
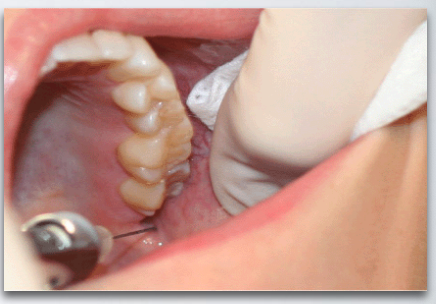
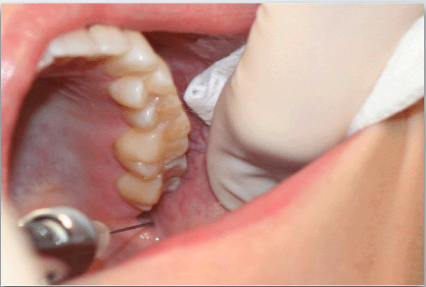
GOW-GATES MANDIBULAR NERVE BLOCK
t/f: it is very important for patients ot open their mouth as widely as possible during GOW-GATES MANDIBULAR NERVE BLOCK
true
what is the proper technique for establishing path of insertion during GOW-GATES MANDIBULAR NERVE BLOCK?
thumb palpating anterior border of ramus
index finger over intetragic notch of ear
advance needle slowly until bone is contacted (neck of condyle)
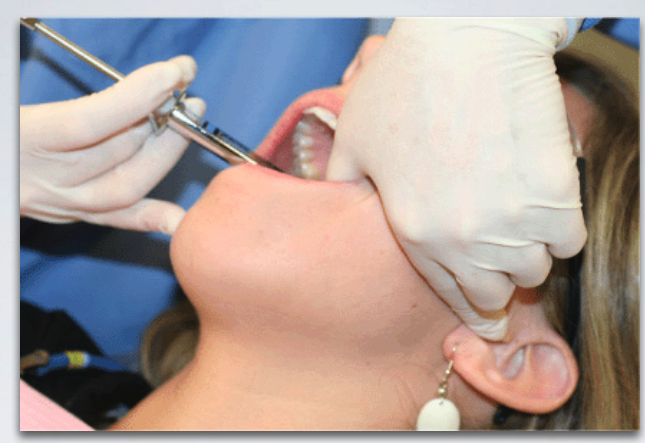
what is the average depth of needle insertion with GOW-GATES MANDIBULAR NERVE BLOCK?
25 mm
the boney contact in GOW-GATES MANDIBULAR NERVE BLOCK is the neck of the ______
condyle
what is the proper operator position for GOW-GATES MANDIBULAR NERVE BLOCK?
7 o’clock right side, 10 o’clock left
what is the proper needle size for GOW-GATES MANDIBULAR NERVE BLOCK?
25 or 27 gauge long needle
what is the proper needle target for GOW-GATES MANDIBULAR NERVE BLOCK?
Neck of the mandibular condyle, just below the insertion of the lateral pterygoid muscle when mouth is wide open
what is the proper bevel orientation for GOW-GATES MANDIBULAR NERVE BLOCK?
Not as significant
what is the proper insertion point for GOW-GATES MANDIBULAR NERVE BLOCK?
Medial to deep tendon of the temporalis muscle at the height of the mesiolingual cusp of the maxillary second molar and slightly distal to the maxillary second molar
what is the proper insertion pathj for GOW-GATES MANDIBULAR NERVE BLOCK?
Through the mucosa and buccinator muscle, usually from the opposite canine or premolars (paralleling the divergence of the tragus), in the plane established by the intertragic notch and the angles of the wide-open mouth, toward the neck of the condyle
what is the proper anesthetic volume for GOW-GATES MANDIBULAR NERVE BLOCK?
1.8-3 ml
which nerves are anesthetized with AKINOSI CLOSED MOUTH TECHNIQUE?
Inferior alveolar nerve
Mental/Incisive nerve
Lingual nerve
Mylohyoid nerve
which technique anesthetizes the following areas?
Mandibular teeth to the midline
Body of the mandible
Buccal soft tissue served by mental nerve
Anterior two thirds of tongue
Floor of oral cavity
Lingual soft tissue
AKINOSI CLOSED MOUTH TECHNIQUE
what are advantages of AKINOSI CLOSED MOUTH TECHNIQUE?
Relatively atraumatic Patient does not need to open the mouth Less post injection complications Lower aspiration rate (<10%)
t/f: it is thought to be more effective if the patient keeps their mouth open for about 30 seconds after administering GOW-GATES MANDIBULAR NERVE BLOCK
true. keeps nerve closer to where LA was administered
what are disadvantages of AKINOSI CLOSED MOUTH TECHNIQUE?
Difficult to visualize path of insertion/depth of insertion
No bony contact
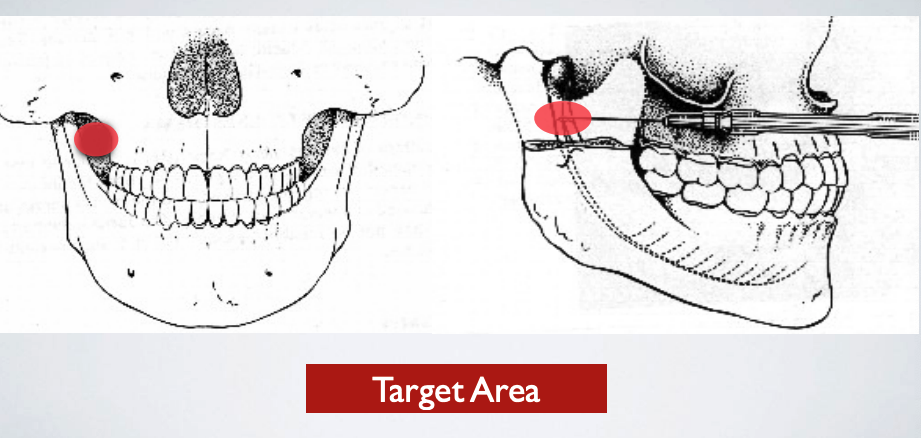
target areas for which technqieu?
AKINOSI CLOSED MOUTH TECHNIQUE
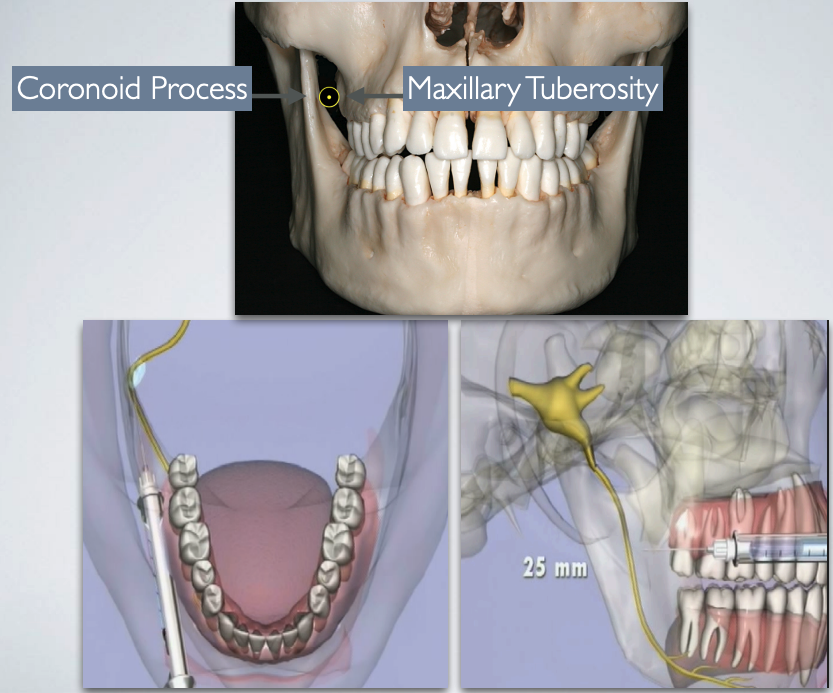
AKINOSI CLOSED MOUTH TECHNIQUE
what is the proper height of insertion with AKINOSI CLOSED MOUTH TECHNIQUE?
mucogingival junction of maxillary 2nd or 3rd molar
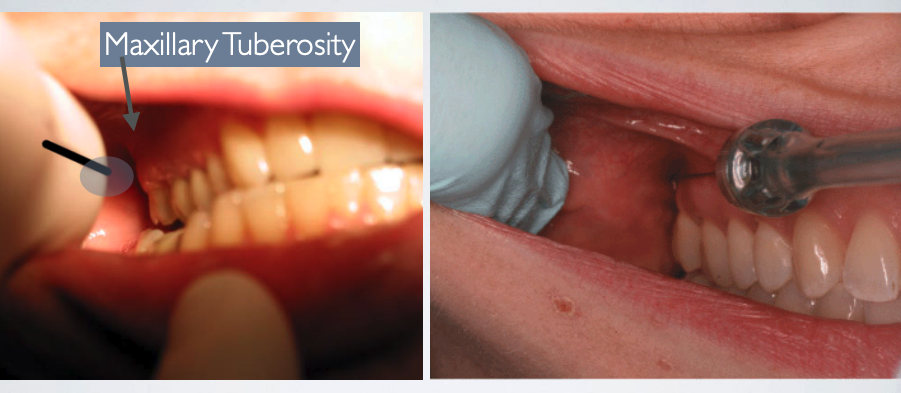
what is the proper insertion depth with AKINOSI CLOSED MOUTH TECHNIQUE?
25 mm (measured from maxillary tuberosity)
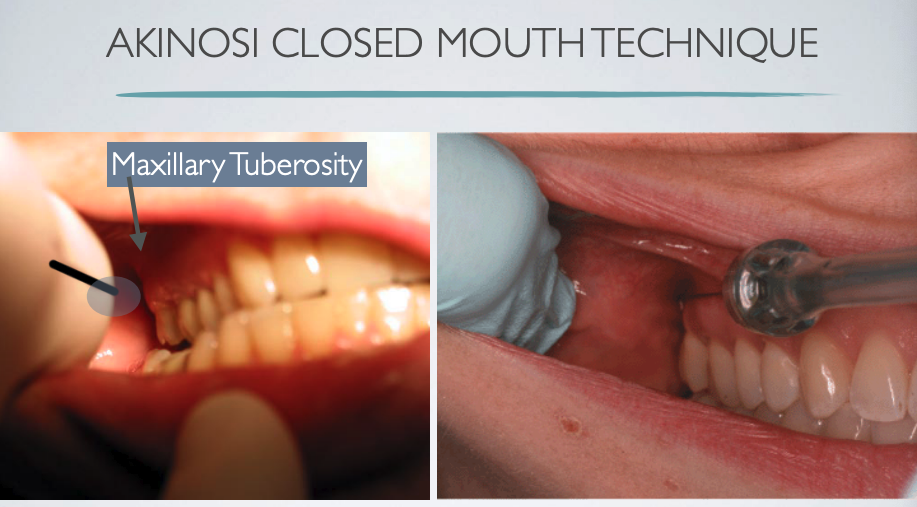
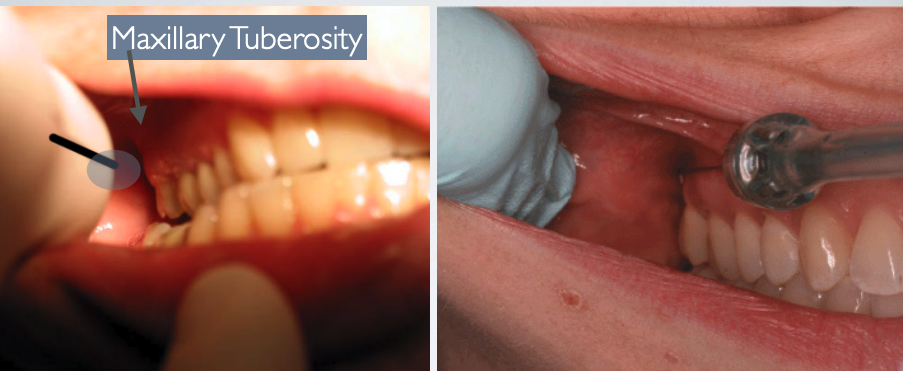
AKINOSI CLOSED MOUTH TECHNIQUE
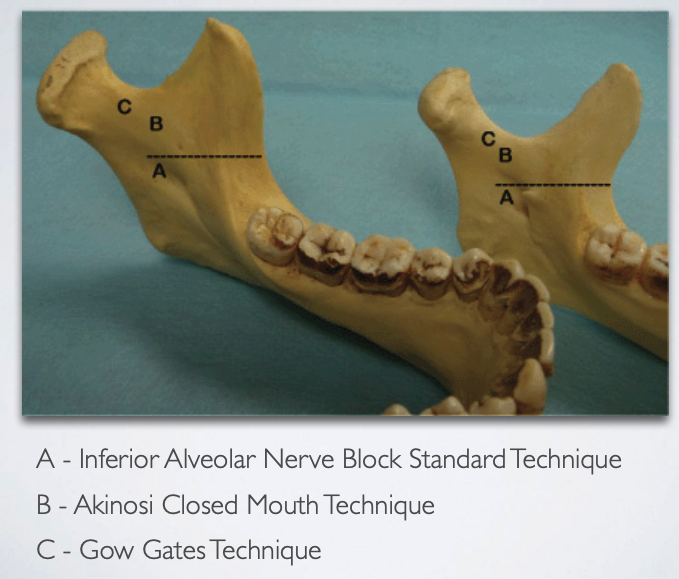
which target site is associated with each of the 3 IAN block techniques?
IAN block standard
akinosi closed mouth
gow gates
what areas are anesthetized with MENTAL/INCISIVE NERVE BLOCK?
Buccal soft tissue anterior to the mental foramen (around the 2nd premolar to the midline)
Skin of lower lip
Pulps of premolars, canines, and incisors
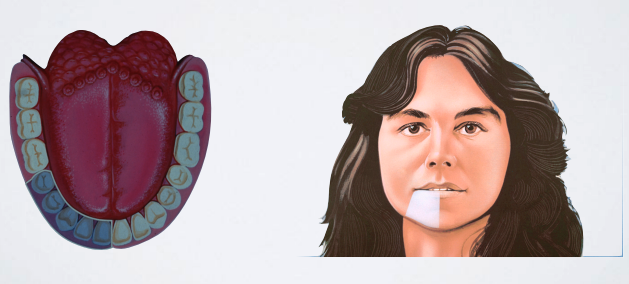
MENTAL/INCISIVE NERVE BLOCK
what are advantages of MENTAL/INCISIVE NERVE BLOCK?
If treatment on mandibular anterior teeth, this block negates the need for bilateral inferior alveolar blocks
Does not block lingual nerve. No tongue numbness
High success rate
what are disadvantages of MENTAL/INCISIVE NERVE BLOCK?
Midline difficulty, may require a supplemental injections
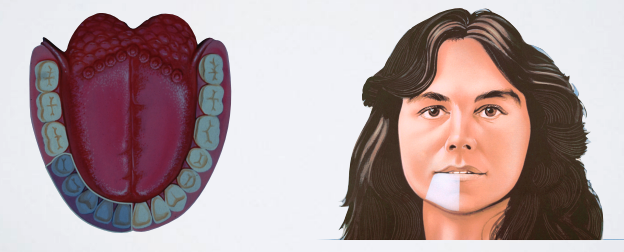
target site for which nerve block?
MENTAL/INCISIVE NERVE BLOCK
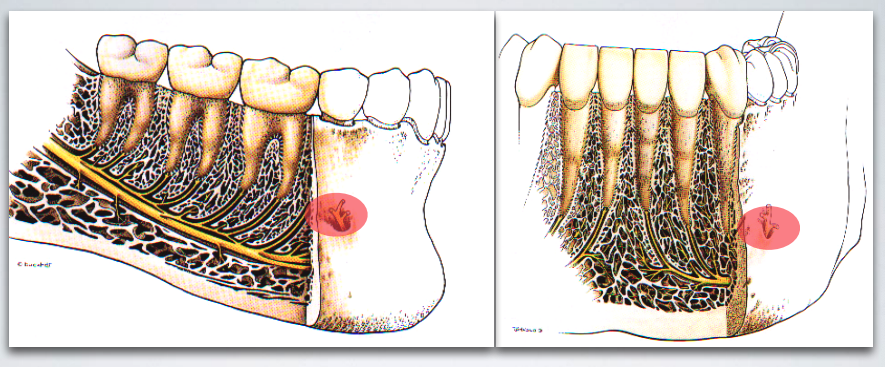
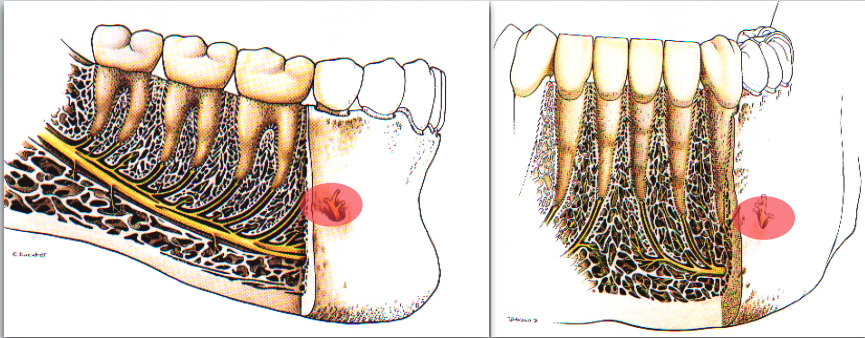
what is the proper target site for MENTAL/INCISIVE NERVE BLOCK?
Mental nerve as it exits mental foramen (between apices of the 1st and 2nd premolar)
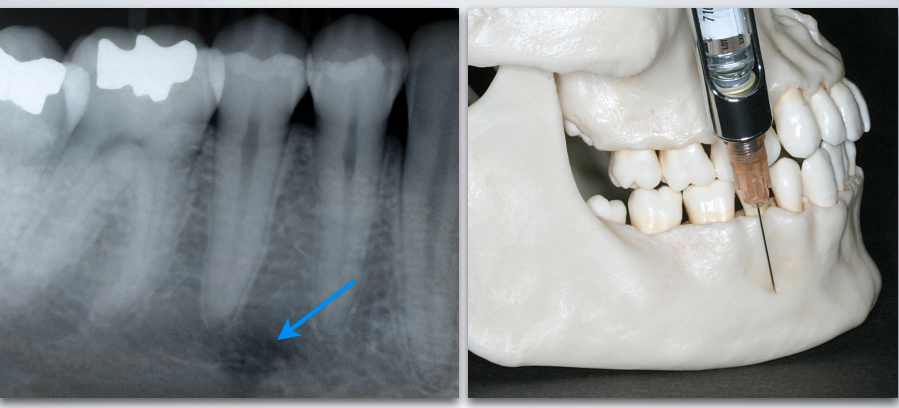
MENTAL/INCISIVE NERVE BLOCK
when doing MENTAL/INCISIVE NERVE BLOCK, locate the mental foramen with the aid of…?
radiographs and gentle palpation
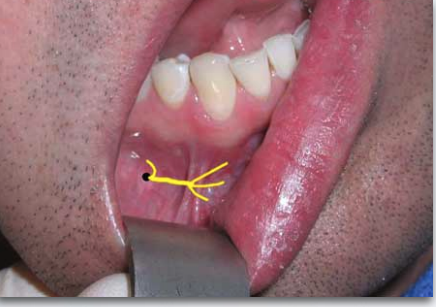
what nerve is indicated here?
mental/incisive nerve
what is the proper operator position for akiosi closed mouth technique?
7 o’clock right side, 11 o’clock left
what is the proper needle size for akiosi closed mouth technique?
25 or 27 gauge long, may bend needle 15 – 30 degrees near hub
what is the proper needle target for akiosi closed mouth technique?
Midway anteroposteriorly in the superior portion of the ptergygomandibular space several mm medial and inferior to union of the mandibular ramus and condylar neck
what is the proper bevel orientation for akiosi closed mouth technique?
Not as significant
what is the proper insertion point for akiosi closed mouth technique?
Retromolar mucosa midway mediolaterallly between the maxilla and ramus of the closed mouth at the height of the maxilliary posterior and mucogingival junction
what is the proper insertion point for akiosi closed mouth technique?
Through the mucosa and buccinator muscle posteriorly in the sagittal plane between and the posterior maxilla and parallel to the occlusal plane until the needle tip is halfway between the anterior and posterior plane of the ramus
what is the proper insertion depth for akiosi closed mouth technique?
25 (23-27 mm)
what is the proper anesthetic volume for akiosi closed mouth technique?
1.5-1.8 ml