Action Potentials
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
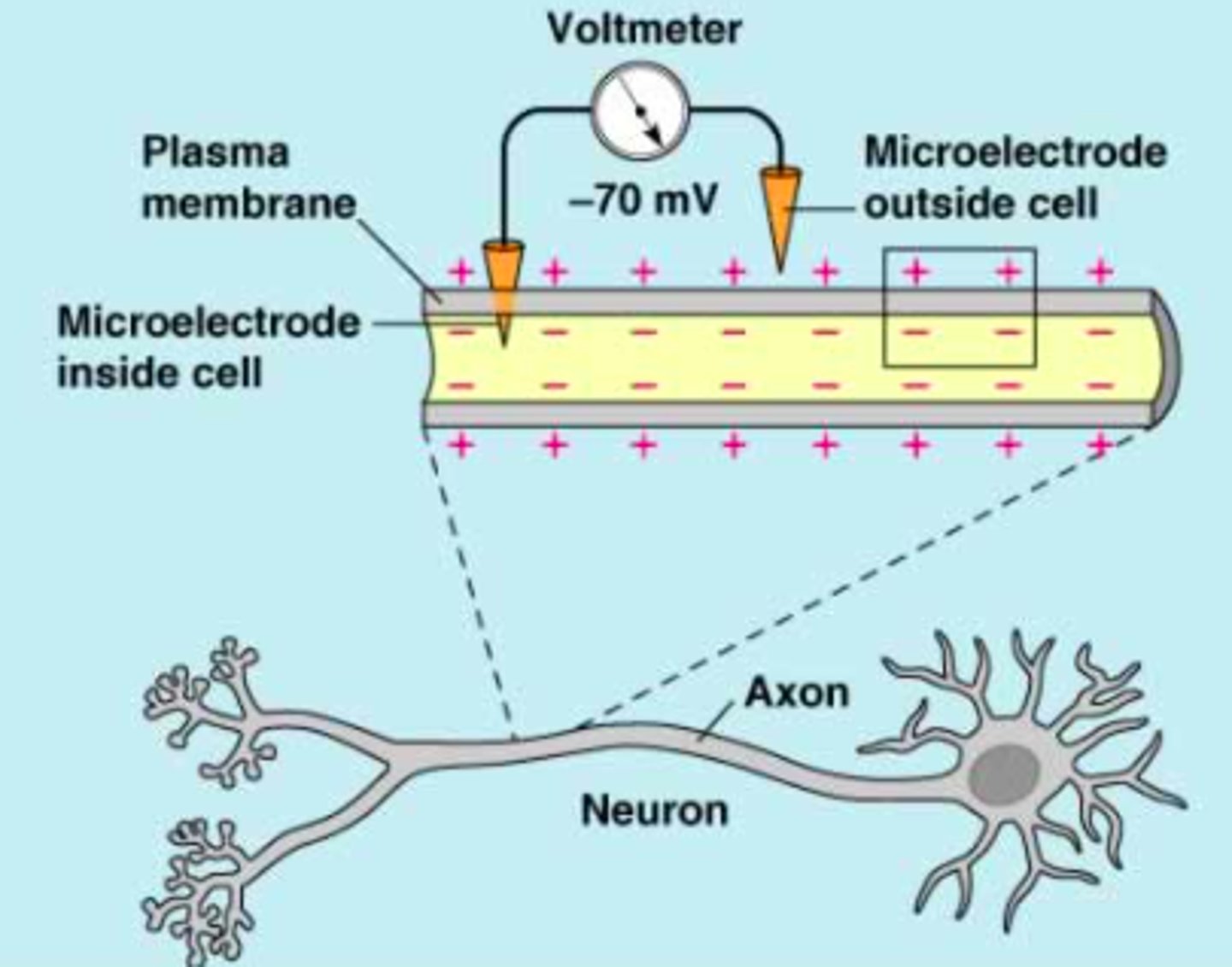
resting membrane potential
-70mV; voltage inside an unstimulated neurons
threshold potential
-55mV; voltage that must be reached to trigger an action potential
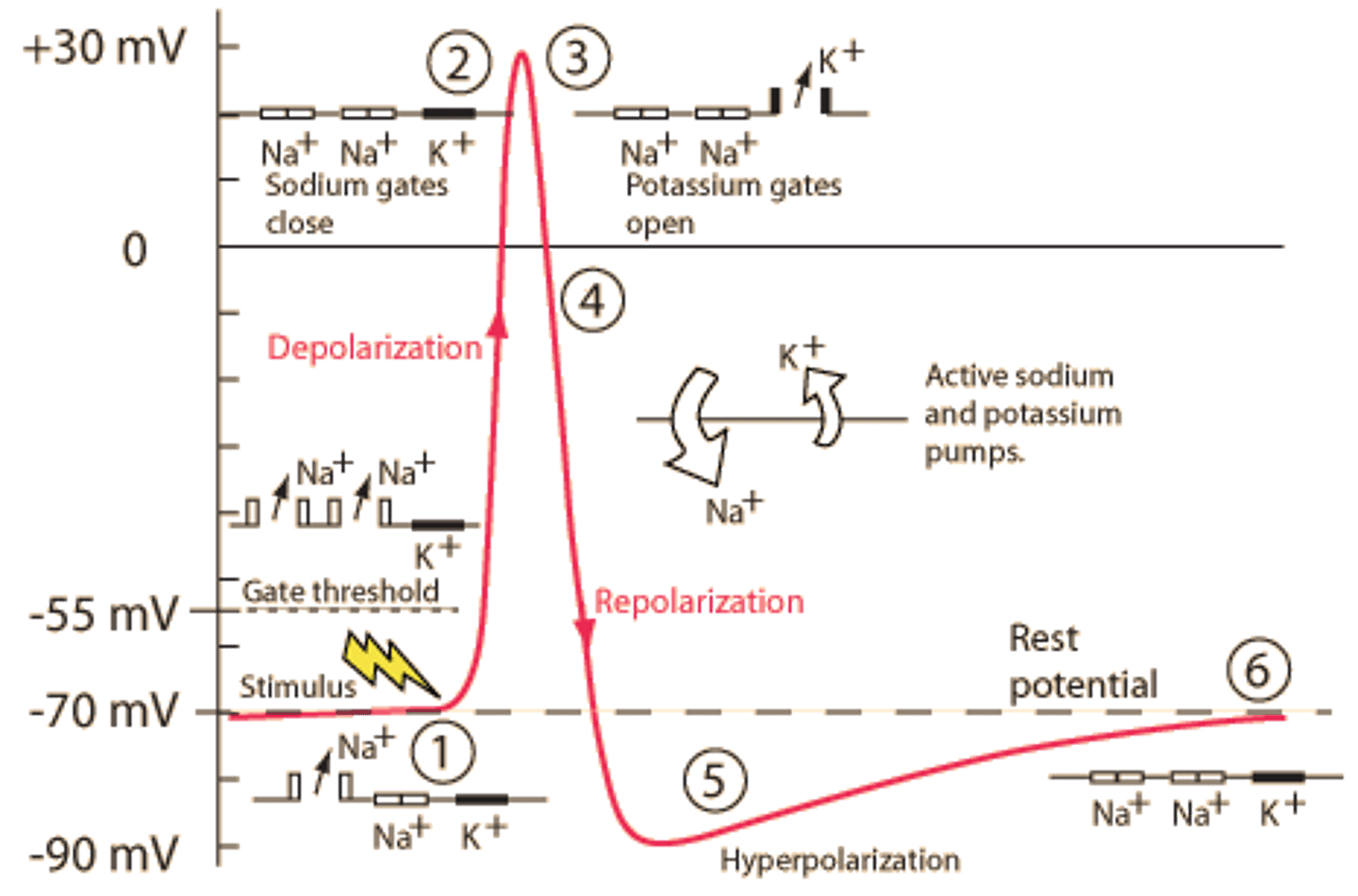
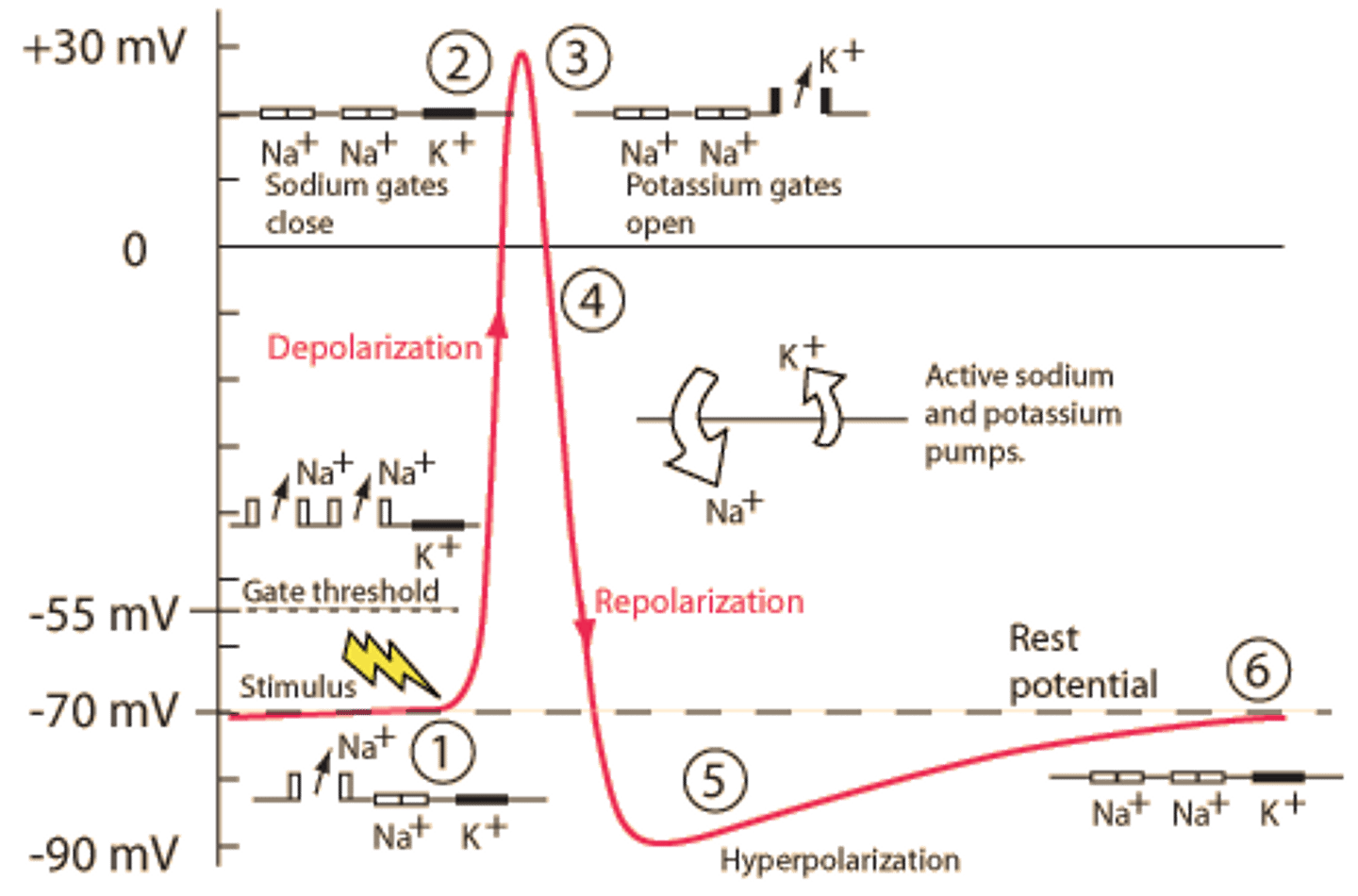
depolarization
part of the action potential when Na+ gates open, Na+ rushes into neuron, the inside of the neuron becomes positive
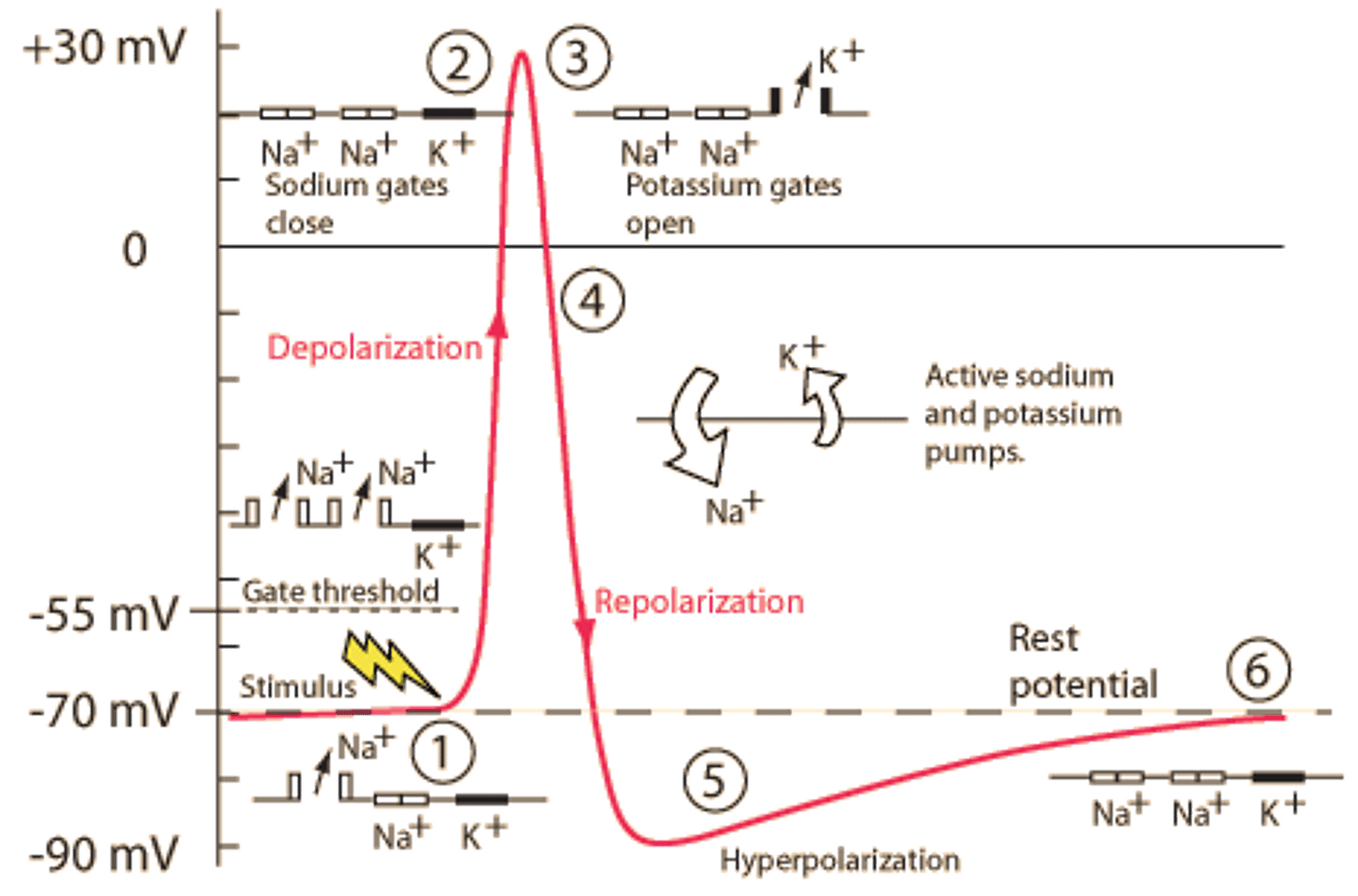
repolarization
part of the action potential when Na+ gates close, K+ gates open, K+ rushes out of neuron, the inside returns to being negative
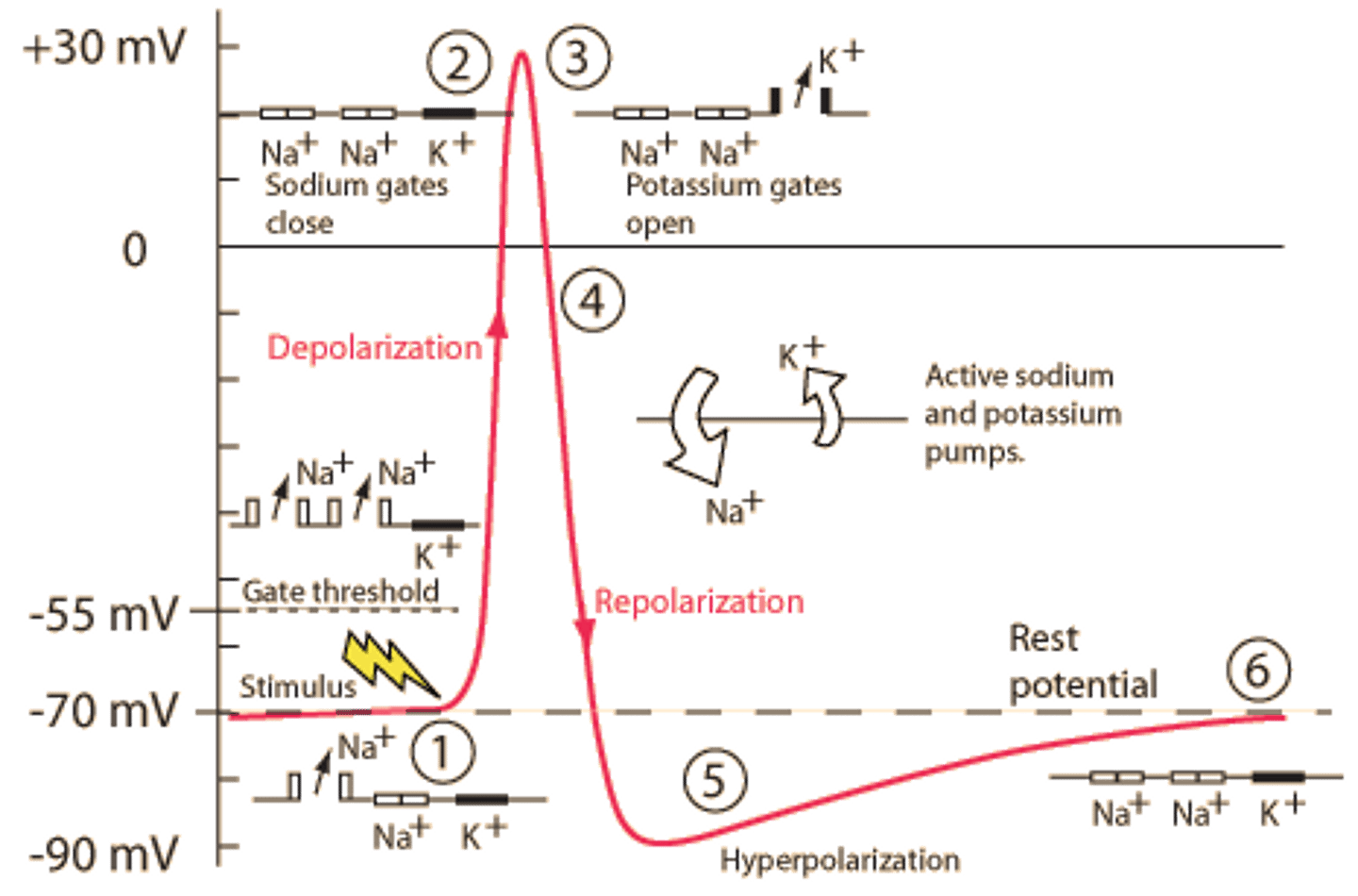
hyperpolarization (undershoot)
K+ gates remain open a little longer, membrane potential reaches -90mV
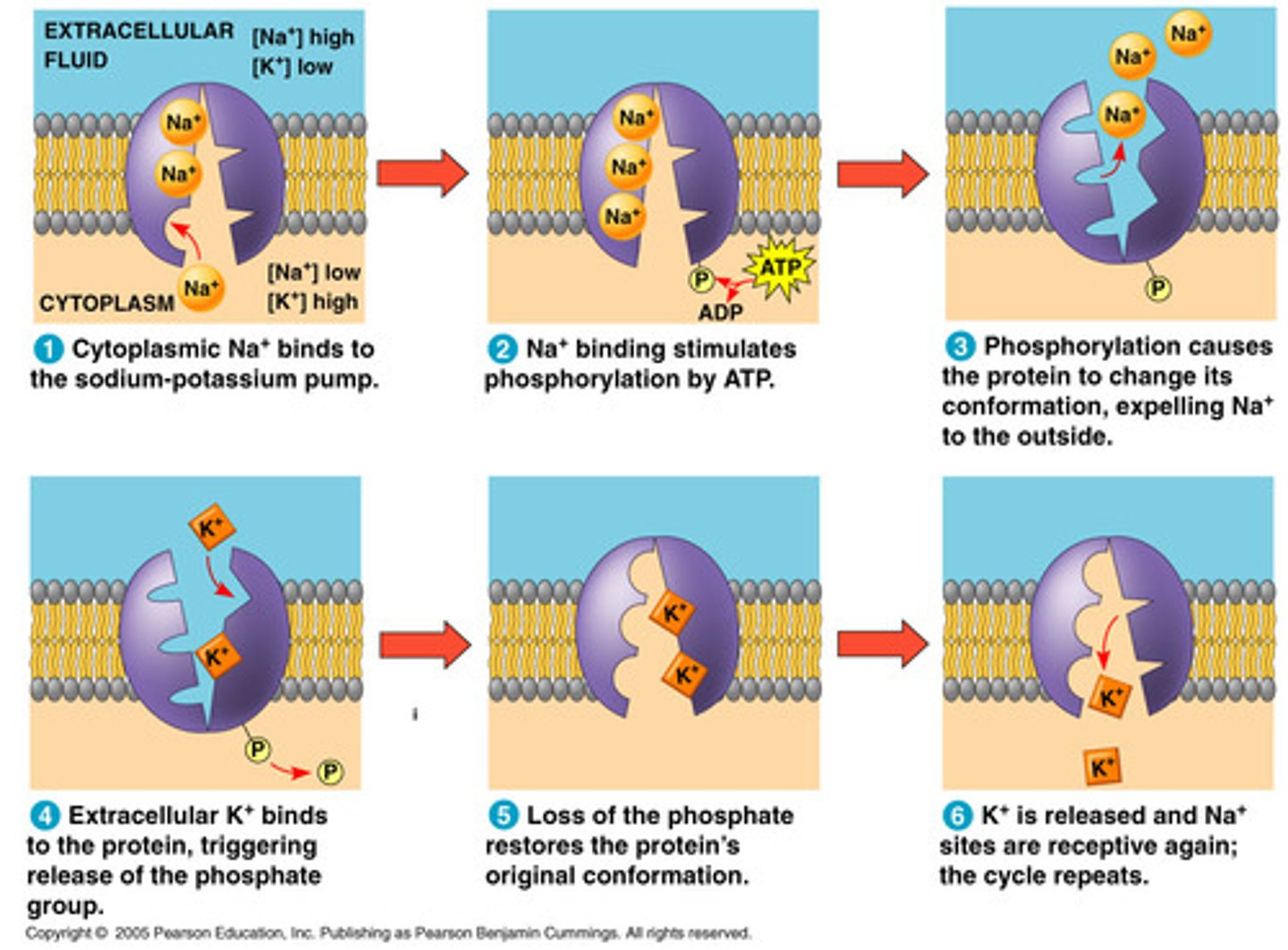
sodium-potassium pump
protein that uses ATP to pump 3Na+ ions out & 2 K+ in (against their concentration gradients) to restore ions to original position after action potential
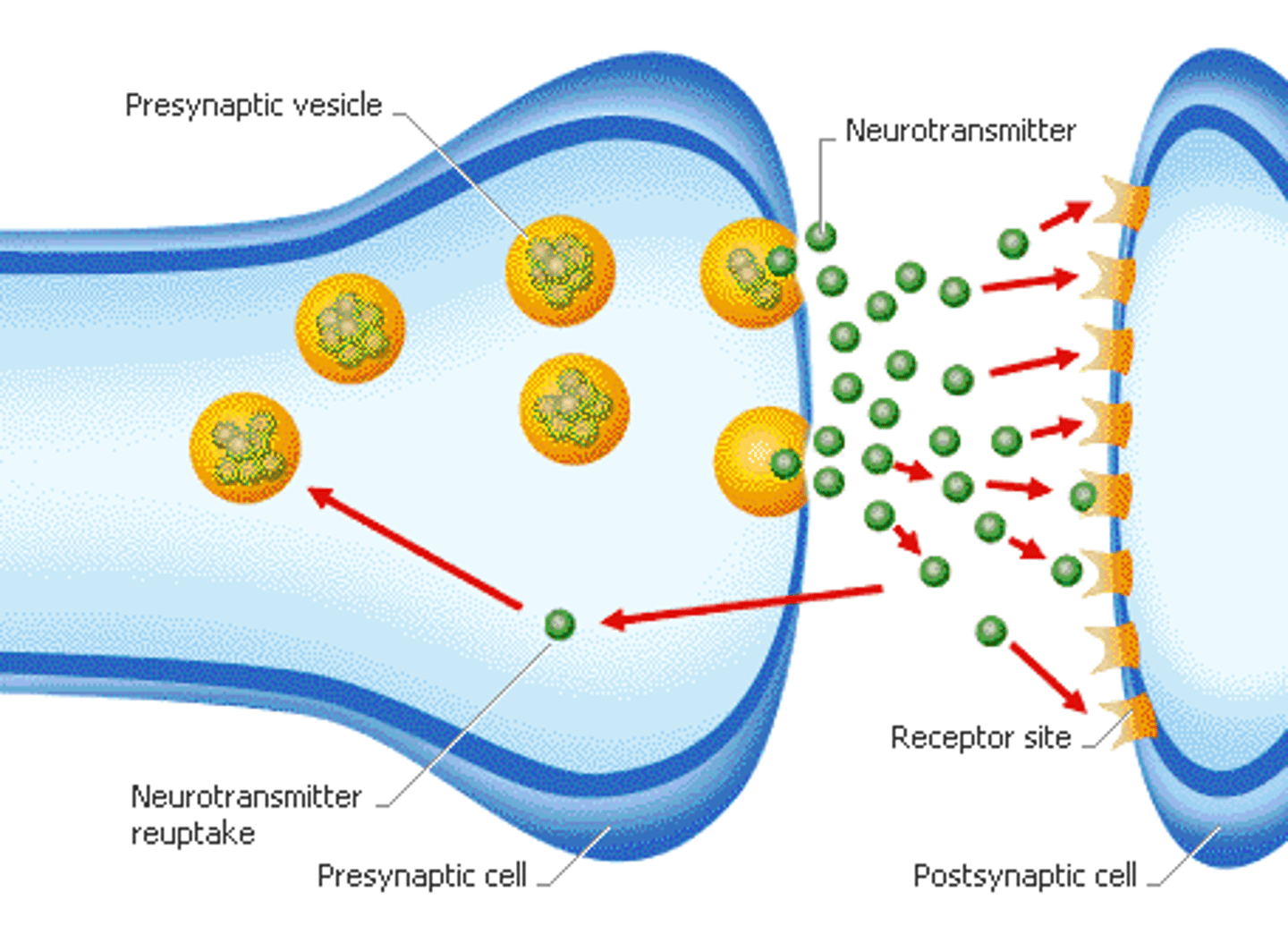
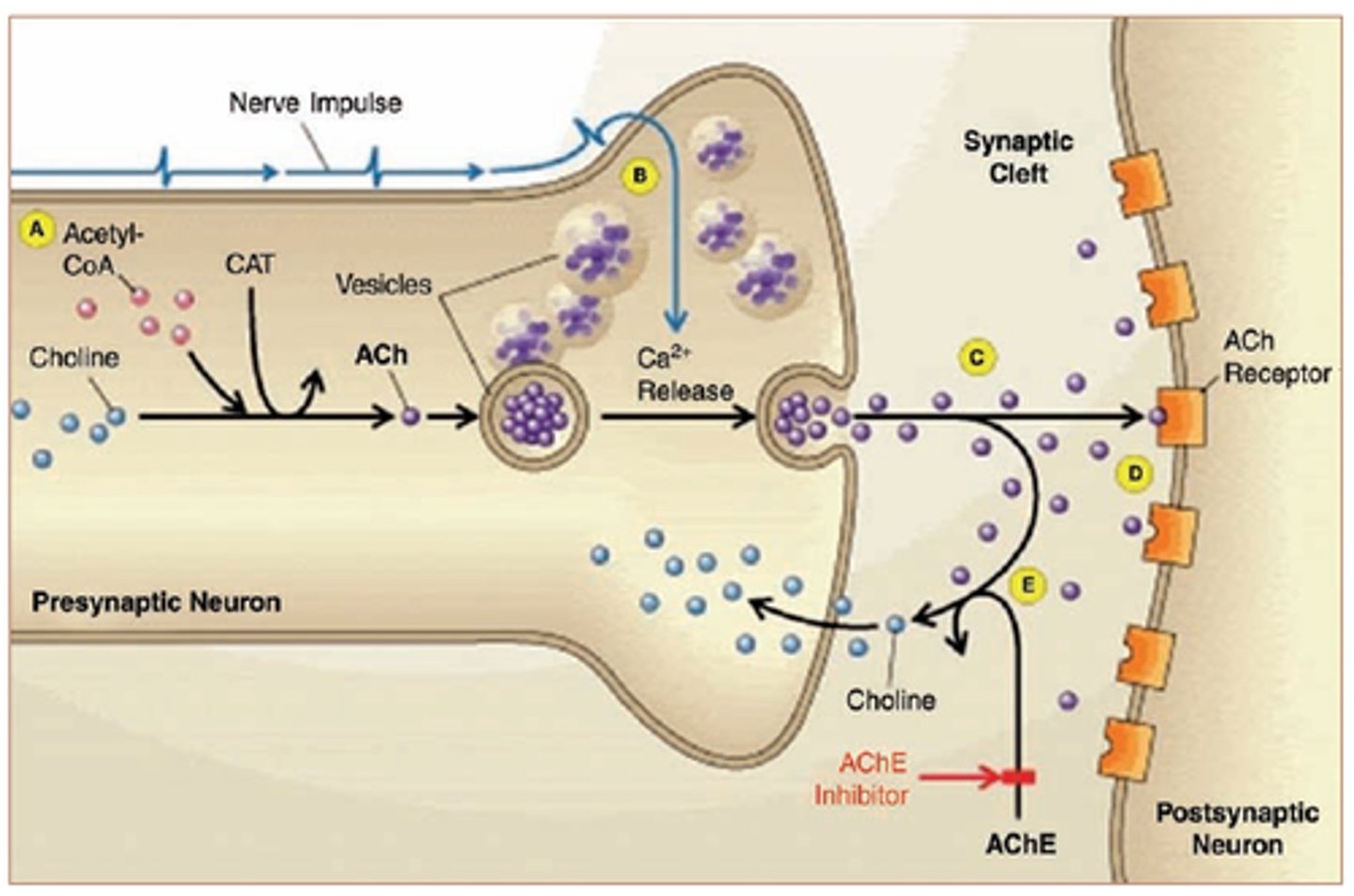
synapse
junction between two neurons or a neuron and a muscle cell
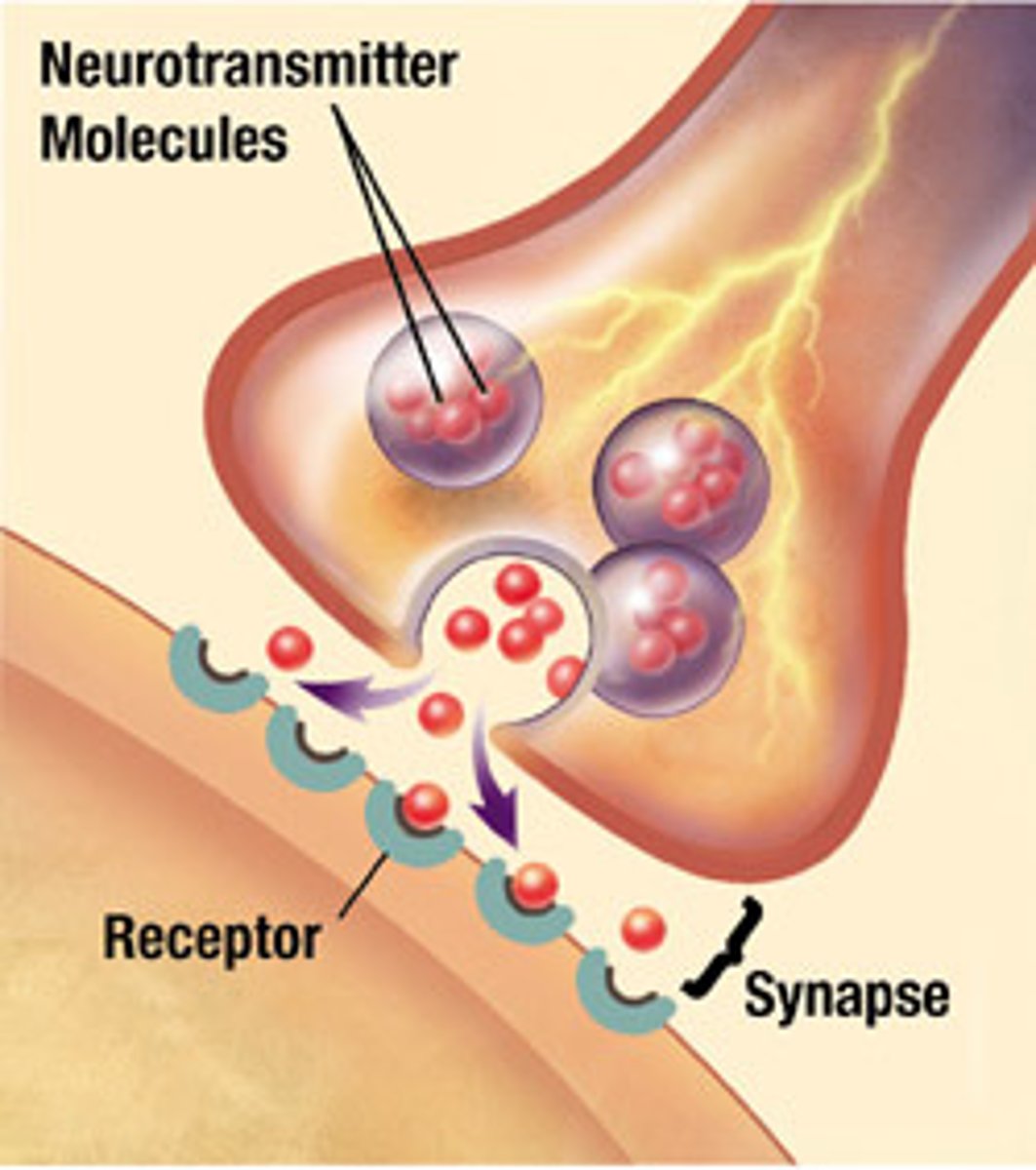
synaptic cleft
gap between two neurons or a neuron and a muscle cell
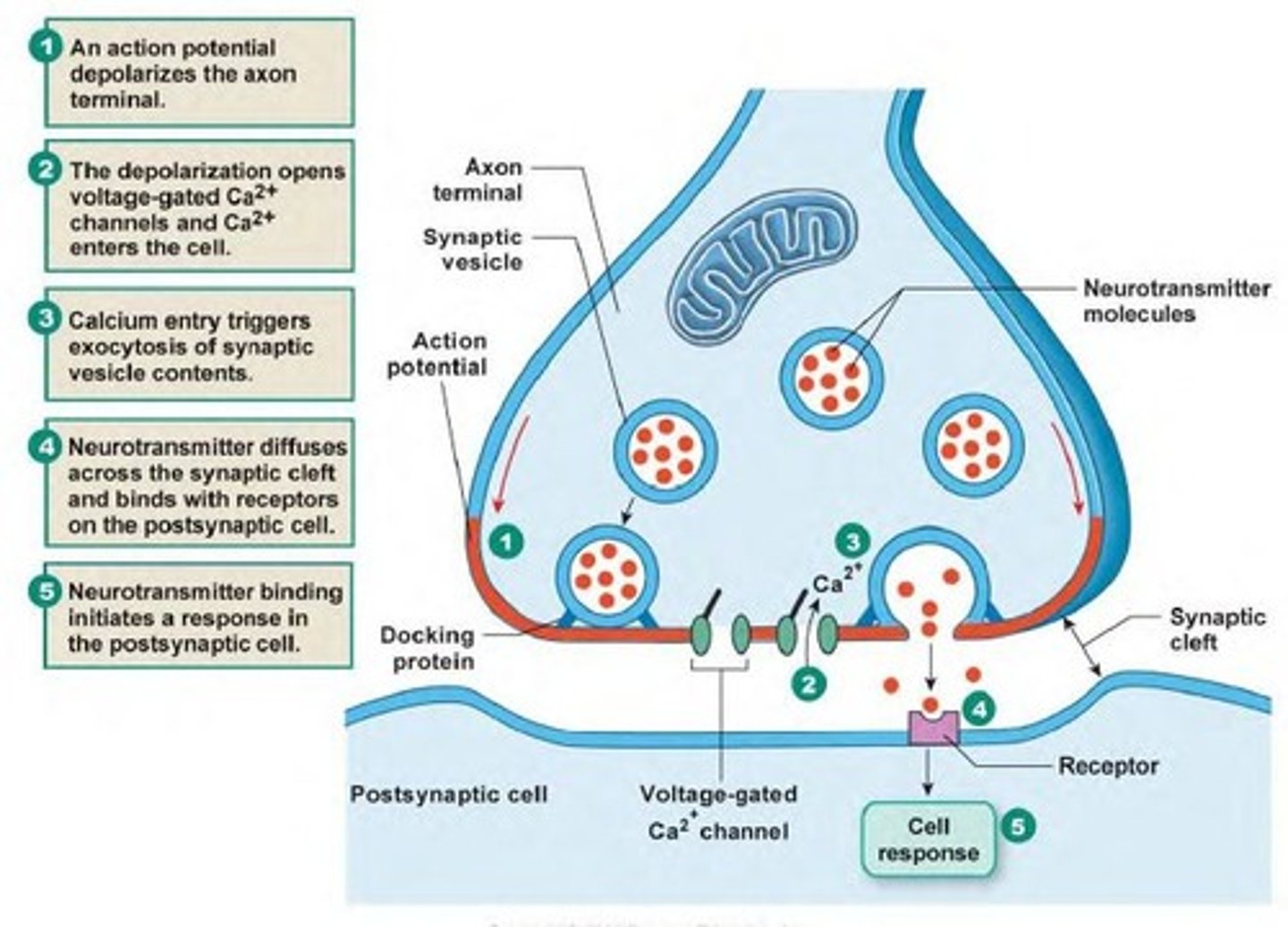
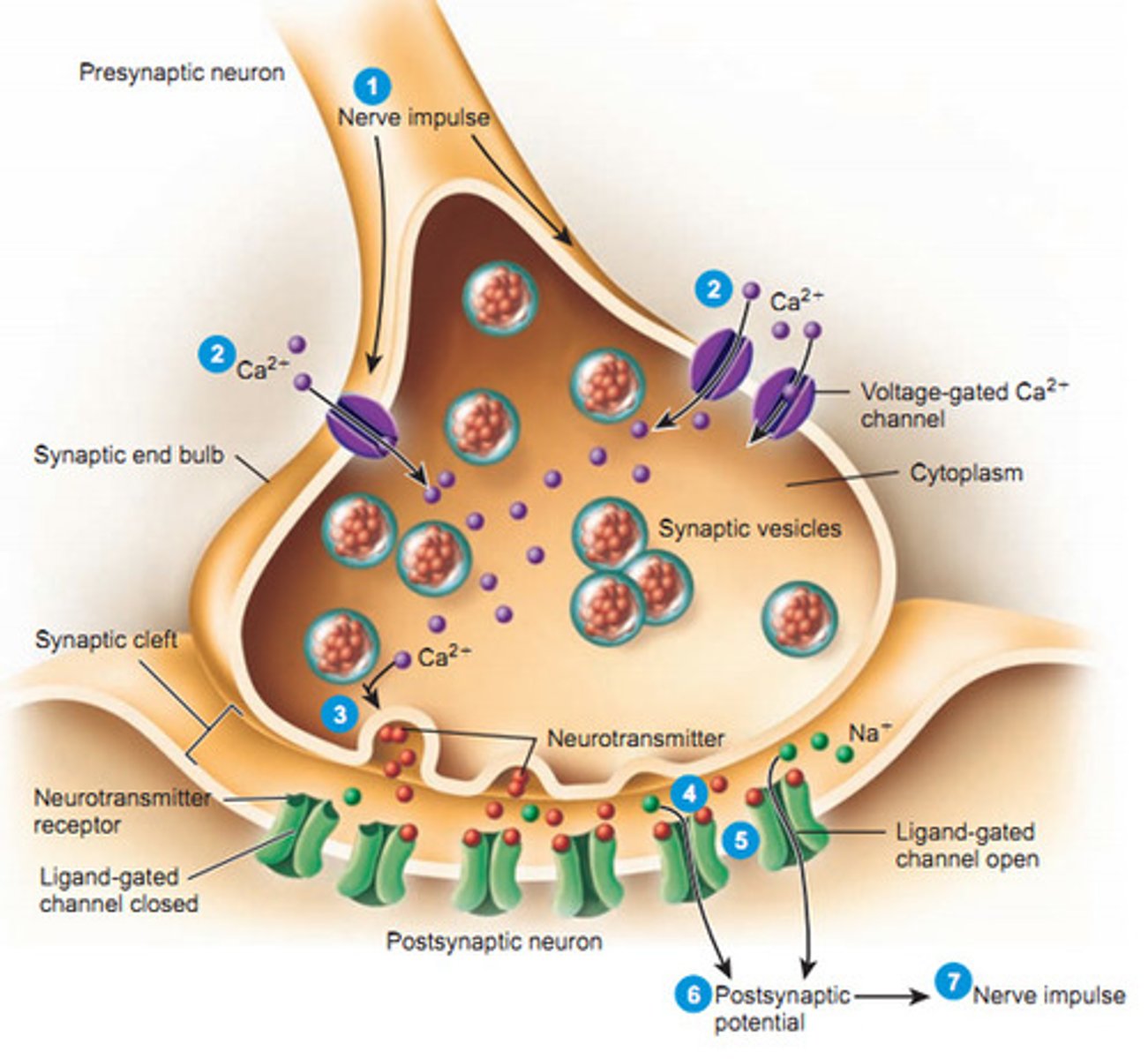
calcium channel
protein channels in axon terminal membrane that are triggered to open by an action potential; calcium rushes in to axon terminal triggering release of neurotransmitters from synaptic vesicles
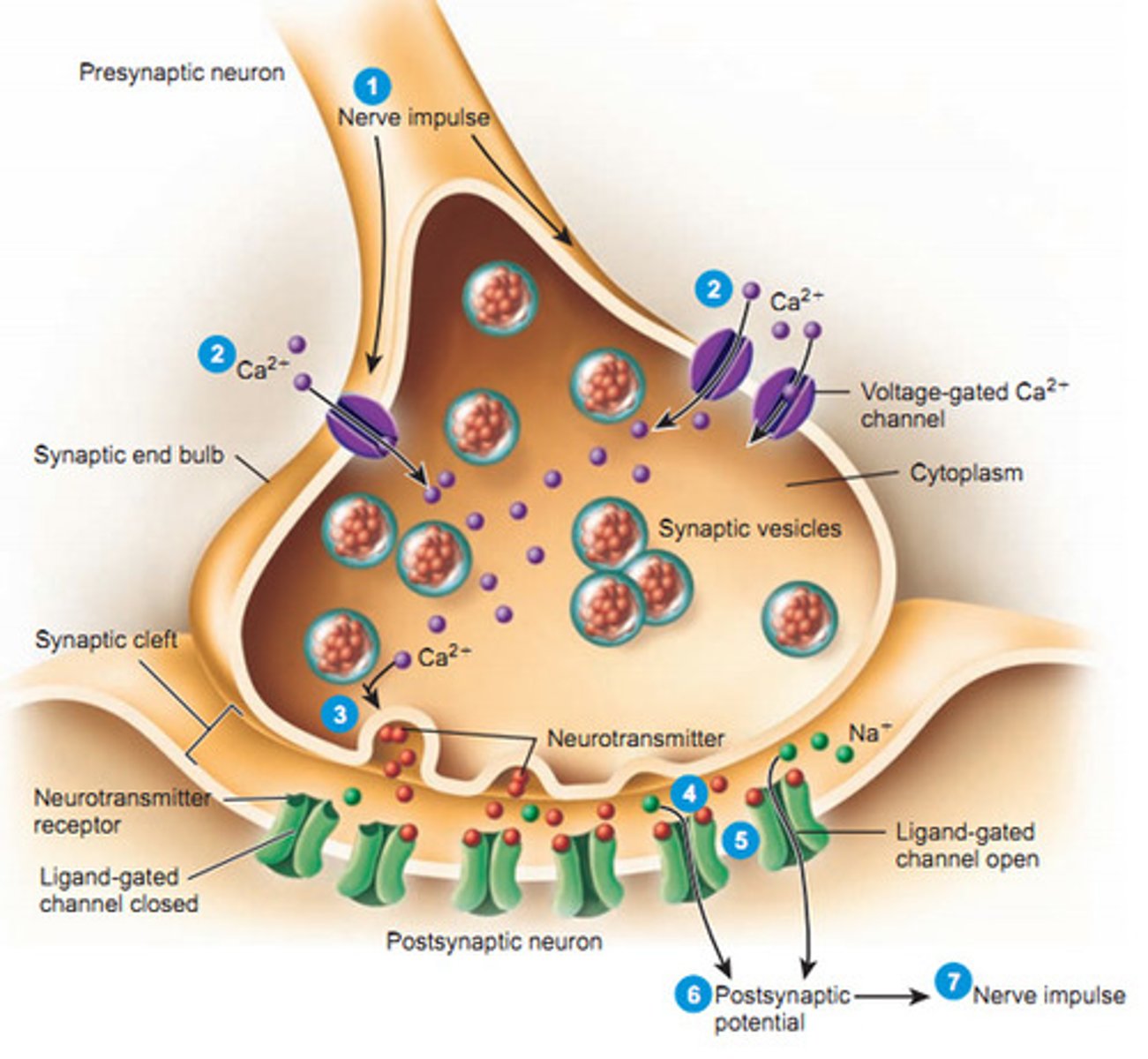
neurotransmitter
chemicals that transfer a signal from one neuron to the next neuron or muscle cell
acetylcholine
neurotransmitter that stimulates muscle cells to contract
acetylcholinesterase
enzyme that degrades (breaks apart) acetylcholine; can be inhibited by chemicals that mimic acetylcholine like snake venom
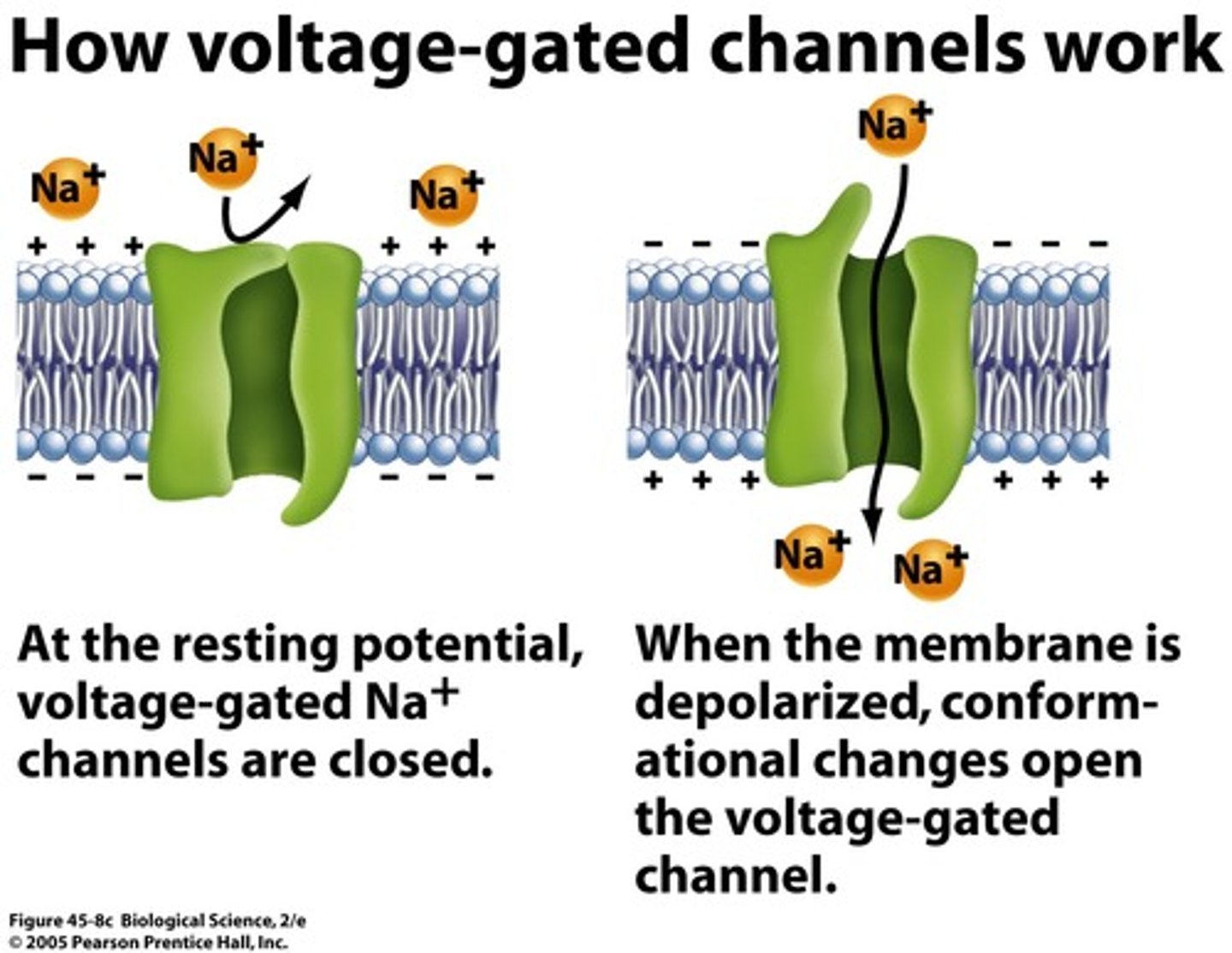
voltage gated ion channels
protein channels that open up in response to a change in voltage inside of a cell
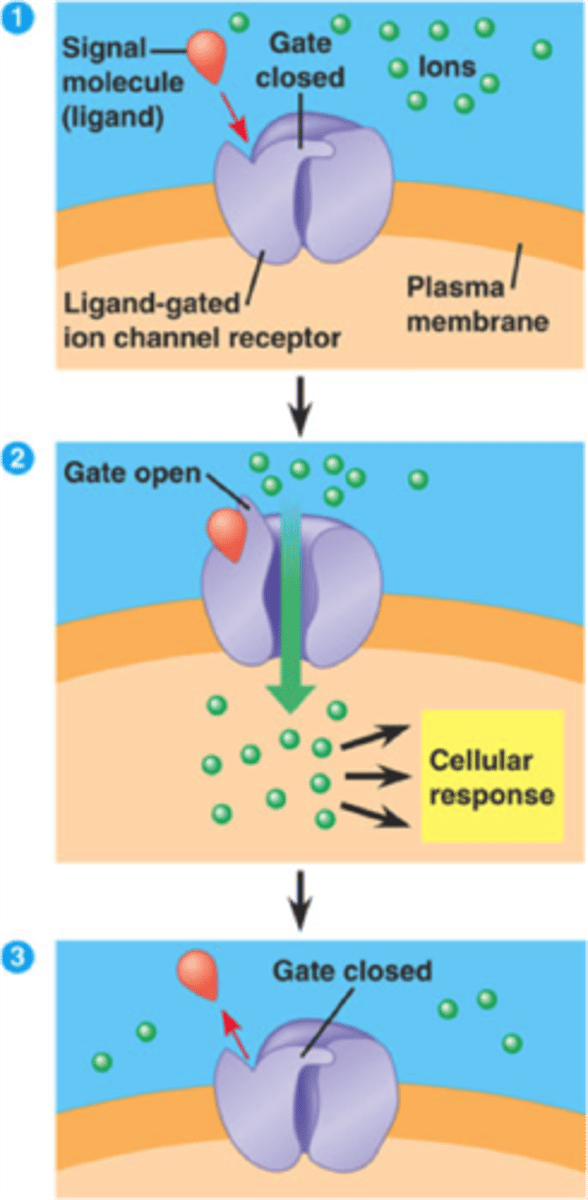
ligand gated channels
protein channels that open when an ion or other chemical binds to them; neurotransmitters bind to ligand gated channels to open them
EPSP
a postsynaptic potential that makes it more likely that the postsynaptic neuron will reach threshold potential; created by neurotransmitters like glutamate that stimulate Na+ channels to open
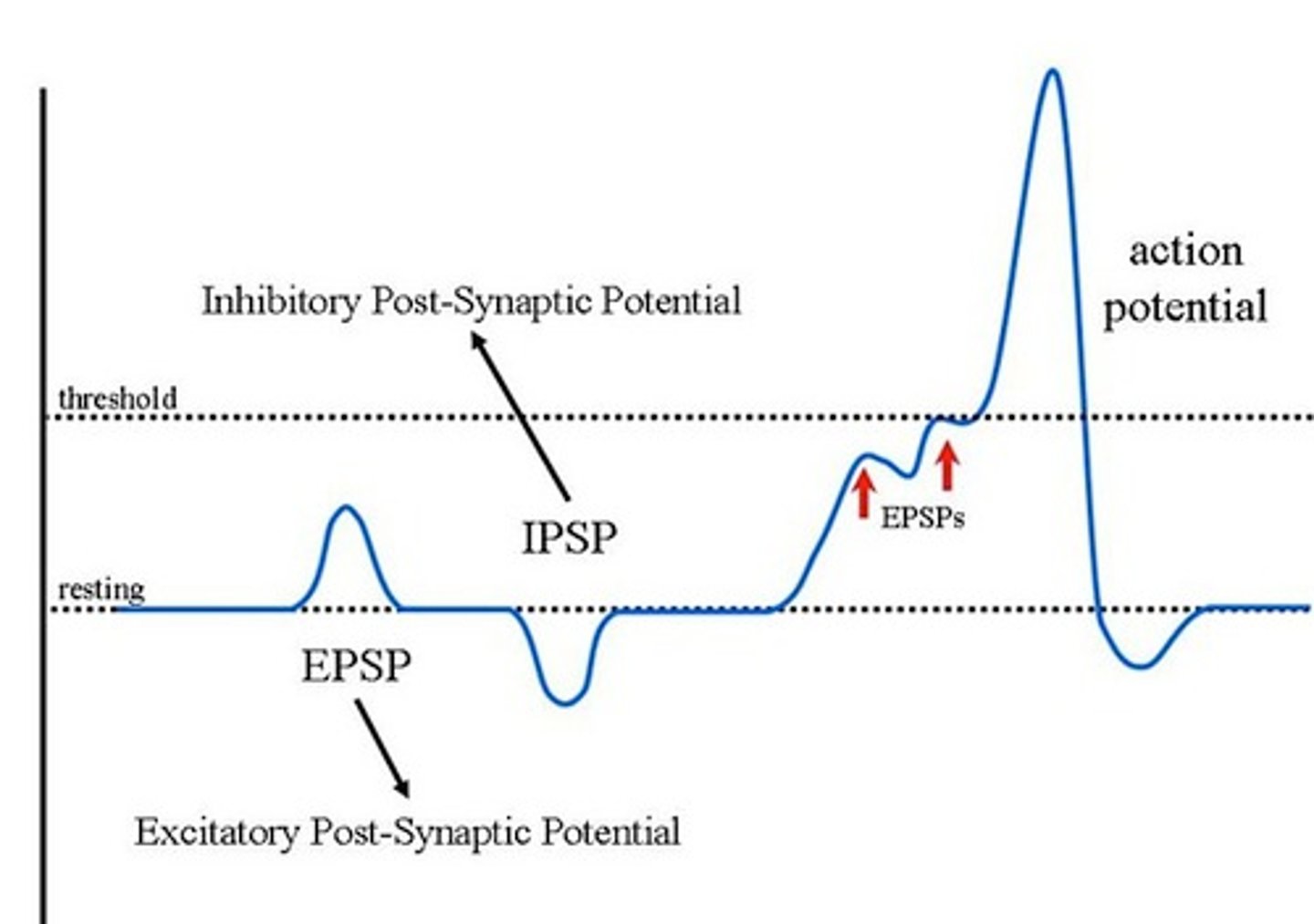
IPSP
a postsynaptic potential that makes it less likely that the postsynaptic neuron will reach threshold potential; created by neurotransmitters like GABA that stimulate Cl- channels to open
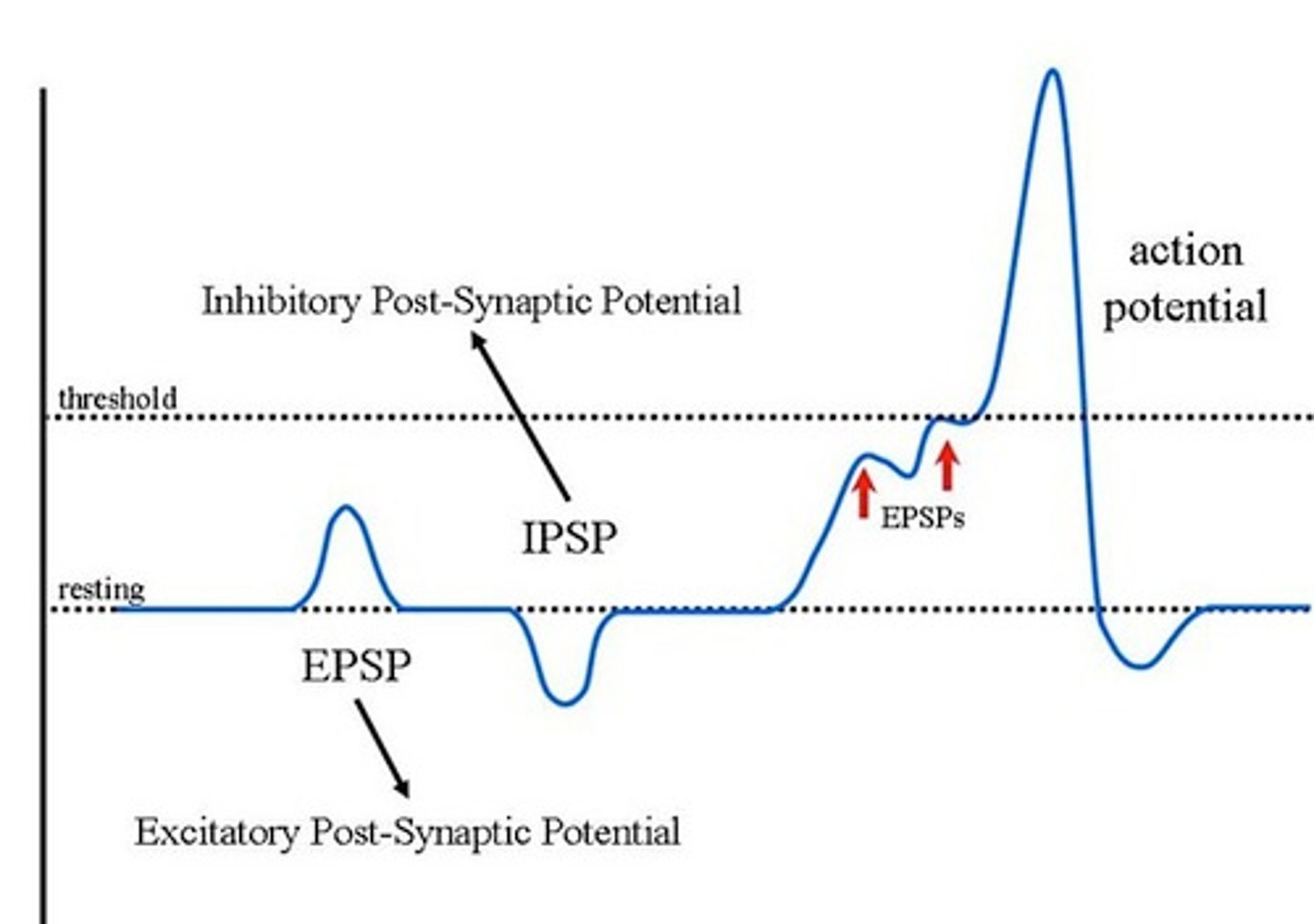
summation
addition of all EPSP's and IPSP's received by a postsynaptic neuron; when added together, if raise membrane potential to threshold, it will send an action potential
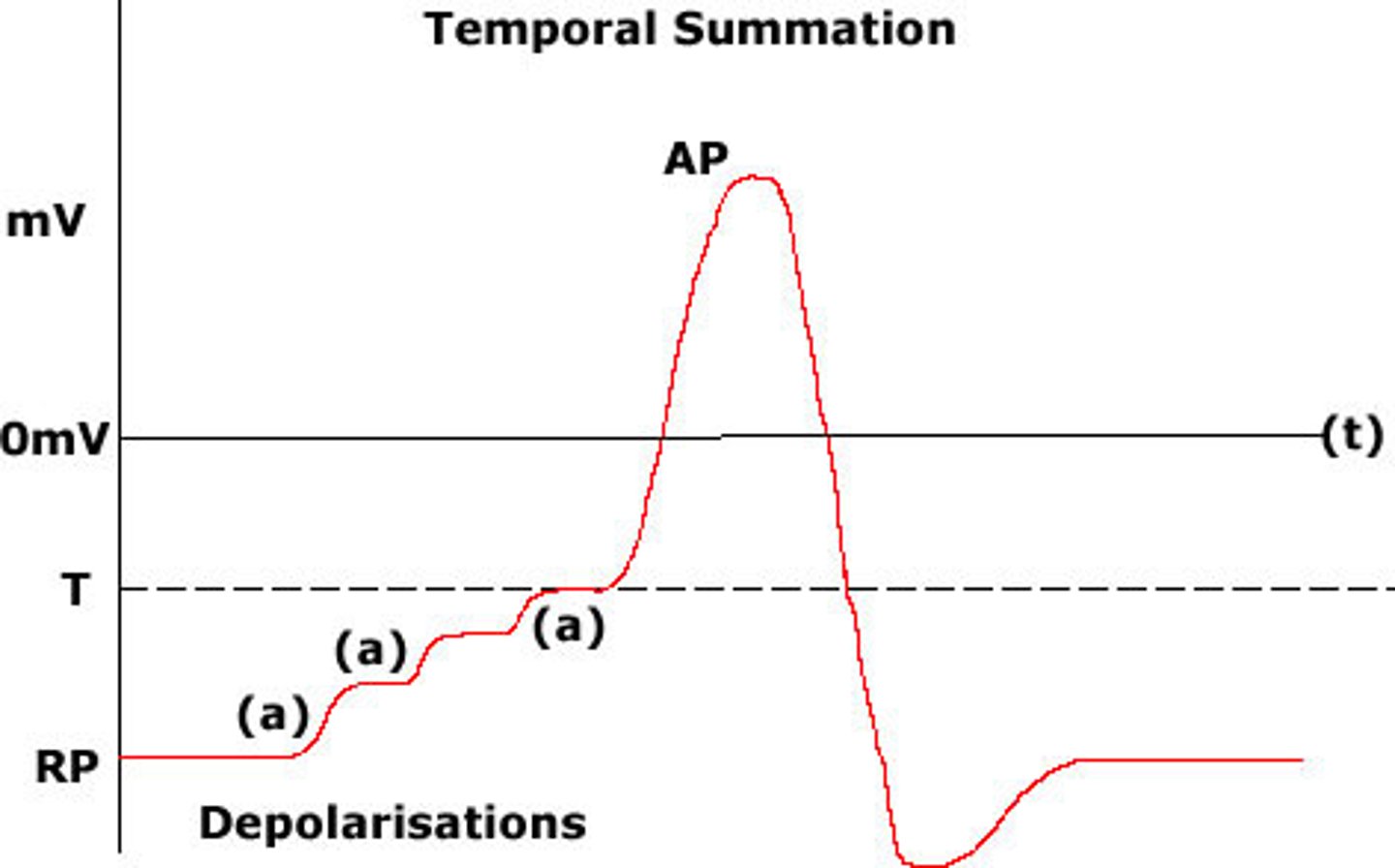
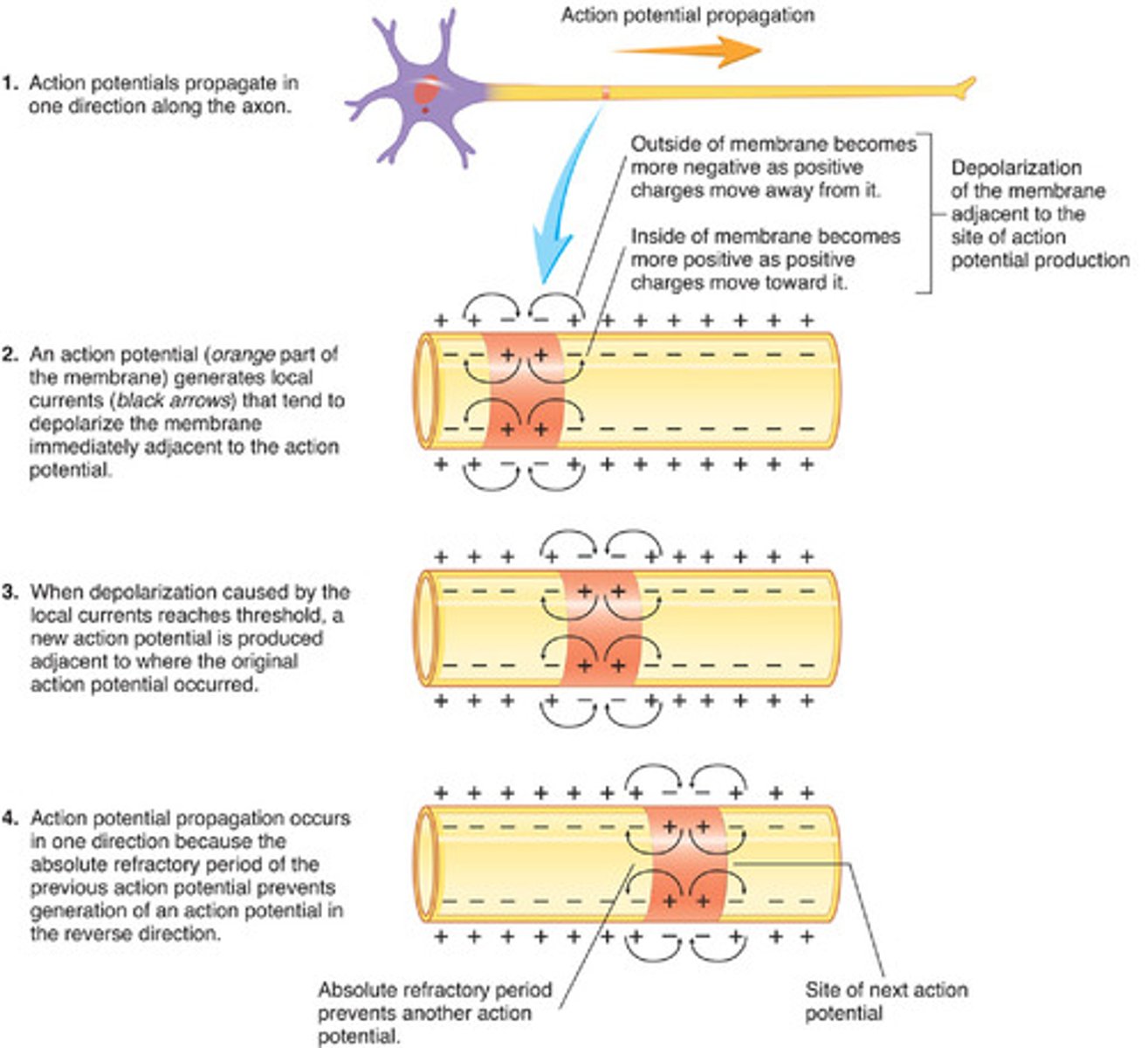
action potential
the electrical impulse that travels down a neuron; membrane potential rises and falls in a predictable, consistent pattern
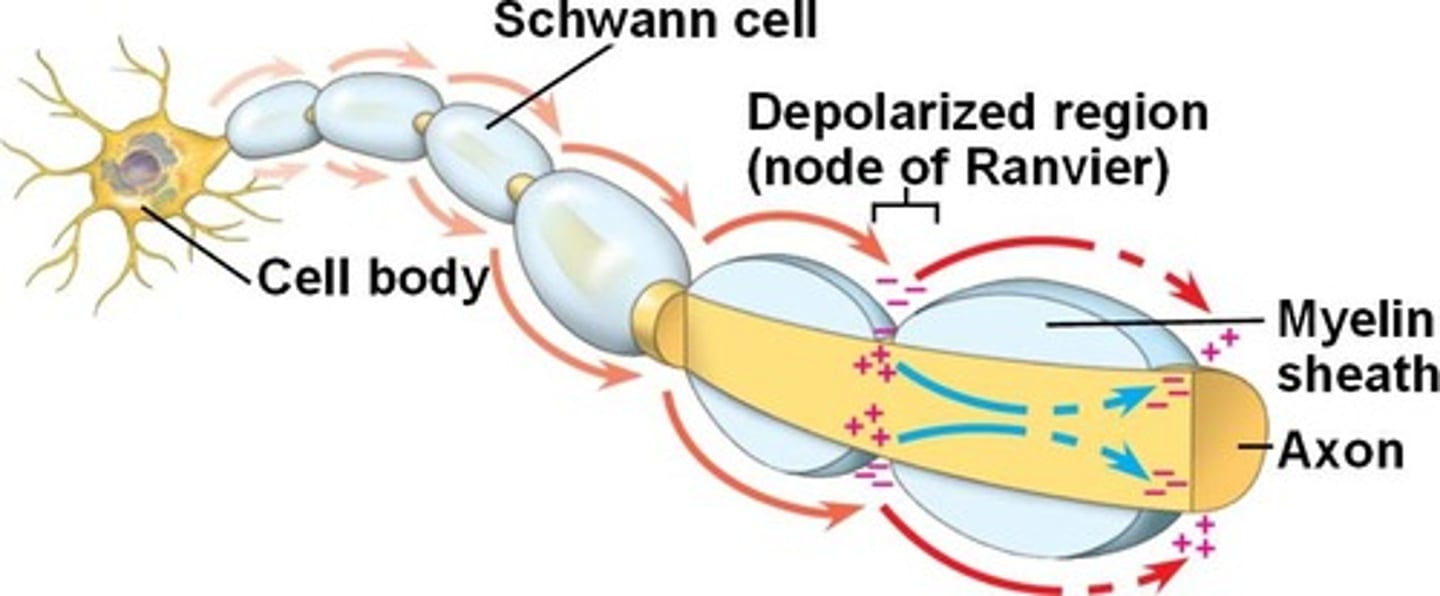
saltatory conduction
action potential jumps from Node of Ranvier to Node of Ranvier; occurs in myelinated neurons; increases speed of transmission of impulse tremendously
continuous conduction
action potential moves straight down an unmyelinated axon without jumping; much slower than saltatory conduction