Biology 3: Embryogenesis and Development
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
A/an [...] is a solid ball of cells resulting from division of a fertilized ovum
morula
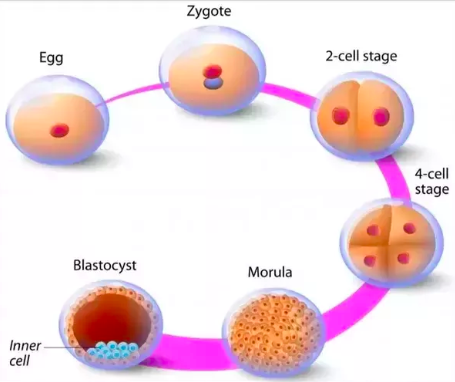
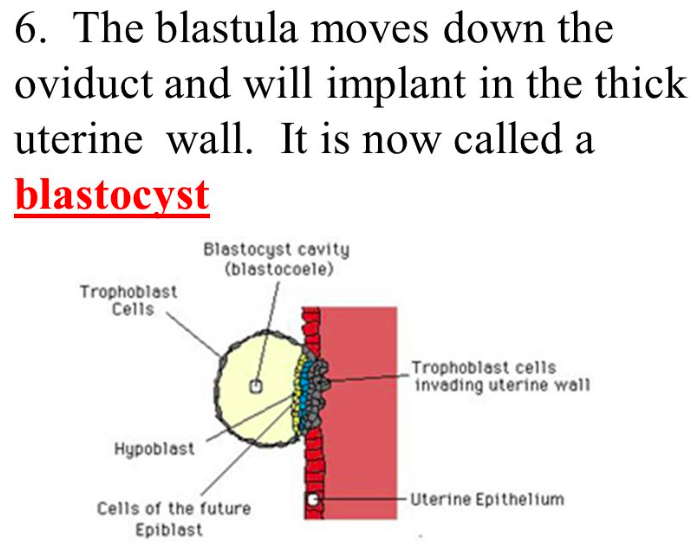
A/an [...] is a hollow sphere of cells, referred to as blastomeres that implants in the endometrial lining
blastula
[Germ layer] develops into the nervous system, skin, hair, nails, mouth, and anus
ectoderm
“atract-oederm’ skin and hair are things people are attracted to
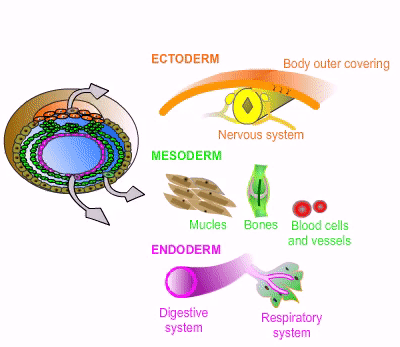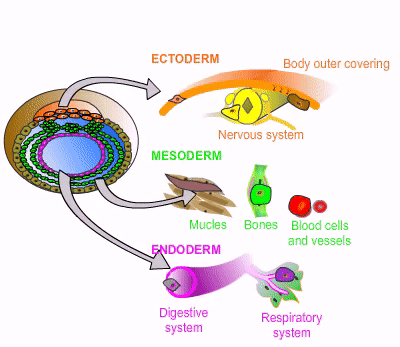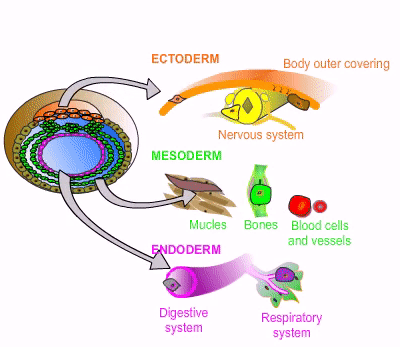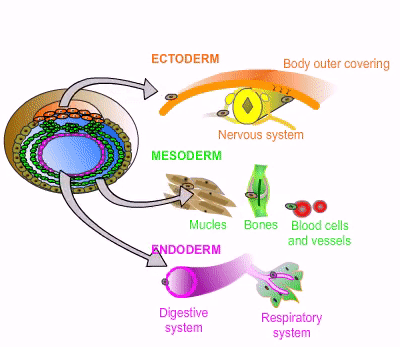
[Germ layer] develops into muscoskeleton, circulatory system, gonads, and adrenal cortex
mesoderm
movem-oderm: involved in moving things such as muscles, RBS, steroids
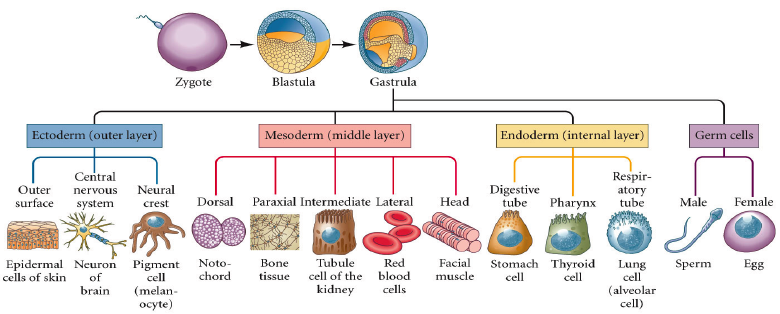
[Germ layer] develops into the GI tract, respiratory tract, endocrine glands, bronchi, bladder, and stomach
endoderm
in-doderm: things that are inside
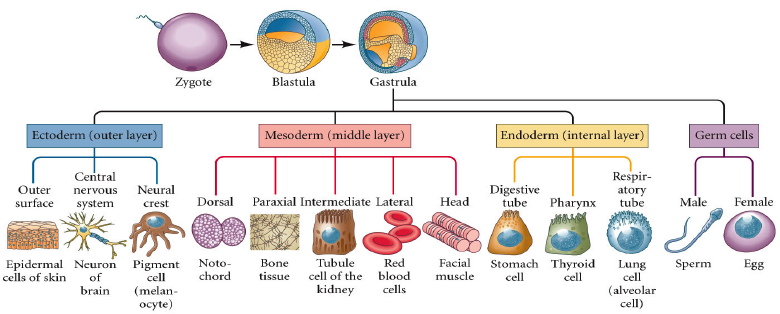
The CNS and PNS derive from the [germ layer]
ectoderm

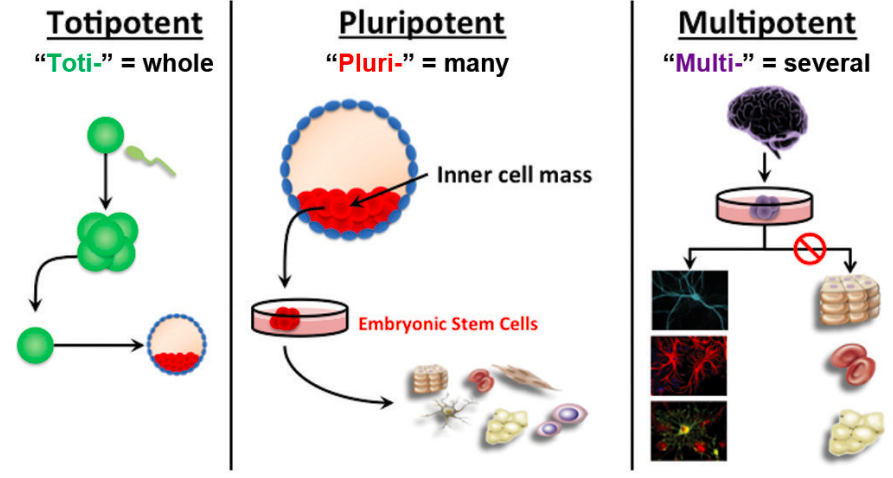
[...] stem cells have the potential to develop into any cell found in the human body
totipotent
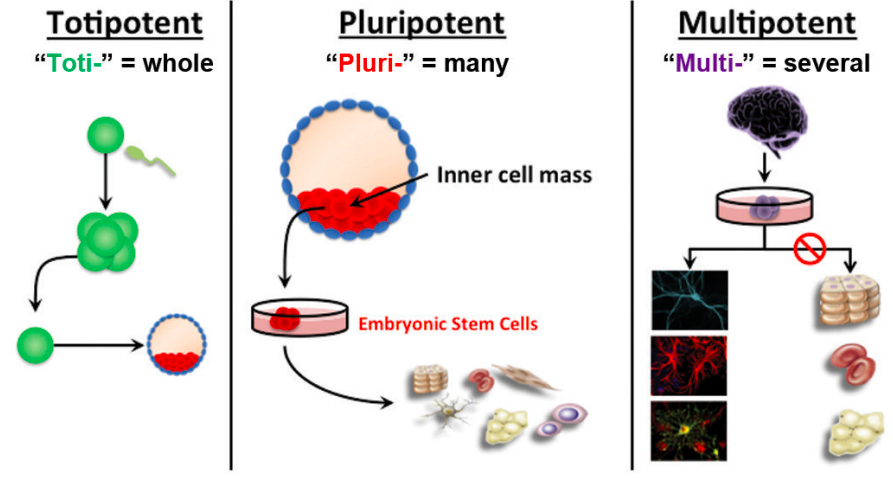
...] stem cells can be any cell except those found in placental structures
pluripotent
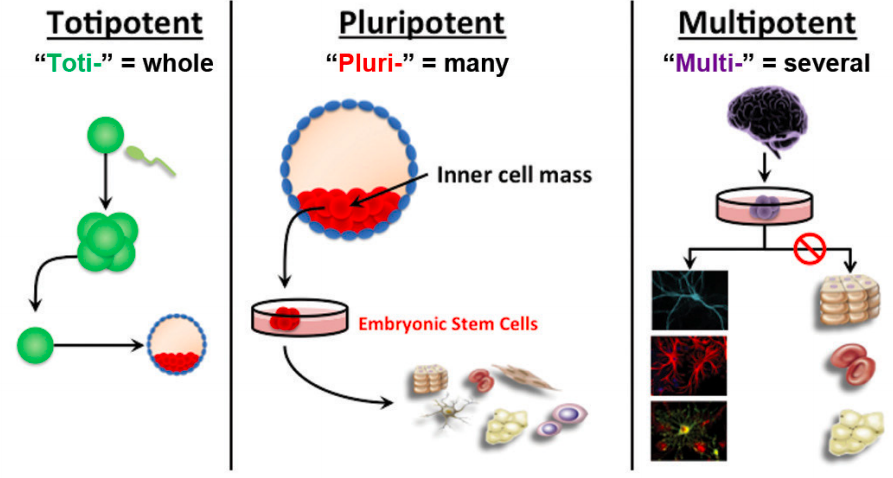
[...] stem cells can develop into multiple specialized cell types
multipotent
most adult stem cells are multipotent stem cells
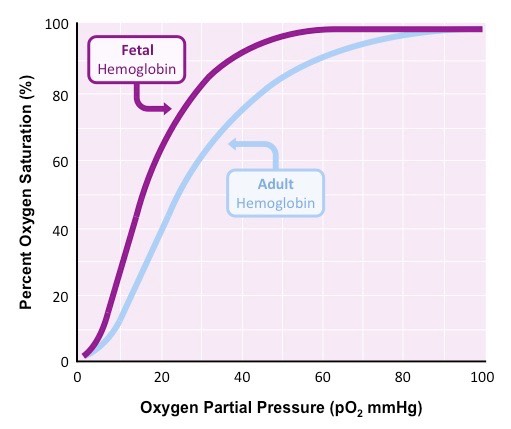
Fetal hemoglobin has a [greater or lesser] affinity for O2 than adult hemoglobin
greater
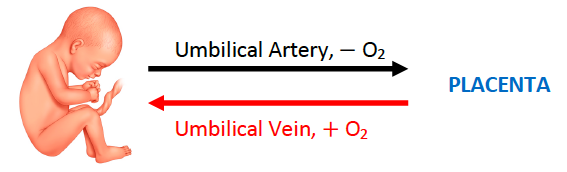
Blood in the umbilical artery is [oxygenated or deoxygenated]
deoxygenated
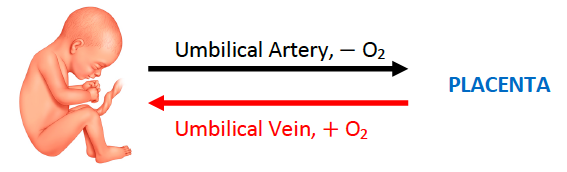
Blood in the umbilical vein is [oxygenated or deoxygenated]
oxygenated
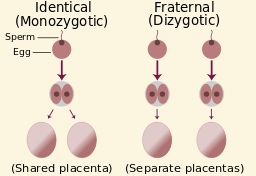
Fraternal twins are [...]
dizygotic
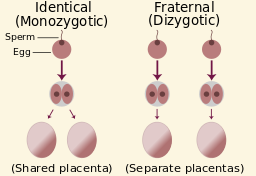
Identical twins are [...]
monozygotic
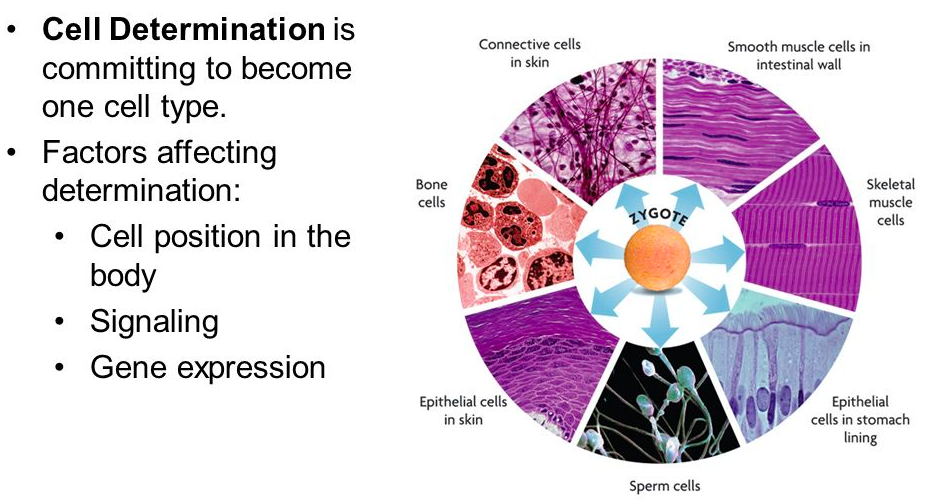
[...] is when a cell commits to becoming a certain type of cell
cell determination
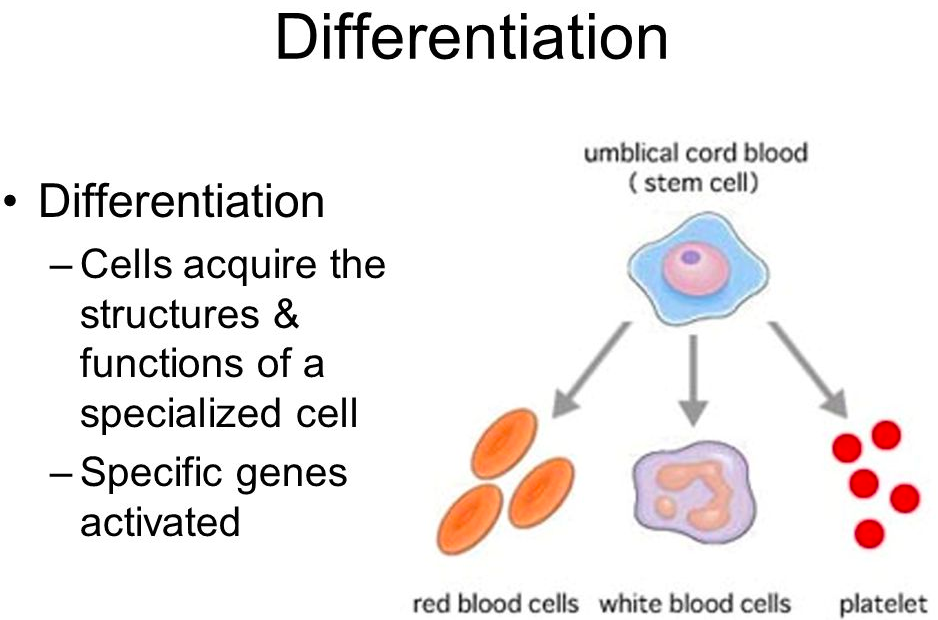
[...] is when a cell acquires the structures and functions of a specialized cell
cell differentiation
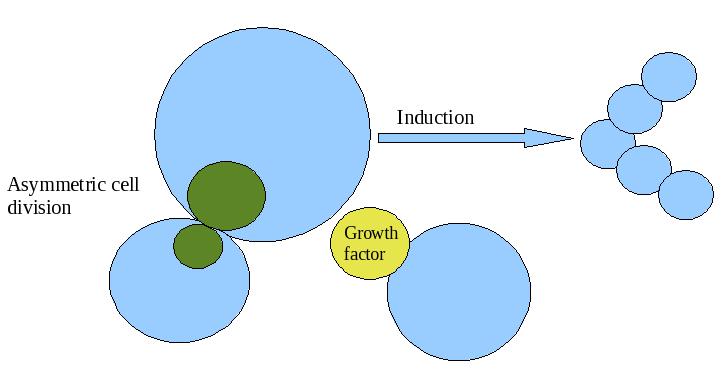
[...] is when a group of cells influence the fate of nearby cells
induction
mediated by inducers, which are commonly growth factors
[...] is when the cell secretes a hormone or chemical messenger that binds to a receptor on itself
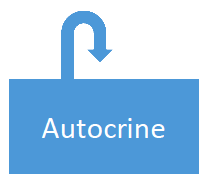
autocrine signaling
...] signaling is when a cell produces a signal to induce changes in nearby cells
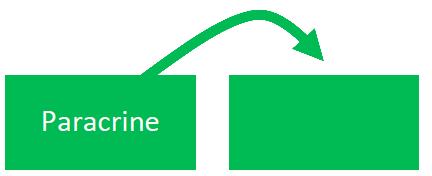
paracrine
[...] signaling is when a cell signals another cell that is directly adjacent or attached
juxtacrine

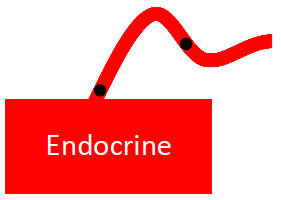
[...] signaling releases signals into the bloodstream, which carries them to target cells in distant parts of the body
endocrine
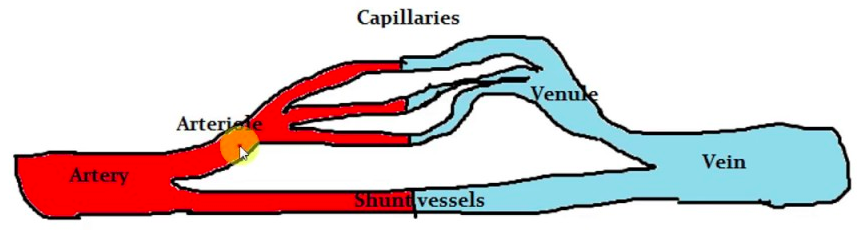
A/an [...] is a hole or a small passage which allows fluid to move from one part of the body to another
shunt
example: shunt vessels connect to an artery directly to a vein so the blood skips the capillaries
[...] is a shunt that allows blood to bypass the fetal lungs
patent foramen ovale
in the wall between the left and right atria of a fetus
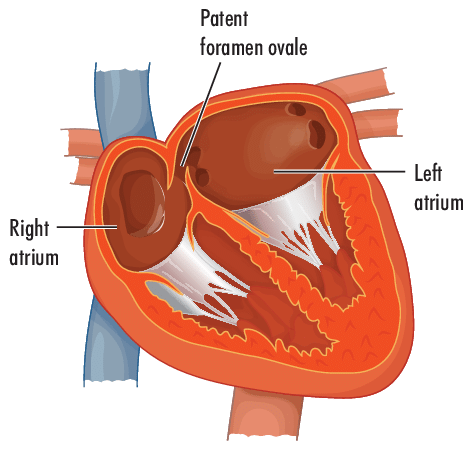
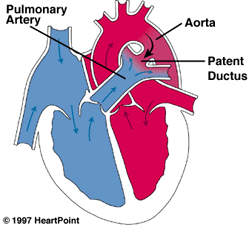
The [...] is a shunt that allows blood from the right ventricle to bypass the fetus's non-functioning lungs
patent ductus arteriosus
it connects the main pulmonary artery to the proximal descending aorta in a fetus