Unit 4: Object Oriented Programming
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
What is JOptionPane
A class enabling programmers to use dialog boxes to recieve user input
4 Key Components of a JOptionPane
Parent Component: Determines the position of the dialog box (set to null to center it)
Message: The object you want ot apepar in the dialog box
Title: The string you want to appear
Message Type: Icon that you want to be displayed
Syntax:
JOptionPane.showInputDialog(null, “Message”, “Title”, Message Type);
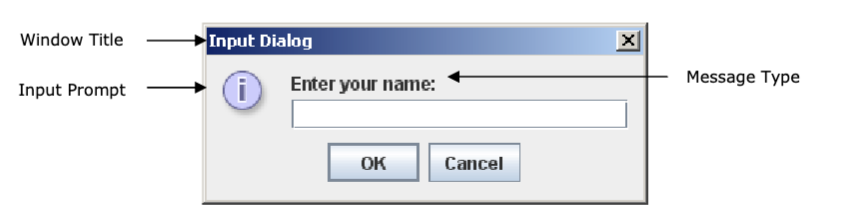
5 Different types of Messages
Error_Message
Information_Message
Warning_Message
Question_Message
Plain_Message
What is polymorphism?
Fuck you nigger Richard

Difference between scanner and JOptionPane
JOptionPane only takes in STRING values and OBJECTS while Scanner can read all datatypes
Difference between showMessageDialog() and showInputDialog()
showMessageDialog() - Does not return or input anything
showInputDialog() - Can read user input
In a showConfirmDialog() what values would be returned based on the button you pressed?
It is very similar to an array, as the first button from the left will be assigned the value 0, the following would be 1 and so on.
How to import custom images in java
Declare and initialize an ImageIcon object
private ImageIcon img;
img = new ImageIcon (“file name“);
How to add buttons to the JOptionPane
Declare an array and fill in the buttons/dialog for each button
String[] buttons = new String[4] {“Yes”, “Yes to all”, “No”, “Cancel”};
JOptionPane.showOptionDialog(null, “Question ?”, “Buttons”, JOptionPane. WARNING_MESSAGE, 0, null, buttons, null);
What is SWING
A package allowing programmers to create applications in the GUI
What is JFrame
The main window where components like labels, buttons, textfields are added to create a GUI
Where do you set the properties of the frame?
In the constructor
What does setting null to setLocatioNrelativeTo(null); do
It sets the JFrame to the center of the users screens
Difference between private, protected, and public modifiers
Private: Makes data fields accessible in a singular class
Public: Makes data fields accessible in all classes within the project folder
Protected: Makes data fields accessible in all classes or subclasses
What JFrame method must always be used
seteVisible(true);
What must be written in main after setting the properties in the constructor?
new [class name](); —> This calls on the constructor
What 2 methods do you need to change the background colour of the frame
getContentPane() and setBackground()
/
getContentPane().setBackground(Color.BLUE);
What is the difference between Graphics and Graphics2D
Graphics: It is used for simple drawings
Graphics2D: Used for more complex and high-quality graphics rendering.
How does drawing strings work in the paint method?
g2.drawString(“message”, x, y);
How to instantiate a font
Font f = new Font(“Papyrus”, Font.BOLD, 18);
How to instantiate a FontMetrics and what is FontMetrics
FontMetrics fm = getFontMetrics(f);
It is used to measure the size of characters, strings, and other text elements in a specific font
How to write custom fonts
Font f = Font.createFont(Font.TRUETYPE_FONT, new FILE(“file”)).deriveFont(30f)
How to draw images?
g2.drawImage(img.getImage(), xPos, yPos, this);
How to draw lines and rectangles?
g2.draw(new Line2D.Double(Origin X, Origin Y, Width, Height);
g2.draw(new Rectangle2D.Double(Origin X, Origin Y, Width, Height);
How to set colours of the shape drawn
g2.setColor(Color.COLOR);
g2.draw(new Rectangle2D.Double(Origin X, Origin Y, Width, Height);
How to import JPanel to a class
After the class name write “extends JPanel” and import the package
public class Example extends JPanel {
}
Is JFrame the same as JPanel?
JFrame represents a framed window and a JPanel represents some area in which controls
Where does JFrame go when using JPanel
Instead of writing Extends JFrame at the top, JFrame will be instantiated in side the constructor, and the name given must be used to set the JFrame properties
Ex:
JFrame jf = new JFrame();
jf. setSize(100, 500);
Biggest change in the JFrame when using JPanel
the setContentPane(this);
When the keyword this is set inside the parameters, it tells JFrame to add all components of JPane to the JFrame so we can see it.
What’s the difference between a method and a constructor?
A constructor instantiates field, named after the class, and has no return type
A method is named everything but the class name and has a return type, either void or a datatype
What makes up a method header
public int max(int num1, int num2){}
Visibility: Public
Return Type: int
Method Name: move
Parameters: int num1, int num2
What are the 3 keywords that a class containss?
Fields: Defines the global variables
Constructors: Initializes the fields
Methods: Defines the methods of the class and returns the data type
How to access another class in main
[Class name] [name] = new [Class name]();
[name].[method in class]();
Ex: Dice dice = new Dice();
dice.getRoll();
What is a Unified Modelling Language (UML) Diagram
A diagram used to help programmers organize their code to help non-programmers understand.
What is a UML made up of
Class Name
Fields
Constructors and Methods
How are the components of a UML denoted?
Fields: field name: Data Type
Constructor: [Constructor Name](Parameters)
Methods: [Method Name](Parameter): [Data Type]
</p><p><strong>Methods: </strong>[Method Name](Parameter): [Data Type]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/d63047c5-a180-4894-b41d-84cbc993e20b.png)
Which symbols indicate the visibility?
Public: +
Private: -
Protected: #
What is an accessor and mutator?
Accessor: An accessor method, or getter, is used to retrieve the value of an instance variable. It typically follows a naming convention where the method name starts with "get" followed by the name of the variable with the first letter capitalized.
Mutator: A mutator method, or setter, is used to set or update the value of an instance variable. It typically follows a naming convention where the method name starts with "set" followed by the name of the variable with the first letter capitalized.
How does the RGB Color work?
There are 3 numbers that represent Red, Green and Blue
(0, 0, 0)
Timer Class
Has a Timer object that is used to time certain events in the program. For the case of Animation, the swing package is used and no the the util one (that brings your computer’s actual clock in).
Events
Objects created when something changes in the GUI of a program
Timer Object
Generates events at regular intervals and has a listener that listens when an “event” occurs → ActionListener
Methods
Timer Class Methods
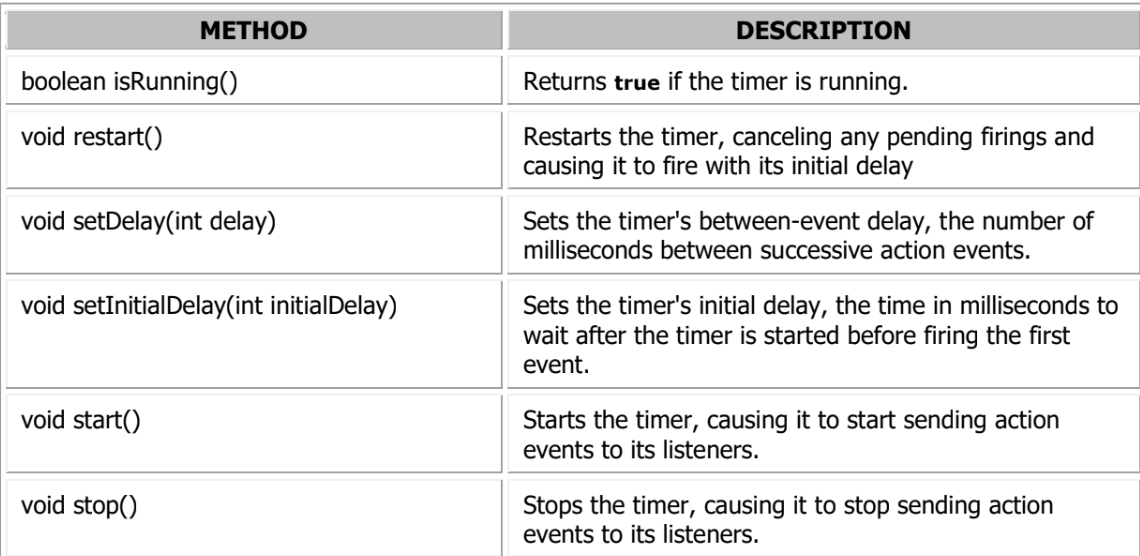
Methods we Only Care About
.start() → starts the timer
.stop() → stops the timer
initializing a timer
Declare timer as a field first
The first parameter/argument is measured in milliseconds
The second parameter is the ActionListener interface
interface
Similar to a class but contains abstract methods like actionPerformed().
Multiple Timers
The actionPerformed method will always the take the fast timer if e.getSource() is not used.
if (e.getSource() == exampleTimer)
Grabs the specified timer if there are multiple timers and runs the code below the if statement.

Thread Class
Creates sleep() method which stops the code from running for a specified amount of time. Ex: Code stops for half a second (measured in milliseconds)
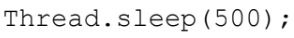
interrupt()
method that is called within the thread class given an error. The error is the InterruptedException error.
repaint()
cleans the JFrame and rebuild it very quickly, placing each “component” in a new location on the screen.
Animation in Multiple Classes
For animation to happen in multiple classes, a few variables and methods must be used:
Direction Variables: RIGHT, DOWN, LEFT, UP
ImageIcon Variables: imgPlayer (imgPlayerLeft, imgPlayerRight, etc.)
Mutator Methods: setDirection(), setX(), setY()
Void Methods: move(int dir)
Boundary Checking Method: (can be used in main or class)
KeyEvent Class
contains keyboard event objects or in other words, events that deal with the user inputting stuff via the keyboards.
keyboard event
generated everytime a user inputs something into the keyboard.
Registering an object for the KeyListener interface
component.addKeyListener(listener);
- Listener → Listens for the key events
- Component → object that generates the key events
KeyListener Interface
And objects that need to listen for key events must have the KeyListener interface implemented.
For the KeyEvent class to work, what code must be initialized in the constructor?
addKeyListener(this); → Tells Java to send key events to this object
setFocusable(true); → Ensures that the component can receive keyboard focus or understand what key is being typed
requestFocus(); → asks for the object to get the keyboard focus right now
Implementing KeyListener Methods
When implementing KeyListener, these three methods must be placed in the class (whether or not they are used).

getKeyChar() vs. getKeyCode() methods
getKeyChar() → returns the inputted character to the KeyEvent Class
getKeyCode() → returns constatns such as “VK_DOWN”
Some Constants
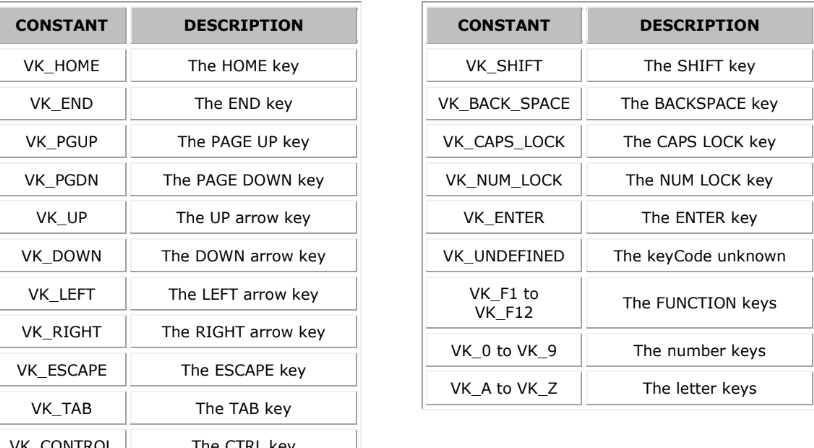
KeyPressed and KeyReleased methods
KeyPressed() example:
if (e.getKeycode == KeyEvent.VK_RIGHT)
right = true;
KeyReleased() Example:
if (e.getKeycode == KeyEvent.VK_RIGHT)
right = false;
The purpose of this is to prevent lag in the movement of the image/character that the programmer puts in place.
actionPerformed method
After adding the code to the KeyPressed and the KeyReleased methosd → it is time to increase or decrease xPos and increase or decrease yPos based on the direction
MouseEvent
A class where mouse object events belong to.
MouseListener & MouseMoveListener
Any objects that need to listen for mouse events must have the MouseListener and MouseMoveListener interface.
What do we initialize in the constructor to let the MouseListener listen to our key events?
addMouseListener(this);
addMouseMotionListener(this);
setFocusable(true);
requestFocus();
MouseListener Methods
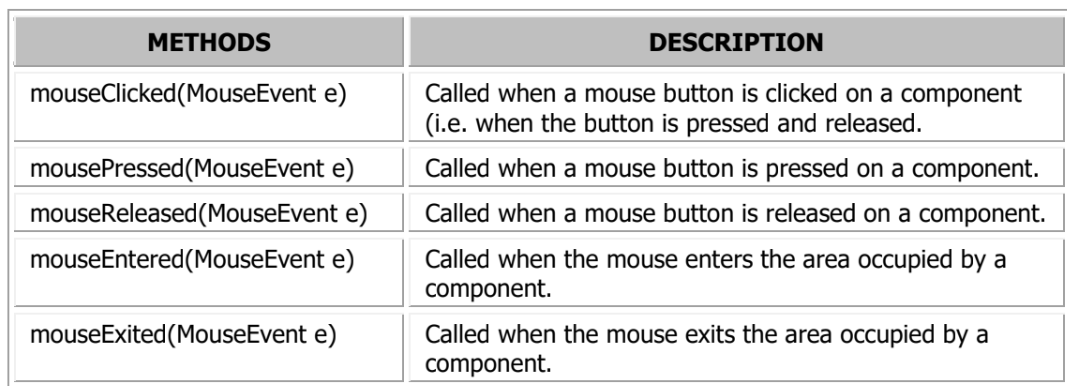
MouseMotionListener Methods
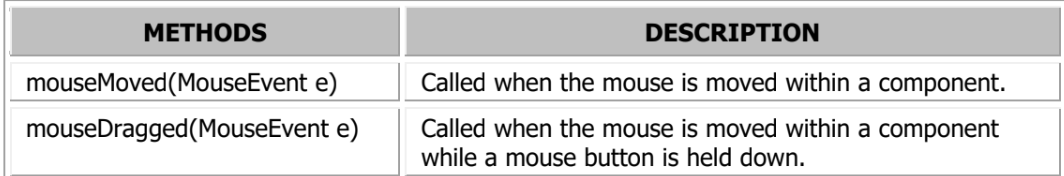
Methods in the MouseMotionListener and MouseListener Methods?
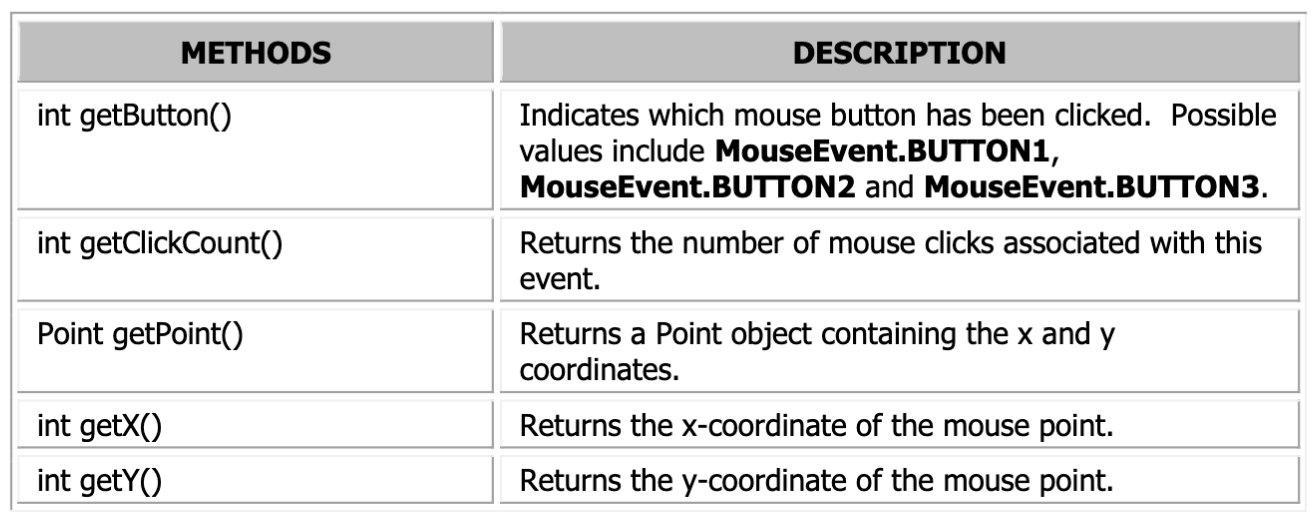
Collision Detection
Used to see if shapes surrounding an object (masks/bounding boxes) collide with each other.
.intersects()
Method part of the rectangle class. At least one of the masks has to be a rectangle.
Ellipse2D vs. Rectangle2D
For images that fit a circle-like frame better. Ex:
// Ellipse variable + Rectangle2D variable
Ellipse2D circle = new Ellipse2D(player.getX(), player.getY(), img.getIconWidth(), img.getIconHeight());
Rectangle2D rect = new Rectangle2D(player.getX(), player.getY(), img.getIconWidth(), img.getIconHeight());
boolean collision = false;
// Checking for collision:
if (circle.intersects(rect))
{
collision = true;
}
ALWAYS PUT THE RECTANGLE 2D SECOND IF YOU WANT TO CHECK FOR COLLISION BETWEEN A CIRCLE AND A RECT MASK!
Projectiles
Steps:
Set the x and y pos out of bounds initially for the image and the rect to prevent early collisions
If player is playing → utilize a keyboard pressed event such as VK_SPACE
When user presses VK_SPACE → set position of the projectile to the player’s x and y pos
Used a boolean variable such as “IsFired” to prevent the user from firing prematurely
Adding Sounds in Java
Java Supports:
MIDI
WAV
RMF
AU
AIFF
Packages Needed
java.io → FileInputStream class to get the needed audio
javax.sound → AudioInputStream and clip class
Starting and Stopping audio
// what ever your Clip file is
clip.start();
clip.stop();
Looping a song entirely
clip.loop(Clip.LOOP_CONTINUOUSLY);
Playing more than one sound
try
{
// Open an audio input stream.
File soundFile2 = new File("Music.wav");
AudioInputStream audioIn2 =
AudioSystem.getAudioInputStream(soundFile2);
clip2 = AudioSystem.getClip();
clip2.open(audioIn2);
clip2.start();
}
catch(Exception e)
{
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null, “File not Found”);
}
// Copy and paste this format into things such as keyPressed method to play it everytime there is a key event.