Biological molecules topic 2
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
BIO SL
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
what is a covalent bond?
a bond that forms when 2 atoms share a pair of electrons
how are electrons shared in nonpolar covalent bonds?
share electrons equally
how are electrons shared in polar covalent bonds?
share electrons unequally
How many covalent bonds can a carbon atom form?
4 covalent bonds
What does the term "unsaturated" mean in relation to carbon compounds?
Unsaturated carbon compounds contain double or triple bonds between carbon atoms
Define the term functional group.
A functional group is a specific group of atoms within a molecule that gives organic compounds their individual properties.
what makes an “organic” molecule
carbon-based with hydrogen presence
what’s the anatomy of a carbon atom?
6 protons 6 neutrons 4 valence electrons
what’s another word for outer shell
valence
what is a covalent single bond?
when carbon shares ONE pair of valence electrons w/ another atom
what is a covalent double bond?
when carbon shares TWO pairs of valence electrons w/ another atom
what are the 4 major classes of carbon compounds used by living organsms
carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, nucleic acids
define a chemical bond
an attraction between atoms, ions, or molecules when atoms transfer or share electrons between atoms
what is an ionic bond?
when atoms transfer electrons. its the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions in a chemical compound.
what are the 3 function groups?
hydroxyl, carboxyl, phosphate
define function group
an atom or group of atoms within a molecule that has similar chemical properties
How do hydroxyl (-OH) form hydrogen bonds?
polar covalent bonds between O & H allows hydroxyl to form hydrogen bonds
molecules with which function group will be hydrophilic/ soluble in water?
hydroxyl (-OH)
what is an example of hydroxyl (-OH)?
beta glucose
what are the properties of carboxyl (-COOOH)
carboxyl group is acidic
it can lose it’s hydrogen ion (H+) to form a stable anion (-COO^-)
-OH of carboxyl is polar = form hydrogen bonds w/ other molecules
what’s an example of carboxyl (-COOOH)
Fatty acid, amino acid alanine
what is Phosphate (-PO4^-) group made of? what does it form
4 oxygen atoms
forms a negatively charged, highly polar & hydrophilic functional group that can form hydrogen bonds
can also make ionic bonds
whats an example of Phosphate (-PO4^-)
ATP (adenosine triphosphate)
define a monomer
basic building block molecules that are capable of being linked together to form larger structures
how to break covalent bonds
hydrolysis, no enzymes (?)
how do monomers make biological polymers
they combine through condensation reactions
define polymers
large complex molecules made of repeating monomers aka. a chain of monomers = polymer
what are examples of biological monomers → biological polymers
nucleotides → nucleic acids (DNA RNA)
monosaccharides → polysaccharides
amino acids → proteins
what are condensation reactions
what builds polymers from monomers
what are the properties of condensation reactions
its an anabolic process that requires energy (ATP)
builds large molecule from smaller molecules through a metabolic pathway
forms water as a byproduct
what is a metabolic pathway
series of chemical reactions that happen inside a cell where each chemical reaction is controlled by a specific enzyme
whats an example of condensation reaction?
monomer_1(hydroxyl -OH) + monomer_2(hydrogen -H)
→ water_byproduct
→ new covalent bond, polymer
what’s an example of polymerization (a type of condensation reaction)
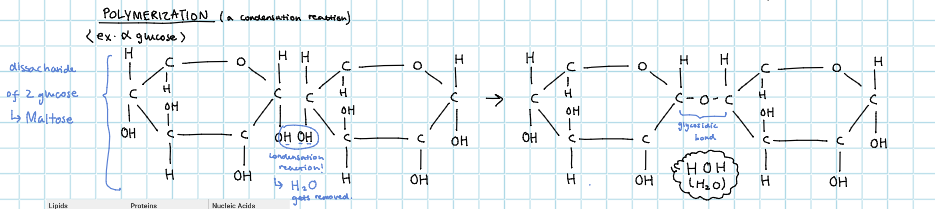
what happens in condensation reaction for carbohydrates?
2 monosaccharides link together to make disaccharides
multiple monosaccharides link together to make polysaccharides (aka carbohydrates)
what are the examples of condensation reaction for carbohydrates (monosaccharide → disaccharide → polysaccharides)
glucose → maltose (glucose + glucose) → starch
fructose → sucrose (glucose + fructose) → glycogen
galactose → lactose (glucose + galactose) → cellulose
what is an example of condensation reaction for lipids
glycerol undergoes condensation reactions with 3 fatty acids molecules to form triglycerides
what is an example of condensation reaction for proteins
amino acids undergo condensation to form dipeptides then tripeptides and eventually long polypeptide chains that fold into functional proteins
what is an example of condensation reaction for nucleic acids
nucleotides connect via condensation reaction between the phosphate group of one nucleotide and the pentose sugar of the next to create the sugar-phosphate backbone of DNA and RNA molecules
define Hydrolysis reaction
breaks apart complex molecules, making monomers by digesting polymers
→ reverse hydrogen reaction
what are the properties of hydrolysis reactions
catabolic process: metabolic process that breaks down complex complex molecules into simple molecules releasing energy in the process
water is added back yay
what is an example of hydrolysis reaction for carbohydrates
polysaccharides such as starch, glycogen, cellulose break apart to form monosaccharide monomers
what is an example of hydrolysis reaction for lipids
triglycerides undergoes hydrolysis to form glycerol and 3 fatty acid molecules
what is an example of hydrolysis reaction for proteins
polypeptide chains that form functional proteins hydrolysis to make amino acid monomers
nucleic acids
the sugar-phosphate backbone of DNA RNA molecules can go through hydrolysis to break part individual nucleotides
define monosaccharide
simplest carbohydrates, made of single sugar molecules that cannot be hydrolyzed
whats the general formula for monosaccharide?
(CH2O) w/ different amount of carbon atoms
what are pentoses (include example)
five carbon monosaccharides
ribose & deoxyribose
what are hexoses (include example)
six carbon monosaccharides
glucose & fructose
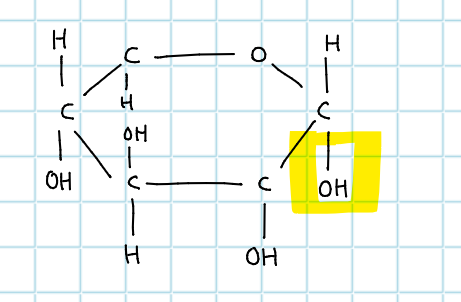
C6H2OH - which glucose is this?
alpha glucose
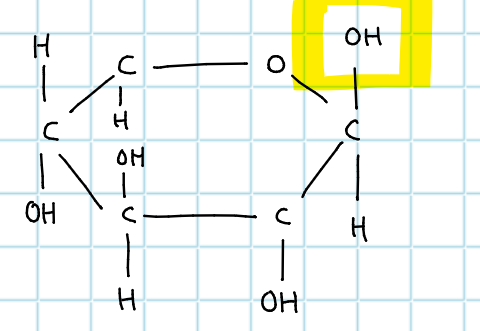
CH2OH - which glucose is this?
beta glucose
define isomer
exactly same formula (atoms) with different recipe (different atom arrangement) e.g alpha beta glucose
what is the strongest bond that holds atoms together within biological molecules?
covalent bonds
what makes a molecule soluable
hydroxyl (-OH)