1/2
what are normative and positive statements
positive economics is a method of analysis that can be proven or disproven. often these are issues that are investigated and can be verifiable through facts, figure and statistics. (e.g. Multinational companies operating in Australia should pay more tax.)
normative economics are statements that often involve personal opinion, bias and is subjective. (e.g. If Australia's annual inflation rate rose to 3.5 percent, this would reduce the purchasing power of some individuals.)
possible scenarios that may have led the economy of [Lemonsville] operating:
inside the curve
outside the curve
on the curve
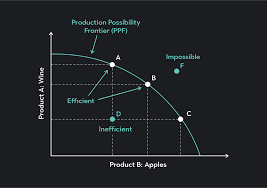
inside the curve is not maximising the output from the resources available, spare capacity, producing inefficiently.
producing outside the curve is not possible because they do not have the resources available to produce outside the curve.
producing on the curve is where they have utilised all economic resources, achieving maximum efficiency.
what is macroeconomics
Looks at the whole economy of a nation and the larger flows that affects the overall economic conditions (e.g. Observing the catalyst of recessions). Macroeconomics generally involves looking at:
National spending and production (GDP)
National incomes and unemployment
National inflation rates
what is microeconomics
Observes the factors that influence smaller stakeholders in the Australian economy such as decisions made by individual consumers or firms
For example
A particular firm (Woolies, Coles, Myer)
An industry (e.g. Childcare, fashion)
A single market (e.g. Labour market, oil market, property market)
what are some examples of needs and wants?
(e.g. Needs: food, water, clothes, shelter
Wants: Lego, games, electronic devices)
what is relative scarcity?
unlimited needs and wants but limited resources (e.g. water)
factors of production such as land, labour and capital
land - raw materials (not man made) that are unprocessed. (e.g. plants, animals, minerals, water, wind, sun.)
labour - are the mental or physical skills required to produce goods and services (e.g. carpentry skills, teaching skills)
capital - are any processed man made items used in manufacturing goods and services (e.g. machinery, buildings, equipment)
what is opportunity cost
opportunity cost relates to the value of production or consumption that is forgone(given up) when resources are allocated to their next best alternative use.
what are material and non material living standards
Material living standards
Income per person
Level of consumption of goods and services per person
The purchase power of incomes
Non-material living standards
The quality of daily life
Life expectancy
Freedom
Crime rates
Literacy rates
identify and describe the 3 sectors or the three sector flow model
Consumer or household sector:
Consists of over 26 million Australians
Are consumers or buyers of goods and services, but some are also owners or suppliers of resources
Producer or business sector
Around 2.5 million large, medium and small firms making goods and services in Australia
Most of these are privately owned and hence make up the private sector
Government or public sector
Includes the activities and decisions of federal, state and local authorities
This group collects taxes and other revenue from those households earning income to pay for government spending on the provision of goods and services for the community(e.g. healthcare, roads, education)
Makes up the public sector
what are the 4 flows of the three sector flow model
Flow 1: the nation's flow of all resources
Household sector supplies or sells wanted resources to the business sector
Flow 2: the nation's flow of all incomes paid
Businesses pay incomes to the household sector in the resource market in exchange for resources to produce goods and services
Flow 3: the nation's flow of total spending on G&S [G+C]
Spending is undertaken by both households [C[, and by governments[G]
Flow 4: the nation's flow of finished G&S produced (GDP)
Businesses adjust production levels in response to changes in spending by consumers and governments
what is leakage?
Leakage: when money is saved and not spent - it is not contributing to the economy
how can the government intervene in the economy?
Government intervention in the economy:
1. Economic stabilization
During booms:
Countercyclically slow total spending by increasing taxes and/or cutting government spending
This would help prevent and inflationary boom
During recessions:
Countercyclically boost spending by cutting taxes and/or raising government spending
Helps reduce the severity of a recession and keep unemployment lower than otherwise
2. Resource allocation
Government laws to promote stronger competition (ACCC)
Some businesses attempt to limit competition and collude with rival firms to grow their market power and increase profit for themselves. Leads to a decrease in allocation efficiency and there is no incentive to reduce costs, improve products and try to maximise competition between rival businesses.
e.g. coles and woolies overcharging, gov investigates to intervene and promote stronger comp
The government provides some socially beneficial goods and services
Socially beneficial goods and services can be expensive to produce and inaccessible to people with lower incomes, with government intervention resources can be allocated efficiently to max consumer satisfaction and living standards.
Laws that discourage socially harmful production
Discouraging socially harmful production
e.g. cigs - age restrictions, no smoking areas
3. Redistribution of income to improve living standards
Taxing the rich more than the poor
identify and describe the 4 parts of the business cycle
Boom
National output is stretched beyond the economy's productive capacity. Shortages of goods and services appear because output can't keep up with spending. Rapid inflation occurs and purchasing power of wages and family incomes decrease.
Recession
National output or GDP falls and causes a rise in unemployment, and hence a drop in average incomes and consumption per person. Overall material and non-material standards are down
Contraction
When a drop in economic activity occurs as spending starts to fall
Expansion
Occurs when spending starts to expand again
what is the difference between public and private sectors of the economy
The public sector is driven by public interest and aims to provide essential services, while the private sector focuses on innovation, competition, and profit-maximization.
The public sector is characterized by government ownership and control, while the private sector is driven by private ownership and decision-making.
Advantages of the public sector include stability, widespread accessibility, and the provision of public goods, while the private sector offers flexibility, efficiency, and technological advancements
Private: cheaper, faster
Public: lower quality services
identify and describe the traditional viewpoint of consumer behaviour
1. Consumers act rationally and in their self-interest.
Consumers act to balance limited income to maximize their overall satisfaction or pleasure. This is why consumers flock to clearance and stocktake sales offered by retailers.
2. Consumers make informed and smart decisions
Get quality factual information, check information from various sources, weigh up potential advantages and disadvantages.
3. Consumers maximise utility and marginal benefits from consumption.
Marginal utility: the extra satisfaction gained from consuming each additional unit of a good or service at a point in time.
The law of marginal utility states that as the number of units consumed increases, satisfaction (utility) decreases
This is why retailers offer special discounts (buy 2 get the third one free) to offset the lowered marginal utility with lower prices.
Exceptions to this rule would be: addicts e.g. smoking, drinking, compulsive shoppers (excited by the act of purchasing) and consumers who purchase things to impress others(conspicuous consumption).
4.Consumers have ordered preferences.
Satisfy immediate needs before non essential spending
what are externalities (consumer viewpoint)
Externalities are the cost or benefits to third parties that are not involves in the transaction
e.g. smoking cigs generates a negative externality as bystanders risk second hand smoking.
A positive externality provides a benefit to a third party whereas a negative externality leads to a cost for a third party
what are incentives and disincentives (consumer viewpoint)
Consumer behaviour can be driven by incentives and disincentives.
Incentives are designed to encourage behaviour that would otherwise not occur at the same extent . e.g. using childcare subsidy to increase consumption of childcare services
Disincentives aim to discourage certain behaviours and are directed towards reducing socially undesirable consumption of certain goods and services. e.g. heavily taxing cigarettes to discourage consumption.
what are taxes and tax rebates (consumer viewpoint)
Taxes are charges collected by the government such as income tax. This serves as revenue for the government, which is then used for the provision of public goods and services.
The imposition of an indirect tax on products like cigarettes or fuel and alcohol) creates a disincentive for consumers to smoke.
However, the fact that these goods are addictive (or necessities) means that the taxes also raise significant revenue for the government.
A tax rebate reduces or offsets the tax you pay (known as your tax payable) on your taxable income. Your taxable income is your income minus any deductions you claim.
what are subsidies and regulations (consumer viewpoint)
A subsidy is a cash payment. Subsidies can be paid to either the consumer or producer. The former is known as a consumption subsidy while the latter is known as a production subsidy.
Regulations and laws can be employed by the government to discourage the consumption of certain goods and services as well.
e.g. cig packaging laws prohibit tobacco companies from adorning cigarette packets with appealing graphics.
what is the traditional viewpoint of businesses
Businesses seek to maximise profit. This is done through making decisions that will maximise sales revenue and/or minimise production costs
In a perfectly competitive market, this behaviour encourages efficiency in resource allocation
While profit maximisation is the "traditional" focus for most firms, there are other factors that drive decision making for business such as:
Reputation and image (e.g. woolies driving up costs)
Giving back to the community (salvos, aldi battery recycling, big w toy recycling, kmart giving back to the needy)
Government policies
identify and describe incentives from a business perspective
Subsidies:
Subsidies are often provided to businesses to encourage the production of socially beneficial goods and services.
These payments usually help production costs thus improve profitability in the short term.
However, long term use of subsidies can negatively impact industries as the overreliance of subsidies can disincentivise businesses from being innovative or seeking to become more efficient.
e.g. Gov subsidised the car manufacturing in Australia by a lot but without the subsidy the businesses would not survive and so they shut down.
Tax rebate:
Tax rebates are mostly used to encourage expansion of businesses, production and employment through increasing after-tax profit
This strategy assists in keeping prices of goods/services down
There are many tax rebates/offsets. For example, tax write offs for small and medium sized businesses to purchase new capital resources
e.g. new refrigerator for a restaurant
Tax rebate only reduces tax but not the actual price of the item
identify and describe disincentives form a business perspective
Taxes:
Direct taxes are levied on the profit or taxable income of firms
For large businesses, the current rate is 30% and for small/medium businesses it is 25% of their profit.
Indirect taxes are levied on selected goods and generally target those that have social costs for the wider community.
These taxes make production more expensive. For example, excise taxes on the production and sale of cigarettes
Regulations, laws and fines:
The government can also impose fines or bring in regulations to influence business decisions to improve the wellbeing of citizens.
e.g. banning or restricting the production or certain goods and services that bring harm to society: plastic straws, vapes
Alternatively, they can also be designed to promote competition between firms or to boost the welfare or workers (i.e. mandated employer contributions to superannuation)