Science: LQ 1 Review
5.0(6)Studied by 51 people
Card Sorting
1/91
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:22 AM on 11/24/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
92 Terms
1
New cards
Electromagnetic Waves
Electrical and Magnetic disturbance that moves through space at the speed of light. (They can travel through empty space)
2
New cards
Electromagnetic Spectrum
EM Waves are often classified by frequency in a schemem called _______
3
New cards
Frequency
The _____ of the wave produced is the number of complete vibrations per second.
4
New cards
frequency and speed
The wavelength of an EM wave depends on its_______.
5
New cards
frequency and wavelength
The waves differ in the way they are produced and interact with matter and from each other in their _____ and ______
6
New cards
Band
Each type of wave occupies a particular range of wavelengths known as _______
7
New cards
Photon
A throbbing pulse of electromagnetic radiation is called ______
8
New cards
Radio Waves
Longest wavelengths and shortest frequencies in the EM Spectrum. Used to transmit radio and television signal.
9
New cards
Global Positioning Systems (GPS)
Measure the time it takes a radio wave to travel from several satellites to the receiver, determining the distance to each satellite.
10
New cards
AM Radio Waves
A type of radio wave that readily bends around builings and other objects that might be present in their path
11
New cards
FM Radio Waves
Type of radio wave that has a shorter wavelength than the AM waves
12
New cards
Radio Frequency
A rate of oscillation in the range of about 3 kHz to 300 GHz, which corresponds to the frequency of radio waves, and the alternating currents that carry radio signals
13
New cards
Microwaves
They are basically extremely high frequency radio waves and have the shortest wavelengths. They have very short wavelengths ranging from approximately 1 millimeter to 30 centimeters.
14
New cards
RADAR (Radio Detection and Ranging)
Used to find the speed of an object by sending out radio waves and measuring the time it takes them to return.
15
New cards
Infrared
A picture that shows regions of different temperatures in the body.
16
New cards
Near Infrared Light
The closest in wavelength to the visible light
17
New cards
Far Infrared Light
Type of Infrared which is closer to the microwave region of the EM spectrum
18
New cards
Thermography/Pyrometry
Determining the temperature of objects
19
New cards
Visible Light
Portion of the EM spectrum that is visible to the human eye.
20
New cards
Ultraviolet
EM radiation with a wavelength shorter than that of visible light, but longer than x-rays
21
New cards
UV Radiation
This is produced by high-temperature surfaces, such as the sun.
22
New cards
X-rays
High-energy waves which have great penetrating power and are used extensively in medical applications and in inspecting welds.
23
New cards
Gamma Rays
Generated by radioactive atoms and in nuclear explosions, and are used in many medical applications.
24
New cards
Gamma Knife Surgery
A procedure wherein multiple concentrated beams of gamma rays are directed on the growth in order to kill cancerous cells.
25
New cards
Electromagnetic Radiation
Energy produced by nuclear reactions at the core of the sun
26
New cards
Radiation
Can be defined as the process of emitting energy by any particles, such as in the case of high-energy, protons, neutrons, atoms, and ions, and waves, either light or sound,
27
New cards
Radioactive Materials
Are composed of unstable atoms that give off its excess energy until it becomes stable
28
New cards
Radioactive Decay
Happens during the spontaneous change of an atom to be more stable
29
New cards
Ionizing Radiation
An especially damaging form of radiation which can create electrically charged ions in the material it strikes
30
New cards
Ionization Process
Break apart atoms and molecules, causing severe damage in living organism
31
New cards
Sievert
Basic unit used to measure exposure to ionizing radiation
32
New cards
Millisieverts or microsieverts
Radiation exposure is expressed in _
33
New cards
1000 microsieverts
An average person is exposed to ___ of whole body exposure per year from all sources
34
New cards
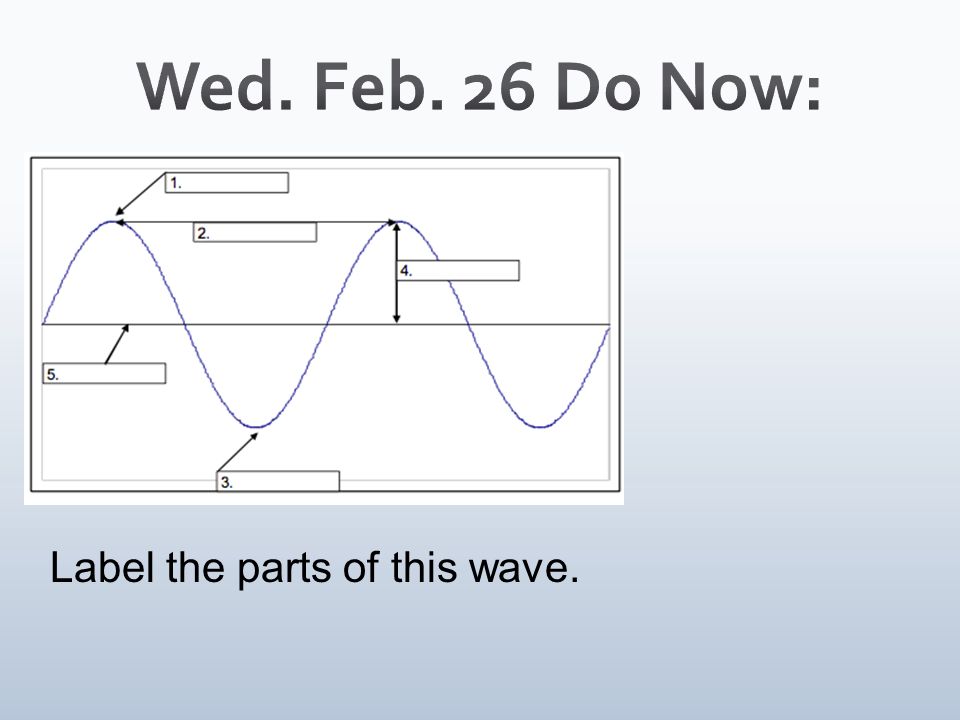
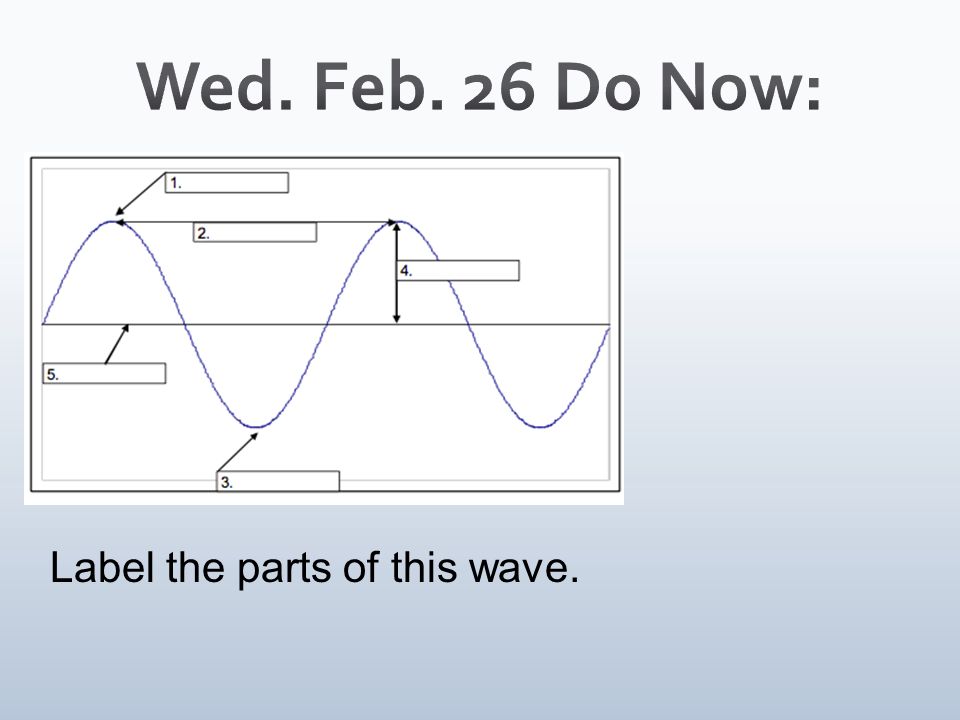
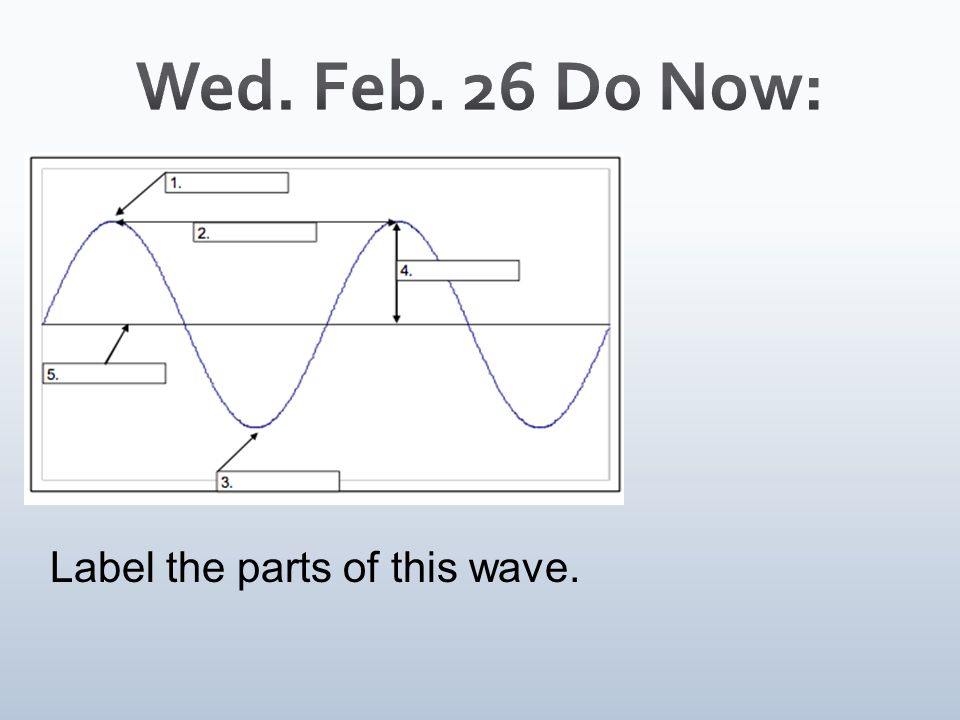
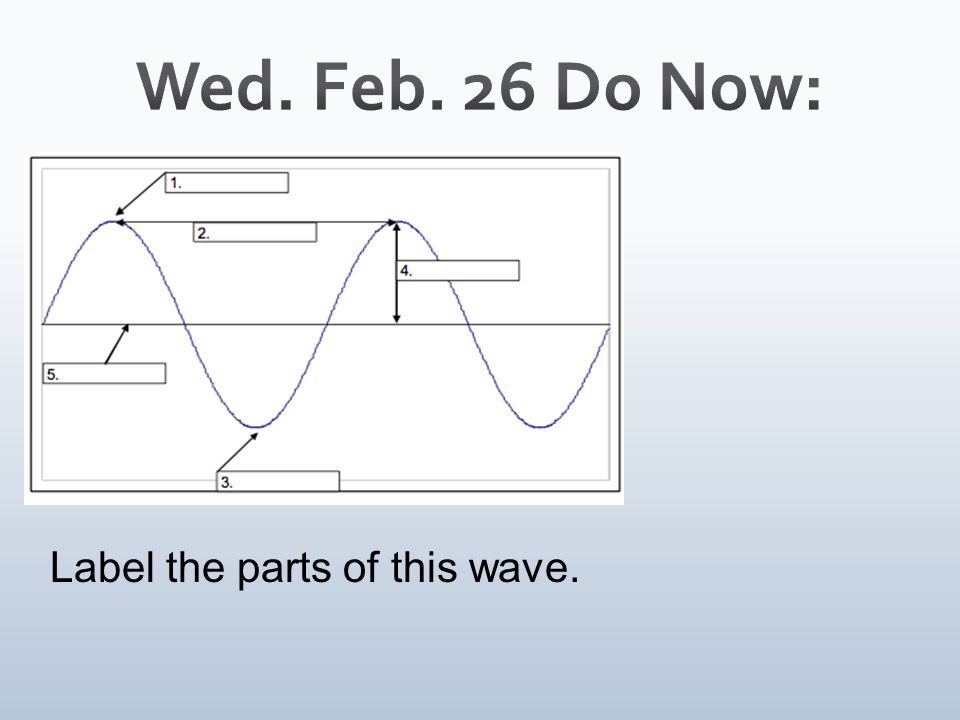
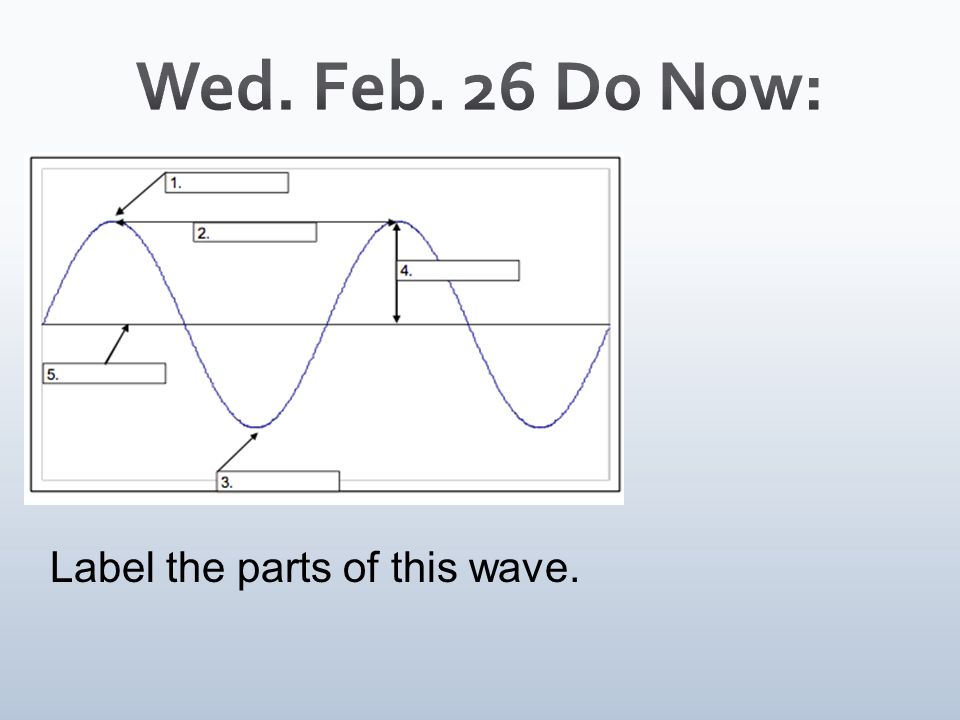
Crest
What part is at number 1?
35
New cards
Wavelength
What part is at number 2
36
New cards
Trough
What part is at number 3?
37
New cards
Amplitude
What part is at number 4?
38
New cards
Transverse Wave
What kind of wave is this?
39
New cards
Waves
Disturbances in space and time, they cannot propagate without a medium and they cannot travel in a vacuum or empty space
40
New cards
Light Waves
Form of an EM Wave that is propagated perpendicular to the source of the energy.
NOTE: They travel in a straight path
NOTE: They travel in a straight path
41
New cards
Refraction, Reflection and Absorption
Properties of Light
42
New cards
Refraction
It is the bending of light as it travels through one medium to another with different refractive indices
43
New cards
Refractive Index
Relative quantification of how a medium propagates a specific wavelength of light
44
New cards
Reflection
It is when light bounces off an object
45
New cards
Virtual, Upright and Reversed
An image formed on a plane mirror is _______
46
New cards
Incident Ray
Light striking the plane mirror
47
New cards
Angle of Incidence
An angle formed by the incident ray
48
New cards
Normal Vector
An imaginary line perpendicular to the surface of the plane mirror.
49
New cards
Reflected Rays
Formed when light strikes the surface of an object
50
New cards
Law of Reflection
The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection
51
New cards
Virtual Image
Image that apperas in a different location than its actual location
52
New cards
Newtonian Physics
There is no speed greater than light; thus, the indices of refraction of different materials are always greater than 1
53
New cards
Transmission
Refers to the process where light passes through an object or medium without being absorbed
54
New cards
Transmittance
Ratio between absorbed light and the incident light. it is unitless and it is used to examine how efficient a medium is in transmitting light.
55
New cards
Absoprtion
Occurs as light passes through a medium with the same natural frequency
56
New cards
Prism
Medium that diffracts light
57
New cards
ROYGBIV
The seven colors
58
New cards
Rainbow
A manifestation that indeed light is composed of seven colors
59
New cards
Spectrum
Components of ight with varying wavelengths
60
New cards
Light
It has both the properties of a wave.
61
New cards
Incident Ray
Beam in the first medium. It hits the boundary at an angel of incidence
62
New cards
Refracted Ray
Beam in the second medium. it leaves at an angle of refraction
63
New cards
Bends toward the normal
When light moves from air to water it _______. Making the angle of incidence greater than the angle of refraction
64
New cards
Slower
Light bending toward the normal indicates the speed is ____
65
New cards
Faster
Light bending away from the normal indicates the speed is _____.
66
New cards
Equal
The angle of incidence is ____ to the angle of refraction
67
New cards
Snell's Law
Describes the relationship between the angle or incidence and the angle of refraction.
Ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction is a constant
Ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction is a constant
68
New cards
Medium and the density
Degree to which light is bent depends on the ____ and the _____ of the medium.
69
New cards
Index of refraction
Light going from a vacuum into another medium is called _____
70
New cards
Medium
Speed of light is dependent on the properties of the _____
71
New cards
Optical density
Determines how much energy is absorbed and re-emitted in a medium and determines the speed of the light in the medium
72
New cards
Higher, slower
The ____ the optical density, the ____ the light wave.
73
New cards
Energy
Light wave is transporting _____
74
New cards
Reflected
When light hits a boundary. Some energy is transmitted to the new medium, some energy is _______
75
New cards
Diamonds
______ sparkle because most of the light rays hitting the stone are internally reflected
76
New cards
Fiber Optics
Transmit information in pulses of light. used in telecommunications, computer networking, by mechanics, and doctors.
77
New cards
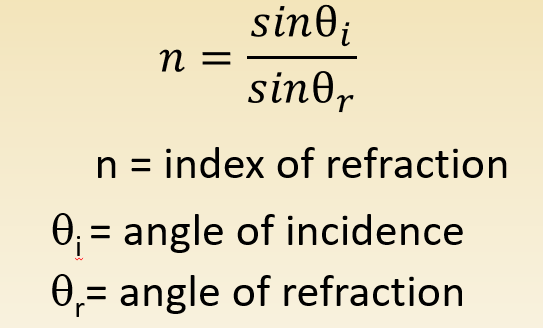
n = sin (angle of incidence) / sin (angle of refraction)
Equation for Snell's Law:
78
New cards
Images
Are formed when light strikes a reflecting surface, such as mirror or a lens
79
New cards
Slows light progress
(The presence of material) Interactions with electrical properties of atoms will ____.
80
New cards
Real Image
Image is made from "real" light rays that converge at a real focal point. Can be projected onto a screen and it is always inverted.
81
New cards
Virtual image
"Not Real" because it cannot be projected, the Image only seems to be there.
82
New cards
Virtual
If light energy doesn't flow from the image, the image is _____
83
New cards
Curved Mirrors
Is a mirror with a curved reflecting surface.
84
New cards
Convex and Concave
2 Types of Curved Mirrors
85
New cards
Concave Mirrors
A type of mirror that curves inward and may form a real or virtual image
86
New cards
Convex Mirrors
A mirror that curves outward, reduces image and forms virtual images.
87
New cards
Index of refraction
The "light slowing factor" is called the _____.
88
New cards
Convex Lenses
Lens that converges. Thicker in the center than edges. Forms real images and virtual images depending on position of the object.
89
New cards
Near Sighted
Eyeball is too long and image focuses in front of the retina.
90
New cards
Near Sightedness
Concave lenses expand focal length
91
New cards
Far Sighted
Eyeball is too short so the image is focused behind the retina
92
New cards
Far Sightedness
Convex Lens shortens the focal length