Biological molecules: Proteins
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
98 Terms
General structure of amino acid
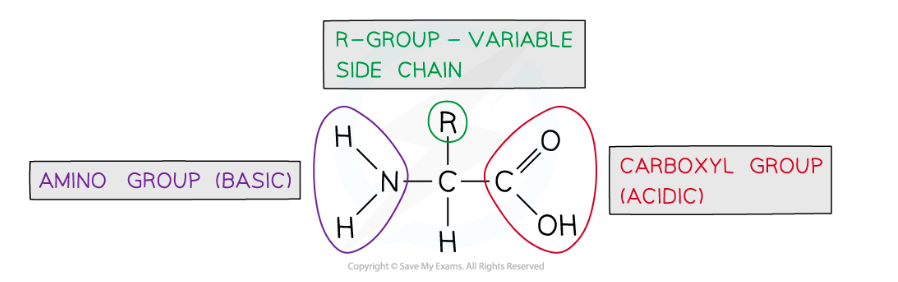
What is an amine group
NH2
Carboxylic acid group
COOH
What is the central C atom bonded to in an amino acid
Amine group, carboxylic acid group, H atom, R group
How do amino acids differ
R group
Functional groups of an amino acid
Amine, carboxyl
What bonds are formed between amino acids
Peptide bonds
What kind of bonds are peptide bonds
Covalent
What kind of reaction forms a peptide bond
Covalent
How many water molecules are released when 2 amino acids bond together
1
Draw the formation of a peptide bond
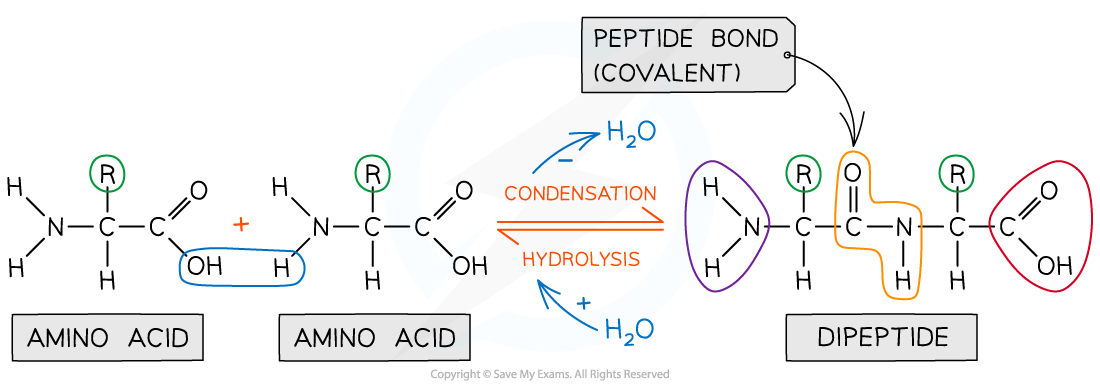
How can peptide bonds be broken down
Hydrolysis reaction
Which groups between amino acids interact to form the peptide bond
OH of COOH; H of NH2
Examples of how can R group affect amino acids properties
Polarity; acidic/basic
What is the primary structure of a protein
Sequence of amino acids
What determines primary structure of a protein
DNA of cell
Is primary structure specific for each protein
Yes
How many amino acids are there commonly found in cells
20
What is secondary structure
Shape of the polypeptide chain due to h bonds forming between amino group and carboxyl group
What creates the secondary structure of a protein
Weak -ve nitrogen/oxygen atoms form H-bonds with weak +ve hydrogen atoms
2 shapes of secondary structure
α-helix or β-pleated sheet
Describe α-helix secondary structure
Hydrogen bonds form between every 4th peptide bond; O of hydroxyl group, H of amine group
Describe β-pleated sheet secondary structure
2 parts of polypeptide chain are parallel; H-bonds form betw parallel peptide bonds; folds into pleated sheet
What is the protein backbone and what affects it
Hydrogen bonds between amino group and carboxyl group; secondary structure
What may break the hydrogen bonds which create the secondary structure
High temperatures; pH changes
What is tertiary structure
Additional bonds formed between R groups
What kind of bonds can be formed to create tertiary structure
Hydrogen; disulphide; ionic; hydrophobic interactions
Describe H bonds in tertiary structure Vs in secondary
Secondary: between carboxyl and amine group; tertiary: between R groups
Describe disulphide bonds in tertiary structure
Strong covalent bonds between sulfur atoms of 2 cysteine amino acids
How can disulphide bonds be broken
Oxidation
Describe H bonds in tertiary structure
Form between strongly polar R-groups
Which are the strongest bonds within a protein
Disulphide bonds - help stabilise proteins
Describe ionic bonds in tertiary structure
Ionic bonds form between oppositely charged R groups
Describe hydrophobic interactions in tertiary structure
Weak hydrophobic interactions between non-polar hydrophobic R groups within interior of protein
Where is secondary structure commonly found
Most fibrous proteins
Most common tertiary structure bond
H bonds
Where is tertiary structure commonly found
Globular proteins
Are ionic bonds or H bonds stronger
Ionic
Are ionic bonds common within proteins (tertiary structure)
No
What does tertiary structure determine
(Shape and) function of protein
Why are there a vast range of protein configurations (tertiary structure)
Each amino acid has unique R group; many dif interactions can occur; therefore proteins fold differently
What is quaternary structure
How different polypeptide chains (subunits) are arranged into a larger functional macromolecule
Example of a protein with quaternary structure
Haemoglobin
What is a protein subunit
Each polypeptide chain in quaternary structure
Describe a globular protein
Compact, roughly spherical, soluble protein
Are globular proteins soluble or insoluble in water
Soluble
Why do globular proteins form a spherical shape when folding into tertiary structure
Non-polar hydrophobic R groups orientated towards centre of protein (away from aqueous surroundings); polar hydrophilic R groups orientate themselves on outside of protein
What aspect of structure is the spherical shape of a globular protein
Tertiary structure
Why are globular proteins generally soluble in water
Water molecules can surround the polar hydrophilic R groups on protein’s exterior
How does solubility of globular proteins affect function
Can easily be transported around organisms and be involved in metabolic reactions
Do globular proteins have specific shapes
Yes
Why do globular proteins have specific shapes
Folding due to interactions between R groups
How does specific shape of globular proteins affect function
Can play important physiological roles e..g catalyse specific reactions, respond to specific antigens
What is a conjugated protein
A protein containing a non-protein chemical group e.g. prosthetic group
What is a simple protein
Protein containing only amino acids
What is a prosthetic group
A permanent, non-protein part of a protein molecule
What kind of protein is haemoglobin
Globular
What is haemoglobin
Globular protein; oxygen-carrying pigment; many in RBCs
Subunits of haemoglobin
Globin proteins; 2 α-globins, 2 β-globins; each has a prosthetic haem group
Describe quaternary structure of haemoglobin
4 globin subunits; held together by disulphide bonds; hydrophobic R groups face inwards; hydrophilic outwards => 3D spherical, soluble
What is a haem group
Prosthetic group containing an Fe2+ ion
How is haemoglobin able to bind to oxygen
Fe2+ ion of haem group can reversible bind to oxygen
How many oxygen molecules can each haemoglobin carry
4 bc/ 4 subunits each w 1 haem group
Uses of haemoglobin
Binds to oxygen in lung; transport to tissue for aerobic metabolic pathways; better bc oxygen not very soluble but haemoglobin is
What kind of protein are enzymes
Globular
Use of enzymes
Biological catalyst; control metabolic pathways; catalyse basically all metabolic reactions
How does quaternary structure affect enzyme
Determines shape of active site where substrate binds
Example of extracellular enzyme
Amylase
Where is amylase secreted
Salivary glands; pancreas
Amylase function
Catalyse hydrolysis of starch
Name an intracellular enzyme
Catalase
Catalase function
Convert harmful hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen to prevent damage
What is insulin
Globular protein; hormone
What does insulin do
Control blood glucose concentration
Insulin quaternary structure
2 polypeptide chains held together by 3 disulphide bridges
What is a fibrous protein
Long strands of polypeptide chains w cross-linkages due to hydrogen bonds
Fibrous proteins tertiary structure
Little to no tertiary structure
Fibrous proteins insoluble or soluble and why
Insoluble due to large proportion of hydrophobic R groups
3 examples of fibrous proteins
Keratin, elastin, collagen
Fibrous proteins amino acids
Limited number; usually v repetitive sequence
How do properties of fibrous proteins make them strong structurally/suitable for structural roles
Highly repetitive amino acid sequence = v organised, strong structures; insoluble
Keratin
Tough fibrous protein; hair, nails, horns, feathers
Elastin
Elastic fibrous protein; connective tissue, tendons, skin
Collagen
Fibrous protein; skin, tendons, ligaments, cartilage
Microfibrils/fibrils
Many molecules of collagen arrange in staggered formation
How does staggered formation of collagen make it strong
No weak spots
Why does collagen have great tensile strength (can be pulled a lot without stretching/breakign)
Many hydrogen bonds within triple helix structure
Test for proteins Name
Biuret test
Why are collagen molecules insoluble in water
Long molecules
Globular proteins amino acids different or same
Irregular, wide range of R groups
Key inorganic Cations involved in biological processes
Ca2+, Na+, K+, H+, NH4+ (ammonium)
Key inorganic anions involved in biological processes
NO3-, HCO3- (hydrogen carbonate), Cl-, PO43- (phosphate), OH-
Hydrogen carbonate ion formula
HCO3-
Phosphate ion formula
PO4 3-
Describe biuret test
Add biuret reagent (sodium hydroxide + copper (ii) sulfate); observe colour change on white tile
Positive result biuret test
Blue to purple
What is sodium hydroxide for in biuret reagent
Make sample alkaline; alkali and copper (ii) sulfate react in presence of peptide bonds
Limit of biuret test
Qualitative; don’t know how much protein present; if sample contains amino acids/dipeptides, result is -ve due to lack of peptide bonds