Homeostasis, Allostasis, and Stress: Pathophysiology for Nursing
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Homeostasis
Remaining stable while staying the same; all systems in balance; equilibrium; an ideal 'set point' despite alterations within the body.
Allostasis
Overall process of adaptive change necessary to maintain survival and well-being; may involve altering multiple physiologic variables to match the resources of the body to environmental demands; helps the body achieve homeostasis.
Stress
Universal experience; result of both positive and negative experiences; important to understand; response to change.
General Adaptation Syndrome
Observed bodily changes produced by stress; has three stages: alarm, resistance/adaptation, exhaustion.
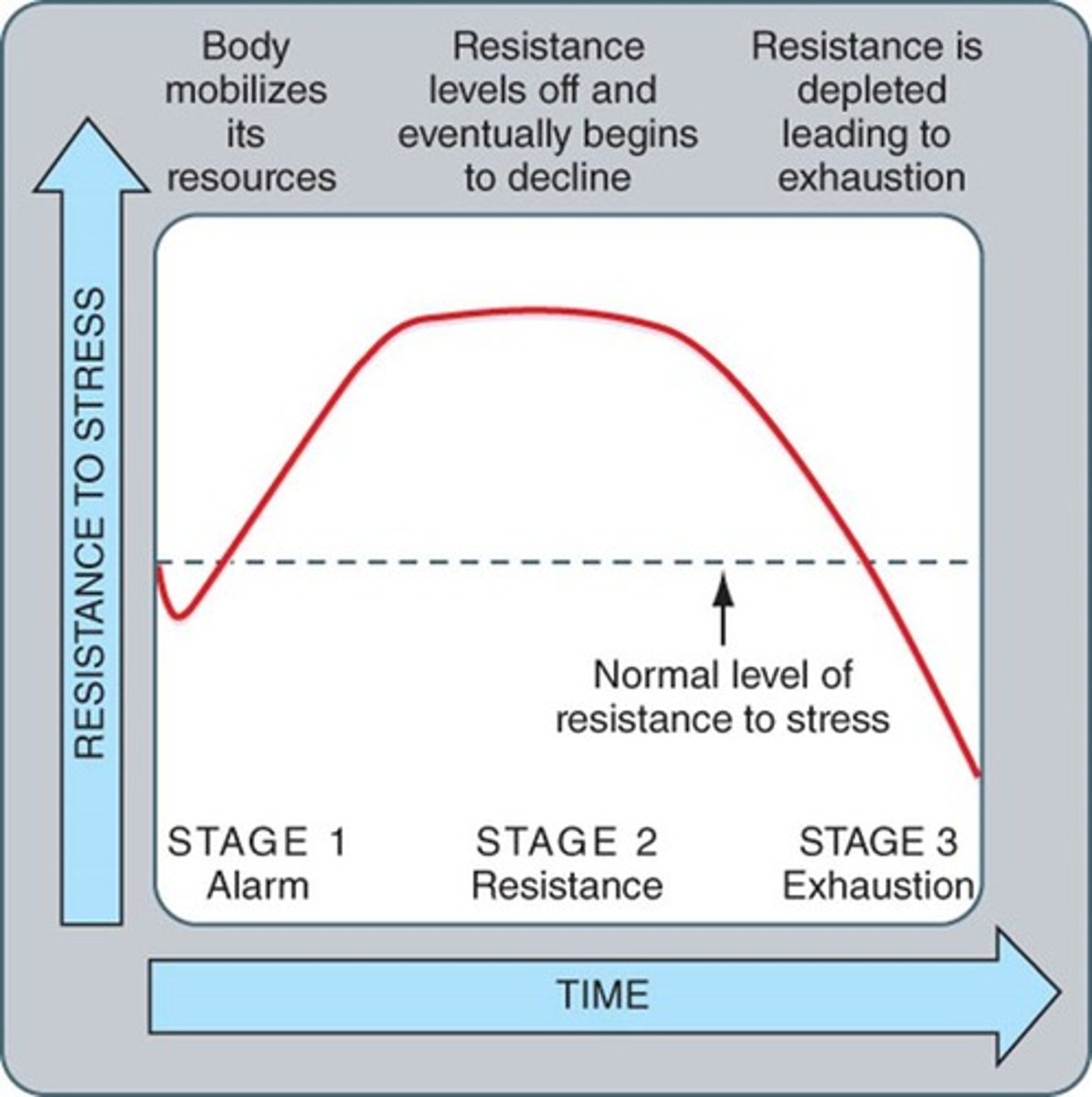
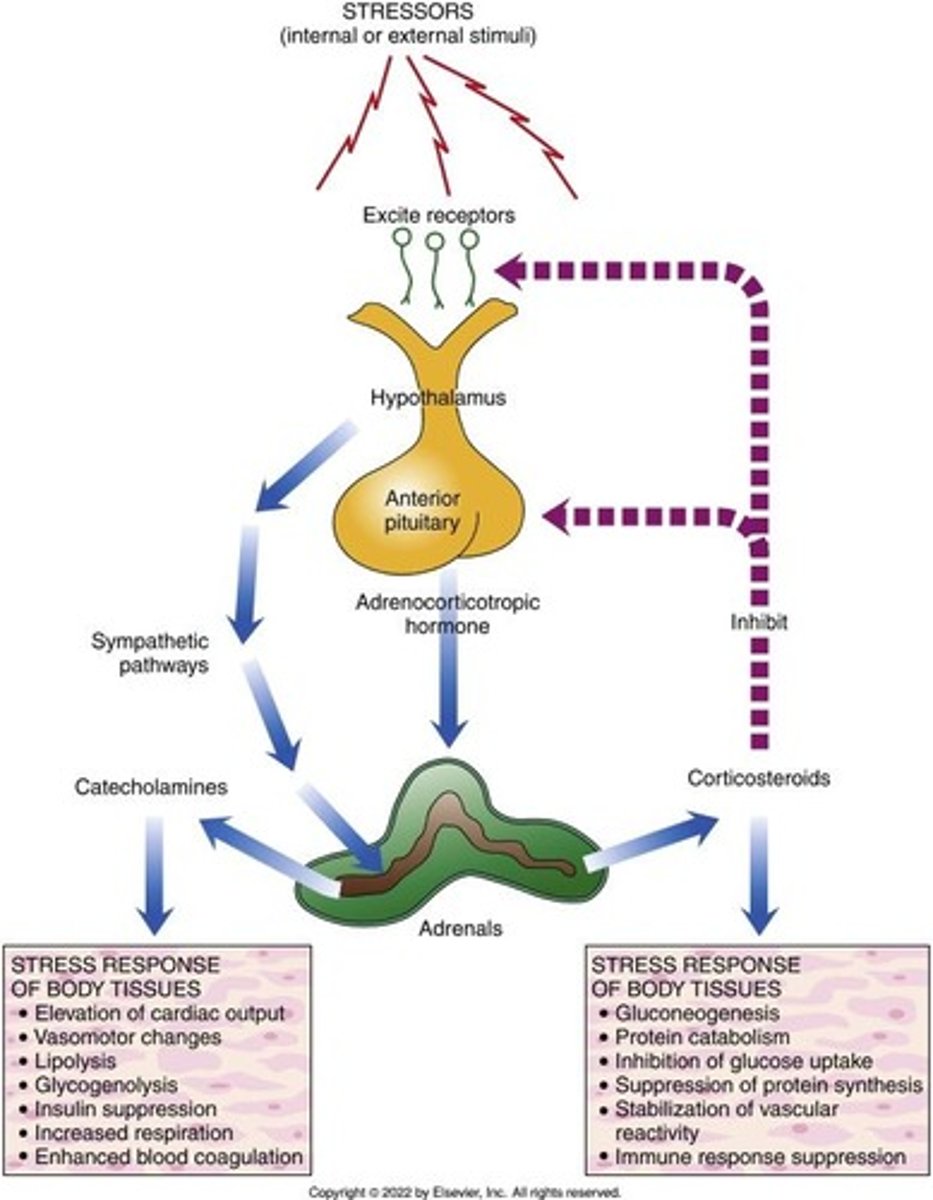
Alarm stage
Fight-or-flight response as the result of stressful stimulus; involves the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis.
Resistance or adaptation
Activity of the nervous and endocrine systems in returning the body to homeostasis; allostatic state: activity of various systems attempting to restore homeostasis.
Exhaustion
Point where body can no longer return to homeostasis; allostatic overload: 'cost' of body's organs and tissues for an excessive or ineffectively regulated allostatic response; effect of 'wear and tear' on the body.
Catecholamines
Norepinephrine and epinephrine; play an integral role in allostasis; sympathico-adrenal system response mediates the fight-or-flight response.
Adrenocortical Steroids
Cortisol and aldosterone; critical to maintenance of homeostasis; may synergize or antagonize effects of catecholamines.
Sex hormones
Estrogen, testosterone, and dehydroepiandrosterone; affect stress responses, influencing allostasis; may help explain gender responses during stress.
Endorphins and Enkephalins
Endogenous opioids; raise pain threshold; produce sedation and euphoria.
Immune Cytokines
Secreted by macrophages during stress response; enhance immune system response; prolonged stress can suppress immune functioning.
Growth hormone
Can increase during stress to enhance immune function.
Prolactin
Similar to structure of growth hormone; role in immune response.
Oxytocin
Produced during childbirth and lactation; associated with bonding and social attachment; thought to moderate stress response and produce a calming effect.
Coping
Ability to deal with the stressor; influenced by genetics, age, gender, life experiences, dietary status, and social support.
Adaptive coping strategies
Include physical activity, adequate sleep, optimal dietary status, relaxation, distraction, and biofeedback.
Maladaptive coping strategies
Include smoking, substance abuse, and overeating.
Effects of allostatic overload
Affects body organs and systems.