efferent and cardio
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
Capalliries
Responsible for exchange with organs and tissues of Co2 , waste and O2, nutrients, and signals
Hearts ultimate goal
Deliver O2 to organs so you don’t die from lack of ATP
blood flow throughout the
body?
Gradients
Pressure gradients
High to low
Gradient creates blood flow
Largest pressure drop in arterioles
Flow
Q = change in pressure/resistance
The magnitude of Q is determined by the size of the pressure difference (P)
The direction of Q is determined by the pressure gradient (high to low)
Flow can be equal if they have the same pressure difference
Poiseulles law
n is viscosity of blood
L is length of vessel
r^4 is radius of vessel to the fourth
Viscosity and length are constants
R = 1/ r4
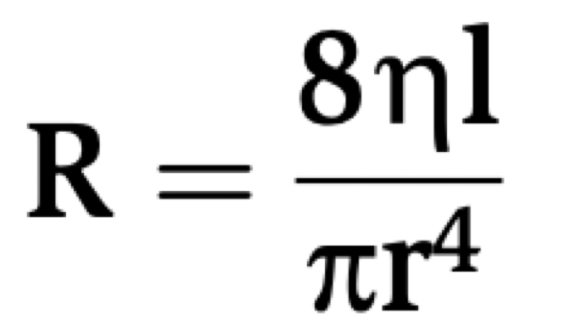
Viscosity is relevant because
• change in volume…e.g. dehydration
• change in # cells (increase in RBC)…e.g. polycythemia
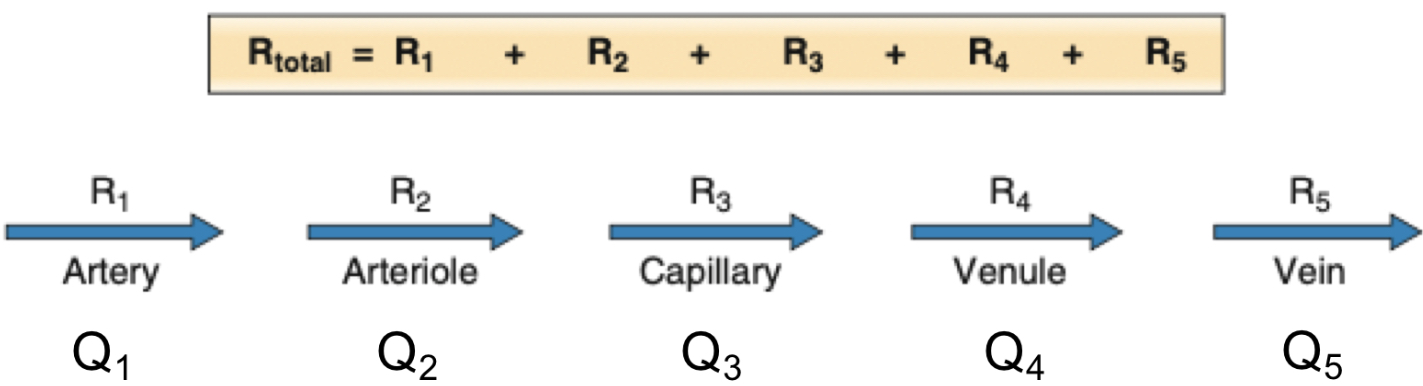
Vessels in series
Vessel categories are all in series
Flow is constant between all categories
Pressure decreases
Vessels in parallel
When branched off
Flow of all categories are not equal to all
Pressure difference is the same for all
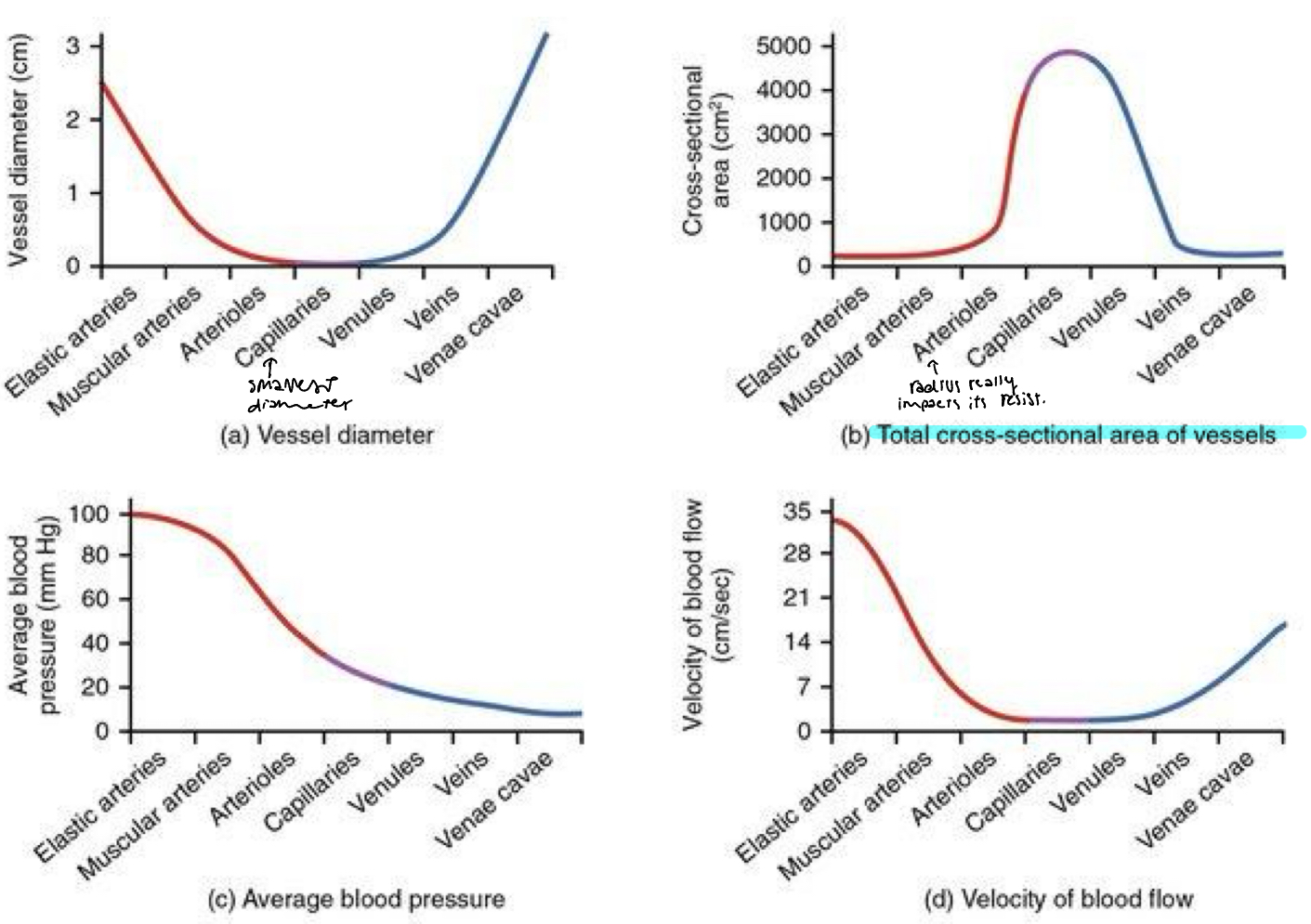
Velocity v
distance a given fluid moves within a unit of time (cm/sec) distance/time or rate of blood flow
Inversely proportional to A
Directly proportional to Q
How fast
v = Q/A
Flow Q
quantity of a given fluid that passes by a certain point within a unit of time (mL/sec) volume/time
Q = v * A
How much
Q vena cava = Q aorta
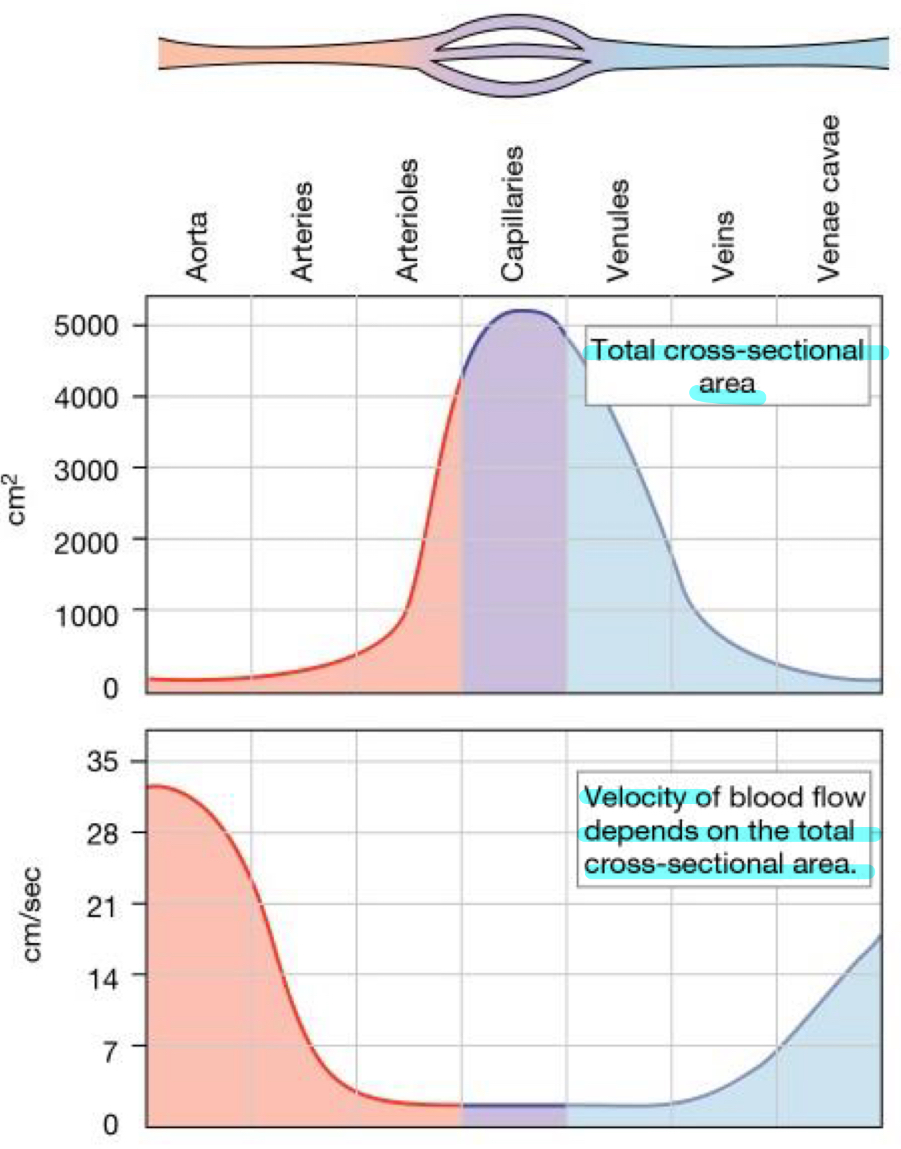
Total cross sectional area
Capillaries has the largest total cross section area so v is lowest here since it wants blood to move slow with exchange with tissues
Radius plays greatest role in determining resistance because
Radius can be regulated By constriction and dialation of vessels
Length and viscosity are constants
Radius factors in the equation to the 4th power