DPT 745 Week 5 Lecture Notes Pt. 2
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
inlet
outlet
Anterior
Lateral
Posterior
Boundaries of pelvic cavity
• Pelvic _____
– Superior opening
• Pelvic _____
– Enclosed by pelvic diaphragm
• _____ pelvic wall
– Bodies of pubic rami & pubic symphysis
• _____ pelvic walls
– Hip bones & obturator internus
• _____ pelvic wall
– Sacrum, coccyx , SI joint and associated ligaments
Heavy
Deep
Narrow
Small
70
Round
Large
Male Pelvis
• General Structure Thick and _____
• Greater pelvis (false pelvis) _____
• Lesser pelvis (true pelvis) _____/deep
• Pelvic Inlet Heart shaped
• Pelvic Outlet _____
• Pubic arch Narrow (<___°)
• Obturator Foramen _____
• Acetabulum _____
Thin
Shallow
Wide
Oval
Large
80
Small
Female Pelvis
• General Structure _____ and Light
• Greater pelvis (false pelvis) _____
• Lesser pelvis (true pelvis) ____/shallow
• Pelvic Inlet _____ and rounded
• Pelvic Outlet _____
• Pubic arch Wide (>___°)
• Obturator Foramen Oval
• Acetabulum _____
Coccygeus
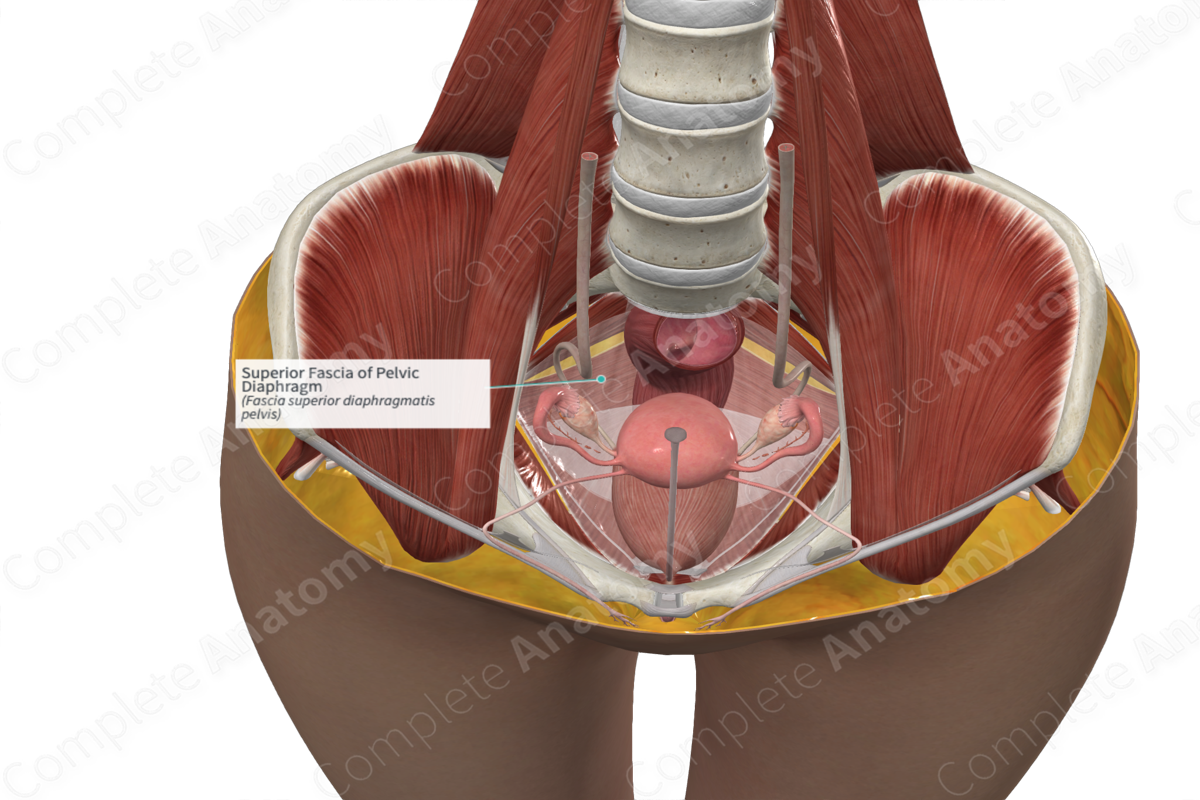
Pelvic Floor
• Formed by the funnel shaped pelvic diaphragm
– Consists of
• Levator Ani
• _____
– The diaphragm stretches from the pubis anteriorly to the coccyx posteriorly
– It also stretches laterally to the walls of the pelvis on both sides
Levator Ani
coccyx
compression
_____ _____
• Most important muscle in the pelvic floor
• Pubococcygeus, Puborectalis and lIiococcygeus
– Origin - body of pubis, obturator fascia, ischial spine
– Inserts - _____
– Innervation - nerve to the levator ani (S3, S4)
• Action
– Forms muscular sling to support abdominopelvic viscera
– Holds pelvic viscera in position
– Assist with abdominoplevic cavity _____, utilized with coughing, sneezing, vomiting, etc.
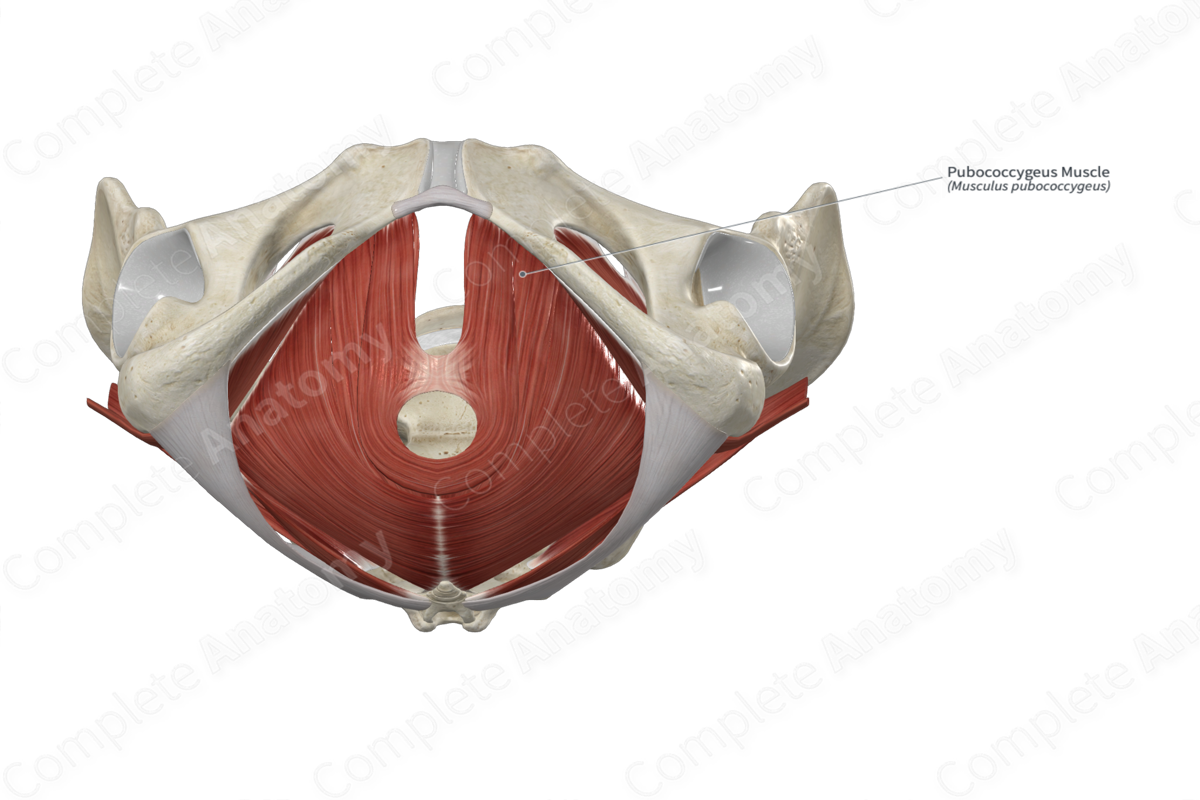
Pubococcygeus
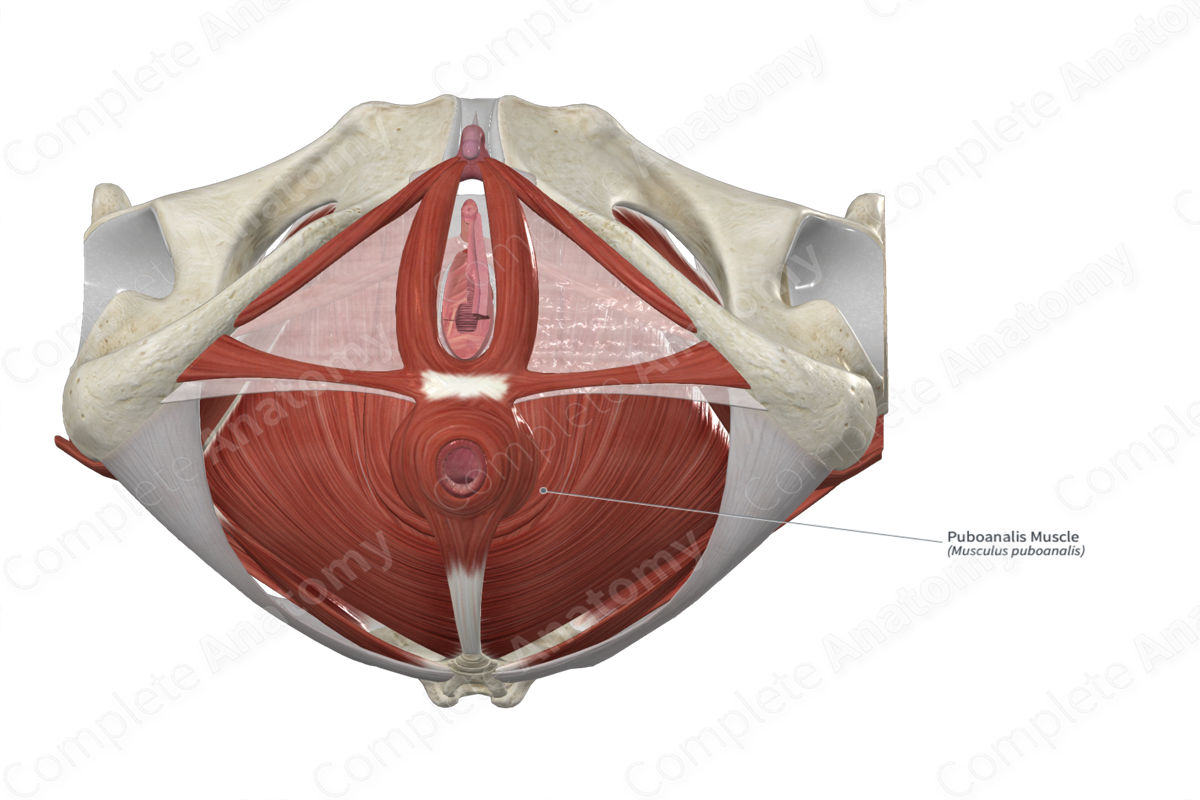
Puborectalis
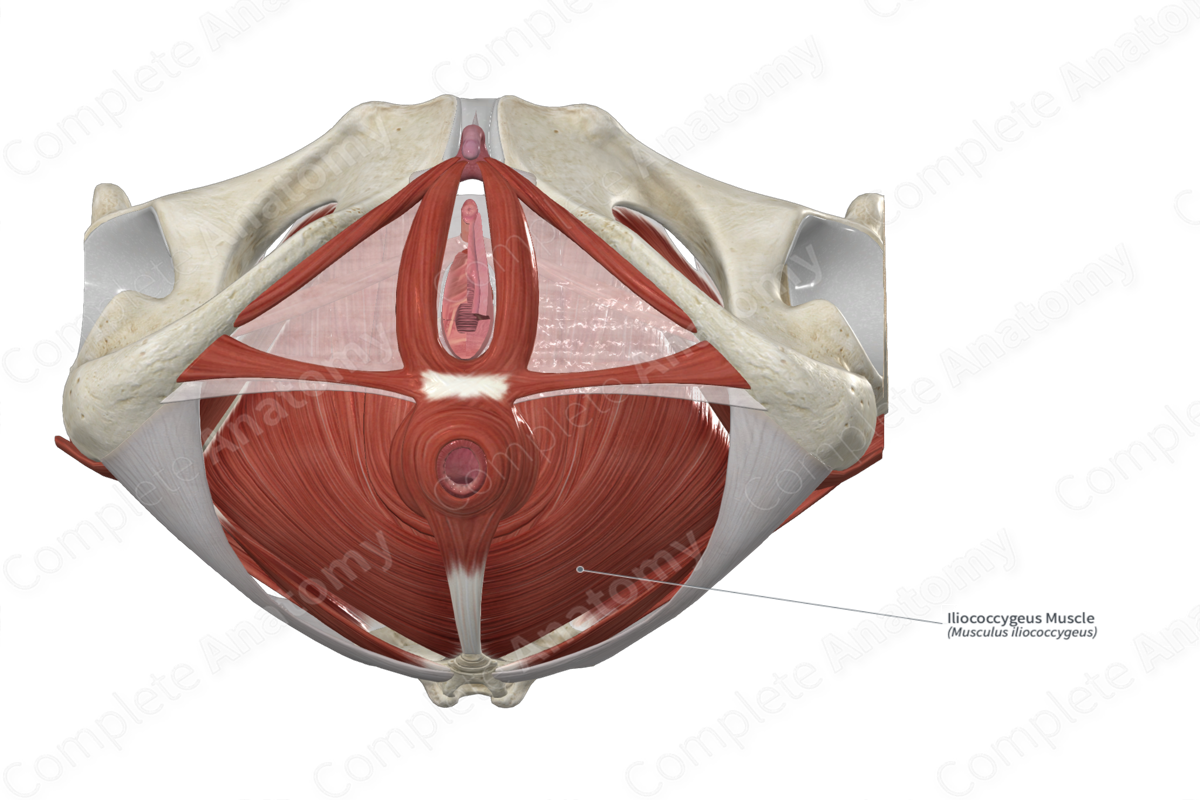
lIiococcygeus
pudendal
sacral
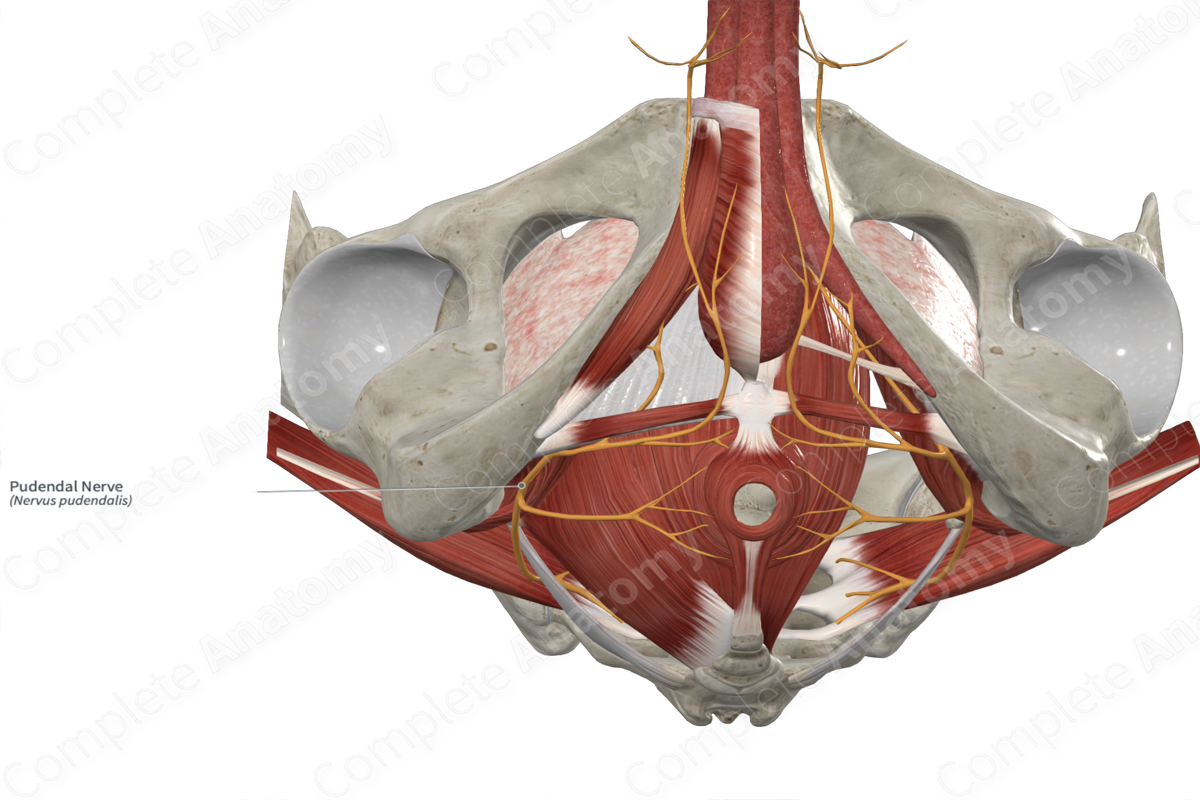
Innervation to Pelvic floor
• Some say innervation comes from the _____ n.
– Some sources are now saying branches direct from the _____ plexus innervate the levator ani
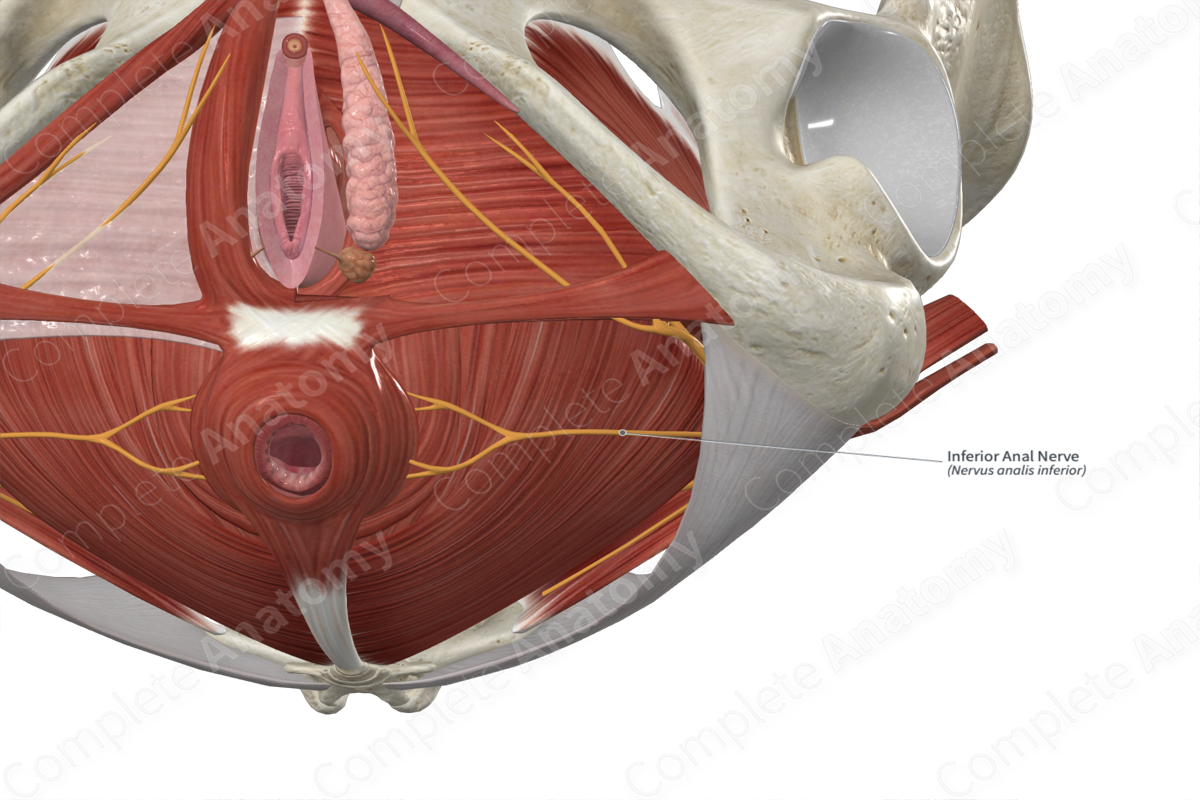
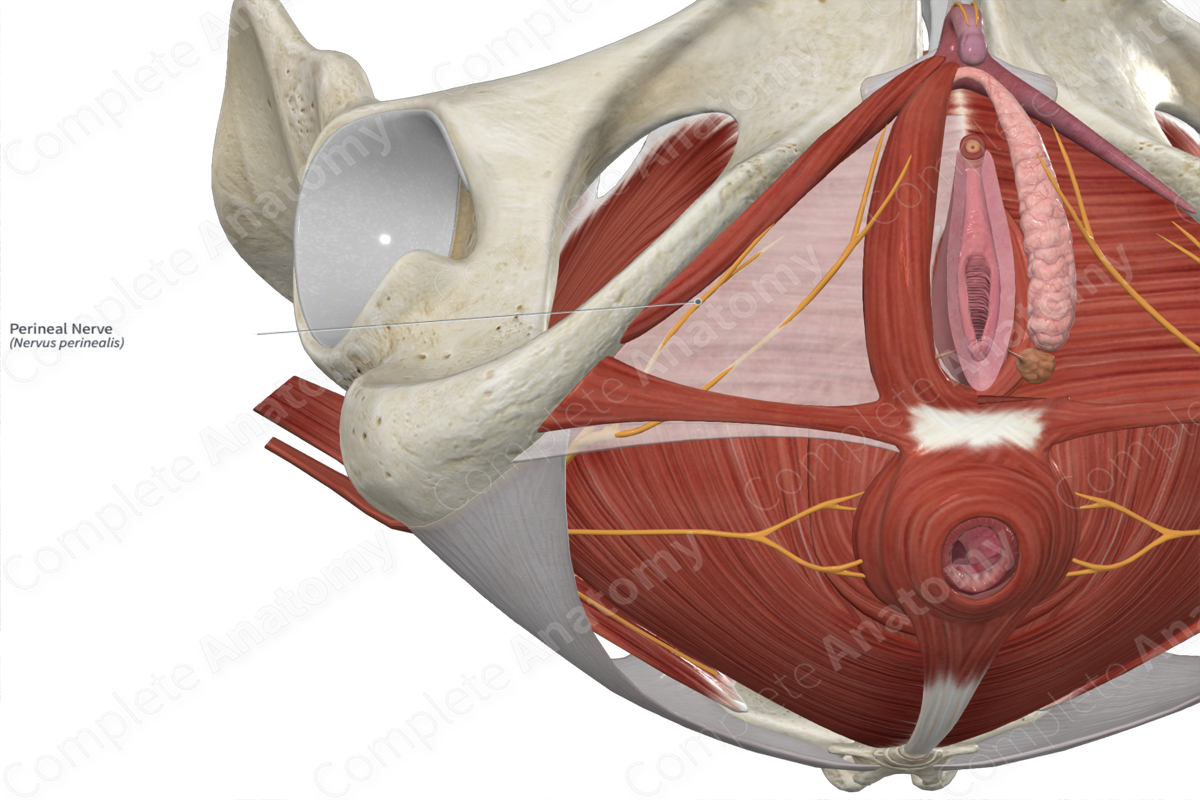
• In general, we can say pudendal and branches innervate pelvic floor
– Inferior anal nerve
– Perineal nerve
– Dorsal nerve of the penis/clitoris
Pudendal nerve
Inferior anal nerve
Perineal nerve
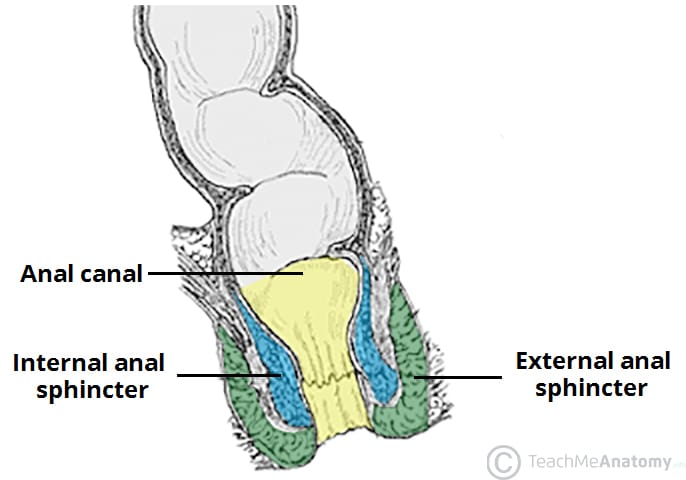
Anorectal angle
increase
contracts
Pelvic Floor Function
During Breathing
• Pelvic floor musculature will loosen so it can _____ the space in the pelvic floor while the diaphragm _____ into the pelvic floor during inhalation
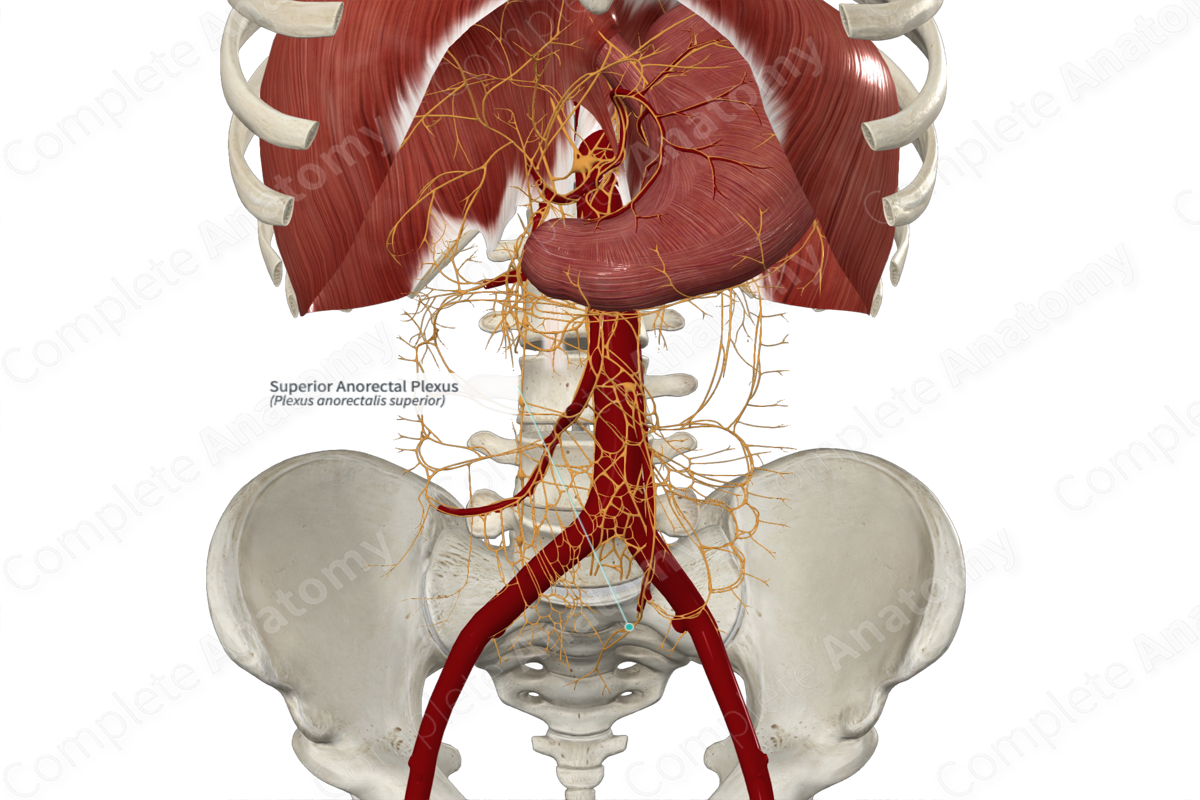
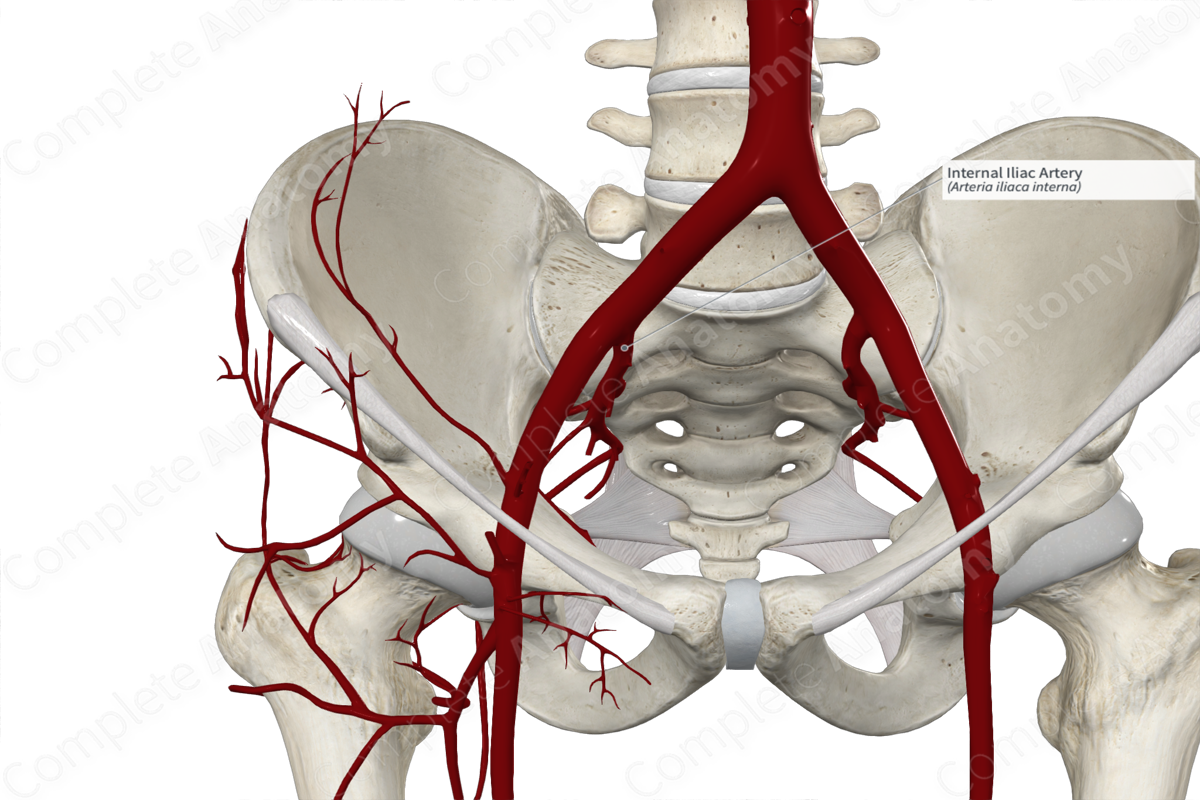
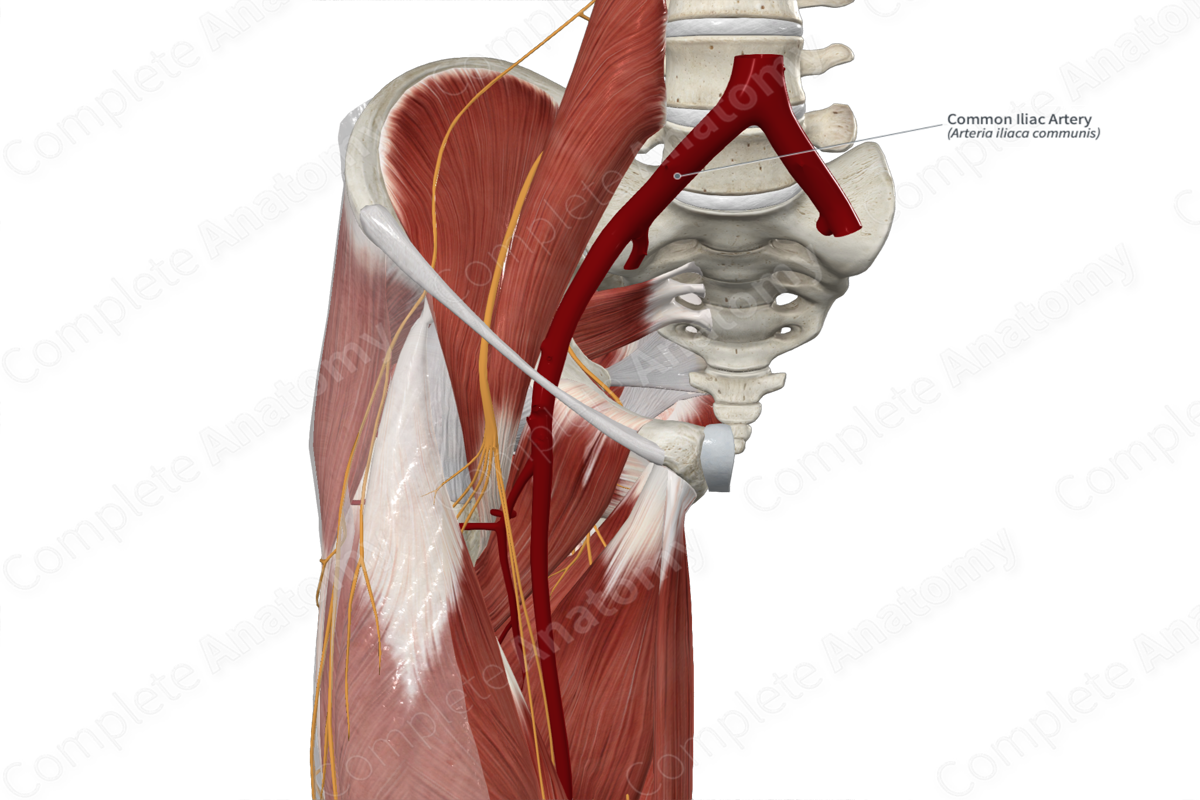
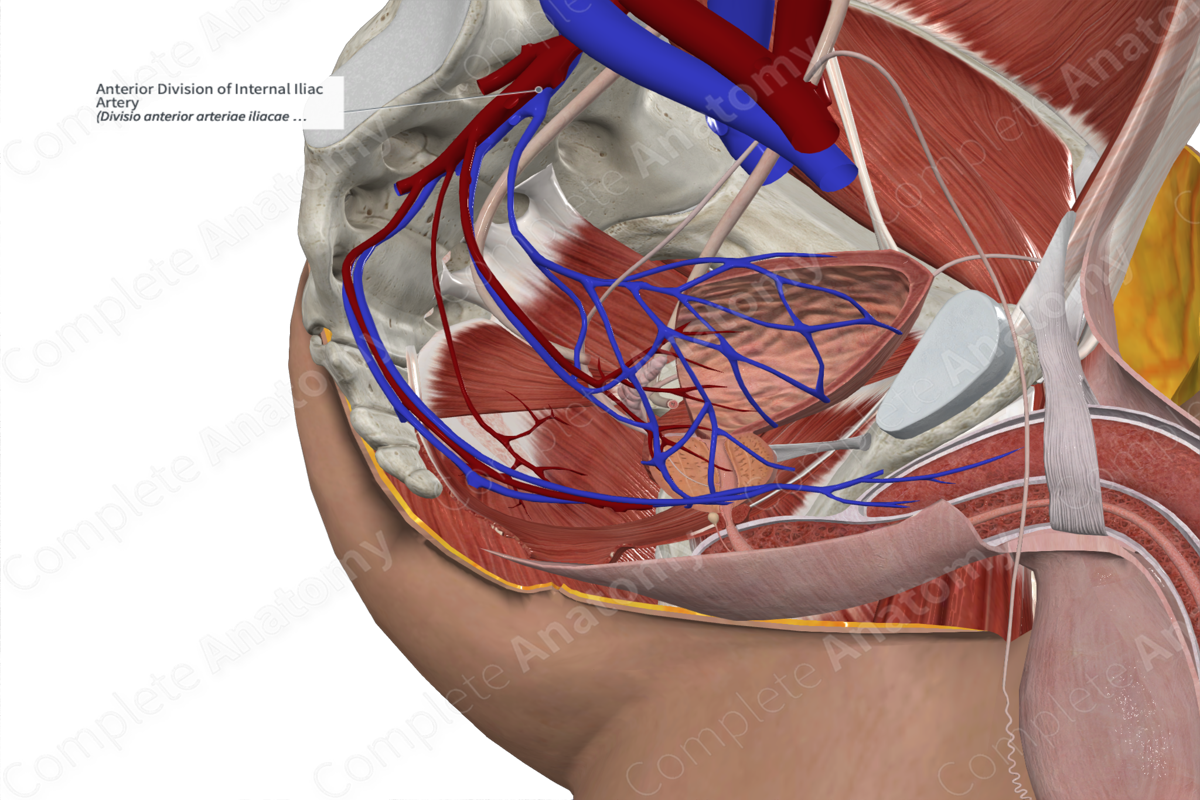
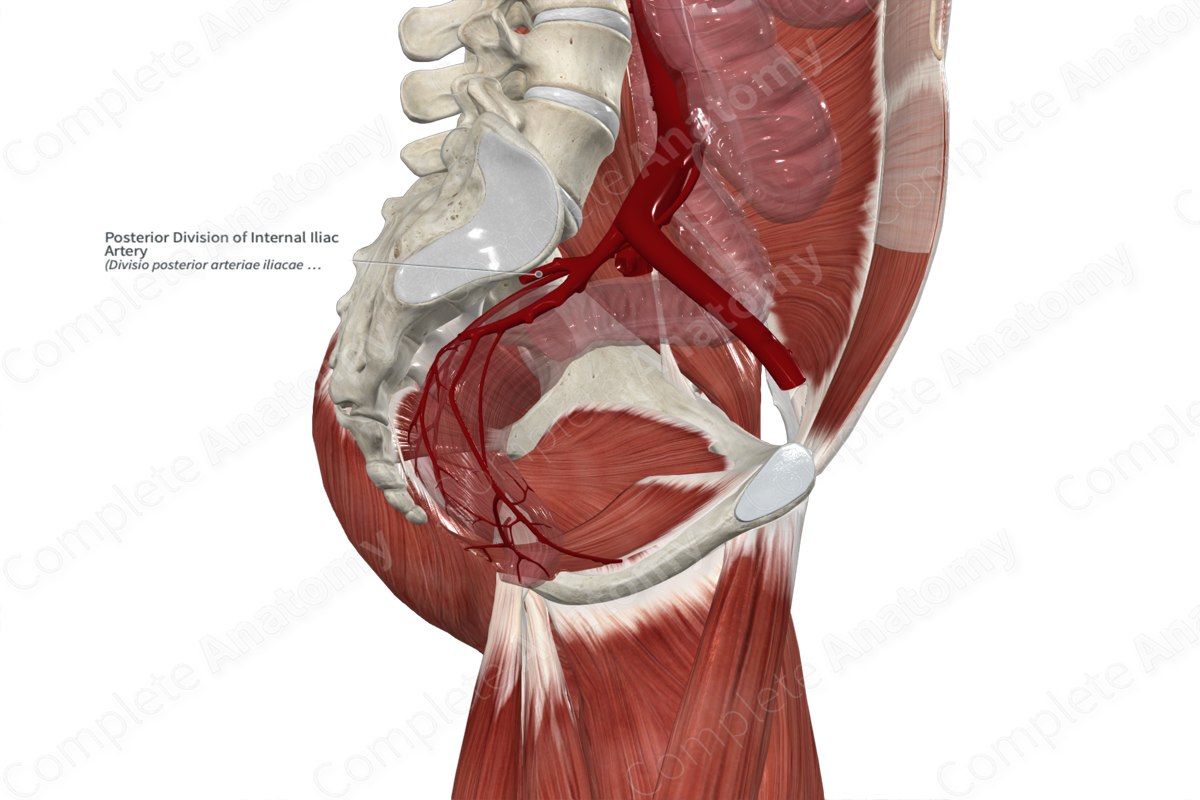
Internal Iliac
_____ _____ artery
• Main supply to the pelvic region
• Branches into two divisions
– Anterior branch
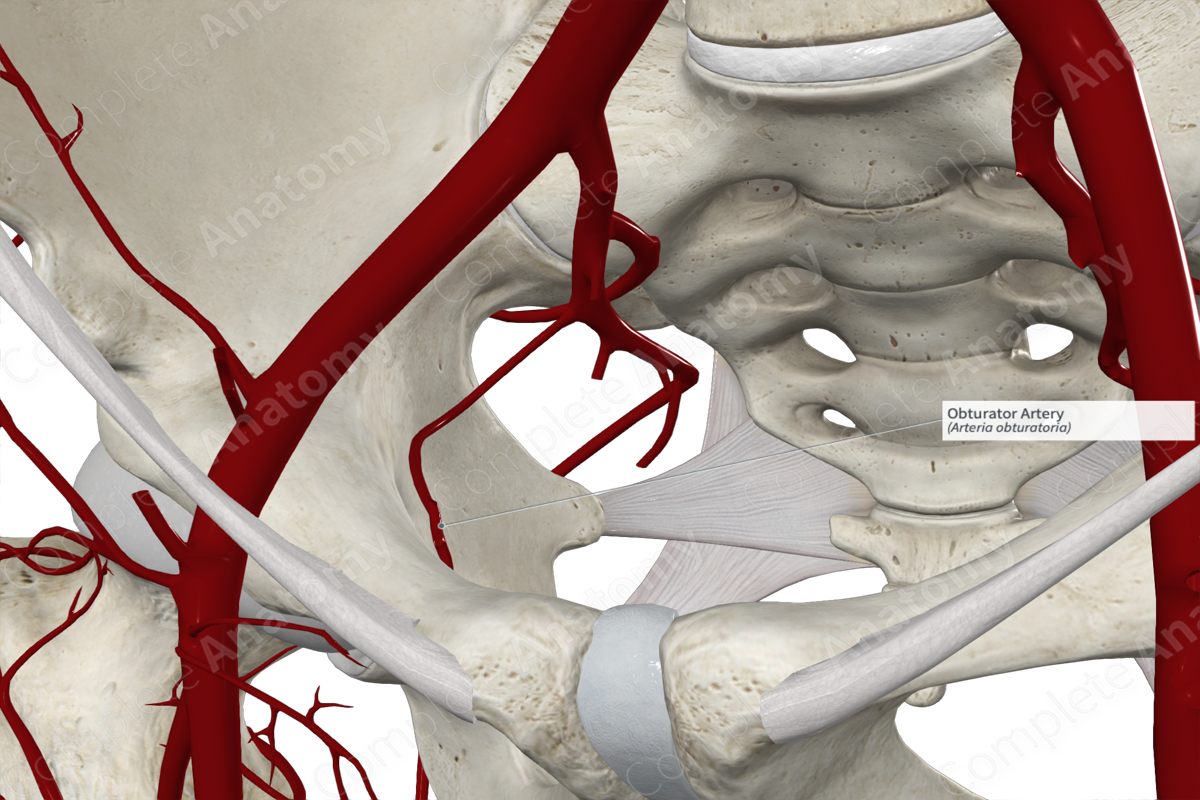
• Obturator artery
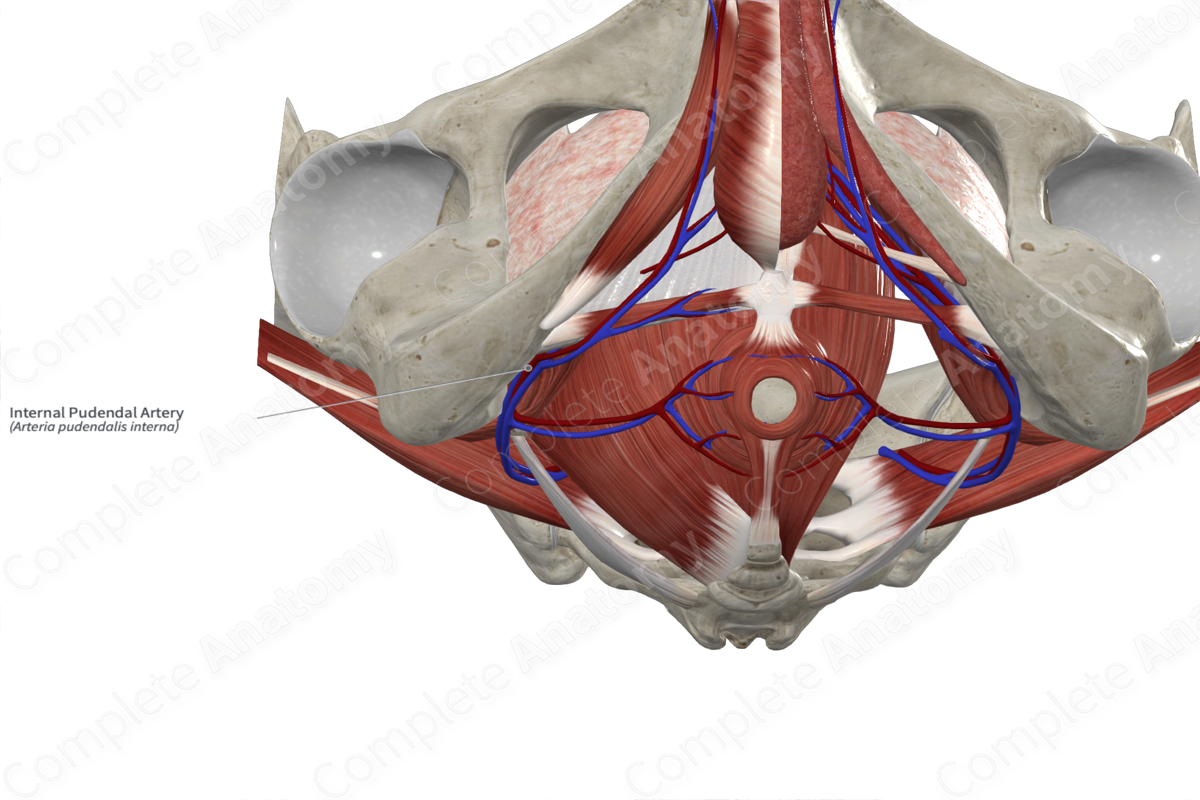
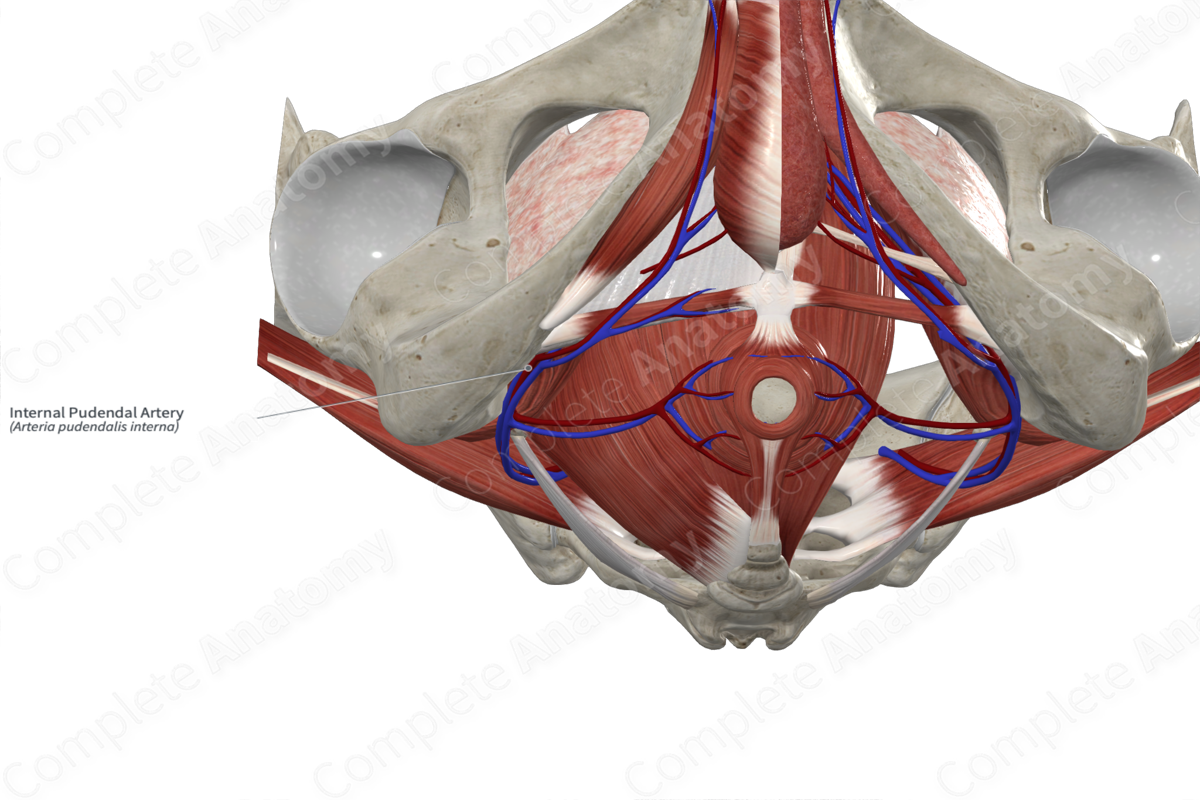
• Pudendal artery
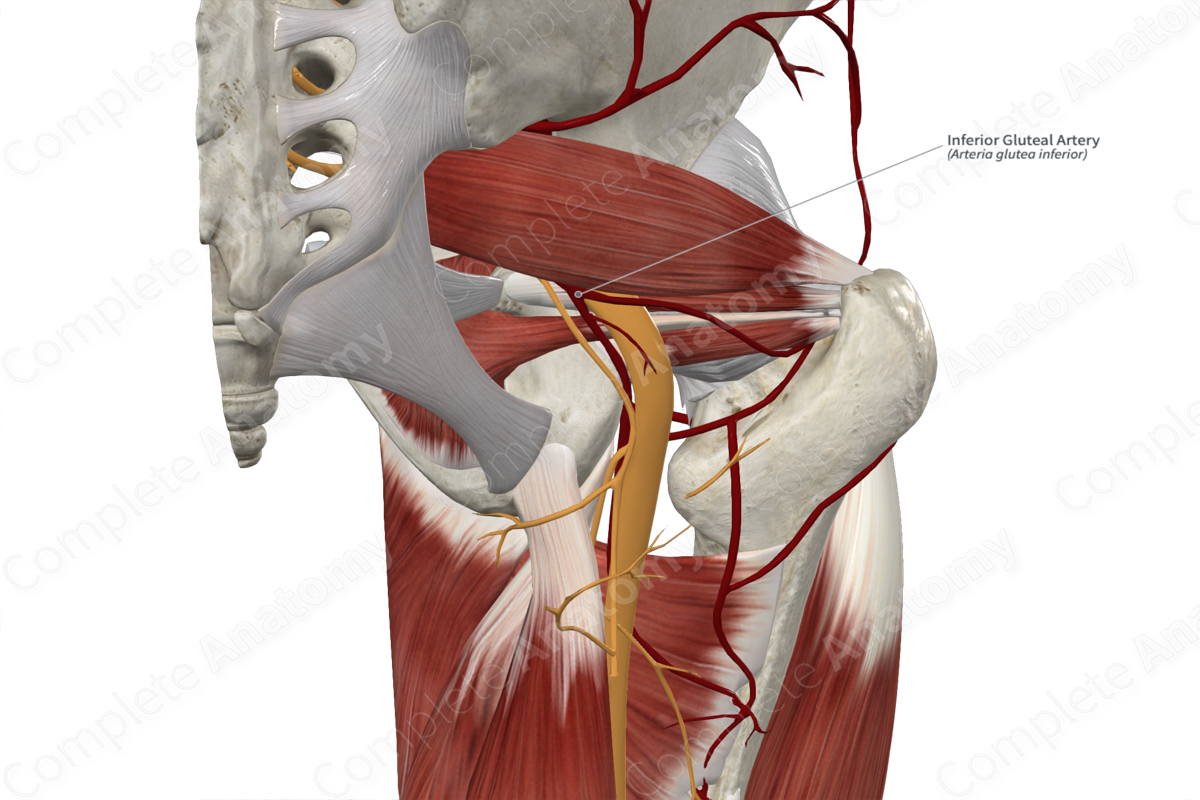
• Inferior gluteal artery
– Posterior branch
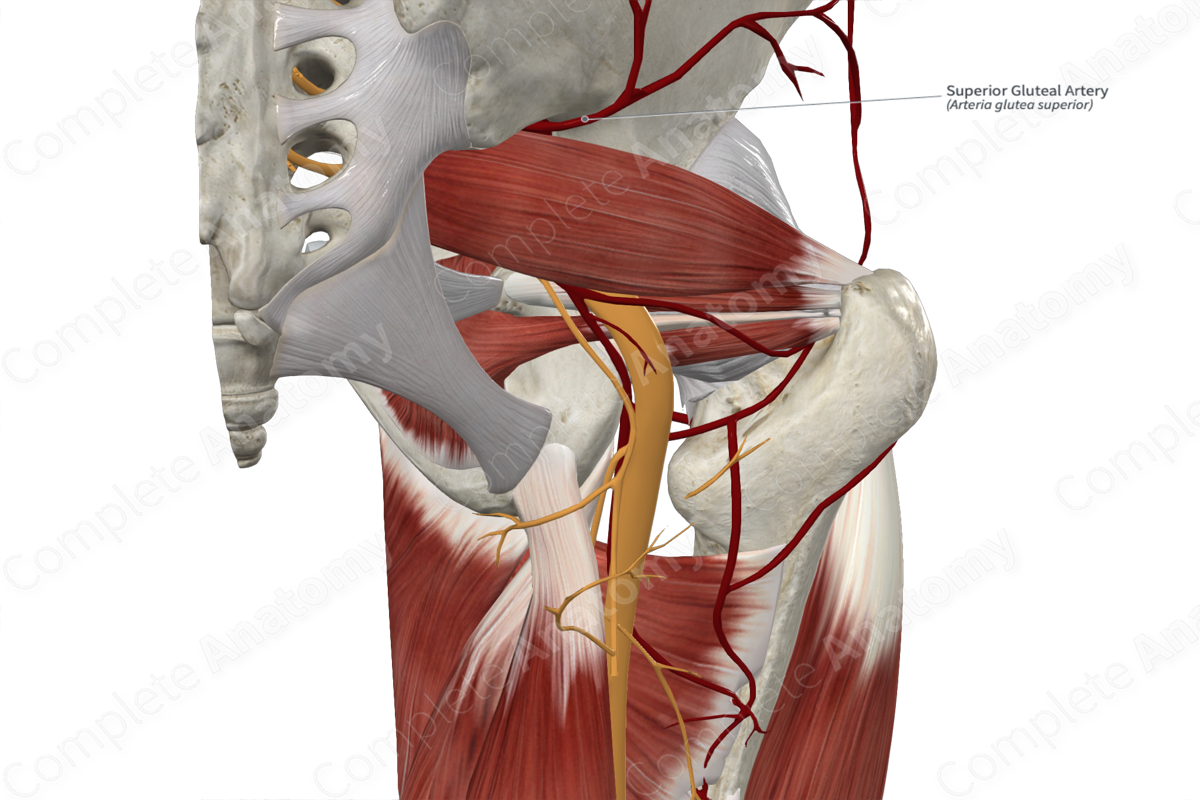
• Superior gluteal artery
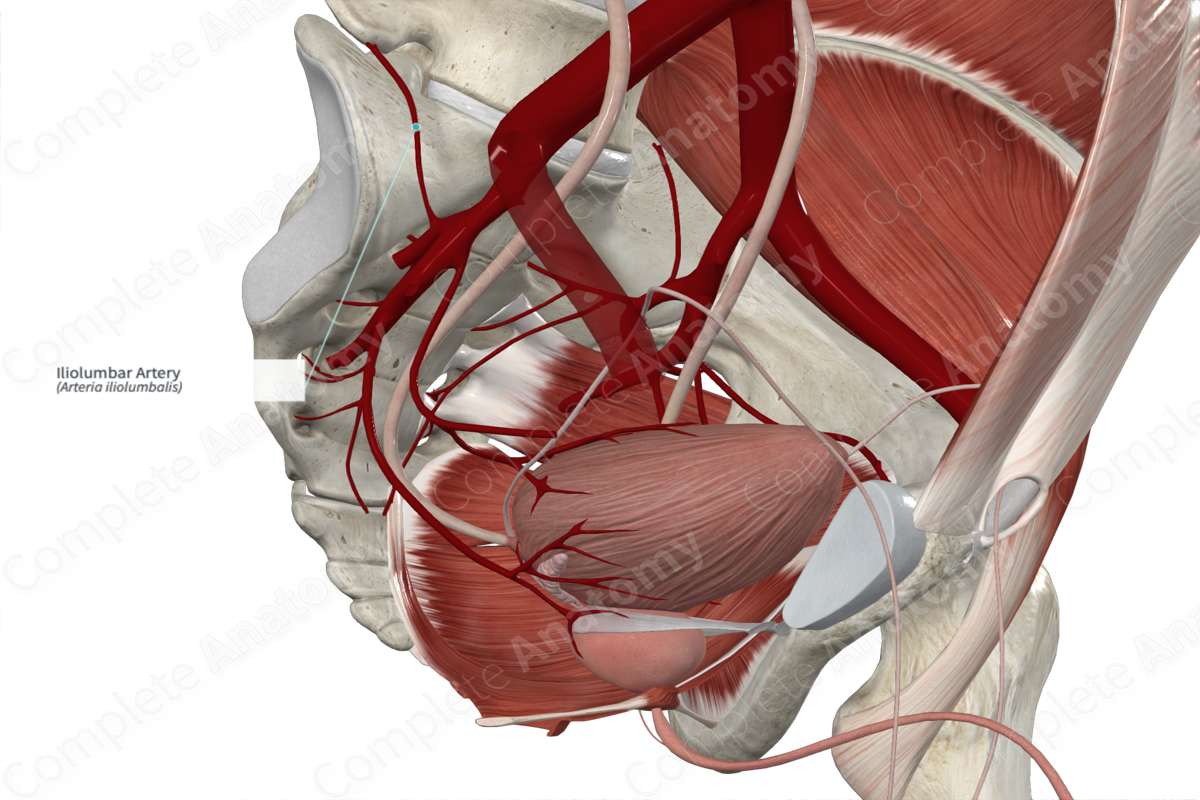
• Iliolumbar artery
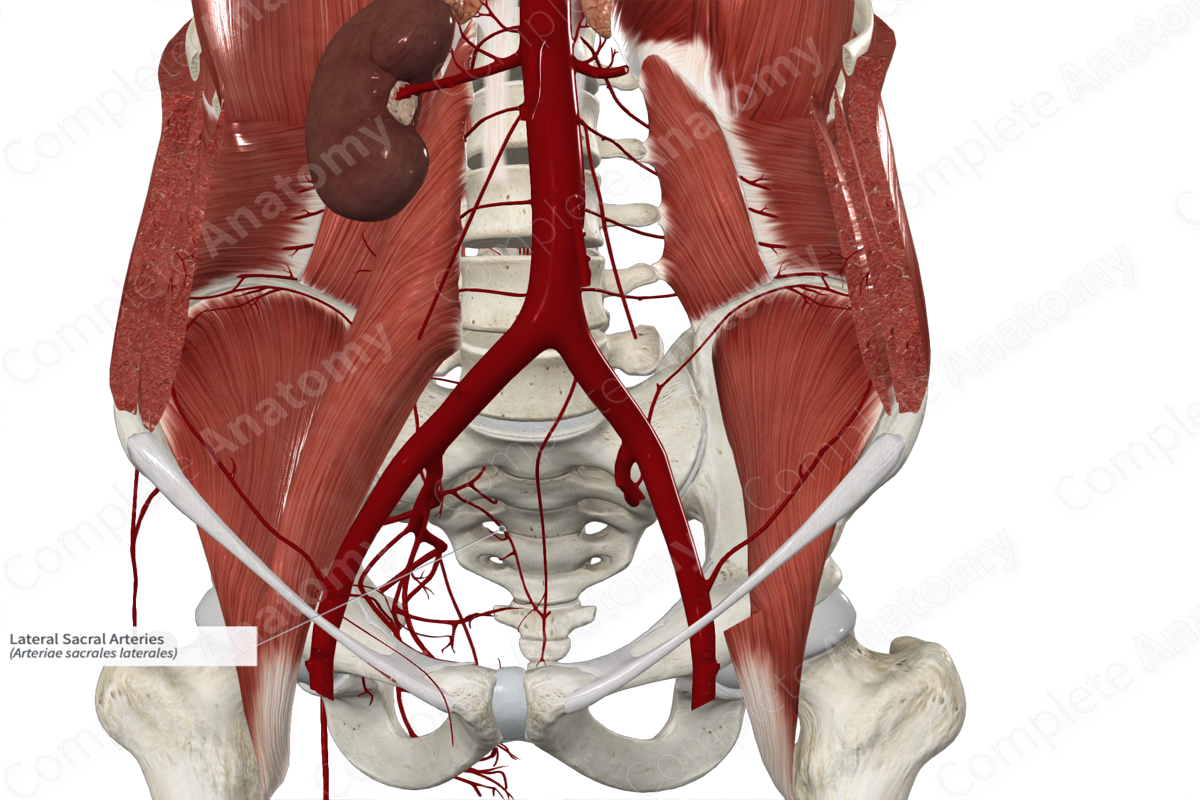
• Lateral sacral artery
Obturator artery
Pudendal artery
Inferior gluteal artery
• Main supplier of blood to the muscles of the pelvic diaphragm
• Exits through the greater sciatic foramen to supply the gluteal region.
Superior gluteal artery
Iliolumbar artery
Lateral sacral artery
Pelvic inlet
The opening that marks the boundary between the false pelvis (above) and the true pelvis (below)
Pelvic outlet
Lower opening of the true pelvis, crucial for childbirth and containing the lower parts of the urinary, digestive, and reproductive systems.
Saddle parasthesias
Refers to a tingling, burning, or prickling sensation in the saddle area
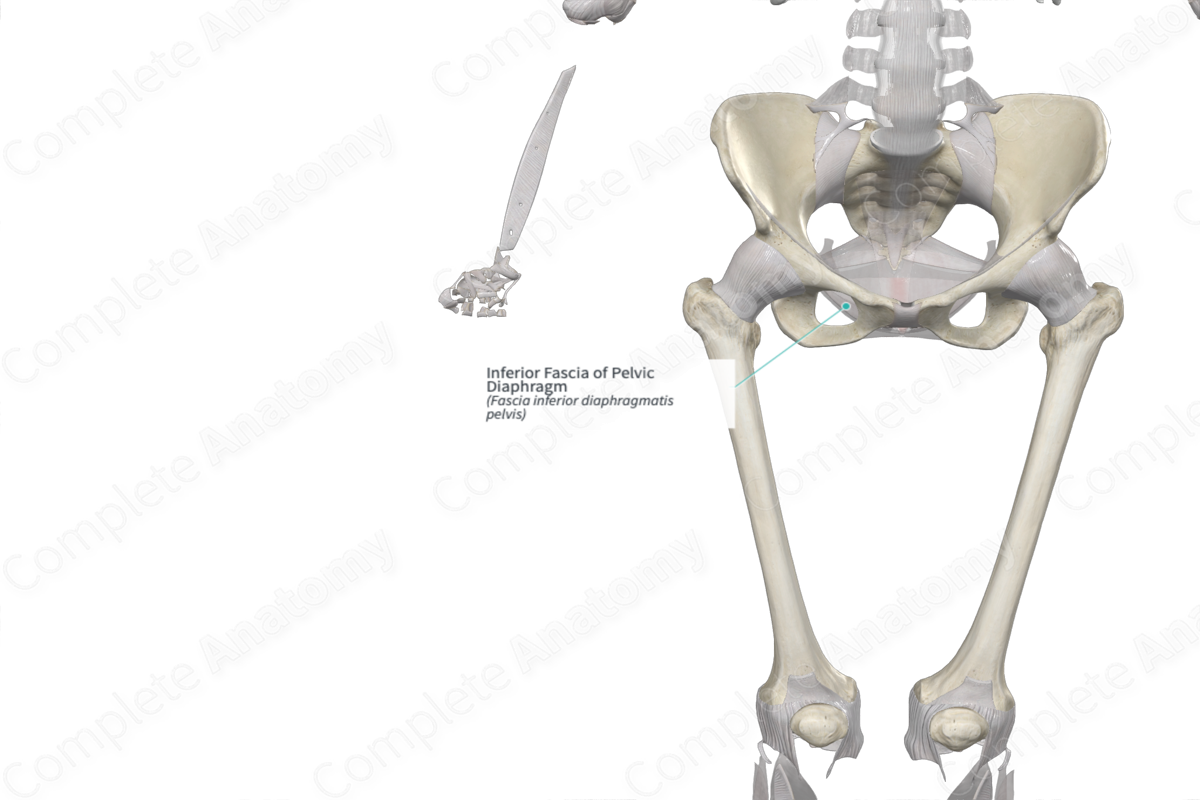
Pelvic diaphragm
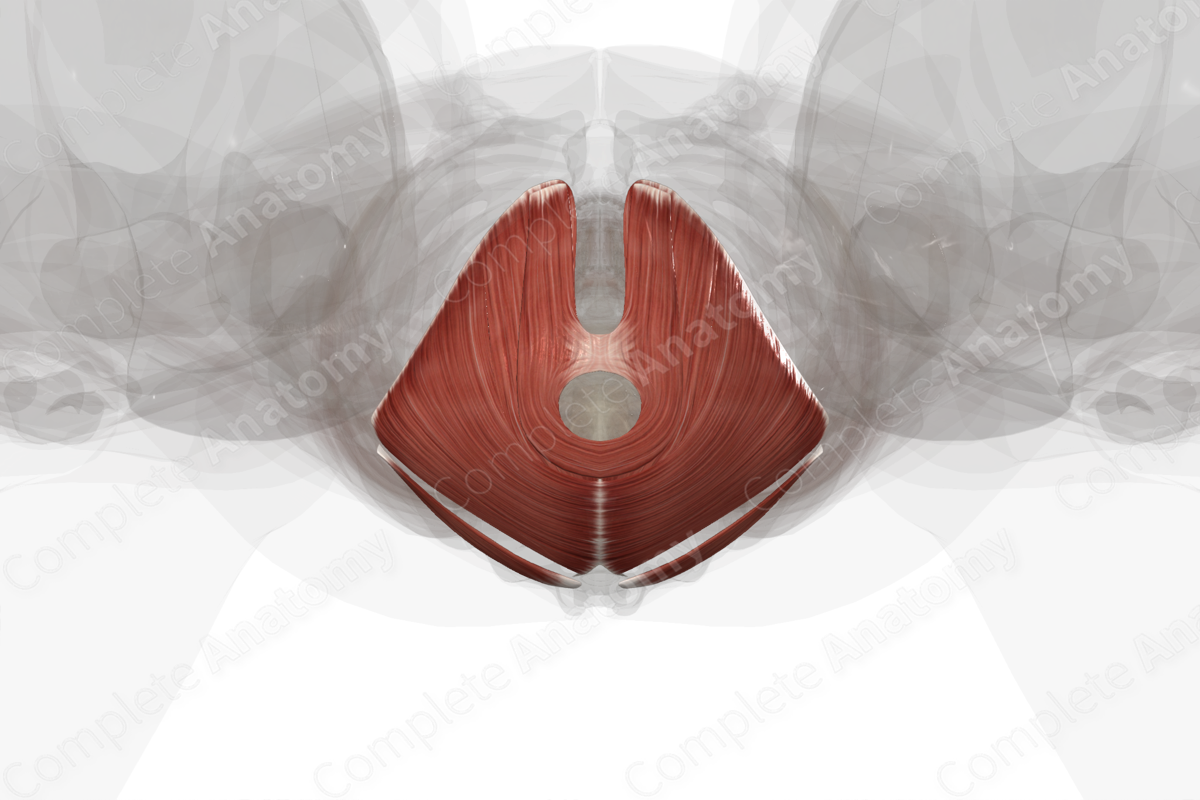
Superior fascia of levator ani
Inferior fascia of levator ani
Anorectal junction
Compressed at rest
Anal sphincter
Common iliac artery
Internal iliac artery Anterior division
Internal iliac artery Posterior division
Internal pudendal artery
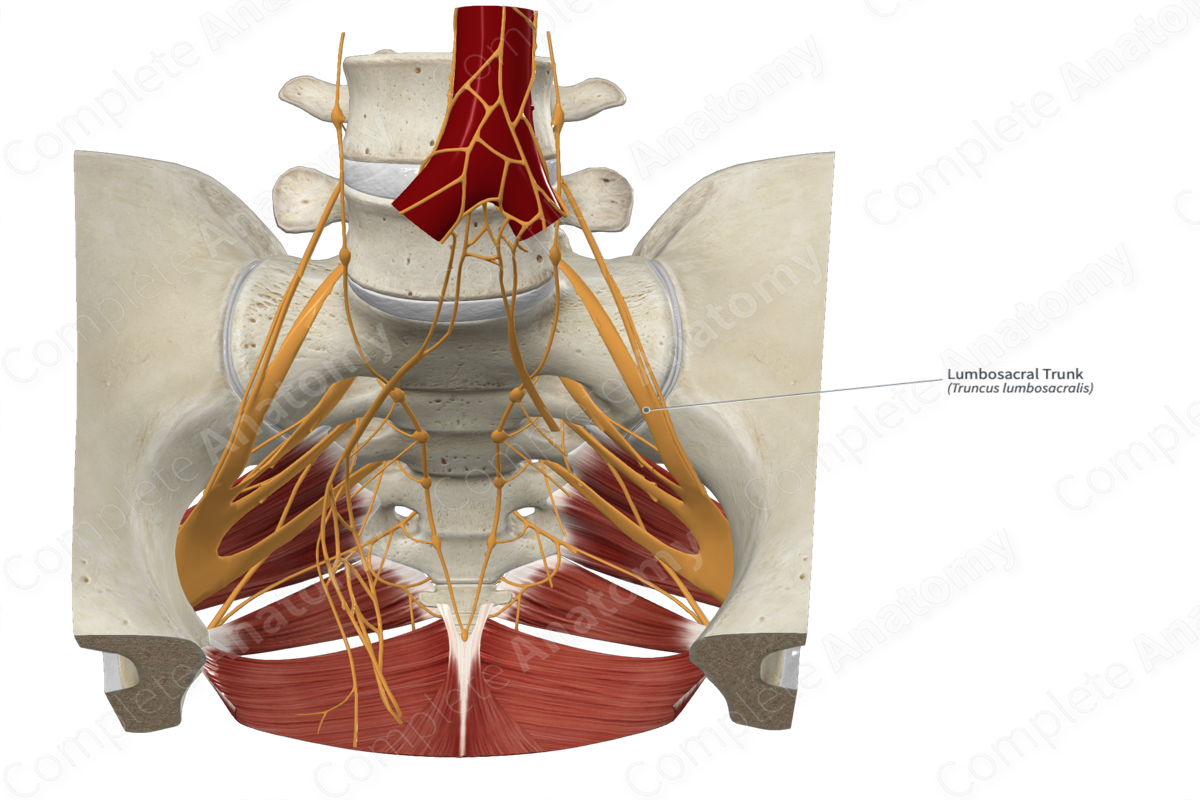
Lumbrosacral trunk
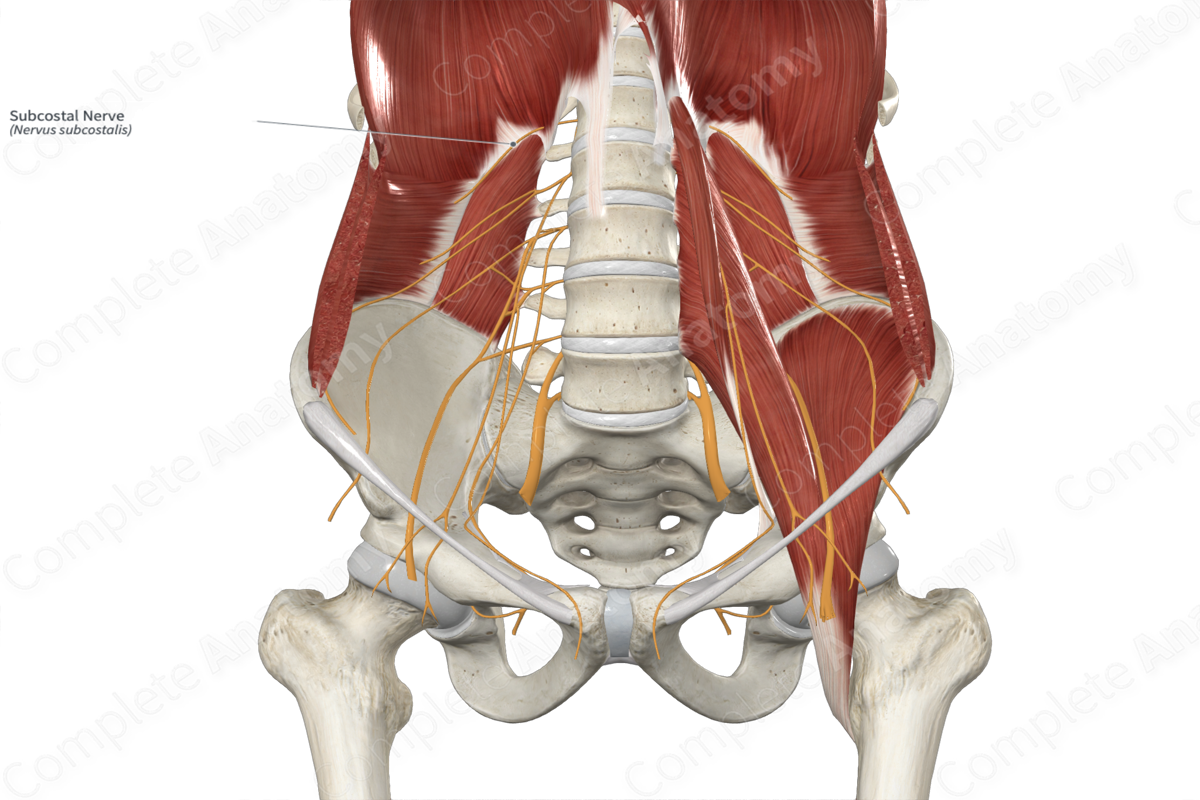
Subcostal nerve
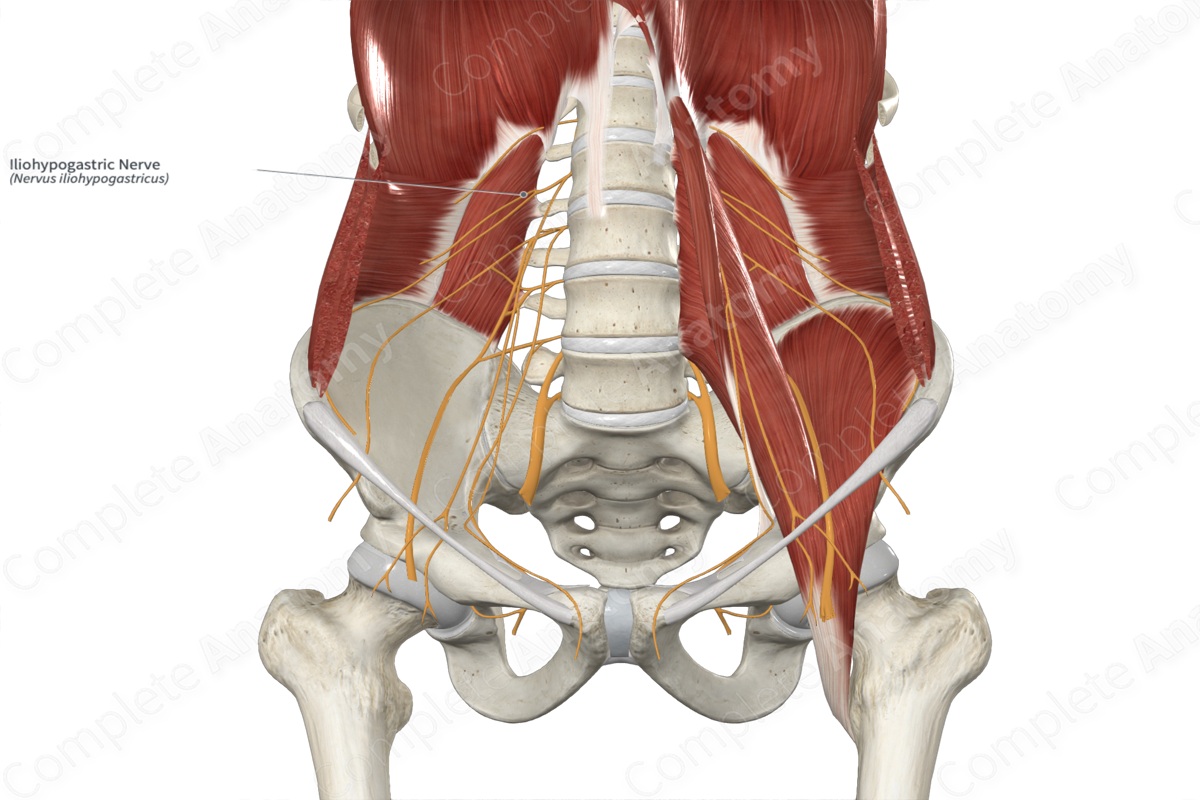
Iliohypogastric nerve
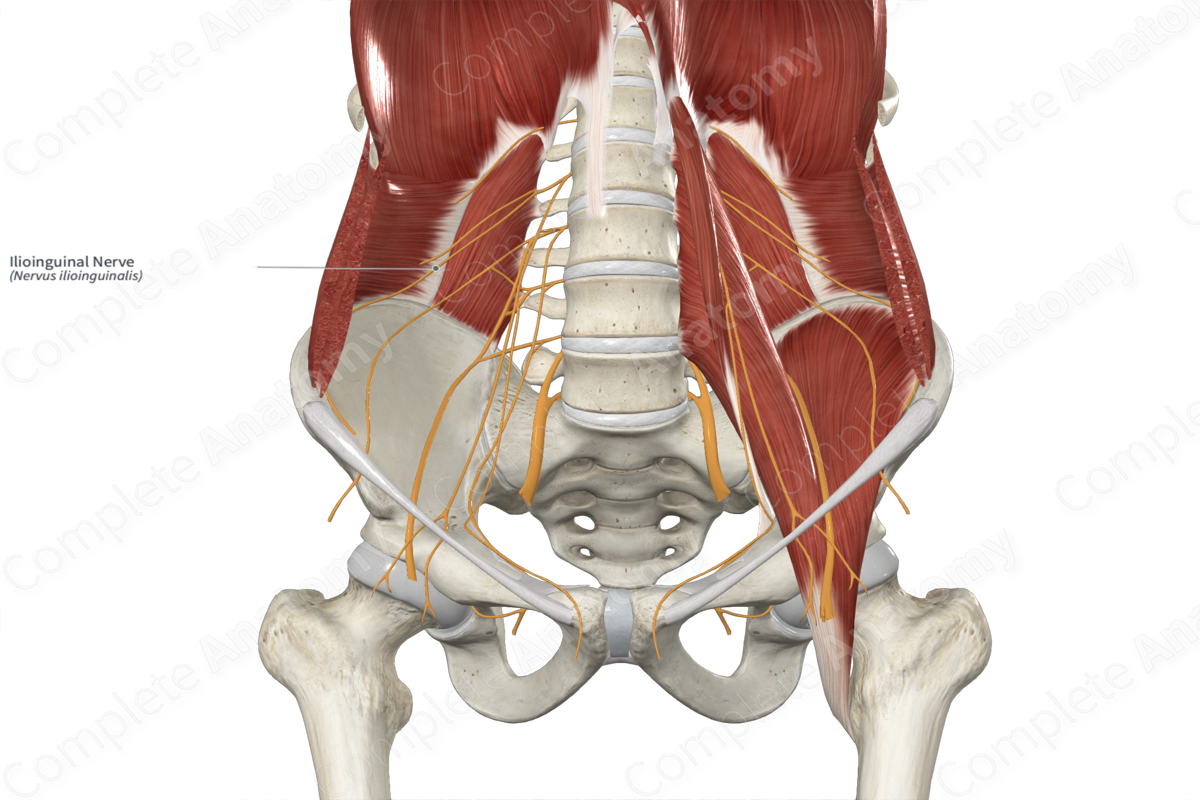
Ilioinguinal nerve
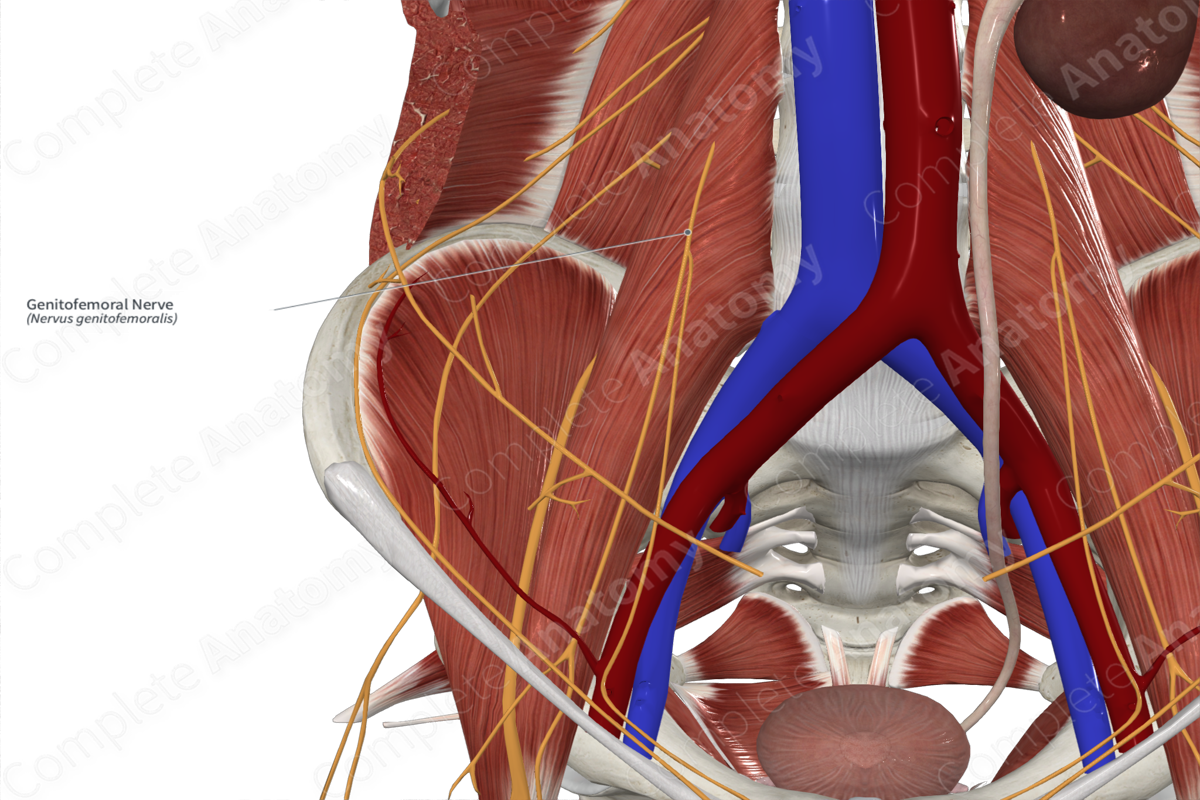
Genitofemoral nerve