mutations
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
give 5 processes which result in an increase in genetic variation w/in a species:
mutations
independent segregation of homologous chromosomes
crossing over between homologous chromosomes
random fertilisation of gametes
all produce new allele combinations
what is a gene mutation?
a change in the base sequence of chromosomes
why may not all base substitutions cause a change in the encoded sequence of amino acids?
the genetic code is degenerate - more than one codon may code for the same amino acid
what is a mutagenic agent?
a factor that increases the rate of mutations
e.g. UV light, ionising radiation
what is a frameshift mutation?
where an insertion/deletion mutation changes the triplets in a DNA sequence as the sequence shifts right/left (respectively) by one base
what is a point mutation?
a mutation where a single nucleotide is altered
how may gene mutations occur?
spontaneously, if DNA is misread during DNA replication
what are the 5 types of gene mutation?
substitution
deletion
insertion
duplication
inversion
what effect may gene mutations have?
change amino acid sequence coded for by gene
→ different polypeptide
→ potentially different tertiary structure
→ potentially changing organism’s phenotype
(if enzyme, potentially different active site shape, preventing E-S complex forming)
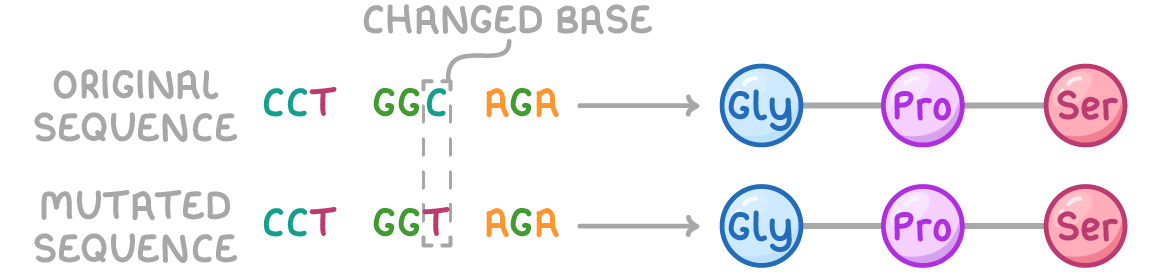
what is a substitution gene mutation?
one or more nucleotides substituted for another in a DNA base sequence
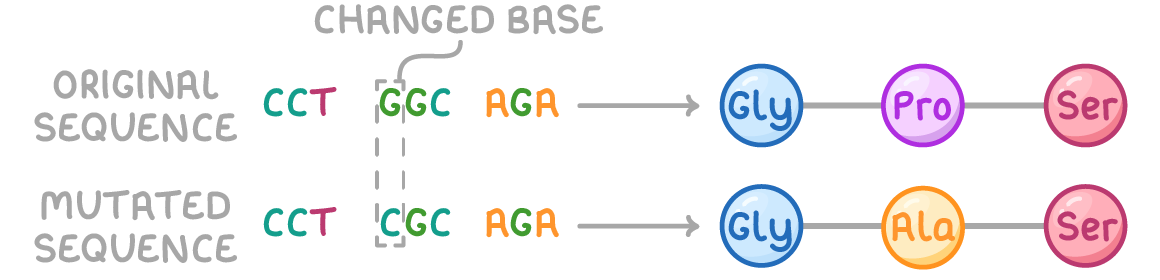
what is a deletion gene mutation?
one or more nucleotides deleted from a DNA base sequence
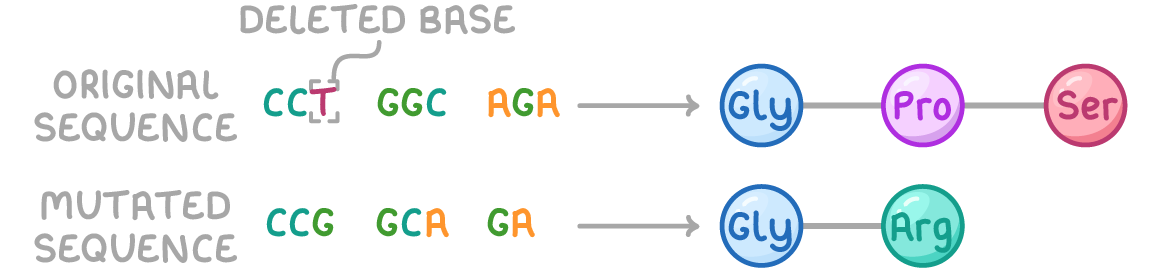
what is an insertion gene mutation?
one or more nucleotides inserted into a DNA base sequence
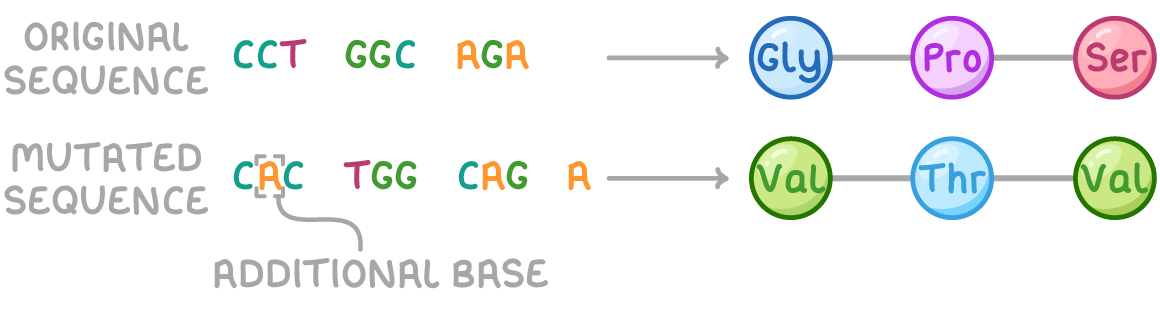
what is a duplication gene mutation?
one or more nucleotides in a DNA base sequence are duplicated
what is an inversion gene mutation?
a group of nucleotides in a DNA base sequence separate and rettach in the same position but in the reverse order
what is a chromosomal mutation?
change in the structure/number of chromosomes in a cell
what causes chromosomal mutations?
errors in cell division
what are the 7 types of chromosomal mutation?
deletion
insertion
duplication
inversion
translocation
non disjunction
what is a translocation mutation?
a portion of one chromosome switches places w/ another non homologous chromosome
what is a non disjunction mutation?
in meiosis, the chromosomes are not separated properly/all chromosomes stay in one cell
chromatids go to different poles
what is polyploidy?
a cell having 3 or more sets of chromosome (e.g. triploid/tetraploid cells)