Chapter 20: Crustaceans: Anatomy, Classification, and Ecology
1/134
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
135 Terms
Females posses what for sperm deposition?
Gonopores
Their appendages are:
Highly variable limbs with protopod, exopod, endopod (exhibit serial homology).
Exites and endites
Lateral and medial processes.
Epipos
Specialized exite modified as a gill
Uropod
Tail fin
In internal Features of Crustaceans they all have a---and persistent---filled with ---
hemocoel, blastocoel, hemolymph
Crustaceans have what kind of muscles?
They have striated muscles oriented in antagonistic groups called flexors and extensions.
-Flexors: draw a part towards the body
-Extensors- extend the part outward
How does gas exchange occur in small and large crustaceans?
In small crustaceans, it occurs across thin areas of cuticle.
The larger species have gills, usually internal, and very delicate.
In the open system of crustaceans the hemolymph returns to where? The valves in arteries prevents what?
Returns to venous sinuses.
It prevents backflow
Depending on respiratory pigment, Hemocyanin or Hemoglobin may be what colors?
They may be colorless, reddish, or bluish
What is the dorsal heart?
The chief propulsive organ of circulatory fluid. (the main part of the body that pumps blood or fluid through the body's circulation system).
An excretory system is a pair of?
Tubular antennal or maxillary glands depending on where they open
-Each gland has a vesicle and a spongy mass called a labyrinth; which is connected to a dorsal bladder by an excretory tubule.
Excretion of nitrogenous waste takes place where?
Across the cuticle and gills
-Their brain is a pair of ----
-It connects to the subesophageal ganglion which---
-supraesophageal ganglia. (two clumps of nerve cells (ganglia) located above the esophagus they work together to control the nervous system)
-innervates most of the "face" (nerves link the subesophageal ganglion to parts of the head area, providing sensation and control to those areas, often referred to as the "face")
Crustaceans have a well developed sense of--
Organs
Their eyes are made up of photoreceptive units called--?It is covered by a---?
Ommatidia, cornea
Why does the eye of crustaceans make a mosaic or apposition image?
Because each segment only sees part of the visual field; it forms a superposition image
Statocysts contains--
Statoliths
Crustaceans have what kind of hair?
Tactile hairs
Crustaceans have what kind of sexes that aid in lots of specialization for copulation
separate sexes
In this subphylum some of them are parthenogenetic
Subphylum Crustacea
In subphylum crustacea most of them brood their---?
eggs
In subphylum crustacea, some have direct development while others have...?
multiphasic life cycles.
The ancestral and most widely occurring larvae is known as a
Nauplius
Cuticle is...?
secreted by the underlying epidermis
Epicuticle
Outermost, lipid impregnated protein
Procuticle
bulk of cuticle, several layers
-Endocuticle:
(within the endocuticle, there's the):
-Chitinous:
and
-Uncalcified:
-The inner-most layer
-Principal layer
-Membranous layer
The intermolt phases are called what?
Instars
What is the first step in molting?
Old procuticle separates from the epidermis.
What is the second step in molting?
Still in premolt, new exocuticle is secreted as molting fluid dissolves the endocuticle
What is the third step in molting?
The old epicuticle and exocuticle is discarded.
What is the fourth step in molting?
The new cuticle is stretched and unfolded. While the endocuticle is secreted
Hormonal control stops the production of what?
Molt inhibiting hormone from the X-organ (neurosecretory cells)
Hormonal control promotes the release of what?
molting hormone from Y-organs which lie near mandibles, initiates molting.
The Androgenic glands in some males lead to the development of...?
Secondary sexual characteristics
Suspension feeders eat what?
Plankton and bacteria
Pistol Shrimp---?
Chelae can be cocked like a hammer, Second fastest animal motion recorded
Class Remipedia has about how many species?
10 species they are all from caves that enter the ocean
How many trunk segments are in Class Remipedia
there are 25 to 38 trunk segments. They are all identical, paired, and biramous swimming appendages.
In what class are the thoracic limbs all similar and the second maxillae is similar to the thoracic limbs?
Class Cephalocarida
This class is a true hermaphrodite and the eggs and sperm come through a common duct
Class Cephalocarida
What are the three orders of Class Branchiopoda?
1) Order Anostraca- fairy shrimp
2) Order Notostraca- tadpole shrimp
3) Order Diplostraca- water fleas
-Class Branchiopoda, mostly live in--?
-Many of them have complex life cycles with extensive periods of what?
-Freshwater
-Dormancy
Class Branchiopoda are very important components of--?
Food webs
Class Maxillopoda, Subclass Mystacocarida--?
Tiny, only 10 species
Class Maxillopoda, Subclass Tantulocarida
Only 12, recently described
Class Maxillopoda, Subclass Branchiura
Mostly fish ectoparasites
Class Maxillopoda, Subclass Pentastomida
Formerly a phylum, wormlike
Class Maxillopoda, Subclass Cirripedia
The barnacles, they are awesome.
-Subclass Mystacocarida are how long?
-They are distributed worldwide, but how many species?
-Where do they live?
-Less than 0.5 mm long
-10 species
-They live in interstitial spaces in sand
Subclass Copepoda are very abundant but usually how long?
Less than 2 mm in length
This subclass has a single pair of uniramous maxillipeds, four pairs of flattened, biramous, thoracic swimming appendages, and a fifth pair of legs that are reduced.
Subclass Copepoda
In Subclass Copepoda most are free living, but many are...?
Parasitic
What kind of development does subclass copepoda have?
Direct development. However, some parasitic species exhibit multiphasic life cycles
What year was Subclass Tantulocarida described and how many species are there?
Described in 1983; about 12 species
-What is the size of organisms in the subclass Tantulocarida,? and
-How many pairs of antennae do sexual females have?
-They are tiny, smaller than 0.2mm
-Sexual females have one pair of antennae
What kind of life cycle does subclass Tantulocarida have?
They have both a pathogenetic and sexual life cycle
Subclass Tantulocarida is parasitic, and the tantulus larvae penetrate the cuticle of host by a--?
Mouth tube
In this subclass, their abdomen and all thoracic limbs are lost during metamorphosis to an adult.
Subclass Tantulocarida
In subclass Tantulocarida how many segments do juveniles bear?
They bear six or seven abdominal segments
Subclass Branchiura has a second maxillae modified as what?
Suction cups
-Subclass Pentastomida has how many species?
-What are they called?
-130 species of wormlike parasites.
-Called the tongue worms
What type of parasites are subclass Pentastomida? and how long do they get?
They are mostly lung parasites of vertebrates and are up to 13 cm
Subclass Pentastomida has transverse rings that make them look---?
Segmented
This subclass has nonchitinous, highly porous cuticle, molted periodically during larval stages
Subclass Pentastomida
This subclass have five short protuberances on anterior end
Subclass Pentastomida
What kind of digestive system does subclass Pentastomida have?
Simple, straight digestive system
Does subclass Pentastomida have circulatory, excretory, or respiratory organs?
No, they do not!
In subclass Pentastomida sexes are separate and the females are usually ---?
Larger than males.
How are the larvae in subclass Pentastomida
The larvae are ovoid, tailed, with four stumpy legs.
Subclass Cirripedia has what kind of organisms?
Barnacles, plus 3 smaller orders of burrowing or parasitic forms.
Subclass Cirripedia are sessile as--?
adults
In subclass Cirripedia the cirri is extended between what--?
Between plates for filter feeding.
How does fertilization look like in subclass Cirripedia
They are mostly hermaphroditic. They have internal fertilization and become free living cyprid larvae. They attach by their first antennae, and metamorphose into adult form.
Which subclass has the longest penis in relation to body size of any animal?!
Subclass Cirripedia
This order has invaded terrestrial habitats all the way to very deep water.
Order Isopoda
Order Isopoda's have direct development, a few---? and have complex----?
A few parasitic forms, and complex life cycles.
-How many species do order Euphausiacea have? and
-How long are they?
-There are about 90 species; the krills
-3 to 6 cm long
In order Euphausiacea, the carapace is fused with all thoracic segments but unable to---?
entirely enclose their gills.
This order has no maxillipeds but has thoracic limbs with exopods
Order Euphausiacea
Order Euphausiacea are bioluminescent because of an organ called a--?
Photophore.
Order Euphausiacea is very important to marine--?
Food webs
•Thoracic segments fused with the head to form a cephalothorax
•Many have a hard covering called a carapace
Crustacean
Protopod:
The basal portion of the limb. It has two parts a basis and a coxa.
Exopod
lateral; farther from the middle of the body borne by the protopod has one to several parts
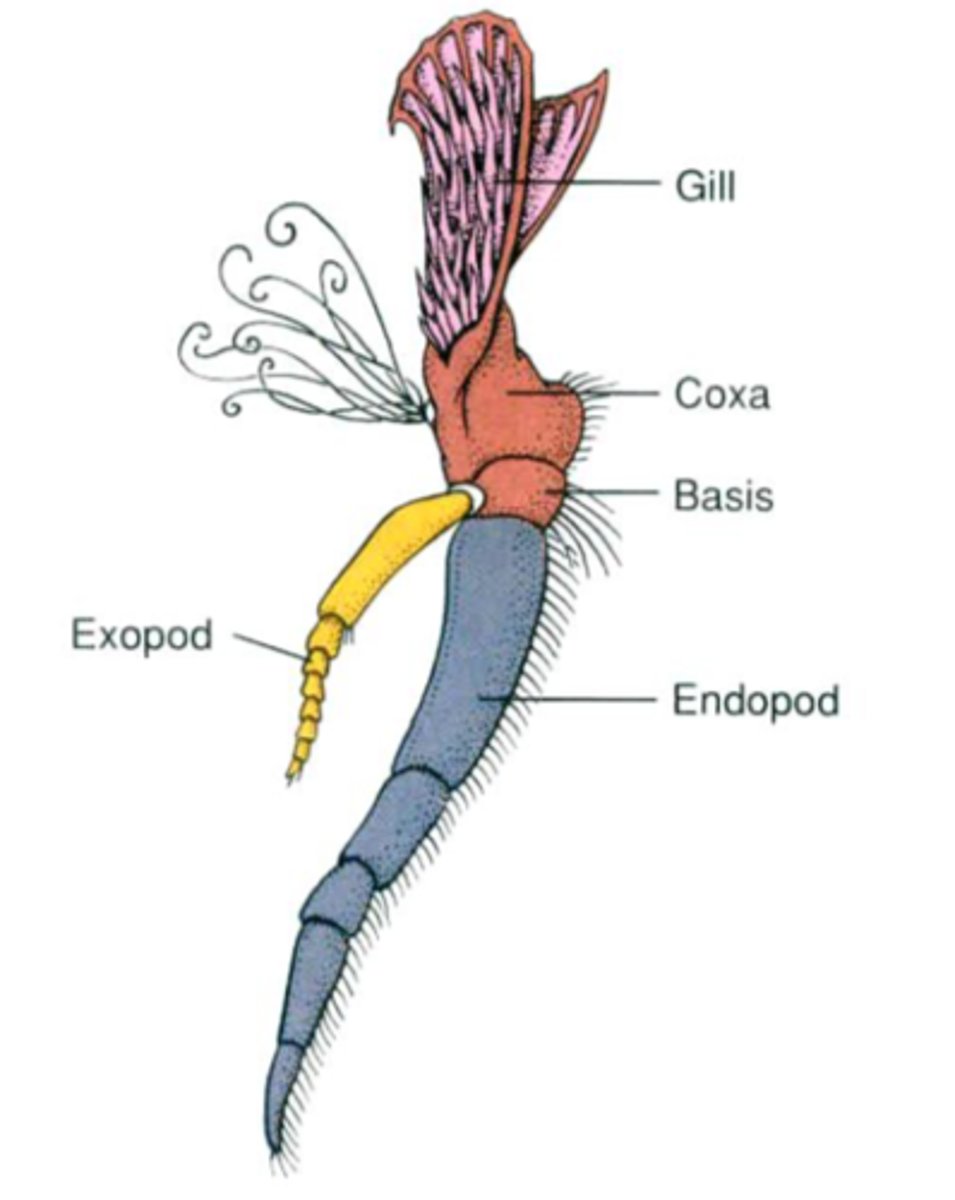
Endopod
Medial; closer to the middle of the body. Has one to several parts
Crustaceans have many similarities with--
annelids
Molting and Ecdysis is the...?
process of shedding the cuticle for growth or wear.
Hormonal control is usually initiated by what?
Environmental stimuli
In hormonal control, the androgenic glands occur in SOME males but don't occur in what?
in females.
Crustaceans feeding varies greatly. They have many specializations, but they all use the same set of what?
mouthparts
-Predators eat what?
Larvae, worms, other crustaceans, snails, and fishes.
Scavengers eat what?
detritus (trash) and dead animals
Mantis Shrimp---?
Has a specialized digit for piercing or smashing prey.
In class remipedia the antennules are biramous the maxillae and maxillipeds are prehensile and adapted for--?
Feeding
Class Cephalocarida has how many species and are how long?
Only 9 species and 2 to 3 mm long
The class has no eyes, carapace, or abdominal appendages
Class Cephalocarida
Class Branchiopoda has how many species?
10,000 species
This class has flattened, leaflike phyllopodia, or legs that serve as respiratory organs
Class Branchiopoda