L5 HTN emergency
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
HTN emergency
severe elevations in blood pressure w/ evidence of acute target organ damage
BP>180 and/or >120 mmHG
admission to the ICU for likely treatment with intravenous medication is recommended
tied to high in-hospital mortality rate or inc one year risk of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality
what to do with elevated blood pressure without target damage
NOT an HTN emergency
likely can use oral med for treatment
ICU admission not required
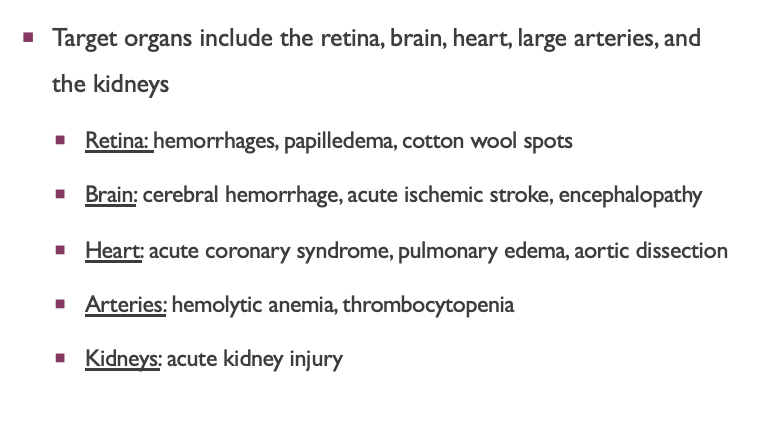
Acute target organ damage for HTN emergency
Target organs include the retina, brain, heart, large arteries, and the kidneys
Retina: hemorrhages, papilledema, cotton wool spots
Brain: cerebral hemorrhage stroke, acute ischemic stroke, encephalopathy
Heart: acute coronary syndrome (STEMI or MI), left ventricular failure + pulmonary edema, aortic dissection
Arteries: hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia
Kidneys: acute kidney injury
gnereal presentation of HT emergency
headaches, neurologic symptoms and/or dizziness
visual disturbances
chest pain
dyspnea - can be tied to hemolytic anemia
+ more un-specific presentation
think the target it affect and damage
BP goal in most HTN emergengencies
systolic BP reduced no more than 25% within first hour
<160/100 mmHg within the next 2-6 hours
SBP of 130-140 mmHg next 24 to 48 hours
BP goal for acute aortic dissection
SBP < 120 mmHg during the first hour
acute sympathetic discharge or catecholamine excess states
debatable
SBP <140 mmHg within 1 hour
general consideration for drug selection in hospital for HTN emergency
IV formulation
quick onset
rapidly titratable
consideration for moa and site of action
IV infusion vs IV bolus
IV infusion - consistent infusion
IV bolus (IVP) - helpful for transition
ex. waiting for drug coming from pharmacy
CCB moa
inhibition of L-type Ca channels in myocyte and vascular smooth muscle → vasodilation
non-DHP: bind to myocytes + VSM
affect nodal conduction, contractility - dec/same HR
DHP: bind more selectively to VSM → greater vasodilation
compensation → inc HR
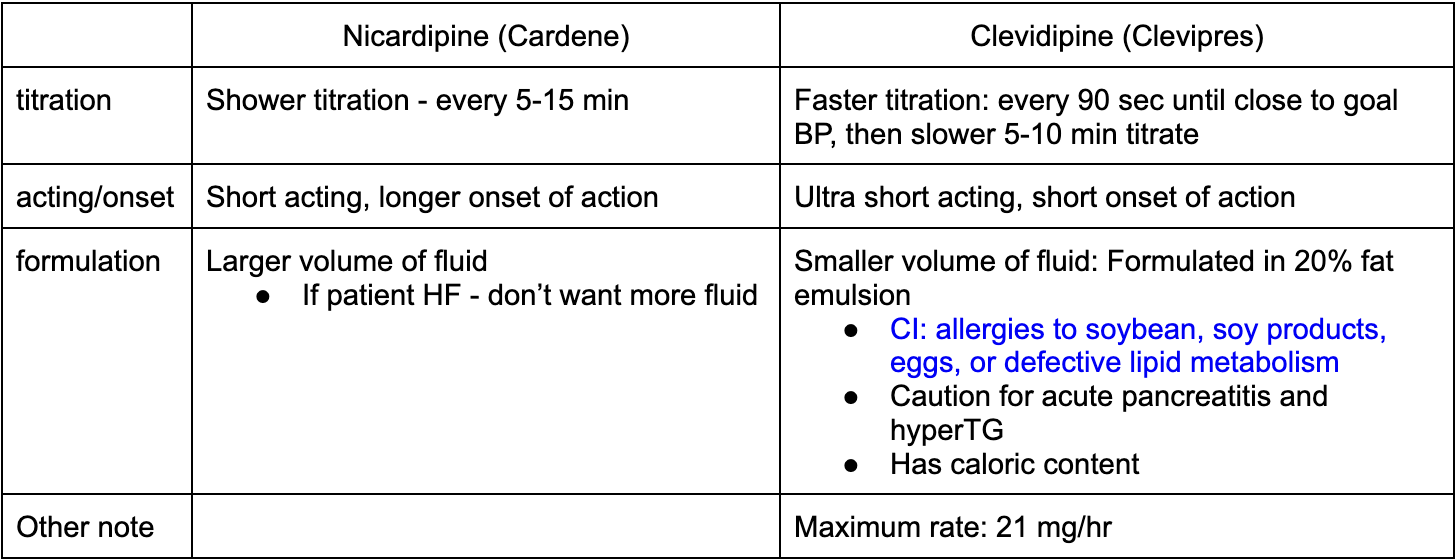
nicardipine (cardene) VS Clevidipine (Cleviprex)
IV or IV bolus
titration
acting/onset
formulation
other note
both IV
adrenergic blocker moa

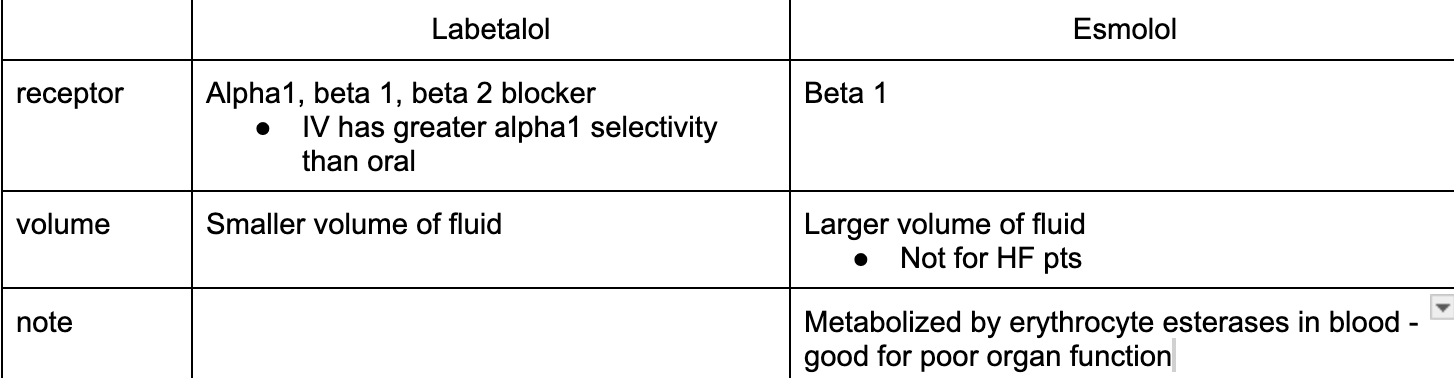
Labetalol (trandate) vs Esmolol (brevibloc)
IV or IVP
titration
formulation
other note
labetalol:
IV - smaller range of titration
IVP
esmolol:
IV - larger range of titration
start with IV bolus but then IV - so primarily IV - NO USE FOR PATIENT TRANSITIONING
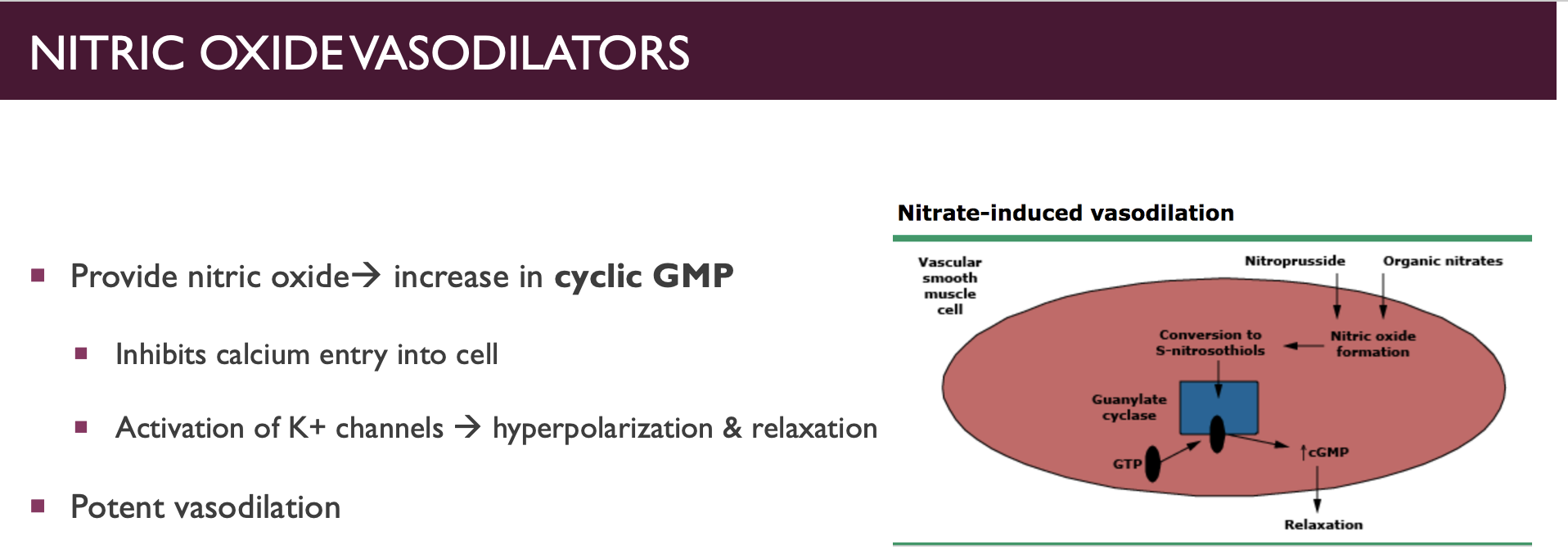
NO moa
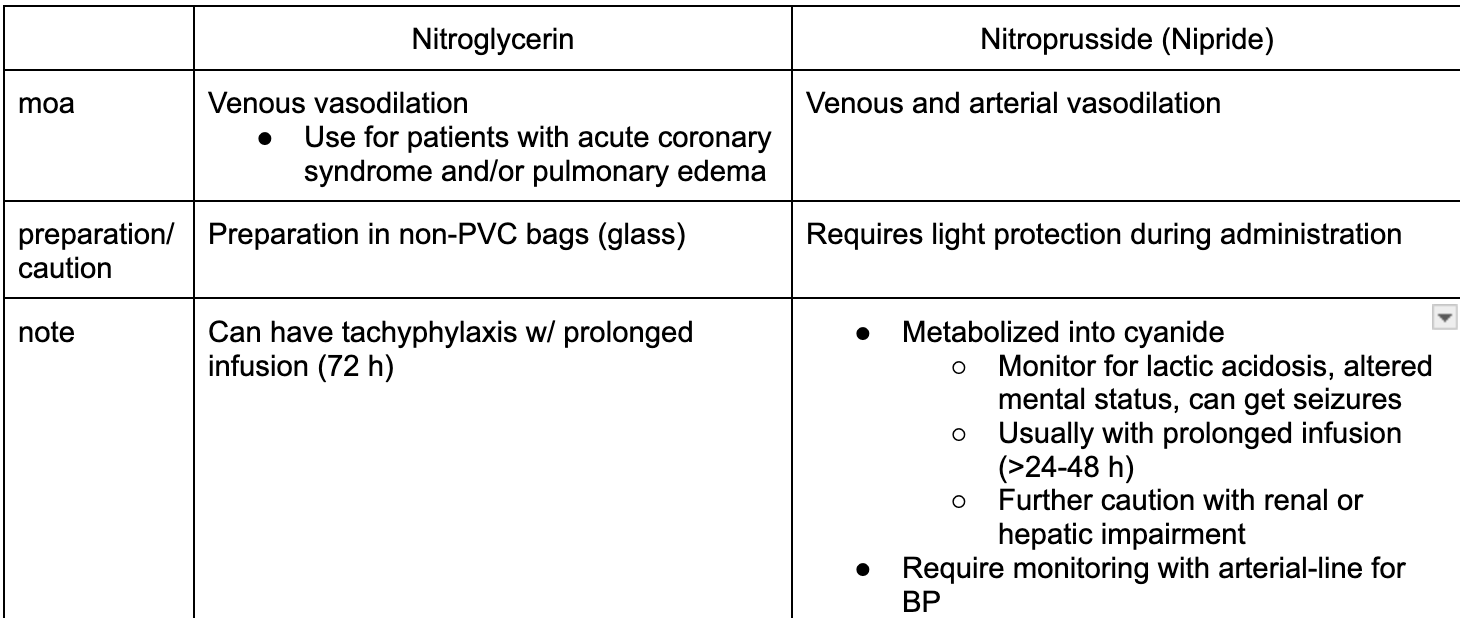
NO vs Nitroprusside
IV or IVP
moa
preparation and caution
clinical pearl
NO
IV - higher range of titration - allow room to move
increment of 5 mcg/min every 3-5 min
Nitroprusside
IV: titrate increment 0l5 mcg/kg/min every 5 min
Hydralazine
moa
duration of action: long or short
IVP or IV
clinical pearl
highly specific for arterial vasodilation
longer duration of action
IVP
less predictable response and potential dose stacking
if add IV push together, they add up → sudden drop of BP
enalaprilat
Uses
IVP or IV
CI
rarely used, for patient with strict No PO
IV ACEi - block conversion AGI to AGII
long acting
CI: pregnancy and bilateral renal artery stenosis
Fenoldopam
MOA
IVP or IV
caution
DA receptor agonist - dec peripheral vasculature resistance (vasodilation) w/ inc renal blood flow and diuresis
IV
caution in pts with glaucoma due - inc intraocular P
dilate vessels in the eye → increased fluid (aqueous humor) formation or reduced drainage → ↑ intraocular pressure.
avoid patients with sulfite allergy
Phentolamine
MOA
IVP or IV
Uses
competitive alpha blocker - antagonism of circulating EP and NE
IVP or IV
useful for HTN emergencies induced by catecholamine excess (pheochromocytoma)
Post stabilization follow-up
pts typically require frequent adjustment of antiHTN med after stabilization
regimen simplification and lifestyle modification may be helpful
monthly follow-ups are recommended until BP is regularly controlled and any residual target oran damage has resolved