NEUR305: Study Exam 2 Questions
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
The concepts of sensation and perception are different because…
sensation is something that happens to your sense organs and neurons; perception is something that happens in consciousness
What is habituation?
The repeated exposure of the stimulus decreased the responsiveness; can still detect the stimulus! For this to be adaptation there would need to be a constant stimulus.
How is sensory information tied to olfaction?
Olfactory bulb sends information to many brain areas, including the entorhinal cortex. The entorhinal cortex sends to the hippocampus.
HIPPOCAMPUS TIES THE MEMORY TO SMELLS.
What is convergence?
Multiple neurons synapse onto one receiving neuron!
What’s divergence?
One neuron synapses onto many neurons!
What are the different types of papilla?
Circumvallate, foliate, fungiform; respond to the five types of taste
Are gustatory maps specific for different tastes?
Yes, different areas areas are activated for different tastes!
Walkthrough of visual pathway (photoreceptors to LGN)!
photoreceptors → interneurons (amacrine, bipolar, horizontal) → ganglion → optic neurons → lateral geniculate nucleus
Make a chart of the ganglion cell types (cell, pathway, resolution, temporal, contrast, layer of V1)
Table:
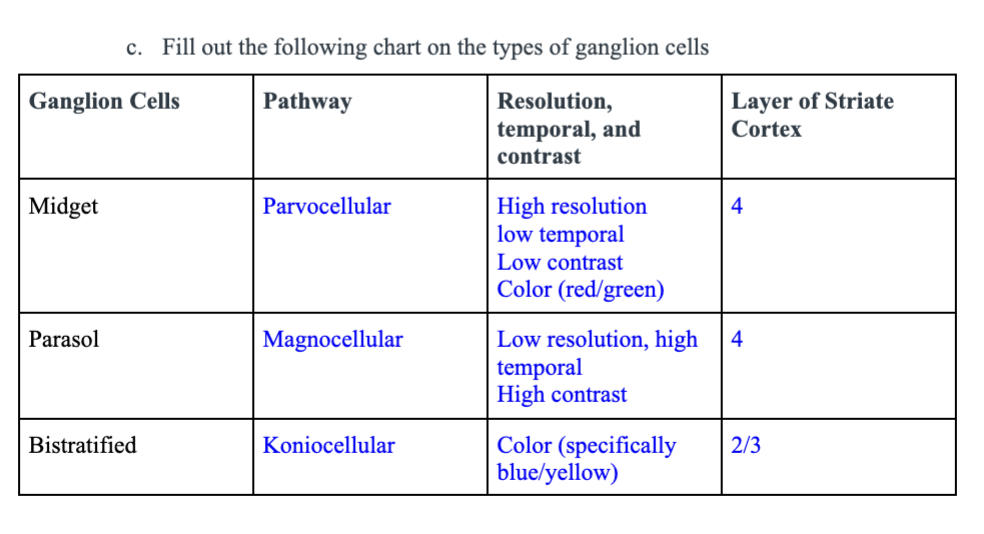
What are three ways V1 is organized?
Pinwheels, ocular dominance columns, blobs
What is ocular dominance?
Refers to the organization of V1; segregation eye of input into columns
EACH VISUAL FIELD GETS INPUT FROM EACH EYE but at this point they’re not joined together to form binocular vision.
What area is involved in good continuation?
V2!
What brain area allows you to see shapes?
Lateral occipital cortex
Outer ear contains the ______ and _________ and is responsible for __________.
pinna, ear canal, localizing and amplifying sound
Middle ear contains the ___________ which is responsible for _____________. This prevents sound from being reflected off the of the liquid in the inner ear.
tympanic ossicles, impedance matching
Next you have the inner ear. Waves enter the ________ through the ______ and exit the ________ through the _________
scala vestibuli, oval window, scala tympani, round window
The cochlea then is able to transduce the mechanical energy into electrical signals. It does in three steps 1)_____ within the cochlea detect traveling wave motion 2) These cells then _____ cilia motion into neurotransmitter release 3) _________ axons form the cochlear nerve
hair cells, transduce, spiral ganglion cells
Auditory nerve pathway to the primary auditory cortex?
Auditory nerve → Cochlear nuclei → Superior olivary nucleus → Inferior colliculus → MGN → Primary Auditory Cortex
Which two areas are part of the brain stem nuclei?
Cochlear nuclei and superior olivary nucleus (SOC)
Which area in the auditory pathway has a full map of sound localization?
Inferior colliclus (from the brainstem nuclei)!
ILD works best at…
High frequencies!
ILDs deal with____, ITDs deal with _____
Sound intensity and difference in time it takes for the sound to reach each ear.
Where does integration of left and right auditory information occur?
Inferior Colliculus!
Make a table touch receptors (touch receptors, sensation detection, adaptation)
Table:

Level of abundance of touch receptors?
Meissner < Merkel < Ruffini < Pacinian
Level of abundance correlates to receptive fields.
Two pathways for somatosensation?
Mechanosensory (Leminscal Pathway)
Anterolateral
When does each path cross?
Mechanosensory → level of brainstem
Anterolateral → level of spinal cord
What are the two types of fibers?
Alpha delta fiber → first pain → lightly myelinated → what where
C fiber (second pain) → unmyelinated → punishment
Difference between primary and secondary somatosensory cortex?
S1 receives information from one side and opposing side receive that; S2 receives information from both hemispheres.