Motor and Sensory Pathways in Speech and Hearing Anatomy
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
110 Terms
Precentral gyrus
The portion of the cortex identified by #1.
Upper Motor Neuron
The type of neuron indicated by #2.
Pyramids
The portion of the medulla indicated by #3.
Pyramidal decussation
The landmark/decussation indicated by #4.
Lower motor neuron
The type of neuron indicated by #5.
Corticospinal tract
The name of this pathway.
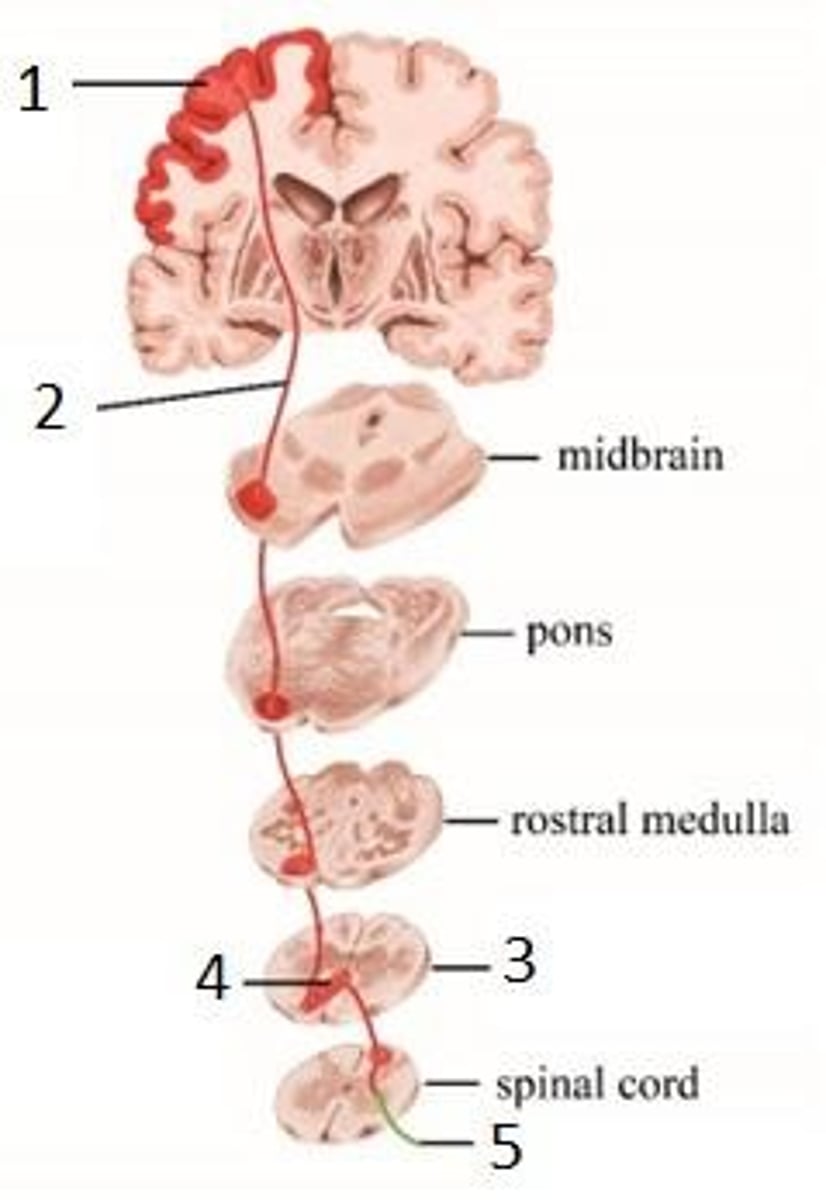
Voluntary motor commands
The kind of information carried by this pathway.
Descending pathway
The direction this pathway is traveling, starting in the primary motor cortex (precentral gyrus) and traveling to the spinal cord.
Four points of weakness
Cortex, Internal capsule, Brainstem, Spinal cord.
Motor weakness or paralysis
What happens when there is damage to any of the four points of weakness.
Upper motor neurons
Found in the primary motor cortex.
Weakness or paralysis, Spasticity, Hyperreflexia, Possible Babinski sign
What happens when upper motor neurons are damaged.
Lower motor neurons
Found in the anterior horn of the spinal cord or cranial nerve motor nuclei in the brainstem.
Weakness or paralysis, Flaccidity, Hyporeflexia or areflexia, Muscle atrophy, Fasciculations
What happens when lower motor neurons are damaged.
Motor homunculus representation
The size of a body part's representation reflects how much fine motor control it requires.
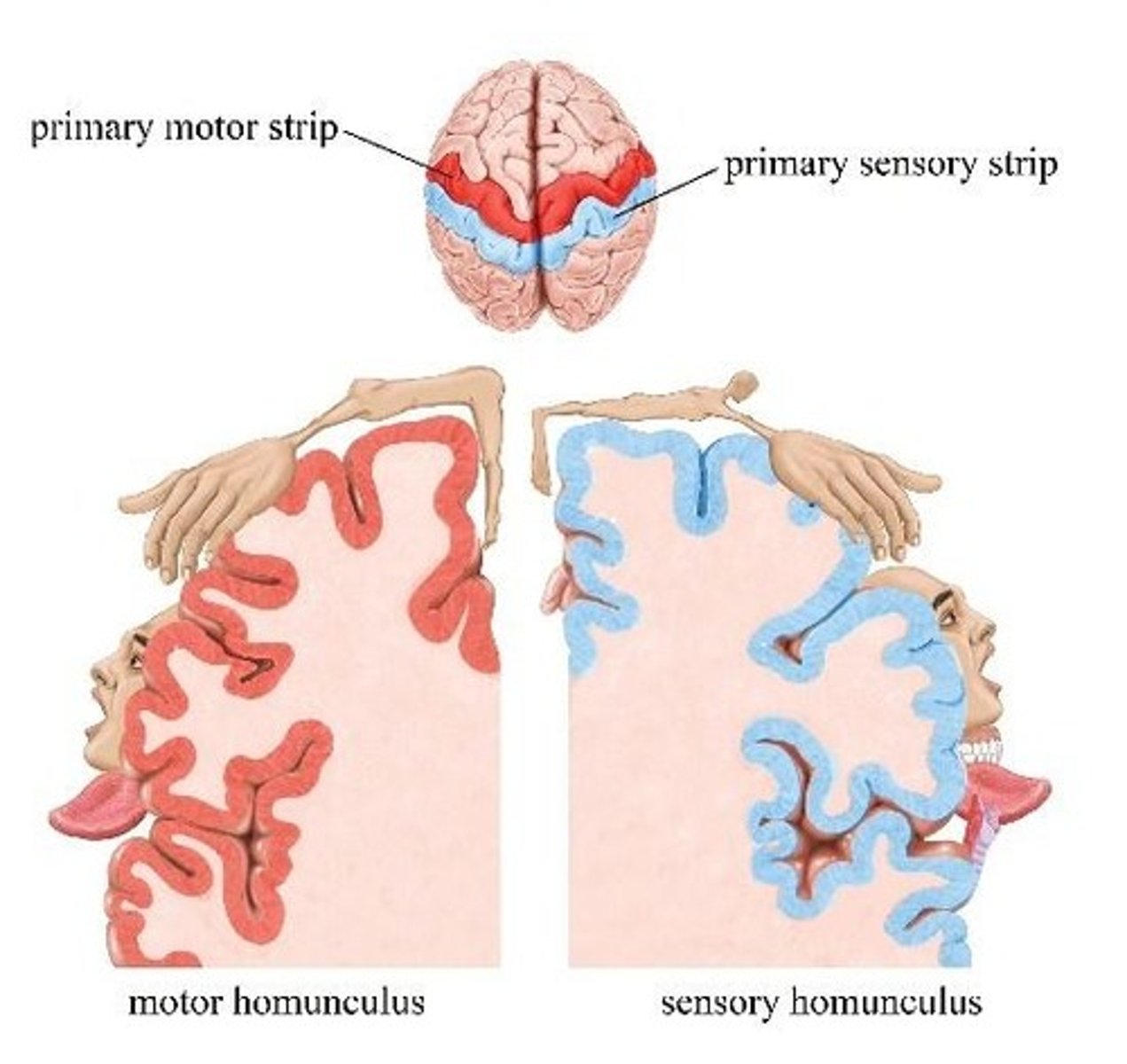
Innervation density
The term that describes how densely an area of the body is innervated.
Efferent pathway
A synonym for 'motor' pathway.
Neuromuscular junction (NMJ)
At the NMJ, the postsynaptic cell is a muscle fiber, not another neuron.
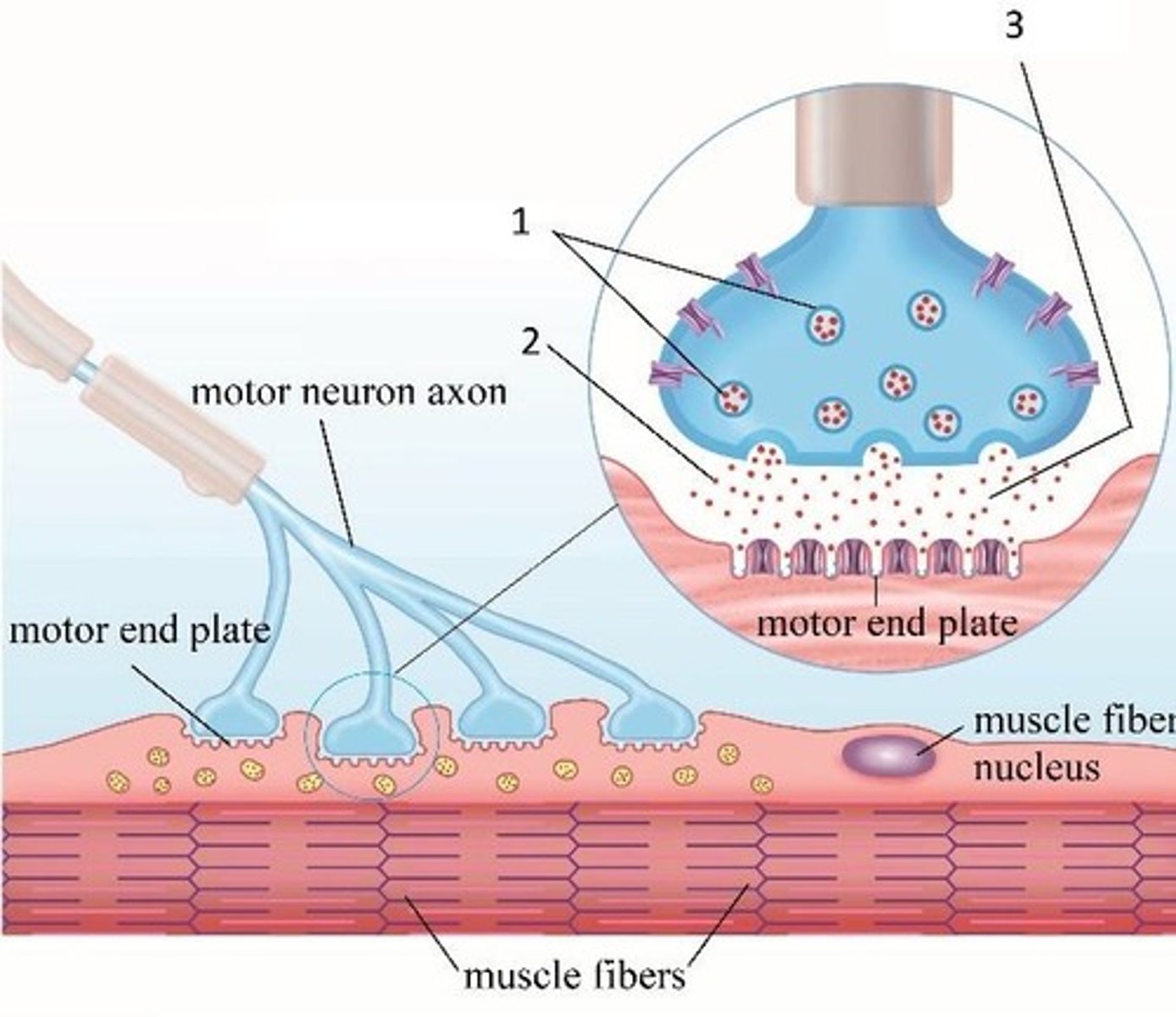
Acetylcholine (ACh)
The one and only neurotransmitter present at the neuromuscular junction.
Femoral nerve
The nerve labeled in the reflex arc.
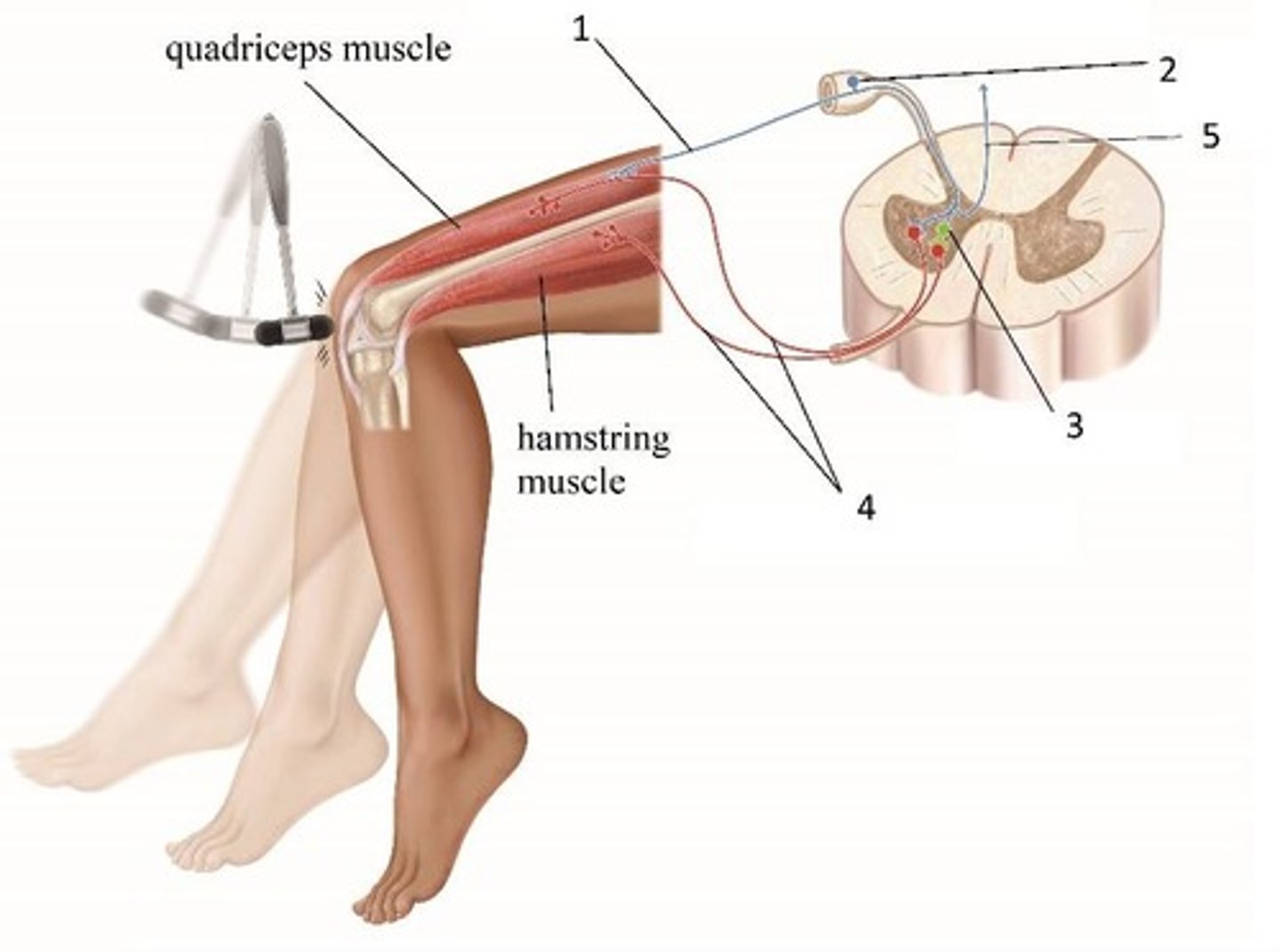
Dorsal root ganglion
The nerve landmark labeled in the reflex arc.
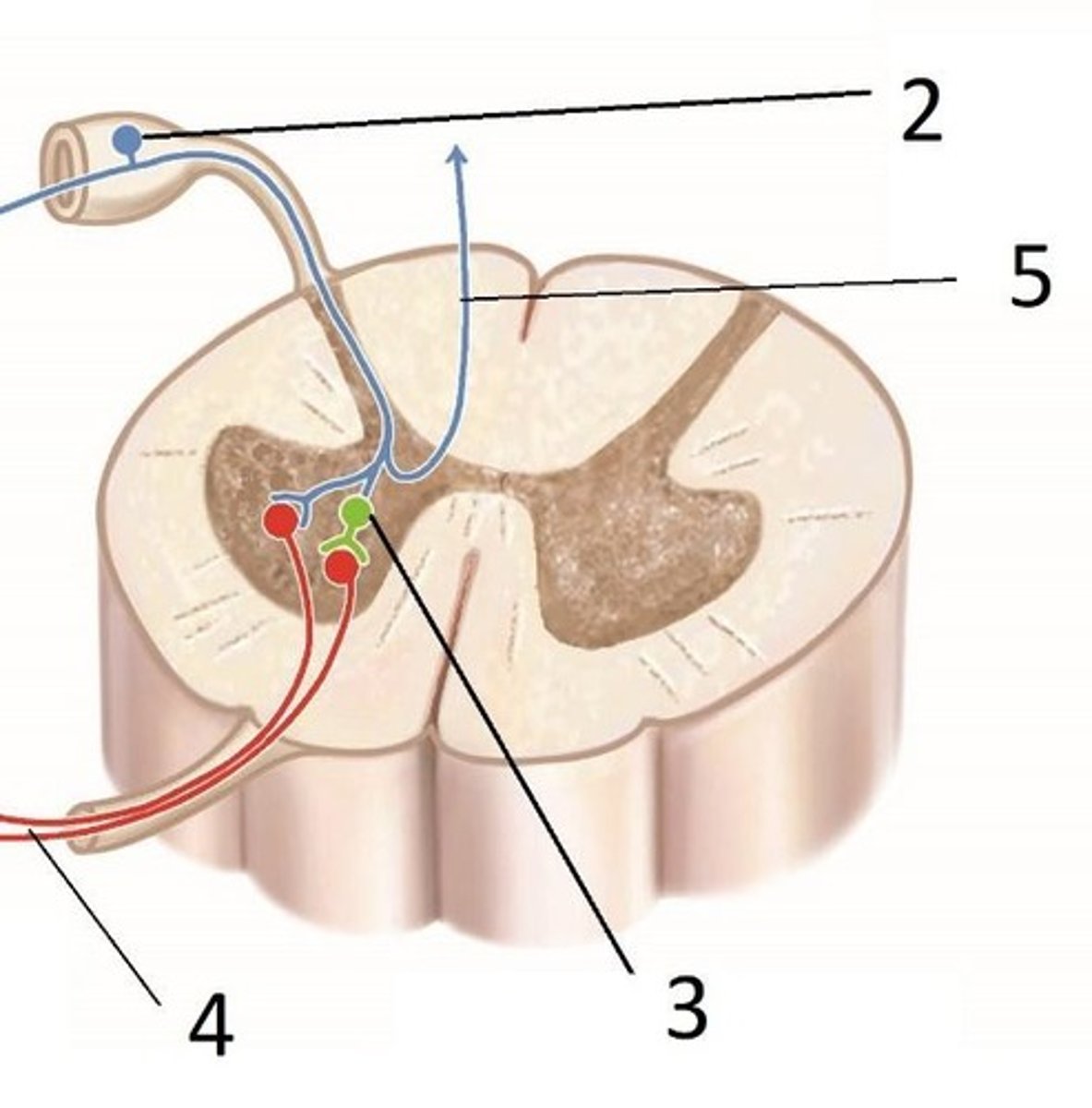
Sensory (afferent) nerve
The nerve labeled in the reflex arc.
Motor (efferent) nerve to the quadriceps
The nerve labeled in the reflex arc.
Motor (efferent) nerve to the hamstrings
Nerve responsible for transmitting signals from the spinal cord to the hamstring muscles, causing them to contract.
Sensory receptor
GTO or spindle afferent that detects changes in stretch or tension.
Sensory (afferent) nerve
Nerve that carries sensory information from the sensory receptors to the spinal cord.
Motor (efferent) nerve to the antagonist muscle
Nerve that transmits signals to the muscle opposing the action of the effector muscle.
Motor (efferent) nerve to the effector muscle
Nerve that carries signals from the spinal cord to the muscle that produces movement.
Effector muscle
The muscle that is stimulated to contract in response to a motor nerve signal.
Primary somatosensory cortex
Region of the brain responsible for processing sensory information from the body.
Primary motor cortex
Region of the brain that generates motor commands to initiate movement.
Upper motor neuron
Neuron that originates in the brain and carries signals to lower motor neurons in the spinal cord.
Lower motor neuron
Neuron that directly innervates skeletal muscles and carries signals from the spinal cord to the muscles.
Spasticity
A condition characterized by increased muscle tone and exaggerated reflexes due to upper motor neuron damage.
Hyperactive reflexes
Reflexes that are exaggerated or increased, often due to upper motor neuron damage.
Flaccid paralysis
A condition where muscles are weak and unable to contract, typically due to lower motor neuron damage.
Hyporeflexia
Reduced or absent reflexes, often associated with lower motor neuron damage.
Areflexia
The absence of reflexes, commonly due to lower motor neuron damage.
Muscle atrophy
The wasting away or decrease in muscle mass, often resulting from lower motor neuron damage.
Fasciculations
Involuntary muscle twitching, often seen in lower motor neuron damage.
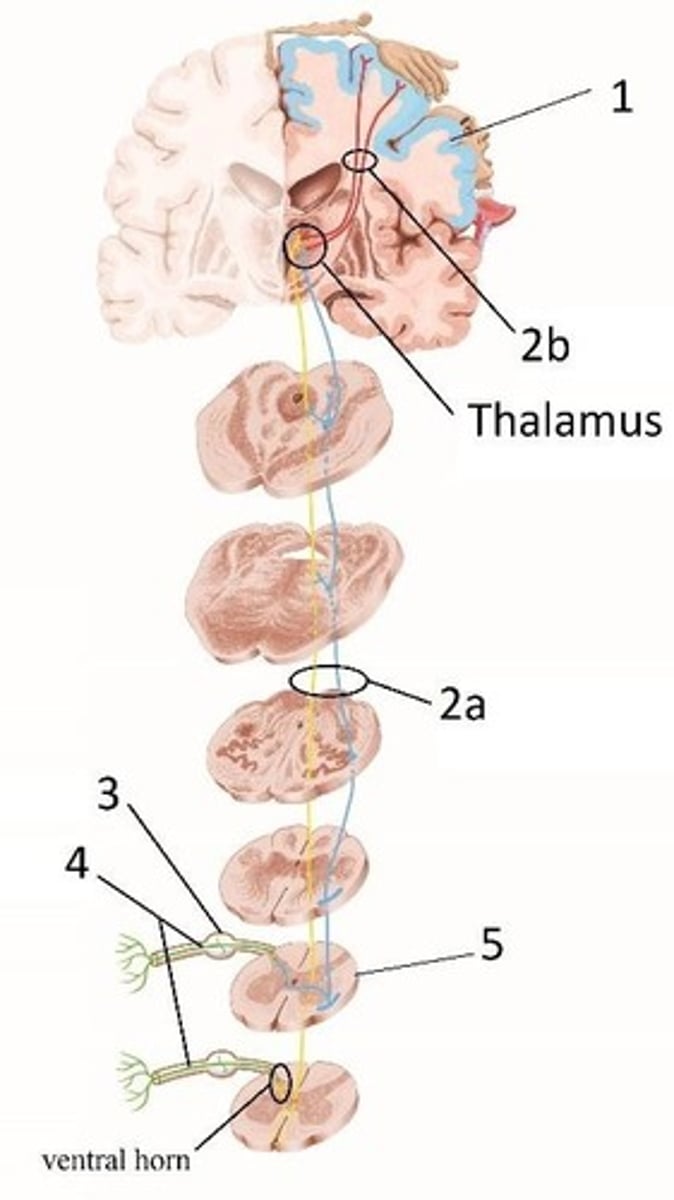
Dorsal column-medial lemniscus (DCML) pathway
Pathway that carries fine touch, vibration, proprioception, and pressure information to the brain.
Ascending pathway
Pathway that carries sensory information from peripheral receptors to the brain.
Spinothalamic tract
Pathway that carries pain, temperature, crude touch, and pressure information to the brain.
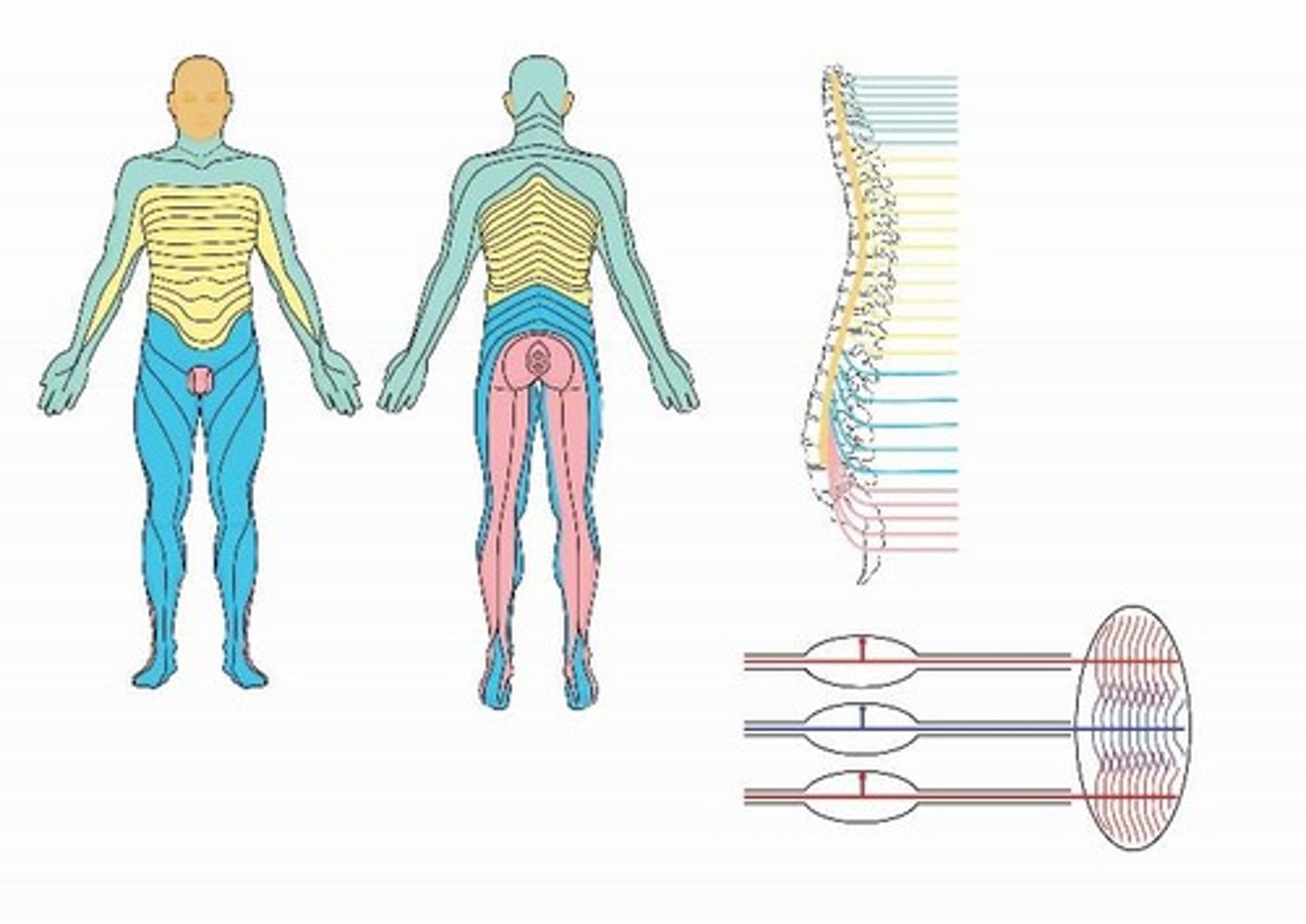
Dermatome map
A map that shows areas of skin innervated by sensory nerves from individual spinal nerve roots.
Second-order neuron
Neuron that transmits signals from the spinal cord or brainstem to the thalamus.
Third-order neuron
Neuron that transmits signals from the thalamus to the primary somatosensory cortex.
Sensory decussation
The crossing over of sensory pathways in the caudal medulla.
First-order neuron
Neuron that carries sensory information from peripheral receptors to the spinal cord.
Sensory homunculus
The size of a body part's representation on the sensory homunculus reflects the density of sensory receptors and the level of fine sensory discrimination, not the physical size of the body part.
Anterior cerebral artery (ACA)
Blood supply distribution labeled #1.
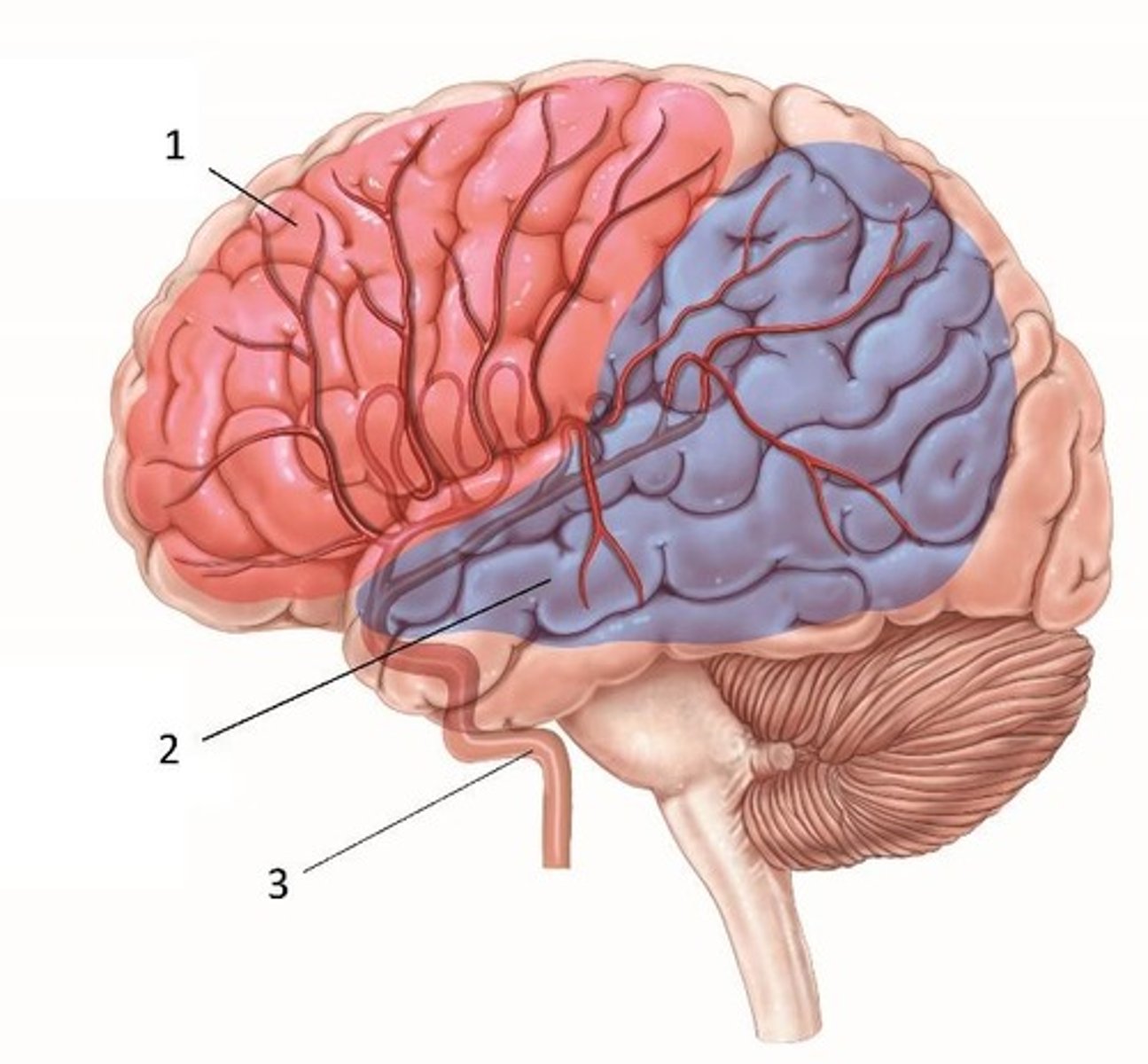
Middle cerebral artery (MCA)
Blood supply distribution labeled #2.
Posterior cerebral artery (PCA)
Blood supply distribution labeled #3.
Broca's area
Cortical area identified by #4.
Wernicke's area
Cortical area identified by #5.
Anterior cerebral artery
Vessel indicated by #1.
Internal carotid artery
Vessel indicated by #2.
Posterior cerebral artery (PCA)
Vessel indicated by #3.
Basilar artery
Vessel indicated by #4.
Vertebral arteries
Vessel indicated by #5.
Posterior communicating arteries
Vessel indicated by #6.
Circle of Willis
The name of this structure.
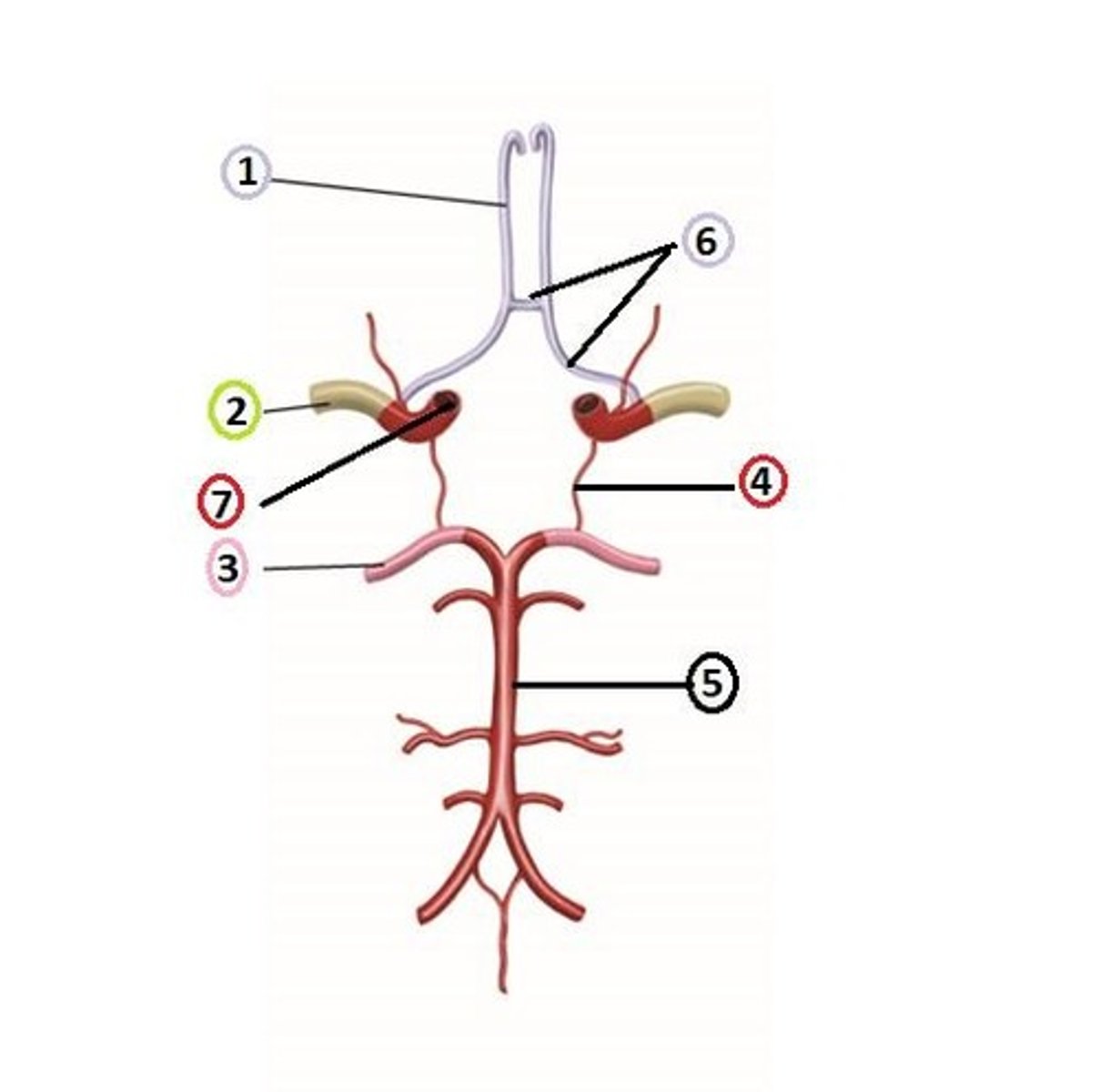
Collateral circulation
The purpose/function of the Circle of Willis is to provide collateral circulation to the brain, ensuring continuous blood flow even if one part of the arterial supply is blocked or narrowed.
Superior division of the middle cerebral artery (MCA)
Branch #1.
Inferior division of the middle cerebral artery (MCA)
Branch #2.
Internal carotid artery
Artery serving the MCA and ACA distributions, identified in the illustration as #3.
Dura mater
Layer of meninges identified by #1.
Dura mater structure
Tough, dense, fibrous connective tissue. Impermeable to cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and most substances. Provides mechanical protection and forms venous sinuses.
Arachnoid mater
Meningeal layer identified by #2.
Arachnoid mater structure
Thin, web-like membrane. Contains trabeculae that extend into the subarachnoid space. Acts as a barrier but allows CSF flow beneath it.
Pia mater
Meningeal layer identified by #3.
Pia mater structure
Very thin, delicate layer directly adherent to the brain and spinal cord surface. Highly permeable to fluids and nutrients. Follows the contours (gyri and sulci) of the brain.
Lateral ventricle
Ventricle identified by #1.
Third ventricle
Ventricle identified by #2.
Fourth ventricle
Ventricle identified by #3.
Cerebral aqueduct (Aqueduct of Sylvius)
Structure identified by #4.
Ventricular system purpose
To produce, circulate, and drain cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), which cushions and protects the brain and spinal cord.
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) functions
1. Protection - cushions the brain and spinal cord from trauma; 2. Buoyancy - reduces the effective weight of the brain, preventing it from compressing itself against the skull; 3. Chemical stability - Maintains a stable environment by removing waste products and distributing nutrients.
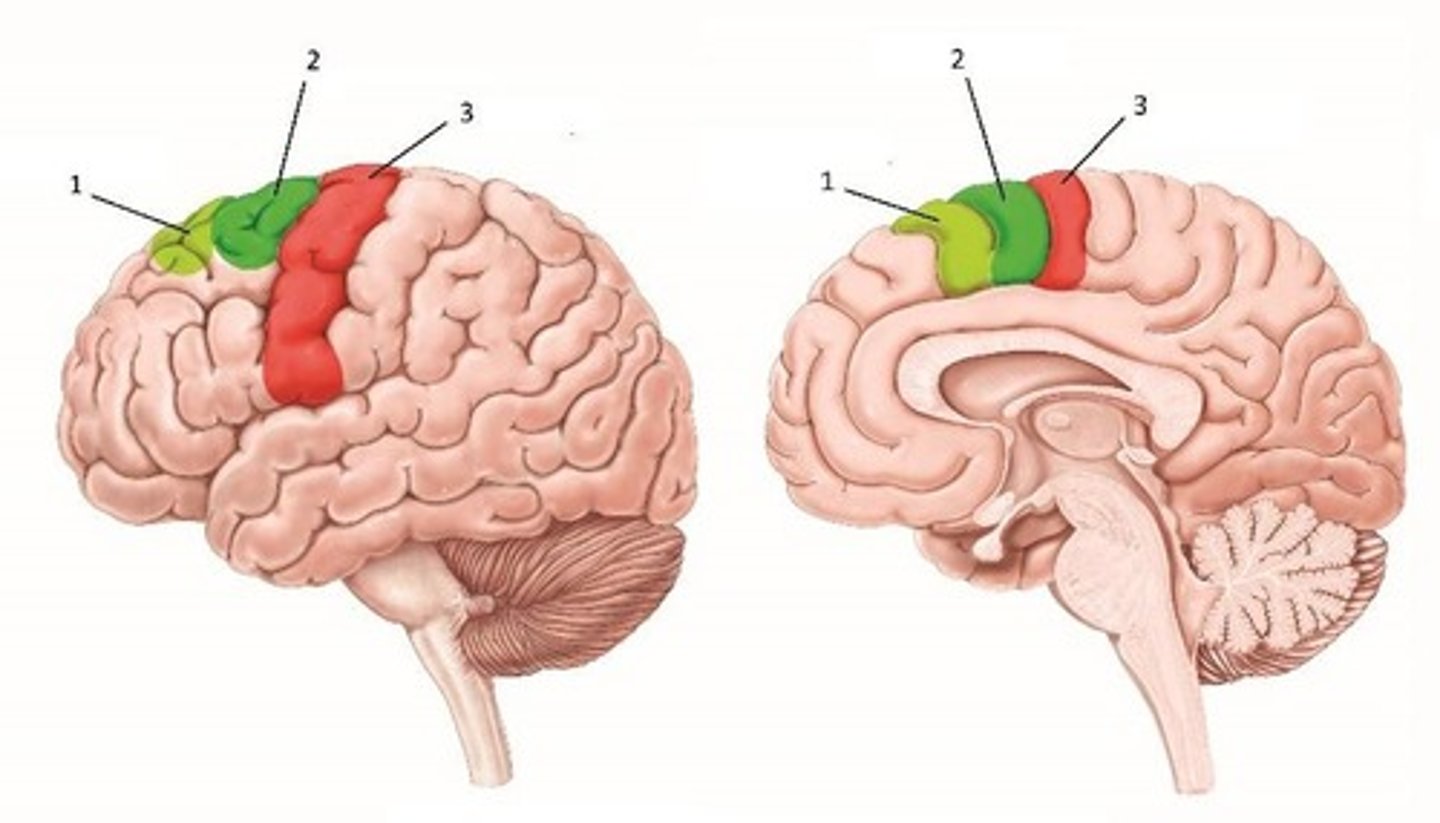
Pre-motor cortex
Gyrus represented by #3, its function is planning and coordination of movement, especially complex and learned movements.
Precentral gyrus
Gyrus represented by #2.
Postcentral gyrus
The area responsible for sensory feedback necessary for precise and coordinated movement.
Collective function of areas 2 and 3
Sensorimotor integration, controlling movement and processing sensory feedback.
Presence of areas in both hemispheres
Yes, they are present in both hemispheres.
Blood supply distribution for areas 2 and 3
Middle cerebral artery (MCA) supplies the lateral portions (face, upper limbs); anterior cerebral artery (ACA) supplies the medial portions (lower limbs).
Central sulcus
The sulcus identified by #1.
Presentral gyrus
The gyrus identified by #2.
Function of gyrus #2
Executes voluntary motor movements.
Collective function of gyri #3 & 4
Broca's area is responsible for speech production and motor planning for language.
Presence of Broca's area in both hemispheres
Yes, the precentral gyrus is present in both hemispheres; Broca's area is usually lateralized to the dominant hemisphere.
Collective name for portions labeled #1-3
Posterior cortex (includes the parietal, temporal, and occipital lobes).
Functions of the parietal lobe
Processes somatosensory information, such as touch, proprioception, and spatial awareness.
Functions of the temporal lobe
Processes auditory information, language comprehension, and is involved in memory.
Functions of the occipital lobe
Processes visual information.
Blood supply distribution for posterior cortex
Middle cerebral artery (MCA) supplies lateral aspects; posterior cerebral artery (PCA) supplies occipital lobe and medial temporal lobe.
Broca's area
Responsible for speech production and motor planning for language.
Wernicke's area
Responsible for language comprehension.
Presence of Wernicke's area in both hemispheres
No, it is primarily found in the left hemisphere.
Functions of the cerebellum
Coordinates voluntary movements, refines motor activity, and helps maintain balance and posture.
Main movement refinement functions of the cerebellum
1. Coordination of voluntary movements; 2. Motor learning and timing.
Balance functions of the cerebellum
Maintains posture and equilibrium; coordinates eye movements and balance via the flocculonodular lobe.
Cognitive functions of the cerebellum
Involvement in attention, language processing, regulating emotional responses, and plays a role in executive function and planning.