Digestive System & Fluoroscopy
1/122
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
123 Terms
What are the three primary functions of the digestive system?
1. intake and digestion
2. absorption
3. elimination
What does the alimentary canal consist of?
oral cavity, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, anus
What are the accessory organs of the digestive system?
salivary glands, pancreas, liver, gallbladder
What are the three salivary glands?
1. parotid (biggest)
2. submandibular
3. sublingual
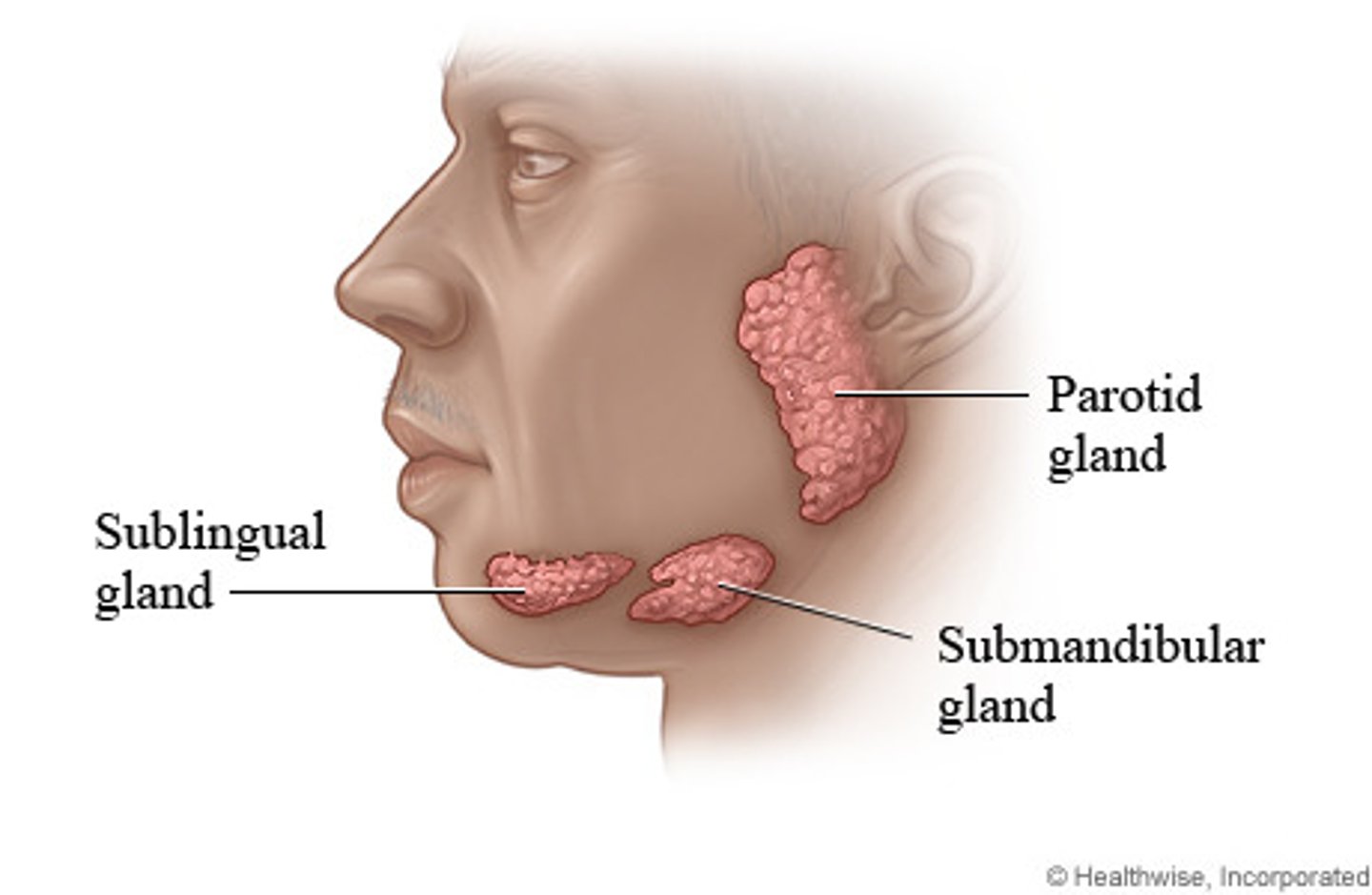
How many mL of saliva do salivary glands secrete daily?
1000-1500 mL
Does endocrine or exocrine deal with digestion?
exocrine
What does the liver do?
produces bile to assist in the digestion of fats
How many quarts of bile does the liver produce per day?
1
What does the gallbladder do?
stores and concentrates bile
What are the two important reactions that occur in order for swallowed food to enter the esophagus?
1. soft palate closes off nasopharynx
2. epiglottis is depressed to cover laryngeal opening
The esophagus is located _________ to the larynx and trachea
posterior
What is characterized by a large out pouching of the esophagus just above the upper esophageal sphincter?
Zenker's Diverticulum
True/False: the esophagus has two indentations as it passes by the aortic arch and left primary bronchus
true
What is the short segment just before connecting to the stomach and after passing through the diaphragm called?
cardiac antrum
What are the two names for the opening between the esophagus and the stomach?
1. esophagogastric junction
2. cardiac orifice
What is the muscle that controls the opening between the esophagus and stomach called?
cardiac sphincter
What is the name of the opening leaving the distal stomach?
pyloric orifice
What is the difference between an orifice and a sphincter?
- orifice is the opening
- sphincter is the muscle that controls the opening
In which part of the alimentary canal does digestion and absorption occur?
small intestine (small bowel)
What are the three sections the small intestine is divided into (in order)?
1. duodenum
2. jejunum
3. ileum
What is the shortest, widest, and most fixed portion of the small bowel?
duodenum
Which section of the duodenum is a common site of ulcer disease?
superior (first) section
What are the four sections of the duodenum?
1. superior
2. descending
3. horizontal
4. ascending
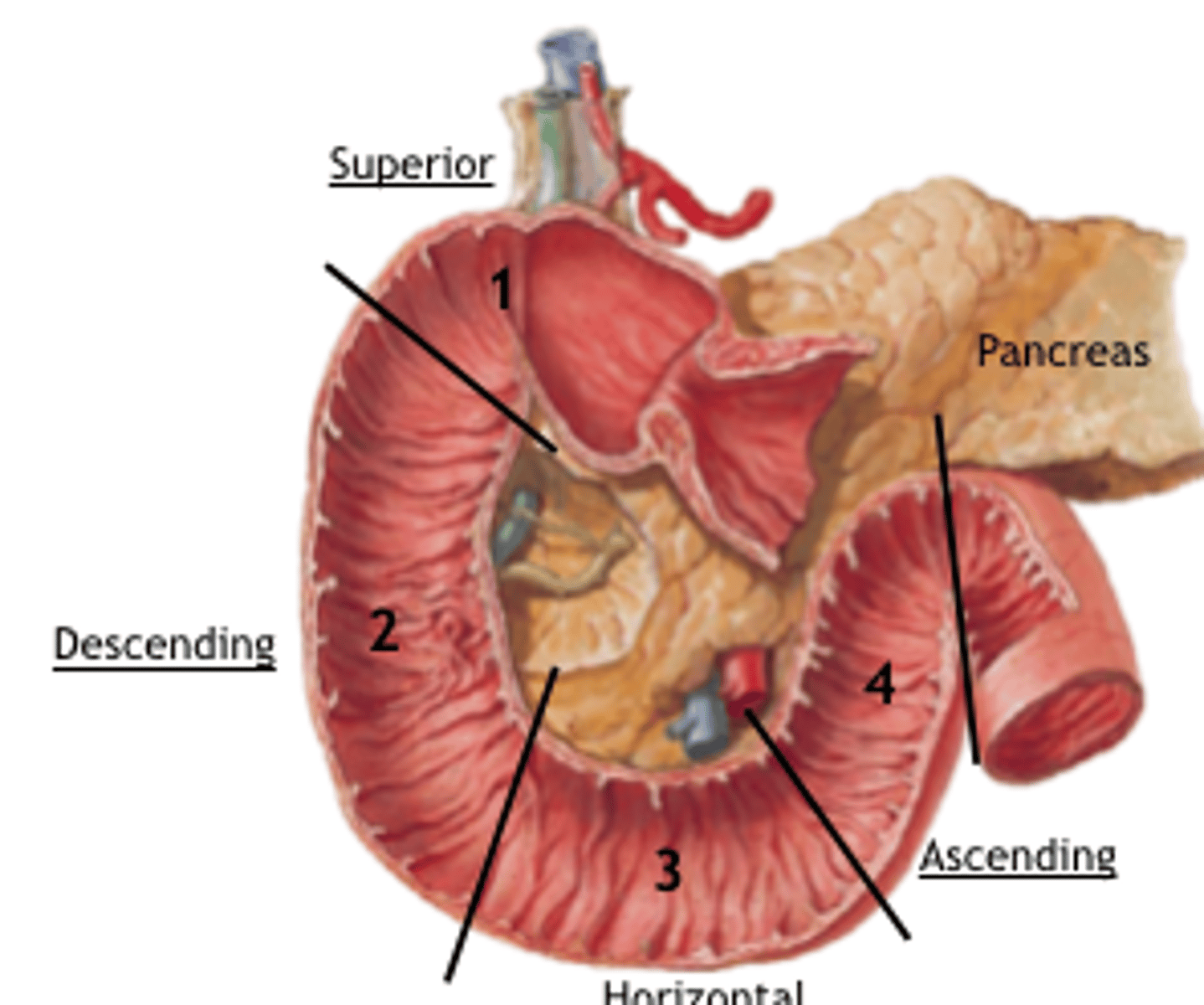
Which section of the duodenum receives common bile and pancreatic ducts?
descending (second) section
What is the duodenojejunal flexure held in place by?
ligament of treitz
The jejunum is located primarily to the ____ of the midline
left
Where does the ileum join the large intestine?
ileocecal valve in the RLQ
What is chyme?
stomach contents mixed w/ stomach fluids
What does NPO mean?
nil per os (nothing by mouth)
What is radiolucent contrast media?
- negative contrast
- swallowed air, CO2 gas crystals, normally present gas bubble in stomach
What is radiopaque contrast media?
- positive
- barium sulfate, water soluble iodinated (gastroview/gastrographin)
When should barium sulfate NOT be used?
if there is any chance that the mixture might escape into the peritoneal cavity
What is the difference between single and double contrast techniques?
- single uses one or the other contrast medias
- double uses both
What is the ratio of BaSO4 to water for thick barium?
3 or 4:1
What is the ratio of BaSO4 to water for thin barium?
1:1
When putting the PT in a trendelenburg position, what are you looking for?
reflux and hiatal hernia
What is the valsalva maneuver?
- bearing down like you have a bowel movement
- usually done to check for hernia's
If you're using barium sulfate what should your kVp be set to?
110-125 kVp
If you're using water soluble contrast (gastroview/gastrographin) what should your kVp be set to?
75-80 kVp
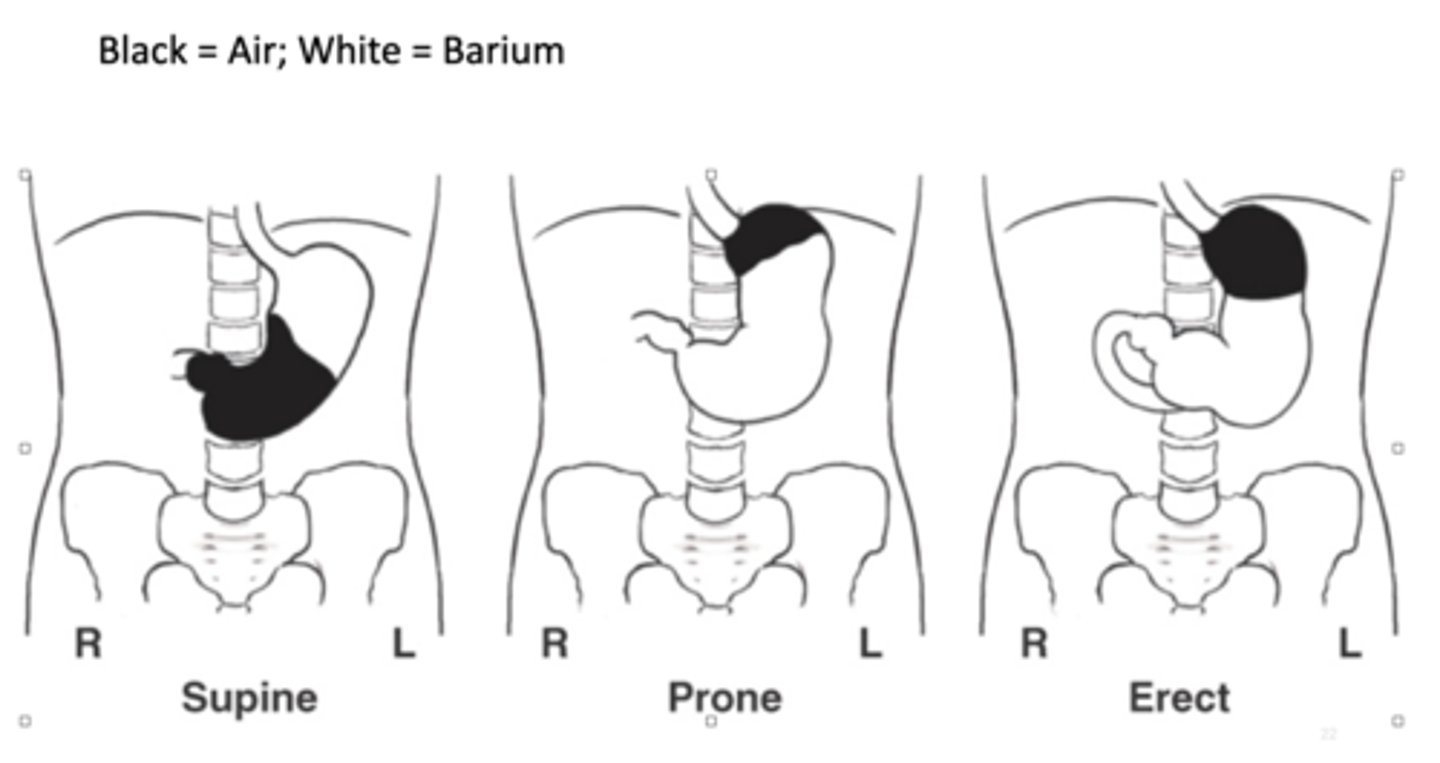
Where is the barium located when the PT is prone (UGI)?
fundus located posteriorly so air will go to fundus and barium will be in body and pylorus
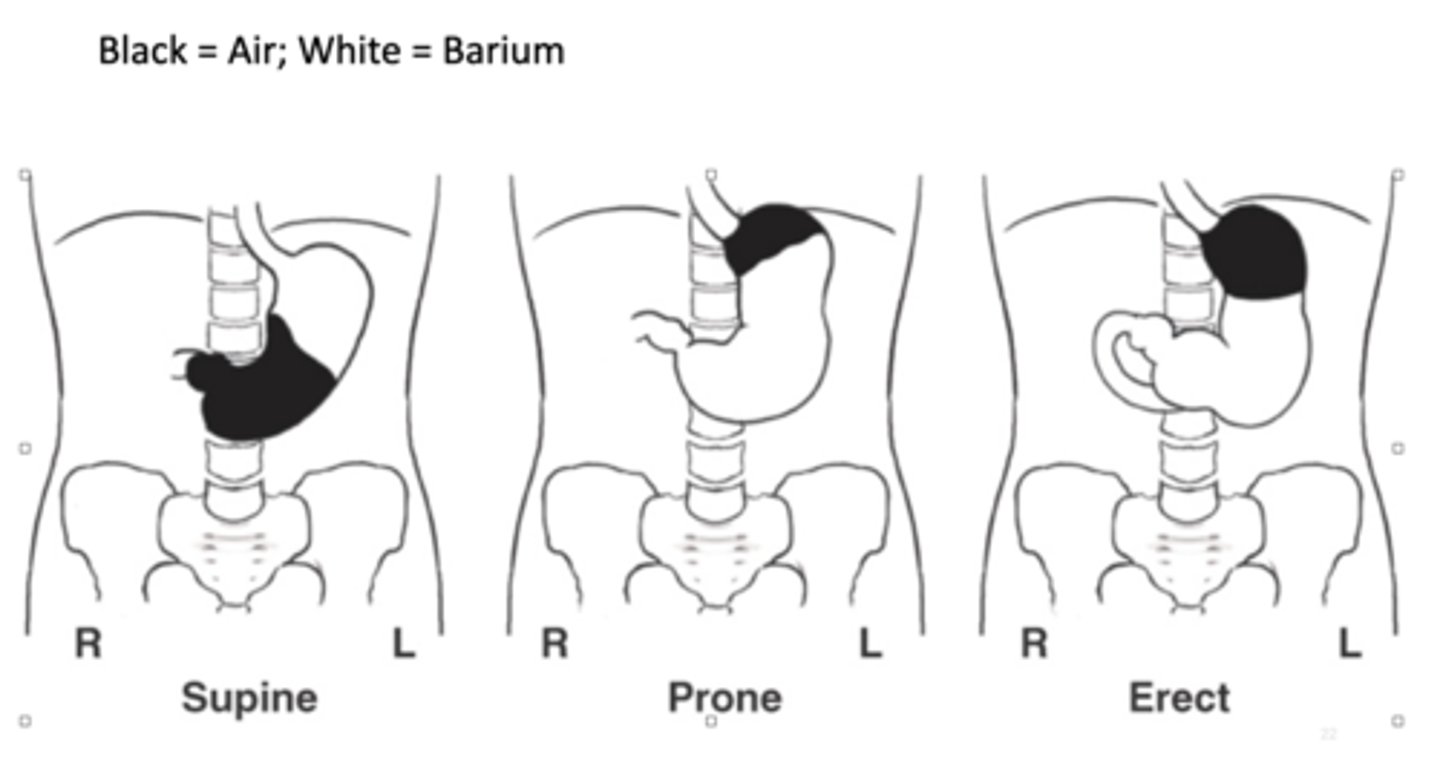
Where is the barium located when the PT is supine (UGI)?
fundus is located posteriorly so barium goes to fundus
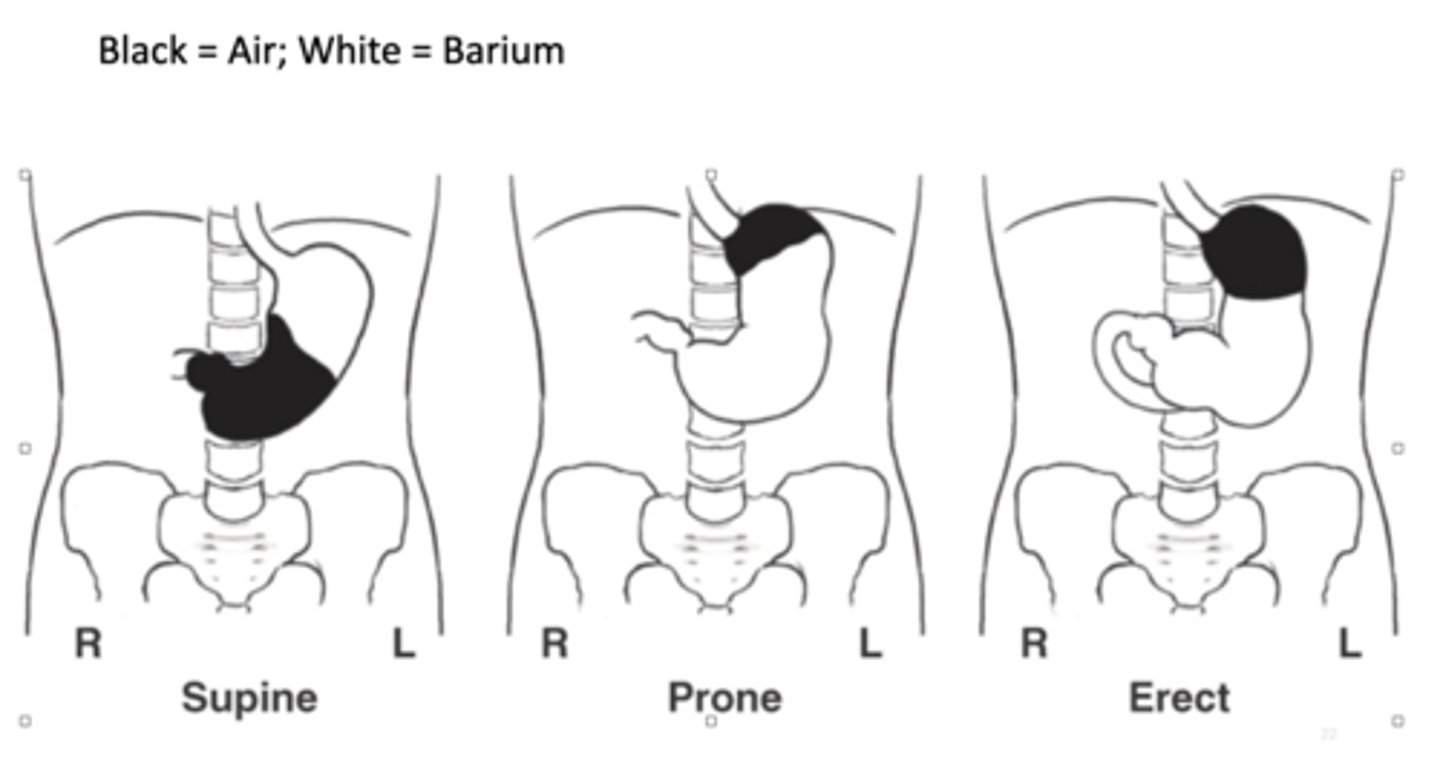
Where is the barium located when the PT is erect (UGI)?
air rises into fundus, air-barium line is straight line
Do the villi belong to the large or small intestine?
small
What is the twisting of a portion of the intestine on its own mesentery leading to an obstruction called?
volvulus
What are the four main parts of the large intestine?
1. cecum
2. colon
3. rectum
4. anal canal
What is located inferior to the ileocecal valve?
cecum
What happens when infectious agents enter the appendix?
appendicitis
What is the rectal ampulla?
dilated portion of rectum located anterior to coccyx
How many anteriorposterior curves does the rectum have?
2
Do the haustra belong to the large or small intestine?
large
Where will the air go in a supine LGI?
transverse color and sigmoid colon
Which one of the procedures for the large intestine is also called the small bowel enema?
intubation method
For the scout radiograph of a small bowel series where is the centering for the first hour? After the first hour?
2" above the crest; at the crest
During a double contrast small bowel procedure (enteroclysis), barium passes through at a rate of how many mL per minute?
100 mL/min
What position should you put your PT in in order to insert the BE tube?
sims
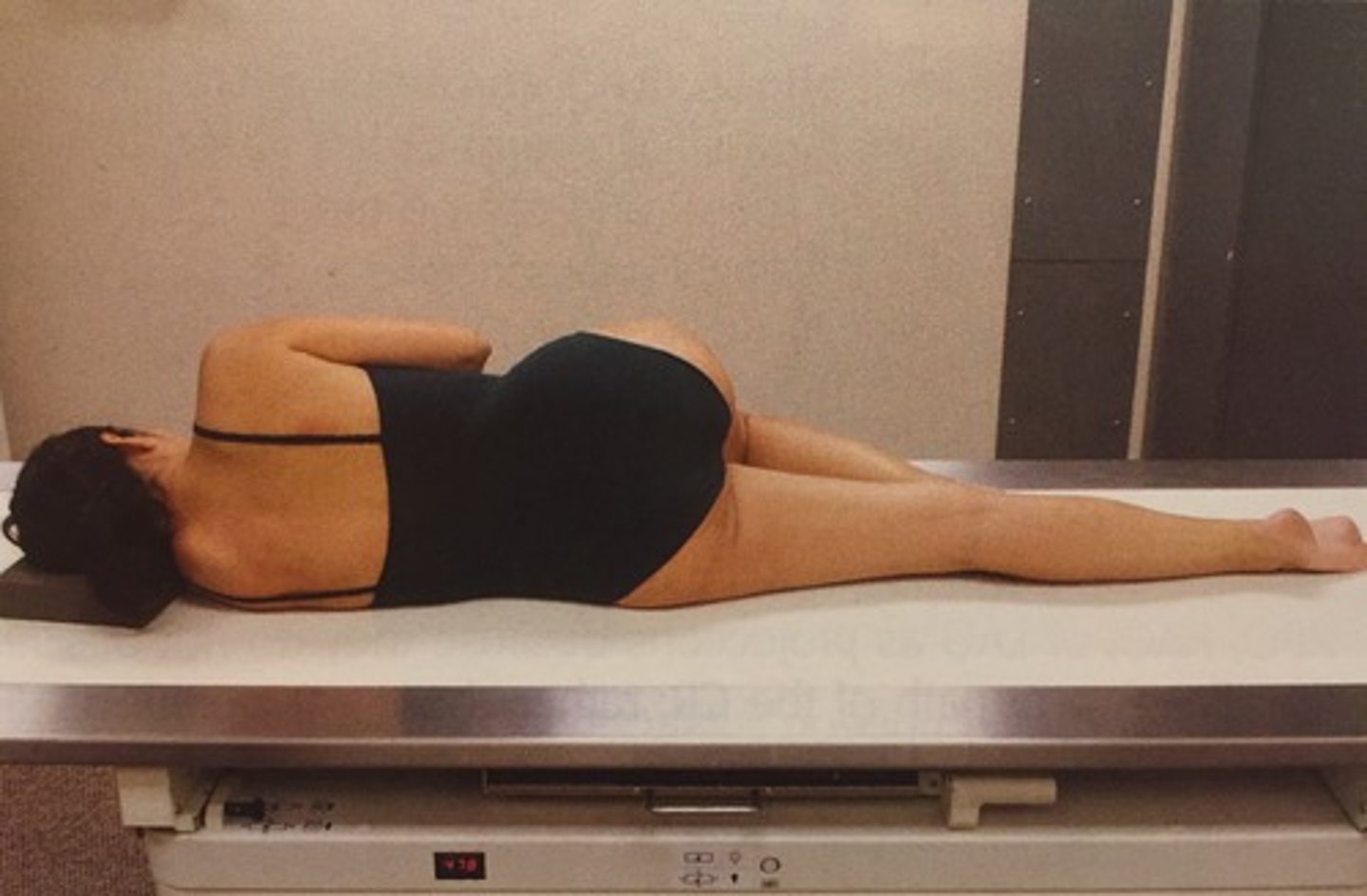
True/False: during a BE procedure the bag should be no more than 24 inches above the table
true
What are the two options if spasms are suspected or occur during BE procedures?
1. lidocaine
2. glucagon
Which of the options for spasms is mixed in the barium bag?
lidocaine
Which of the options for spasms is given intravenously?
glucagon
What are the two intubation procedures?
1. therapeutic
2. diagnostic
What positions are done for a single contrast BE?
AP, RPO & LPO, AP Axial or AP Axial OBL, LAT rectum, post evacs
What positions are done for a double contrast BE?
AP or PA, RAO & LAO, AP Axial or AP Axial OBL, RT & LT LAT Decubitus, Ventral Decubitus rectum
True/False: some BEs can be done through a PTs colostomy
true
What is the correct order for scheduling a PT w/ several exams?
1. ALL non contrast exams
2. nuclear medicine
3. urinary system
4. biliary systems
5. colon exams
6. esophagus, UGI, small bowel
True/False: Fluoroscopy provides a static image
false
When was the first fluoroscope invented and by who?
1896 by Thomas Edison
What is ABC?
automatic brightness control
When were image intensification tubes developed?
1948
How many times brighter do image intensifiers make the image?
1000 to 6000 (some books say 500 to 8000)
What is the principle advantage of image intensifiers?
increased image brightness
True/False: radiographs and fluoroscopy are visualized/performed at illumination levels of 100 to 1000 lux
true
What is the process of an image intensifier (in order)?
1. input phosphor
2. photocathode
3. focusing lens
4. anode
5. output phosphor
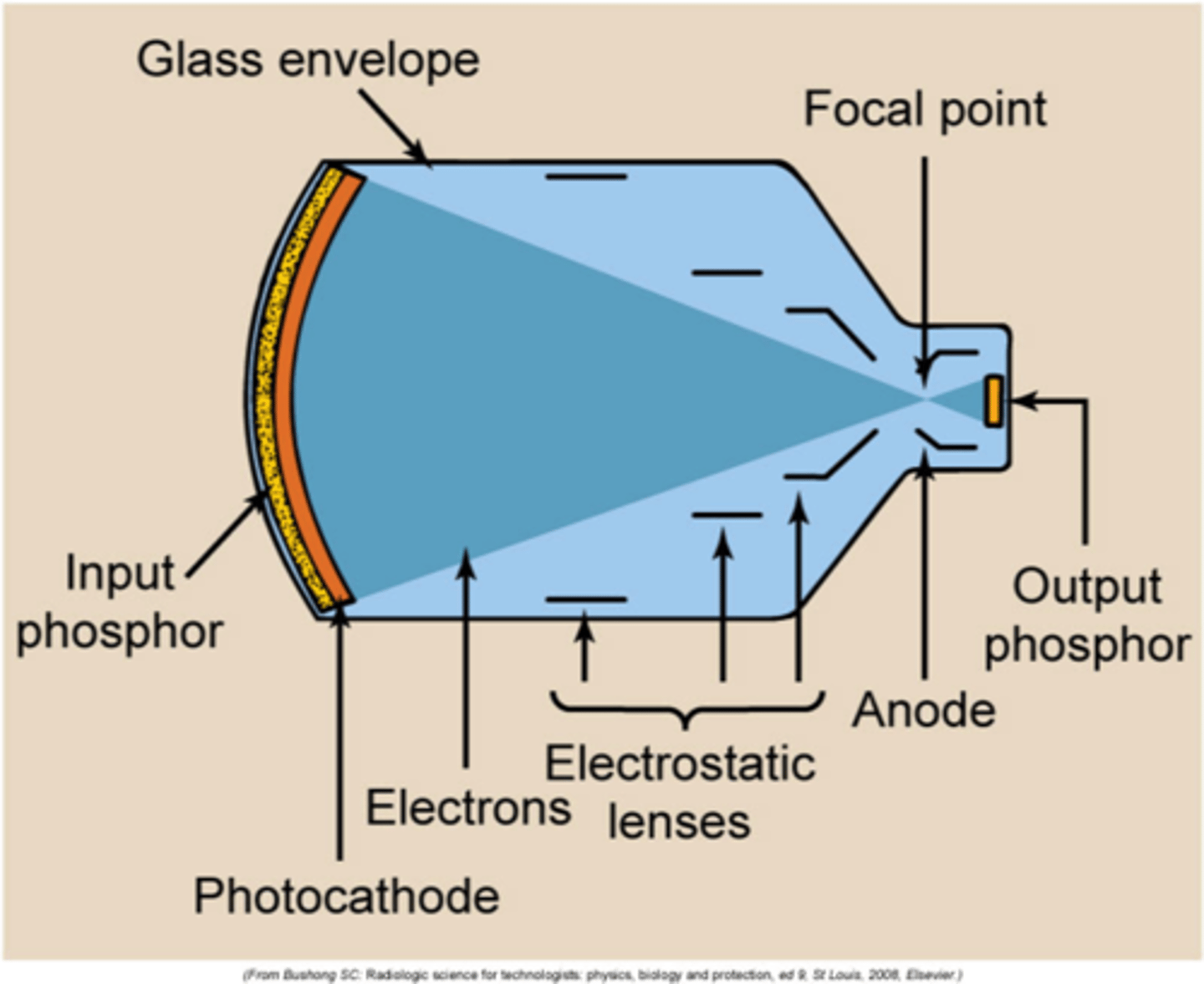
What is the input phosphor made out of?
cesium iodide (CsI)
What is the photocathode made of?
cesium (Cs) and antimony (Sb)
What is the output phosphor made of?
zinc cadmium sulfide (ZnCdS)
What is the flux gain of a typical image intensifier?
50
What is the flux gain formula?
number of output light photons / number of input x-ray photons

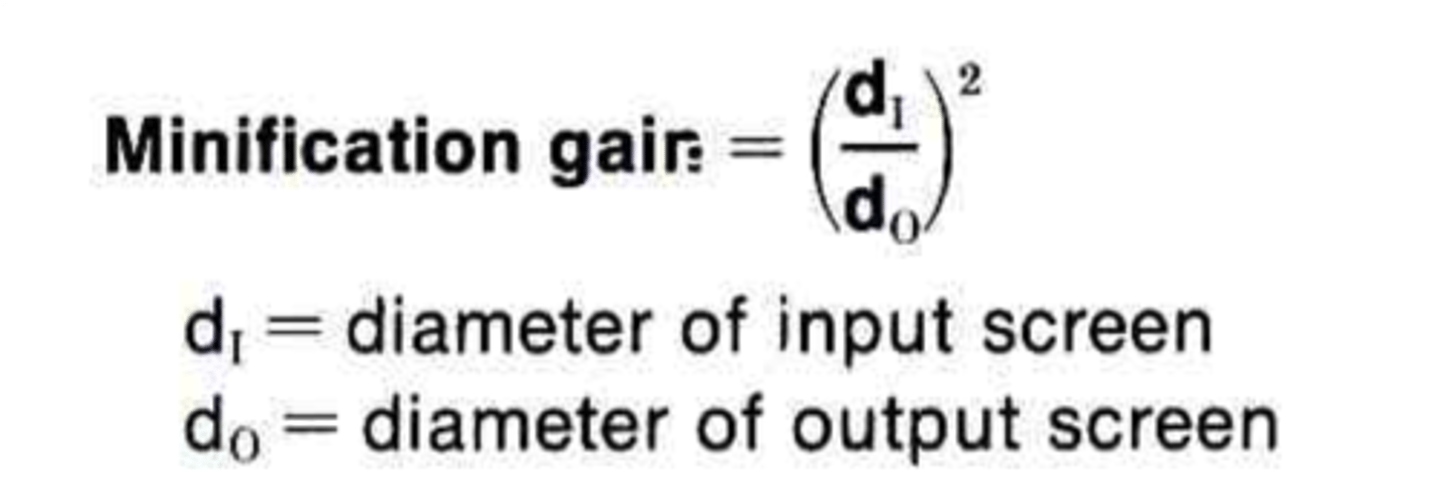
What is the minification gain formula?
(input screen diameter / output screen diameter)^2
True/False: Minification gain happens because the image is larger at the output phosphor and smaller at the input phosphor
false
What is the brightness gain formula?
flux gain x minification gain
True/False: as your tube gets older, PT dose increases to maintain brightness
true
input phosphors (screens) range from ___ to ___ in diameter
6" (15 cm) to 12" (30 cm)
What is the diameter of a typical output phosphor?
1" (2.5 cm)
What are the diameters of dual focus image intensifiers?
- 9"/6" (23 cm/15 cm)
- more commonly 10"/7" (25 cm/17cm)
What are the diameters of tri-focus image intensifiers?
- 10"/7"/5" (25 cm/17 cm/12 cm)
- 9"/6"/4.5" (23 cm/15 cm/10 cm)
Mag mode increases resolution (spatial and contrast) and what else?
PT dose
What is vignetting?
reduction in brightness at the periphery of the image
True/False: the CCD's rapid discharge time eliminates image lag
true
What is cinefluoroscopy used in?
cardiac catheterization
__ or __ mm film cameras are used in cinefluoroscopy
16; 35
__ or ___ mm film cameras are currently used in spot film cameras
70; 105
True/False: spot films produce high PT dose
true
What is the most common type of TV camera used?
vidicon
What kind of lines are TV pixels arranged in?
raster or horizontal scan lines
How many scan lines are on the typical fluoro monitor?
525
What mode does digital fluoroscopy read in?
progressive mode
What is the SNR in old and digital fluoroscopy?
old -> 200:1
digital -> 1000:1
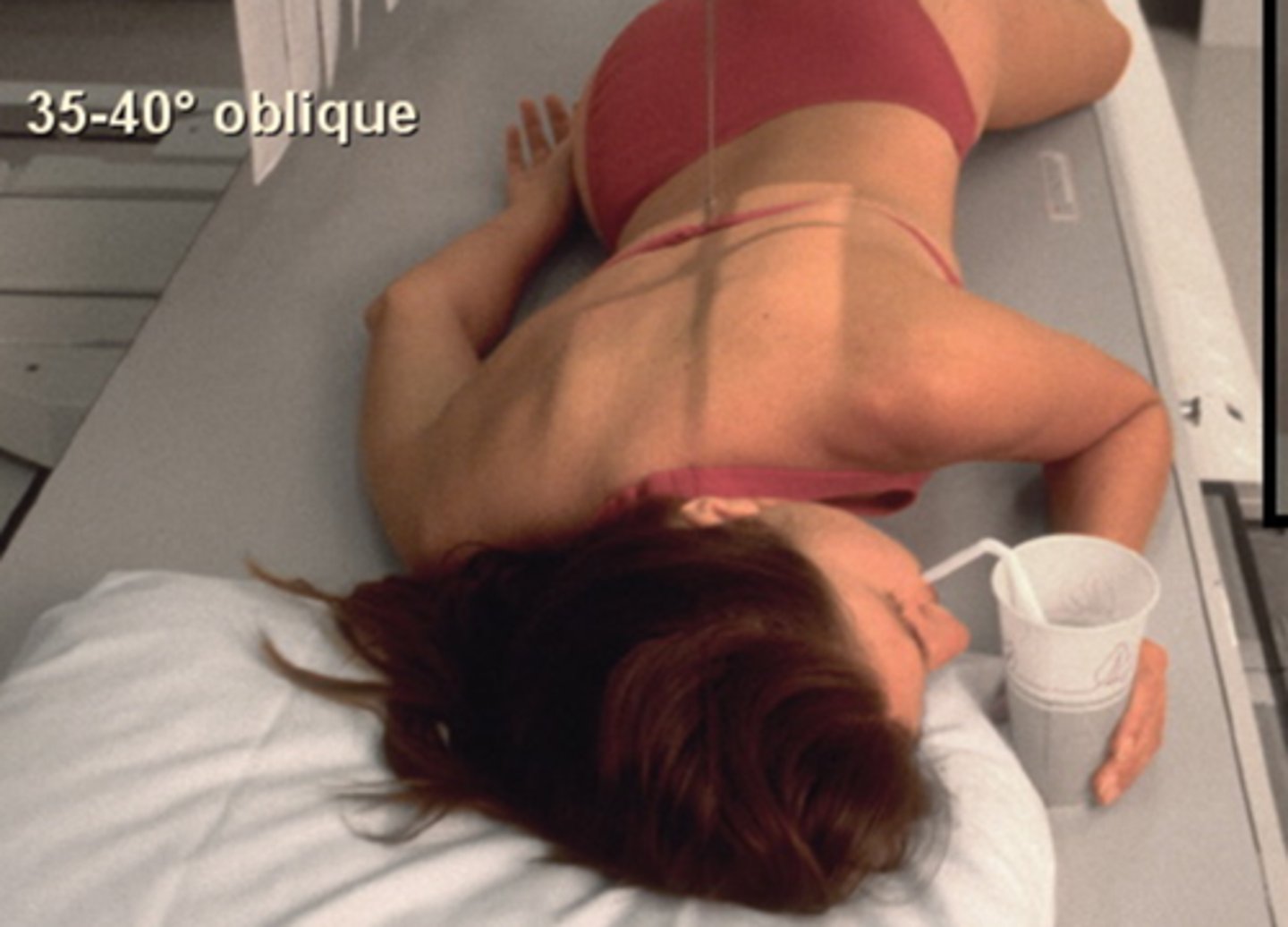
STAMPSBC for RAO Esophagram:
S - around waist
T - center cell @ 110 kVp
A - none
M - R marker on R side
P - PT rotated 35-40 degrees from prone, CR to T5-T6 & 1-2" to upside of midline
S - 40"
B - instruct PT to continuously swallow barium, take image after 3rd swallow
C - 14 x 17 lengthwise, slight side-to-side collimation

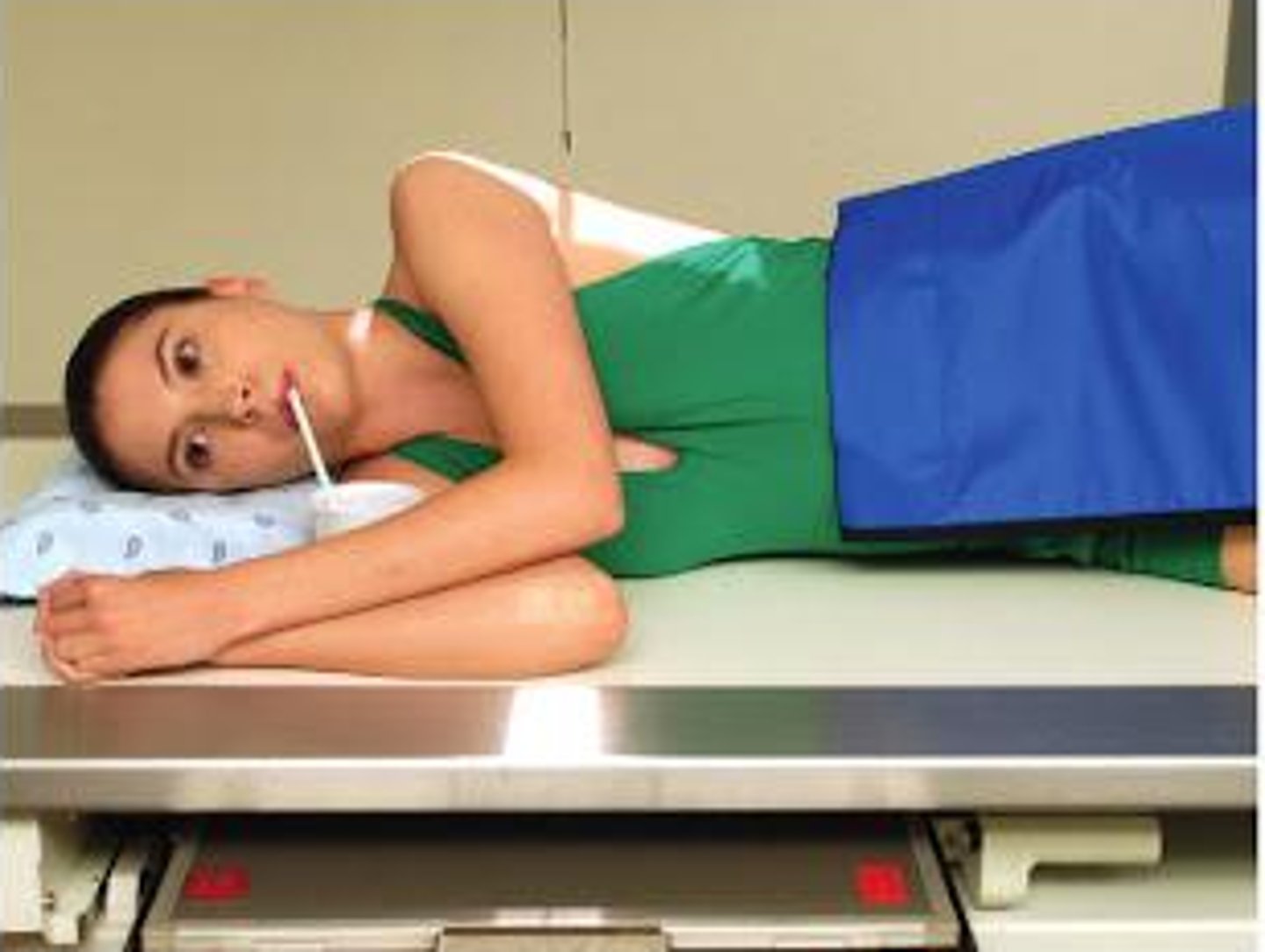
STAMPSBC for Lateral Esophagram:
S - around waist
T - center cell @ 110 kVp
A - none
M - correct marker, correct side
P - PT stands w/ side to bucky w/ arm closest above head and other holding cup, CR T5-T6 & midcoronal plane
S - 40"
B - instruct PT to continuously swallow barium, take image after 3rd swallow
C - 14 x 17 lengthwise, slight side-to-side collimation

STAMPSBC for AP/PA Esophagram:
S - around waist
T - center cell @ 110 kVp
A - none
M - correct marker, correct side
P - PT has back or chest to bucky & holds cup, CR T5-T6 & midline
S - 40"
B - instruct PT to continuously swallow barium, take image after 3rd swallow
C - 14 x 17 lengthwise, slight side-to-side collimation