Life History and Competition
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
life history traits
A set of co-adapted traits designed, by natural selection, to solve particular. ecological problems
evolution, trade offs, energy allocation
what is involved in life history traits?
reproduction
what is the most important ecological problem?
maximize
A species’ life history traits should __________ reproduction
r-K theory
Pianka’s Theory
• describes a continuum of life histories
• idea of trade-offs
• selected for by the environment
r species
favor lots of offspring with little parental care
K
favor few offspring with lots of parental care
C-S-R theory
grime’s theory for 3 way tradeoff in plants
competitive ability, stress tolerance, reproduction
what elements are involved in C-S-R theory?
trophic level
competition is between species of the same _______
exploitive and interference
2 mechanisms of competition
those at the same trophic level
what species use the same resources?
exploitative
competition by using up a resource
2 fish feeding of zooplankton, hawks and owls feeding on mice
examples of exploitive competition
chemical competition, overgrowth (plants), territoriality, encounters
examples of interference competition
interference competition
competition by direct action to keep away from resource
Allopathic
plants that poison neighbors
inverse
competition may cause a ________ relationship between the presence or
abundance of competing species.
competitive exclusion
What can a better competitor cause to the other in simple habitats?
gathering resources or being efficient with them
When resources are scarce, one species is almost always better at either….
select different habitat or different food
In the long run a species can adopt one of these two strategies to escape the negative effects of competition
character displacement
changing a characteristic over time to escape the effects of competition
reduces intraspecies competition for food
benefits of sexual dimorphism in weasels
intraspecific
competition within your own species
interspecies
competition with a different species
niche/resource partitioning
evolution creates specialists that reduce competition for a specific prey
reciprocal
competition is a _________ interaction
both
If 2 individuals use the same resource, ______ suffer negative effects because of its depletion
Grace & Wetzel
studied cattails to study competition
individuals deplete resource, reduces population growth rate, birth and death rates are affected
mechanisms by which resources limit population growth in intraspecific competition
K
population size where births are equal to deaths
1
value for lamda when at carrying capacity
negatively, positively
Birth rate is ________ density-dependent
Death rate is __________ density-dependent
K or lamda =1
in a graph of birth and death rate, what does the place where the lines cross represent?
R*
resource level where births and deaths are equal and lamda=1
0
what is the population growth at R*
Dave Tilman
author of the R* model
K
population size at R*
low
is it better to have a high or low R* when there is competition?
at winning specie’s R*
where do resources stabilize when 2 species compete?
factors that affect food availability other than competition, assumed b/d rates w/ no variation, ignores other species and resources, no predation
R* model assumptions
they are renewable
in competition model, what is assumed about the resources?
how much energy is left after taking out what is necessary for respiration
what is net photosynthesis?
light compensation point
point where plants just make enough sugars to stay alive
R*
what other variable is the light compensation point equivalent to in photosynthetic plants
shade tolerance and fast growing
what trade offs are often seen in trees
natural selection
Within a species, birth & death rates are agents of ____________
lower
in competition, does a higher or lower R* species win out?
territoriality
defense of space
food, resources, nesting sites, mates
what does a territory contain
evolution of a lower R* through delayed and lower allocation to reproduction
What characteristics will be favored by natural selection when intraspecific
competition is strong?
non-random
what distributions show territoriality?
niches must overlap
what must be true for species to have interspecific competition?
Synedra
Which will win when SiO2 is a limiting resource?
-Asterionella – R* = 1.0 or Synedra – R* = 0.4
David Tilman
studied diatoms with silica shells
Gause
Russian Ecologist, studied Parameciums
if they either depend on different resources or live at different conditions
When does Gauses principle state that species can coexist?
Joe Connel
Scottish ecologist, worked with Barnacles
rock space
what are the barnacles in Connells experiment competing for?
the S barnacles are better competitors in the low areas but have lower tolerance and cannot survive up high like C barnacles can
what is the trade off illustrated in the barnacle experiment?
C
which of the barnacle types have a greater fundamental niche?
competition affects almost every natural system and competition is only important in the absence of other natural forces
2 diffferent ecologist views on competition
niche overlap
Amount of _________ determines the degree and intensity of competition
intraspecific competition
When there is little niche overlap, what sets limits to population growth?
interspecific competition
When there is lots of niche overlap, what sets limits to population growth?
lots of niche overlap
when is competitive exclusion and character displacement possible over time?
2 resources needed by a species
What does Dave Tilman’s competition Model consider?
top right
What quadrant in Tilman’s model is good
zero net growth isocline (zngi)
line that separates our quadrants in Tilman model
fast resource usage
what does a long consumption vector mean?
combined usage of the 2 resources that can shift graph
what does the resource vector represent?
supply vector
line on graph that shows replenishment of two resources over time
average the supply and consumption vectors together
Hoe do you determine the environment shift in the 2 resource model?
populations/resources oscillate, neither species goes extinct
what happens in zone 4?
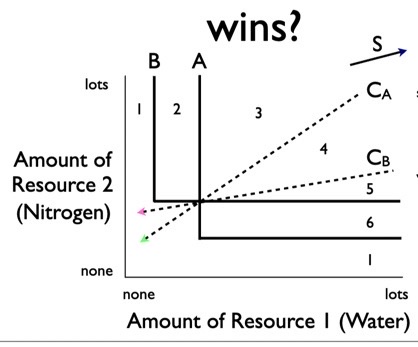
yes
Does Tilman’s model ever predict coexistance?
range of conditions and resource qualities that a species can survive under indefinitely
what is the G.Evelyn Hutchinson (current) definition of niche?