BSC2085L MIDTERM
1/706
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
707 Terms
What is tonicity?
Effect the solution will have on the cell.
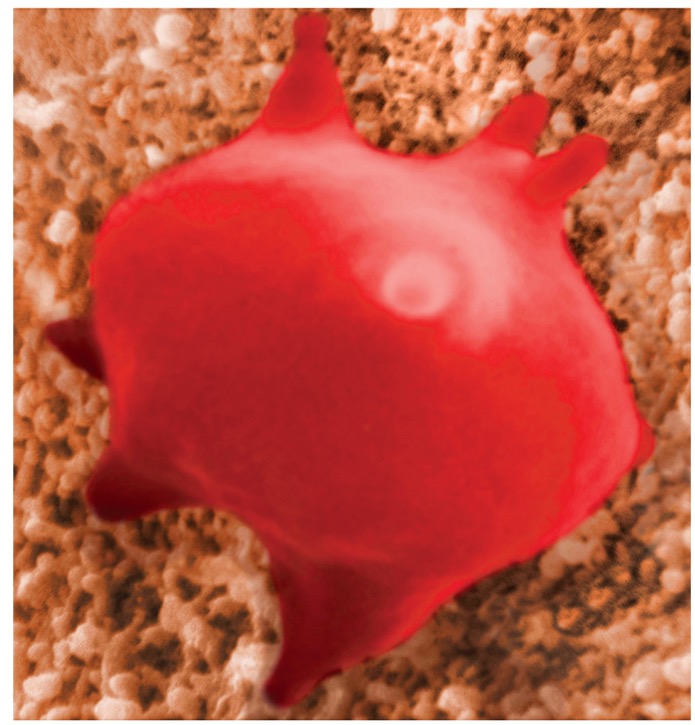

What type of solution is this?
hypertonic solution
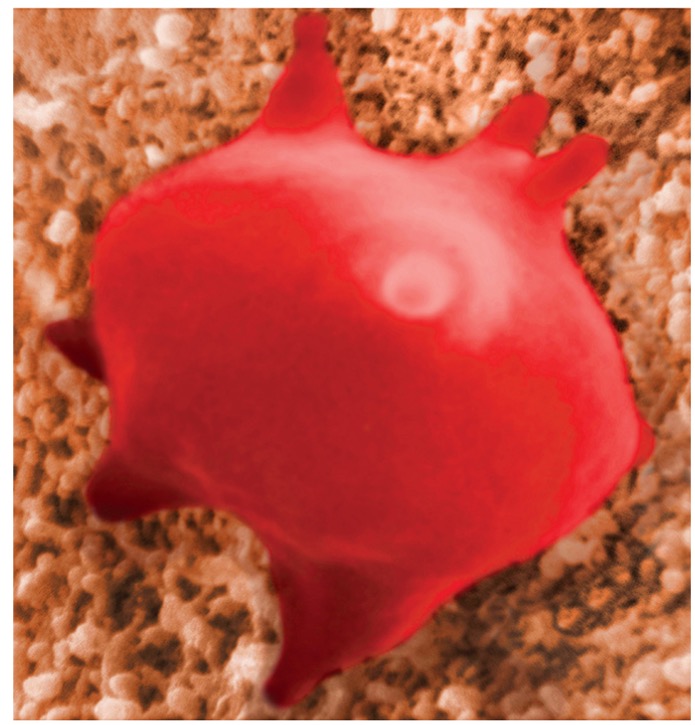

What is hypertonic solution?
Water leaves the cell to follow higher concentration outside the cell, it’s going to shrivel and crenate.
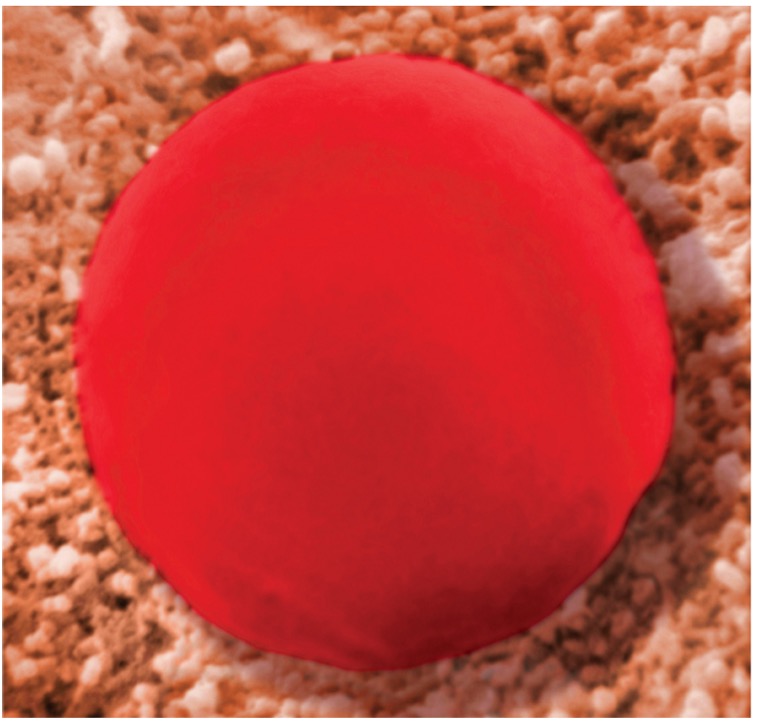

What type of solution is this?
Hypotonic solution
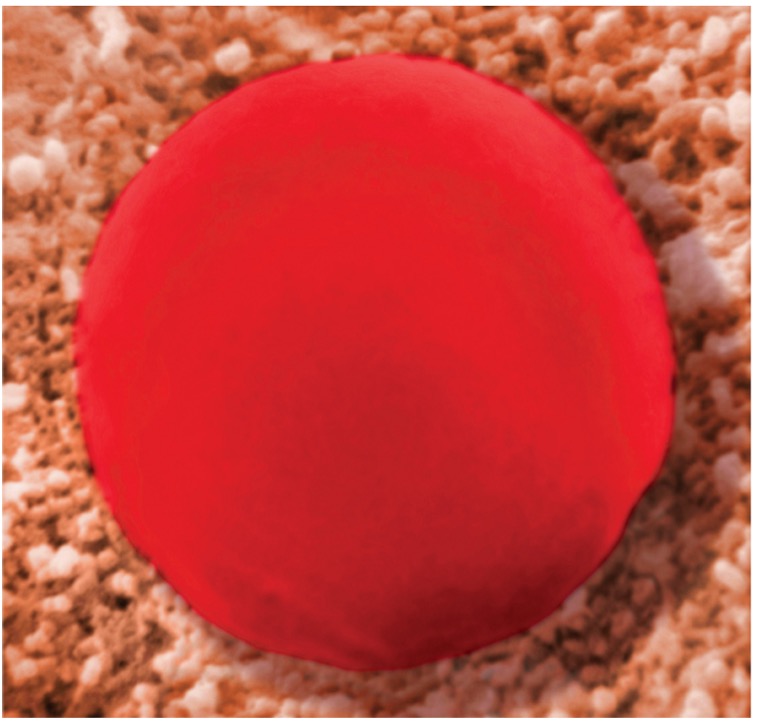

What happens with hypotonic solution?
A higher concentration is inside the cell & lower concentration outside will go inside the cell causes cell to absorb water, swell, and possibly burst (lyse)
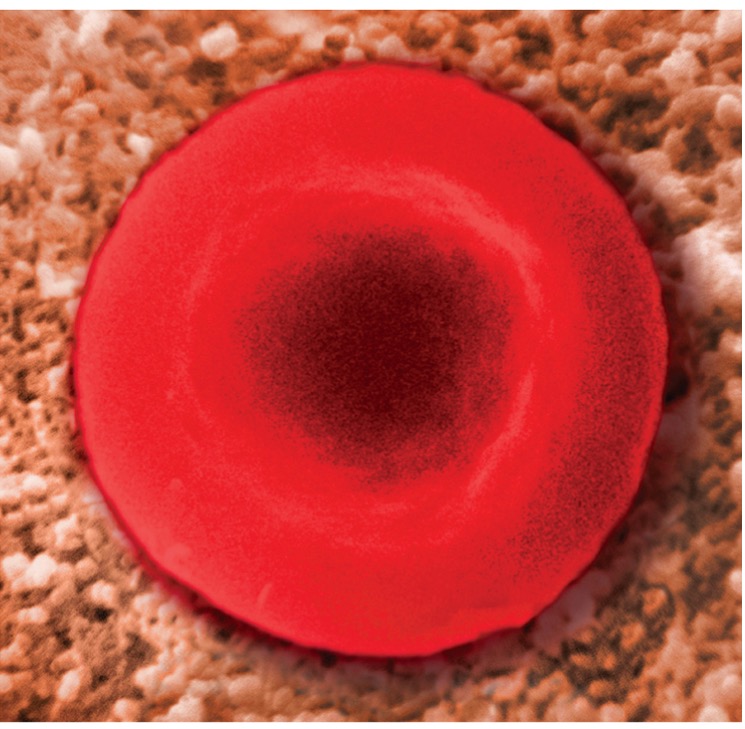
What type of solution is this?
Isotonic Solution
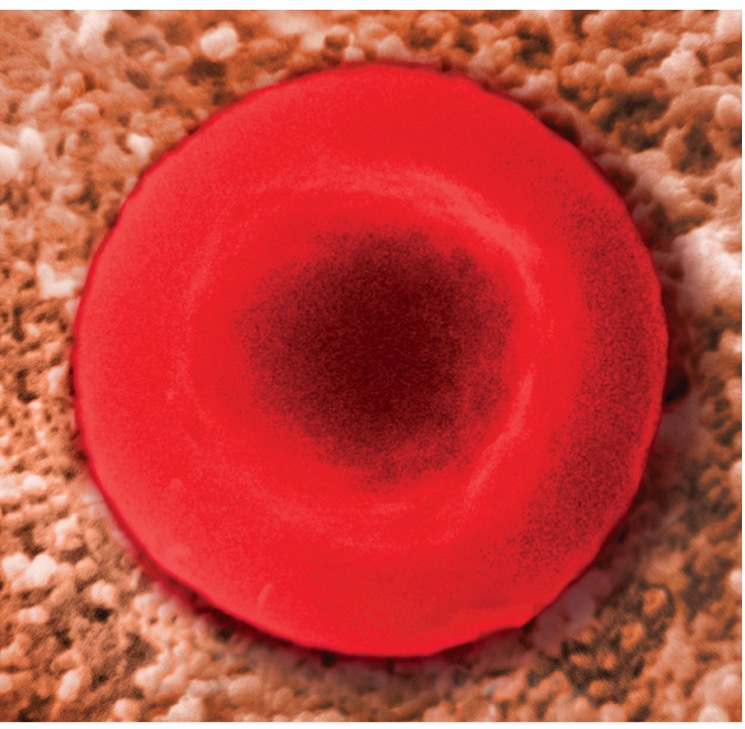
What happens with an isotonic solution?
Solution in the cell and outside the cell have the same solute concentration, so there will be no change in cell volume.
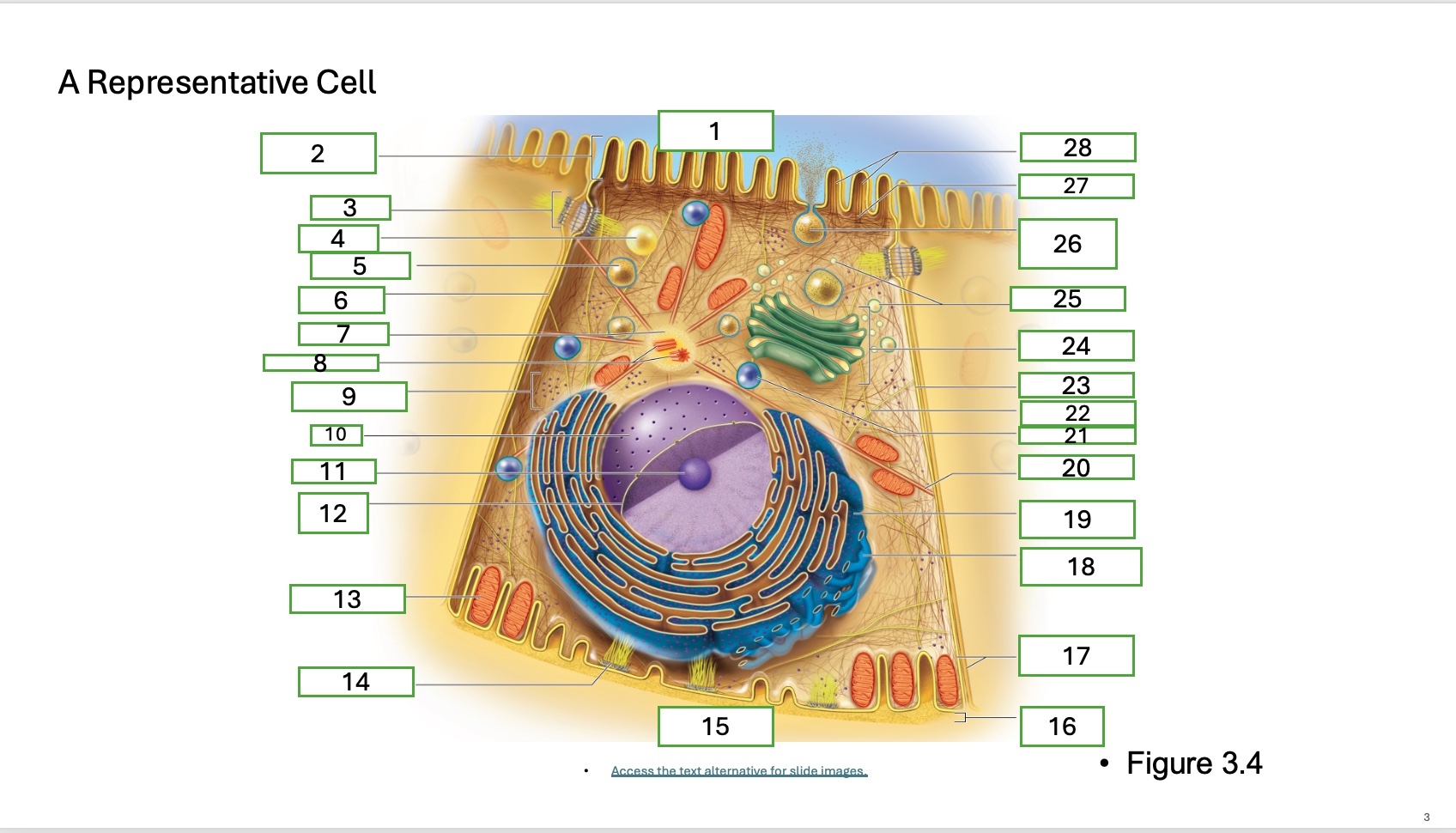
What is organelle 1 of the cell
apical cell surface
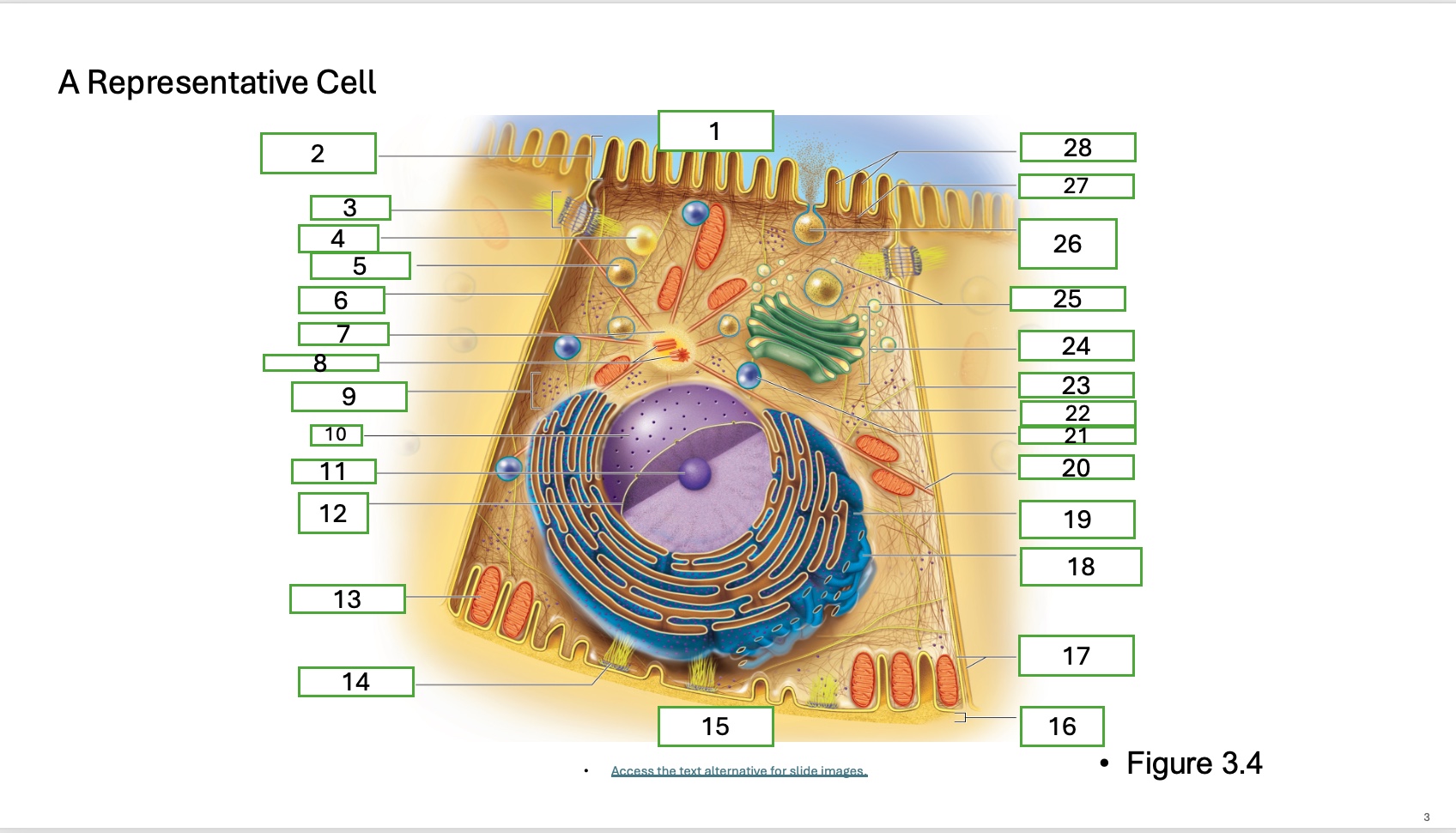
what is organelle 2 of the cell
microvillus
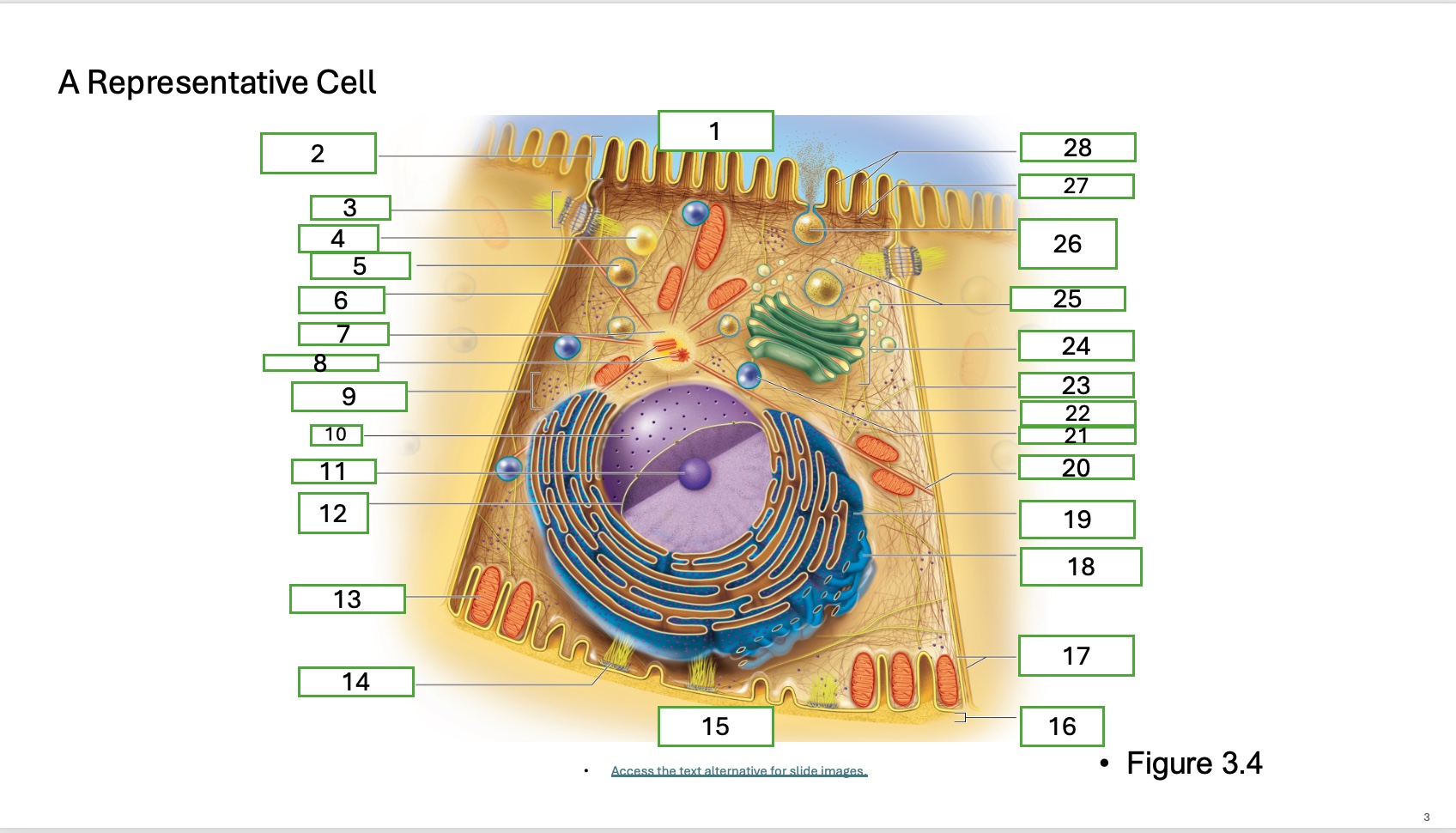
what is organelle 3 of the cell
desmosome
what is organelle 4 of the cell
fat droplet
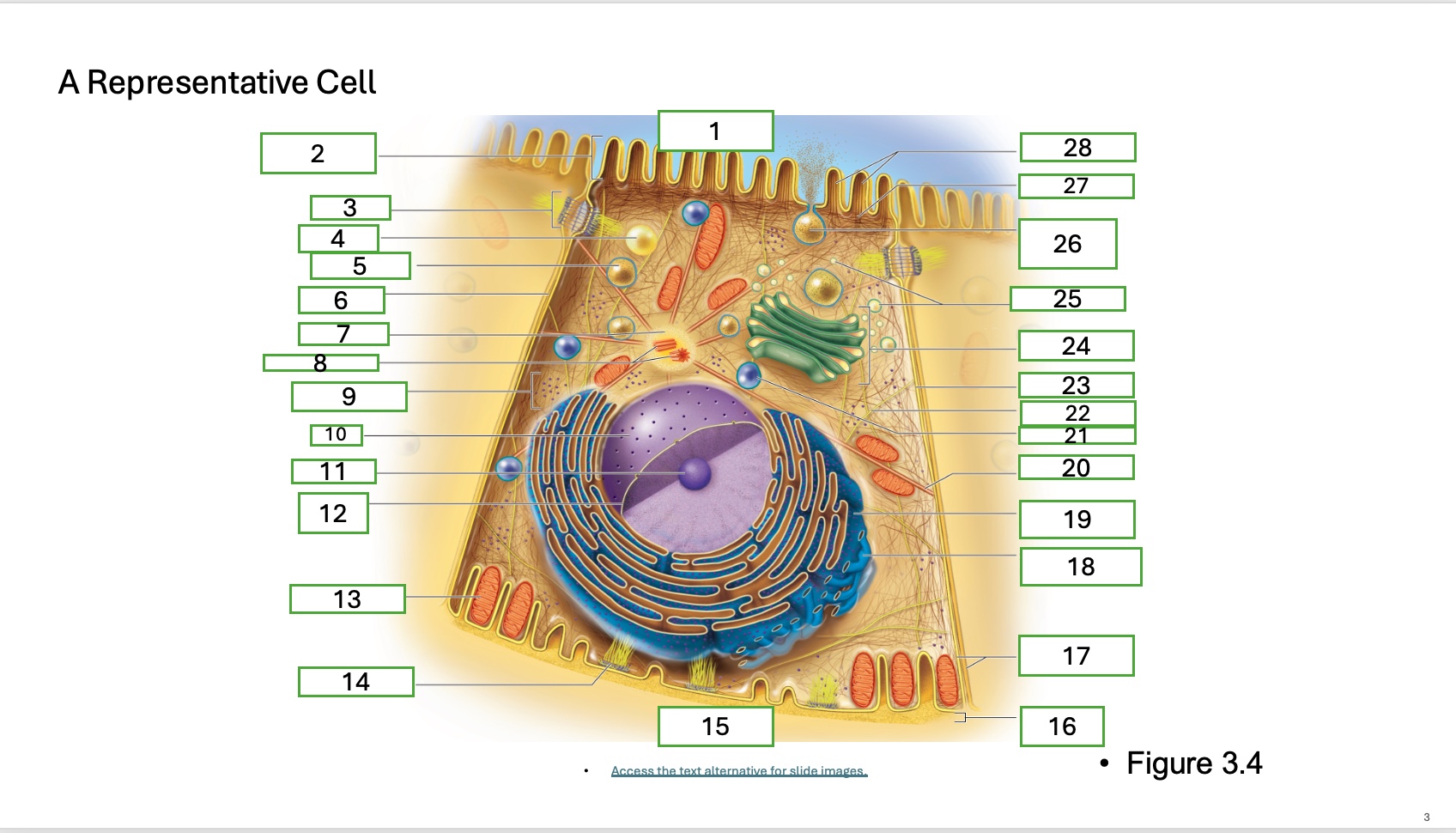
what is organelle 5 of the cell
secretory vesicle
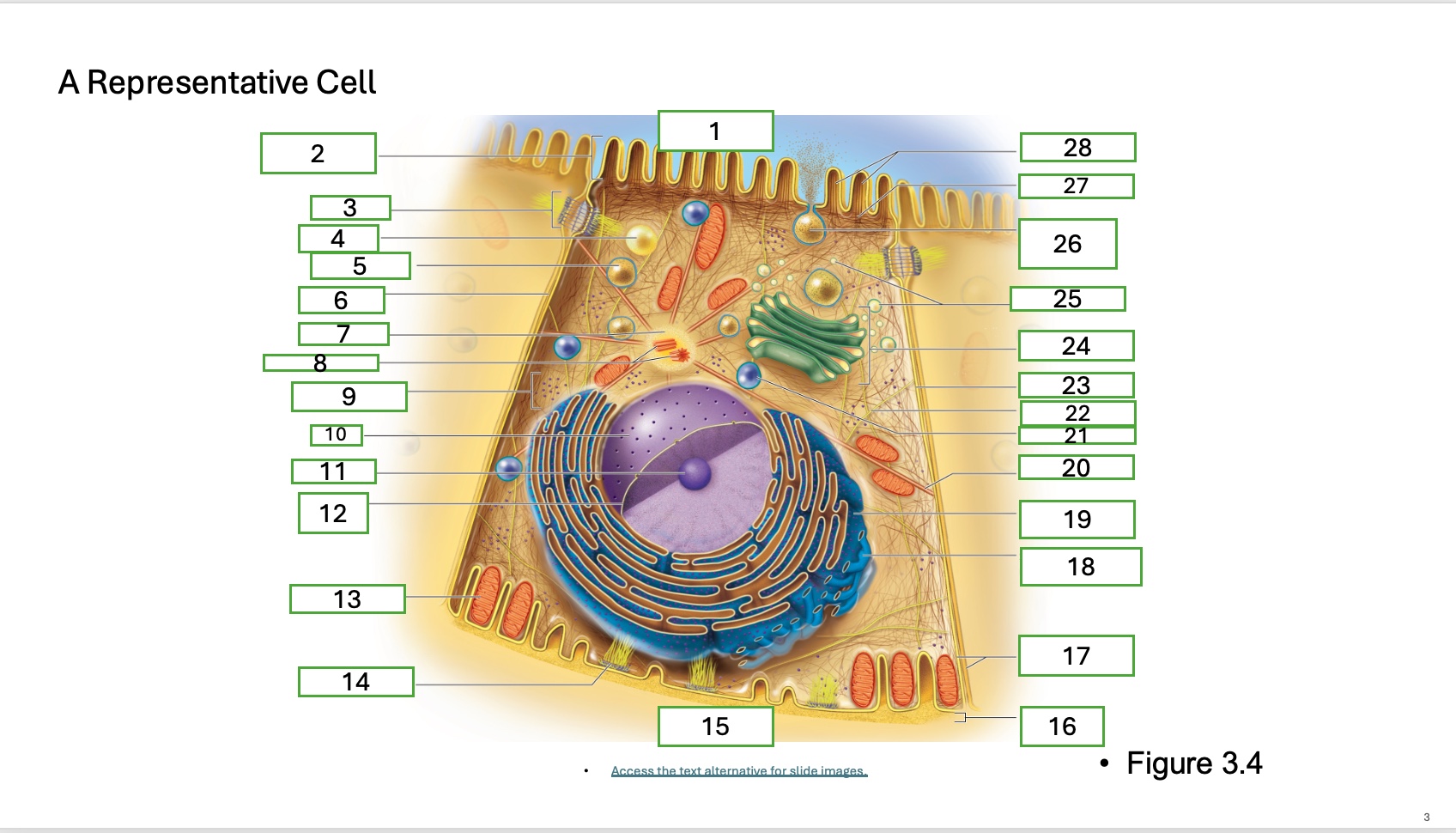
what is organelle 6 of the cell
intercellular space
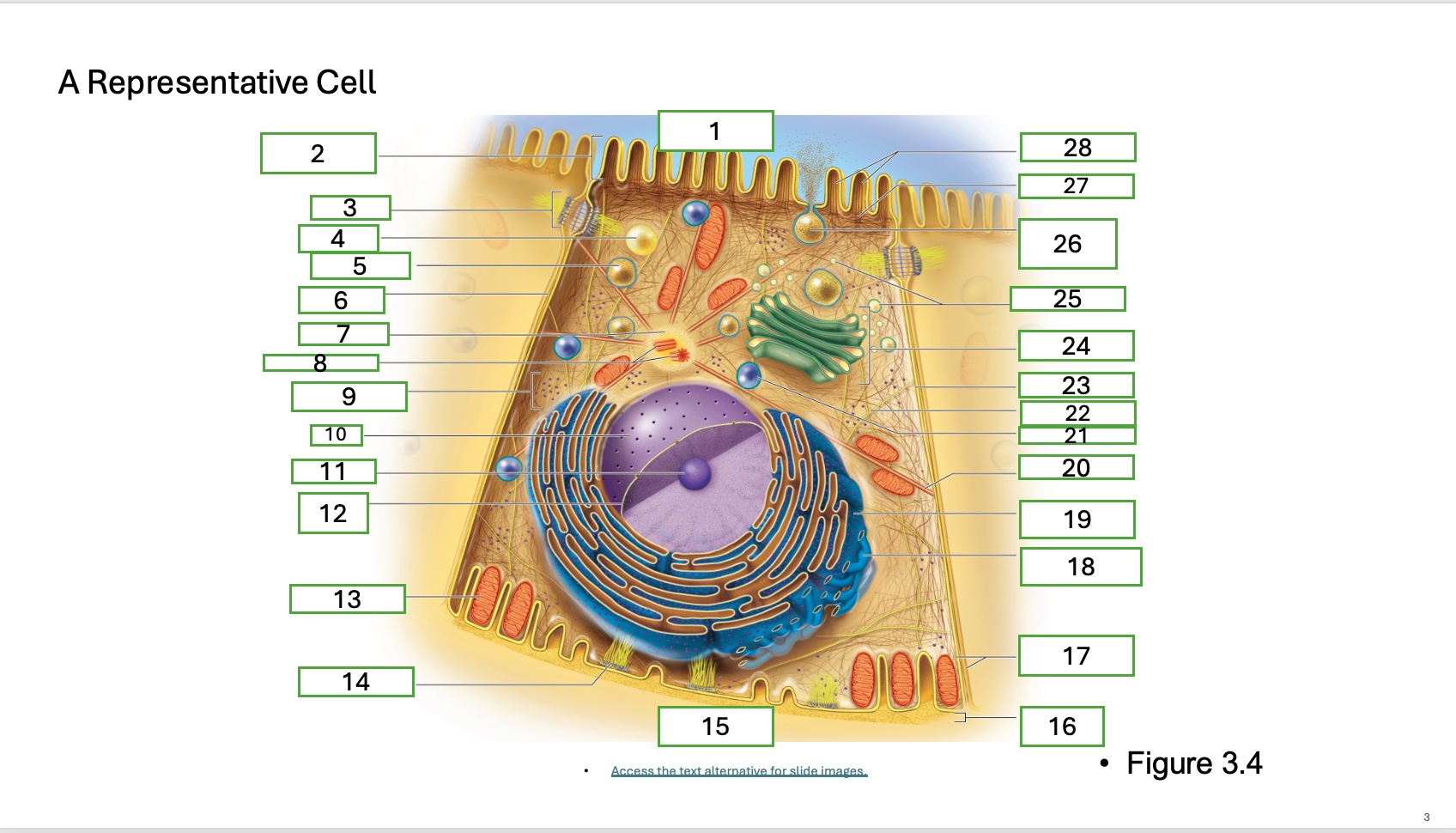
what is organelle 7 of the cell
centrosome
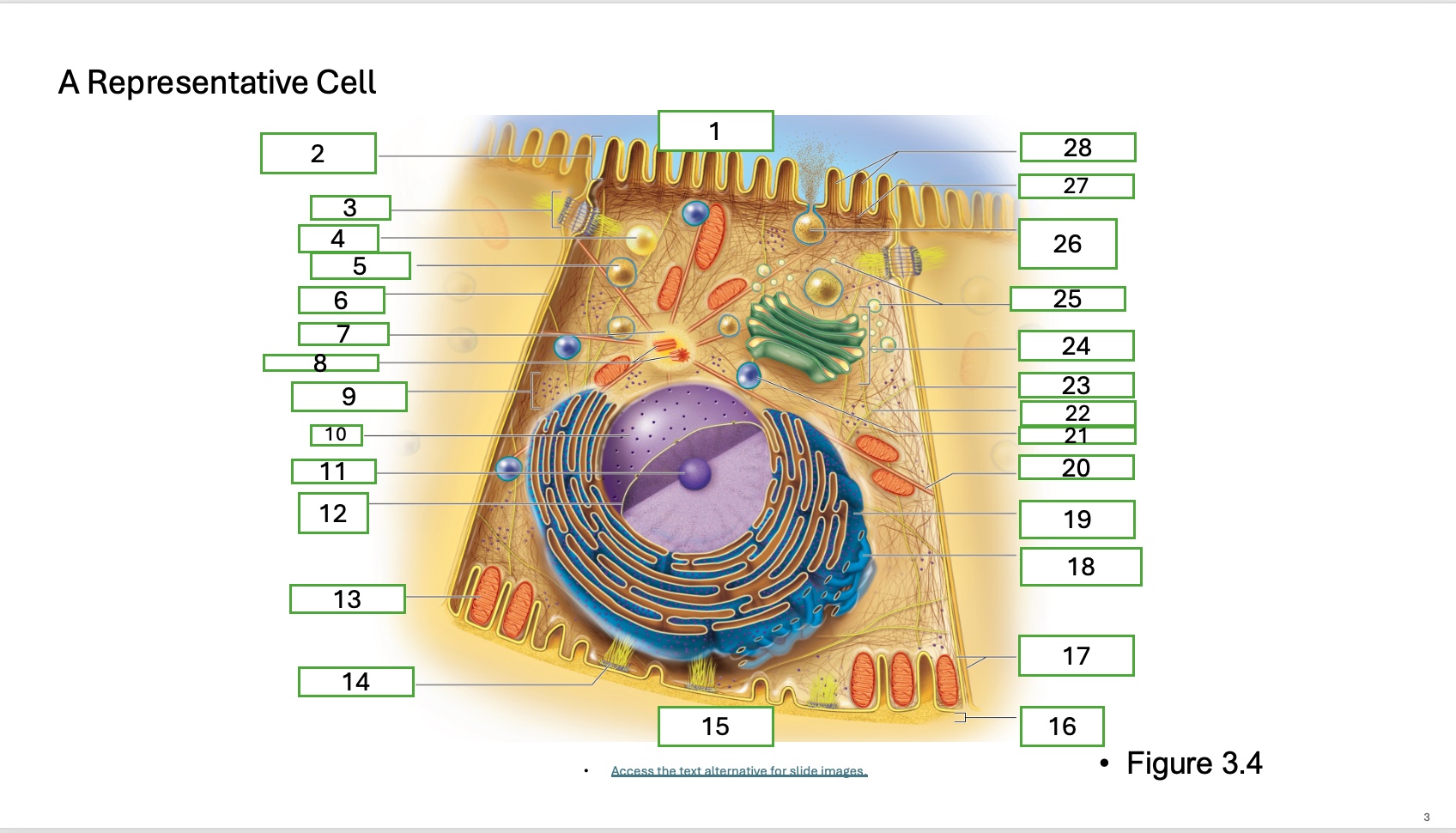
what is organelle 8 of the cell
centrioles
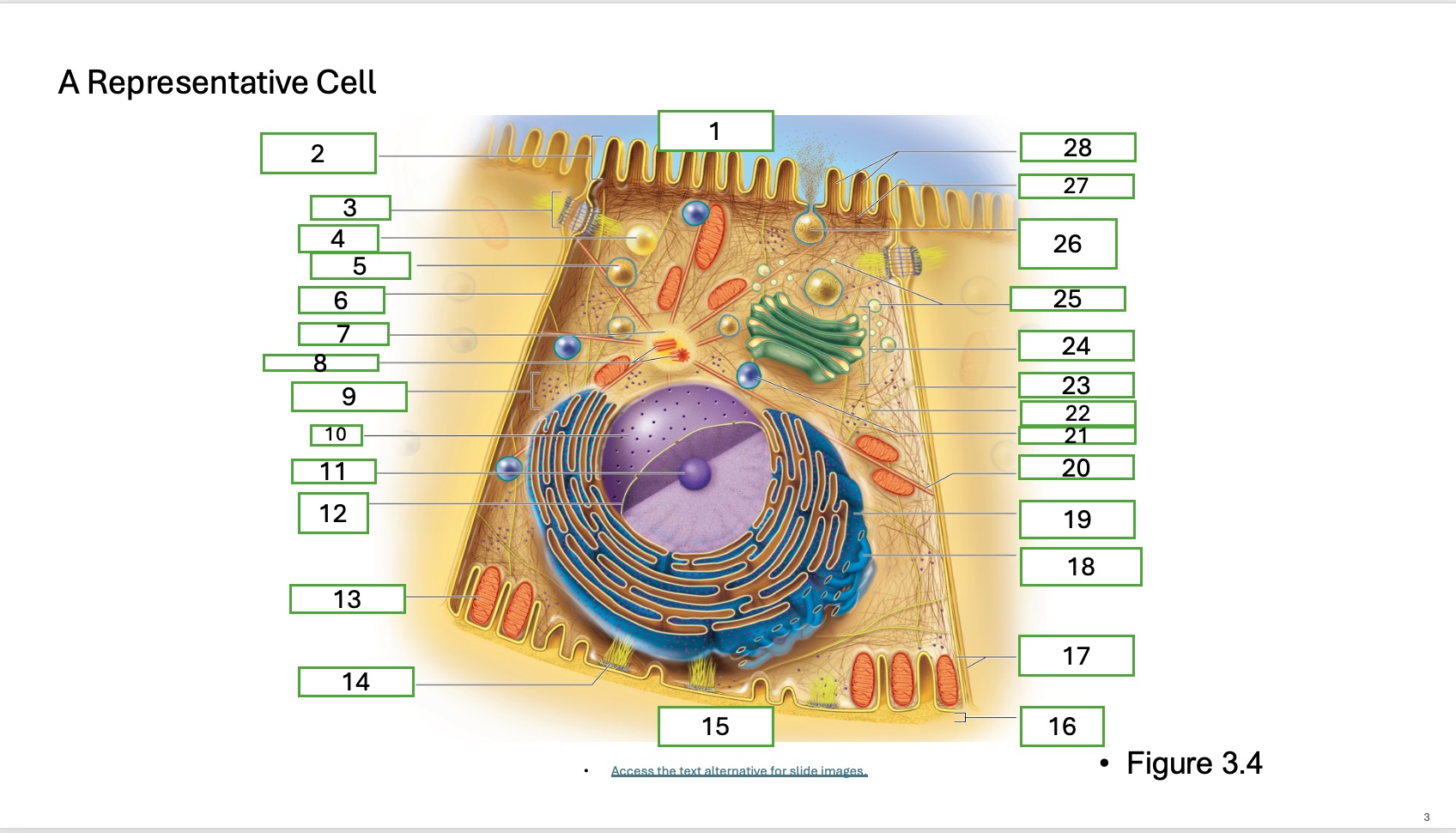
what is organelle 9 of the cell
free ribosomes
what is organelle 10 of the cell
nucleus
what is organelle 11
nucleolus
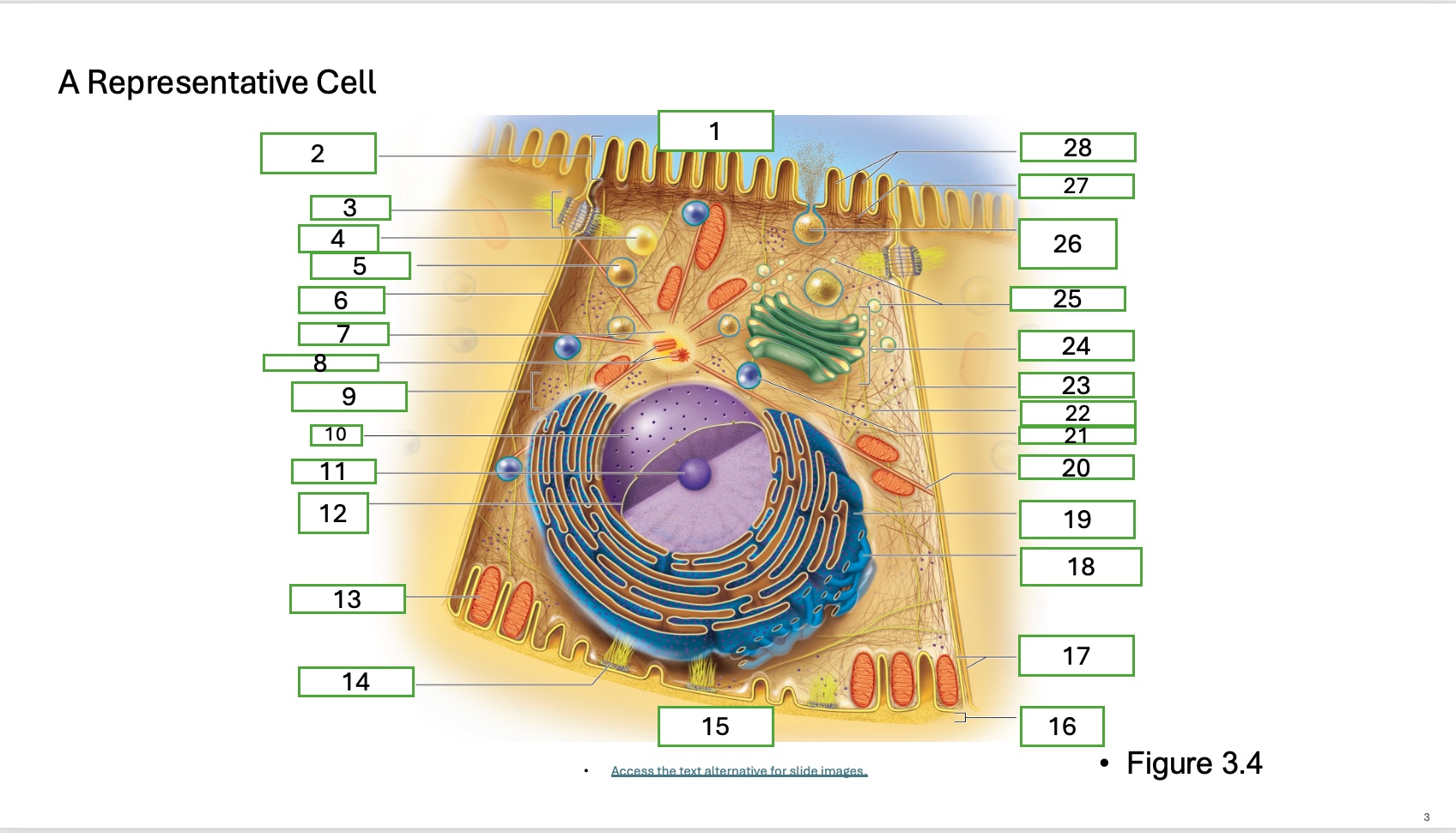
What is organelle 12
nuclear envelope
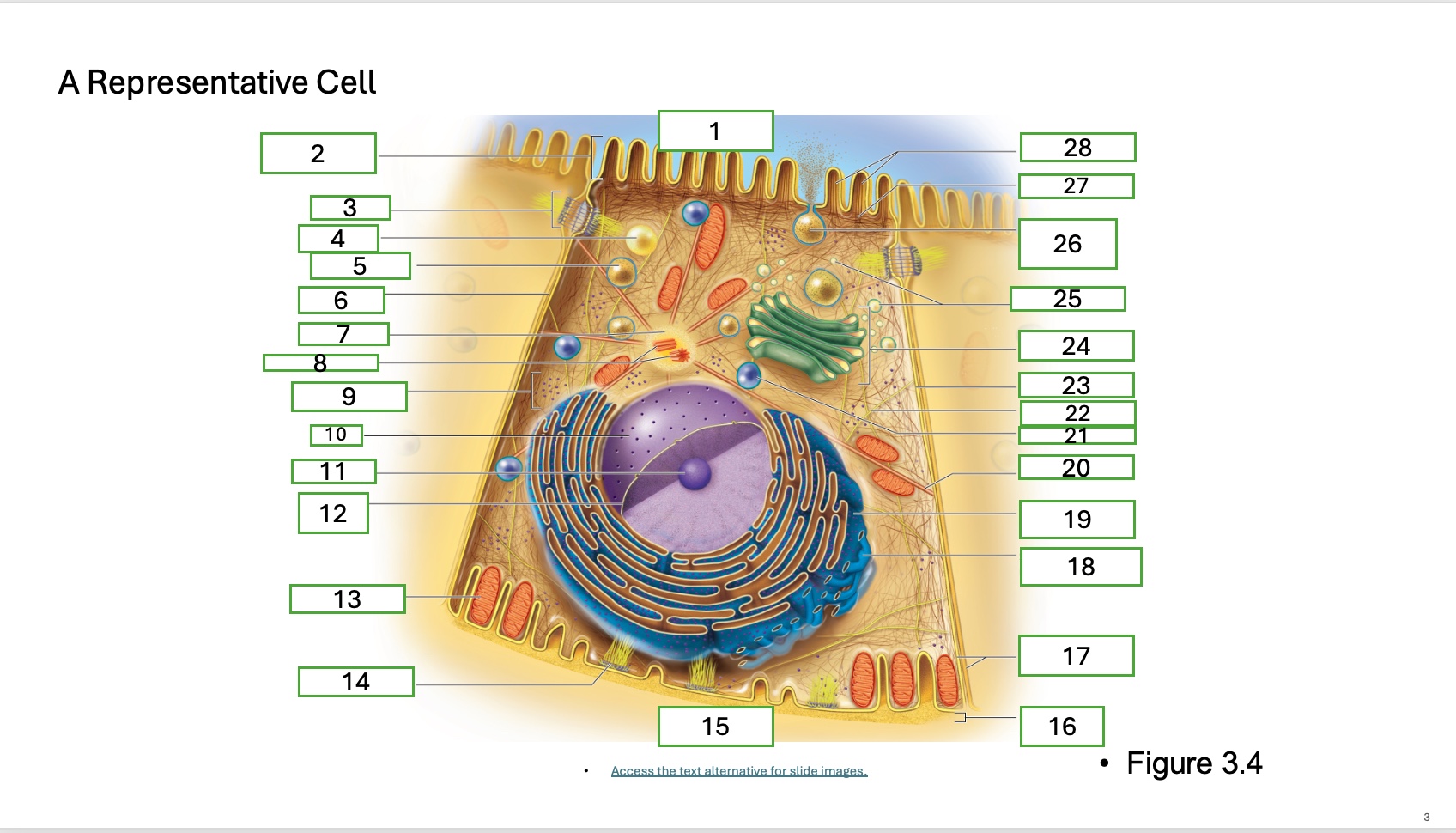
what is organelle 13
mitochondrian
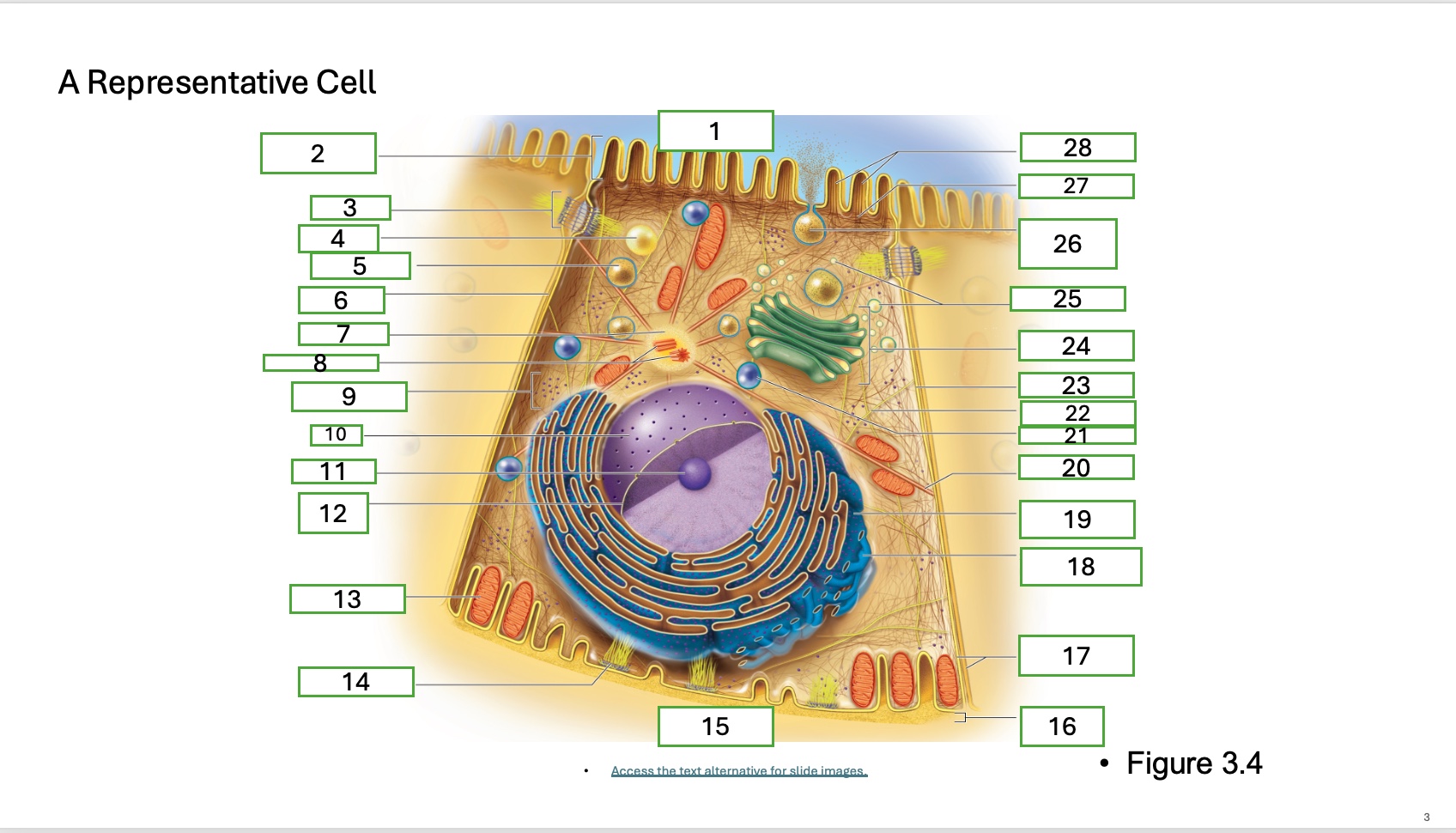
what is organelle 14
hemidesmosome
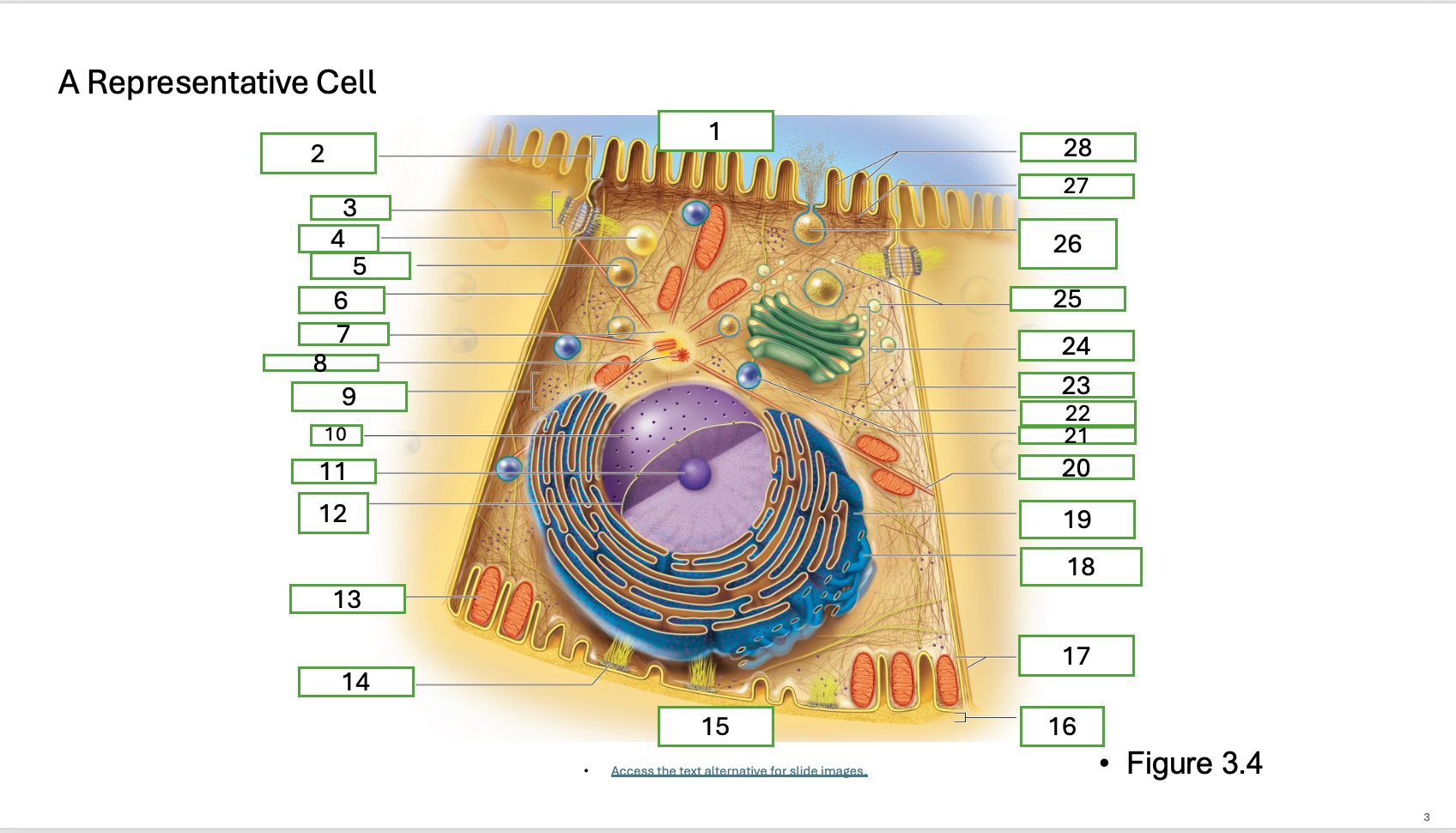
what is organelle 15
basal cell surface
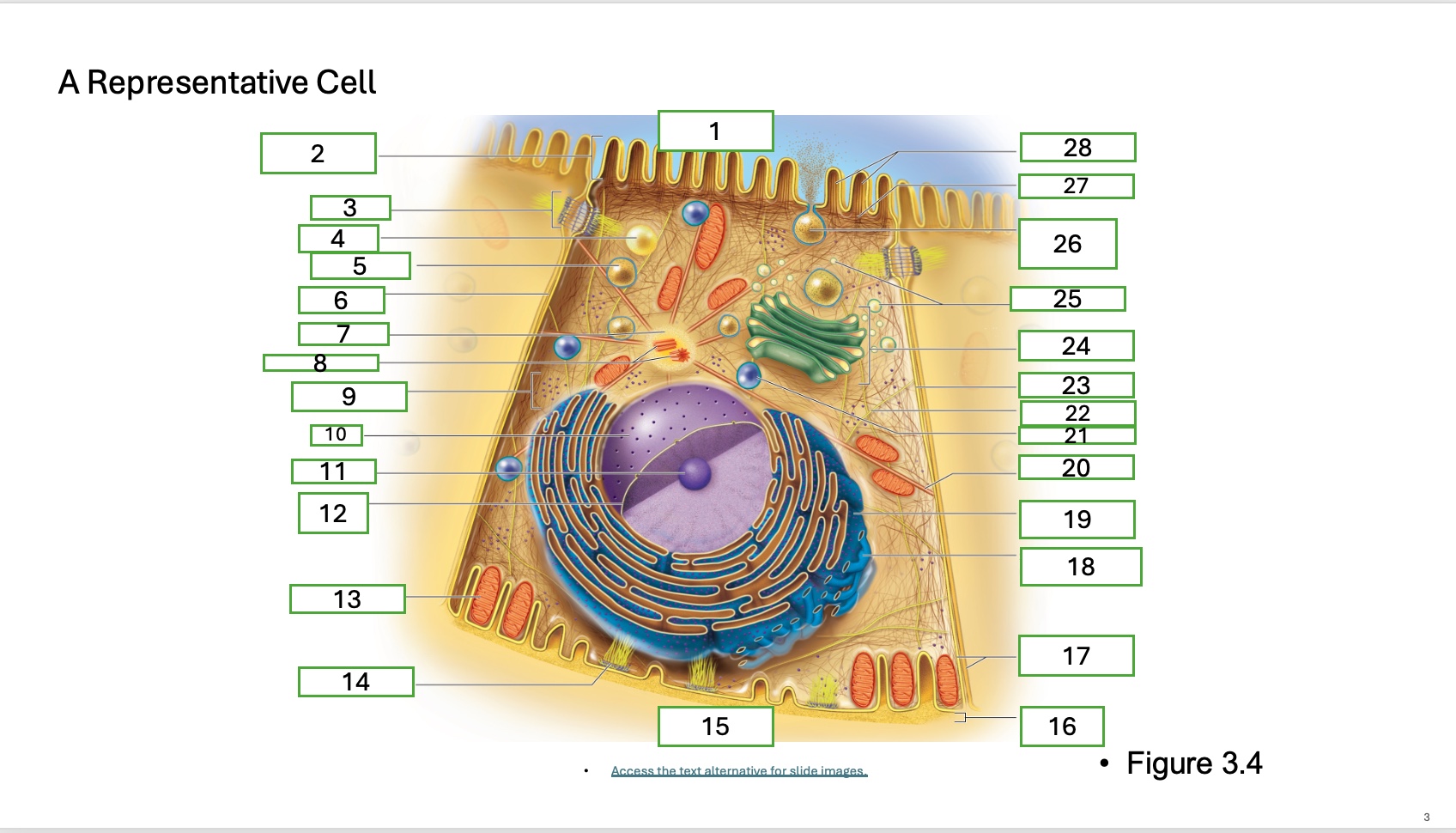
what is organelle 17
plasma memberanes
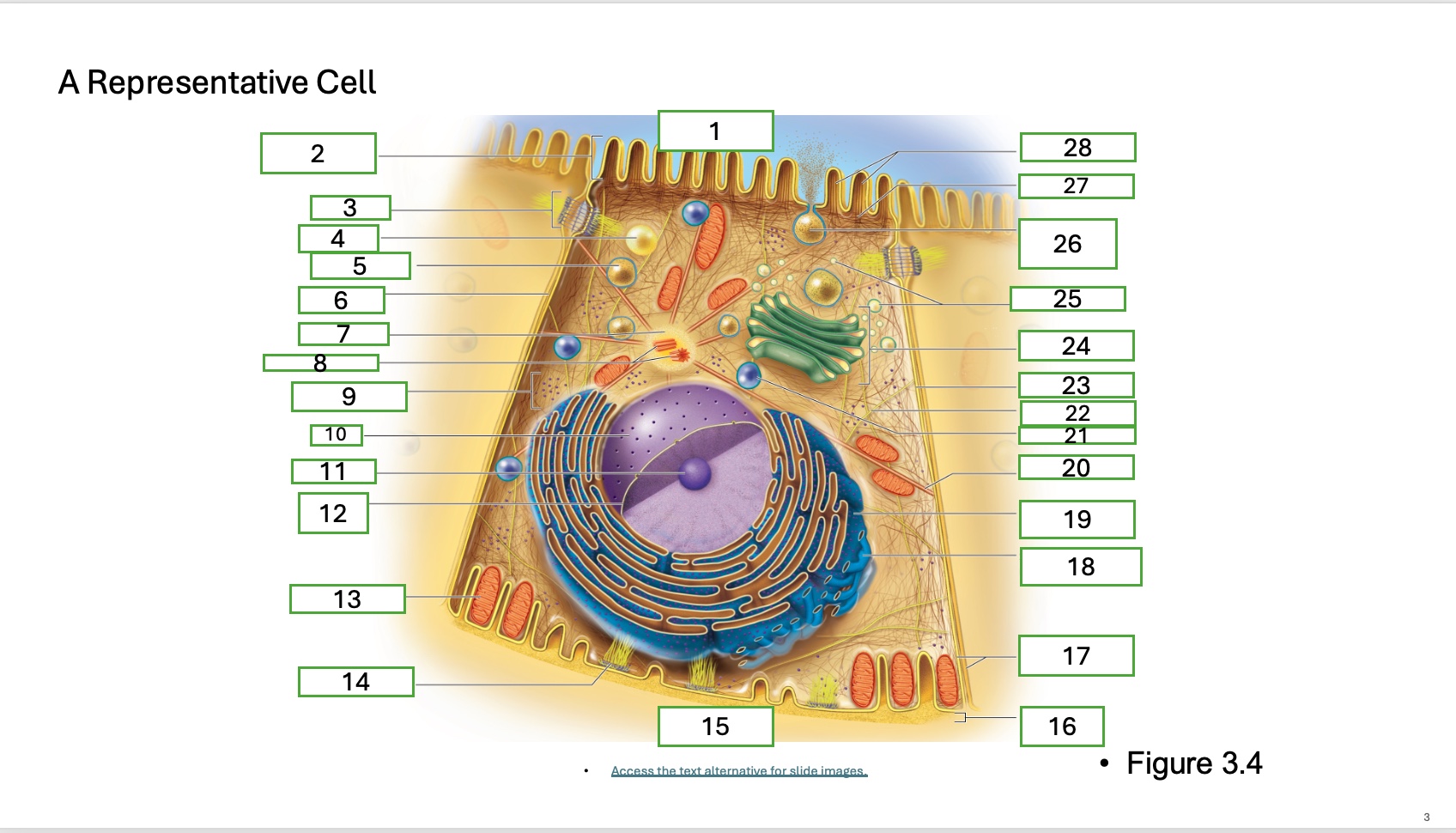
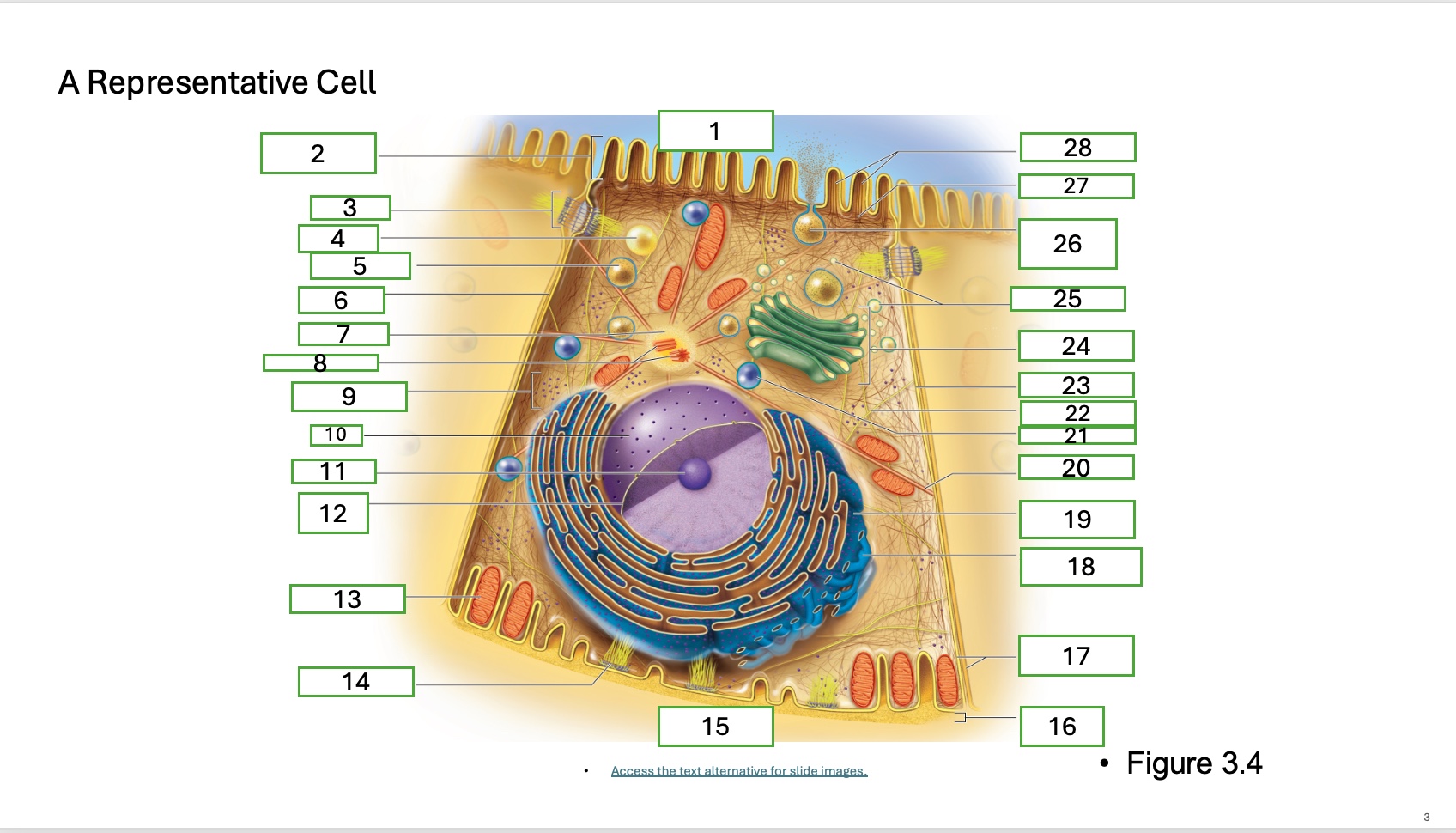
what is organelle 18
smooth endoplasmic recticulum
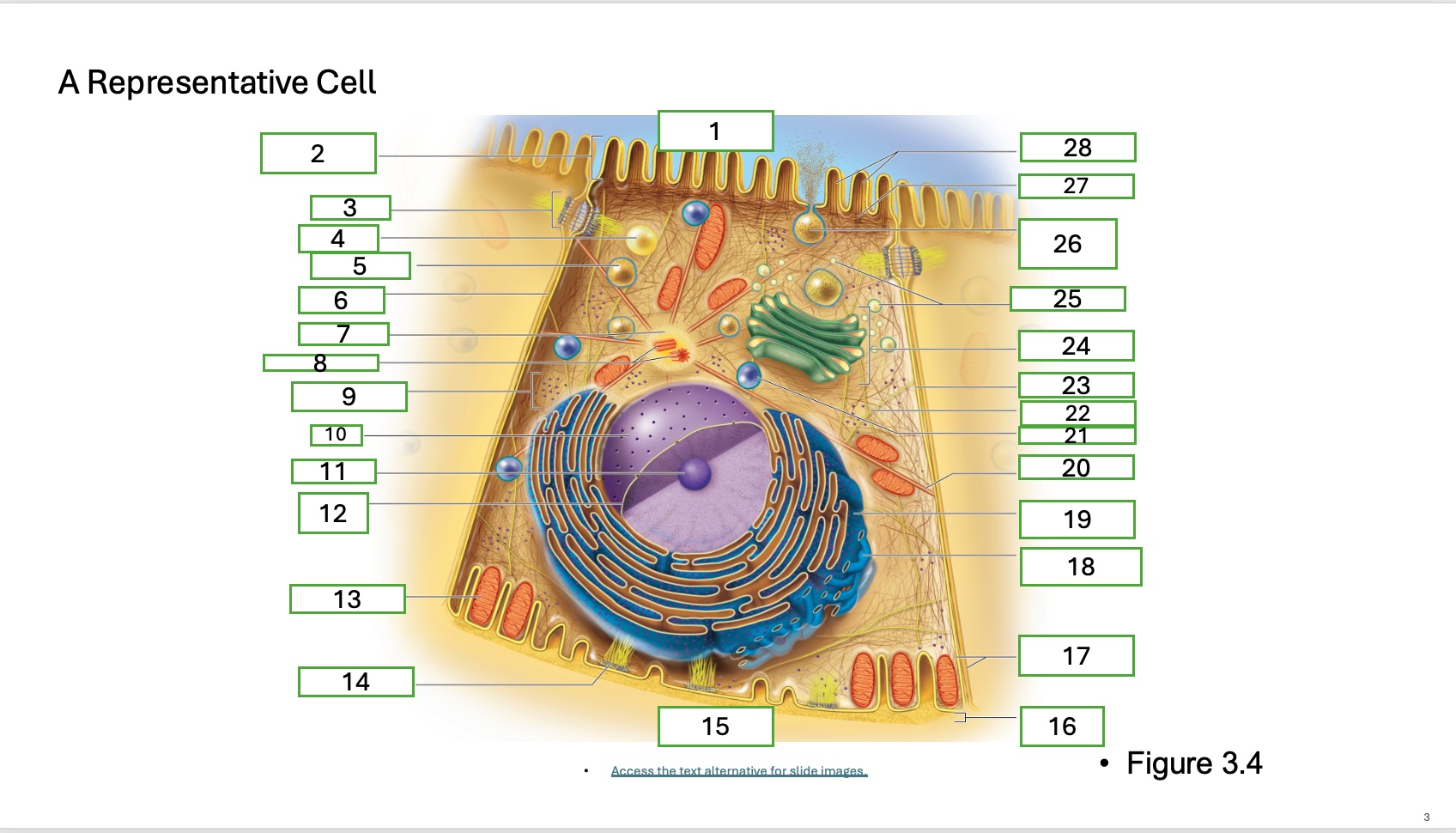
what is organelle 19
rough endoplasmic reticulum
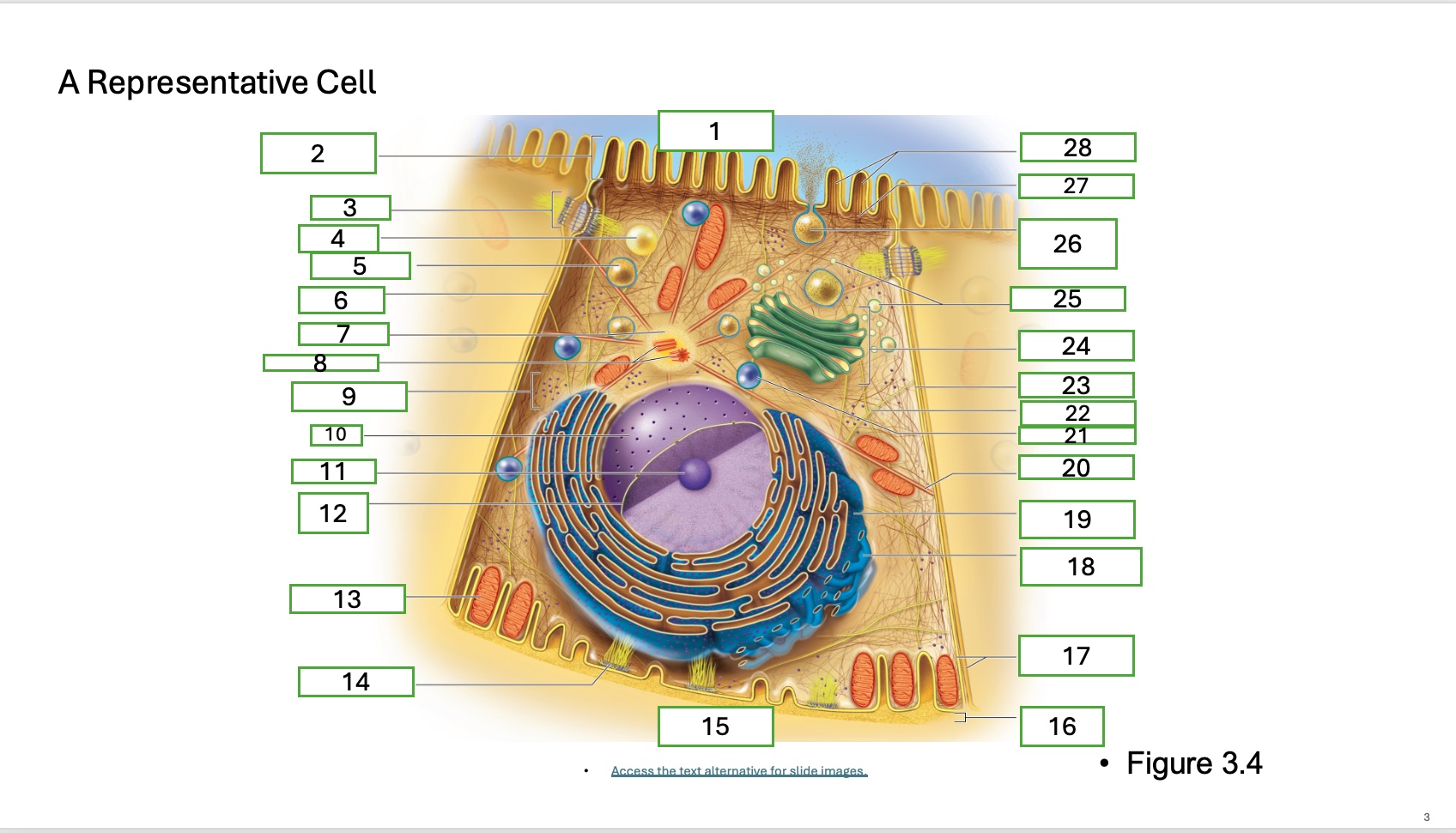
what is organelle 20
microtubule
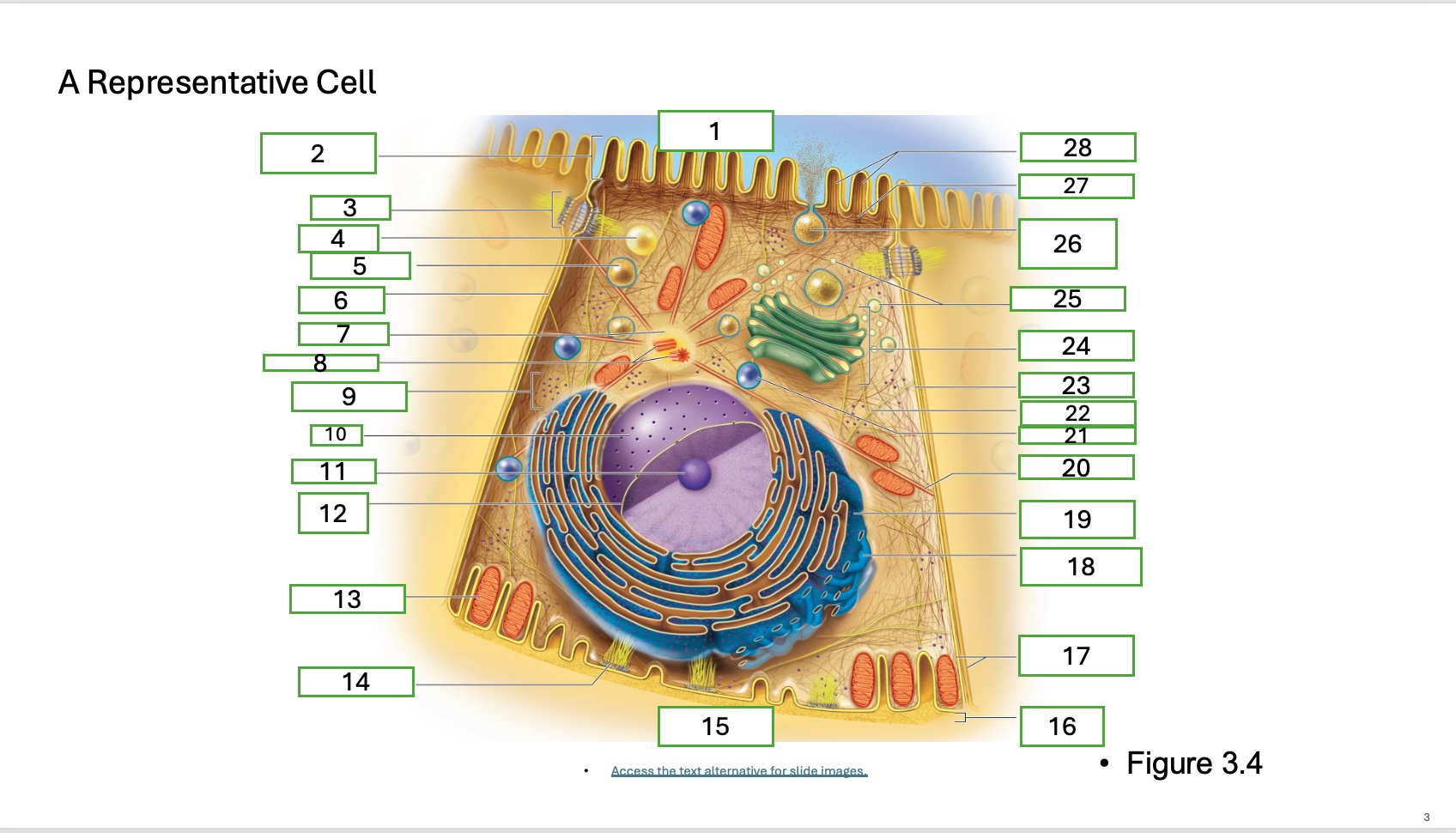
what is organelle 21
lysosome
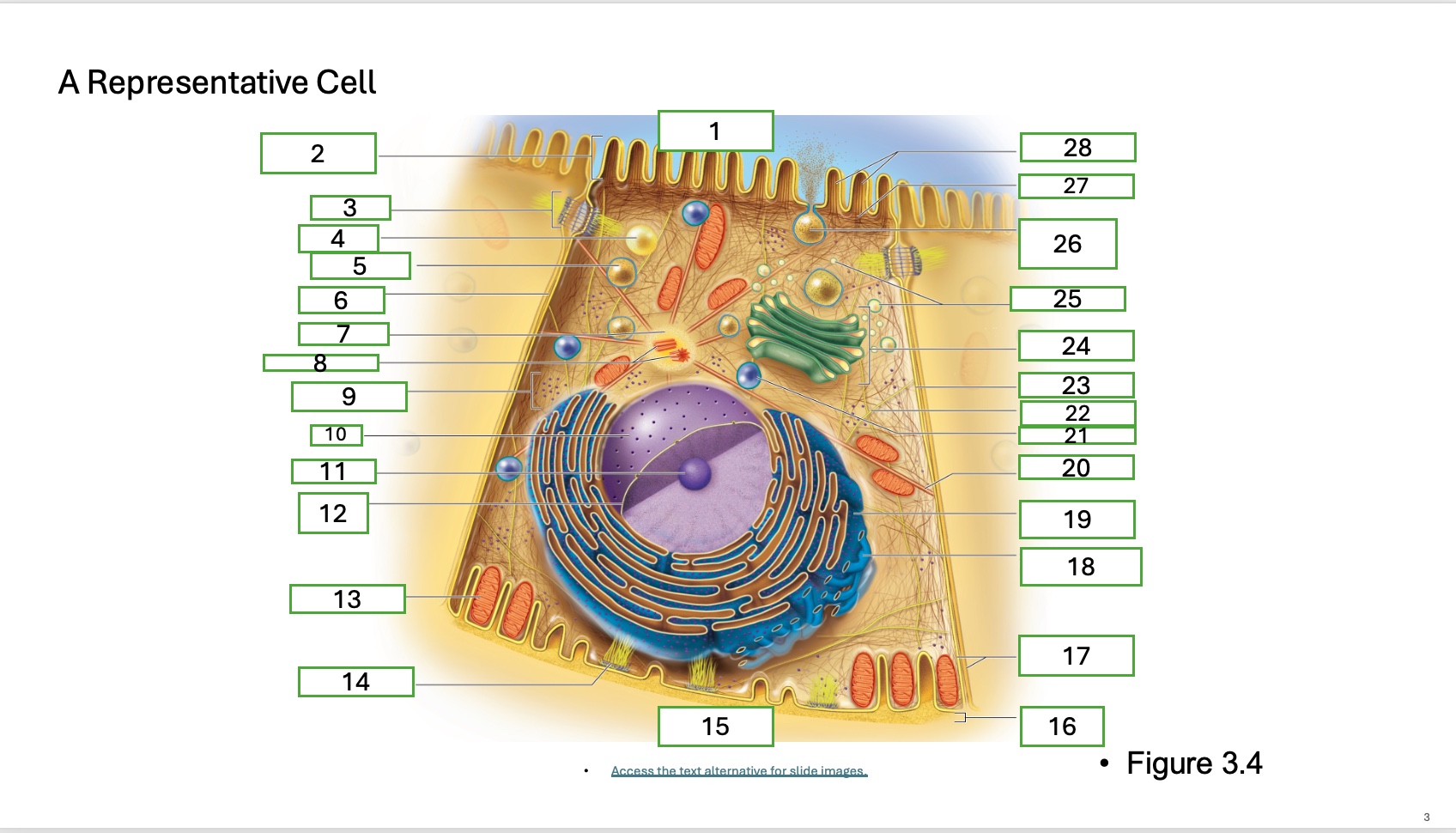
what is organelle 22
intermediate filament
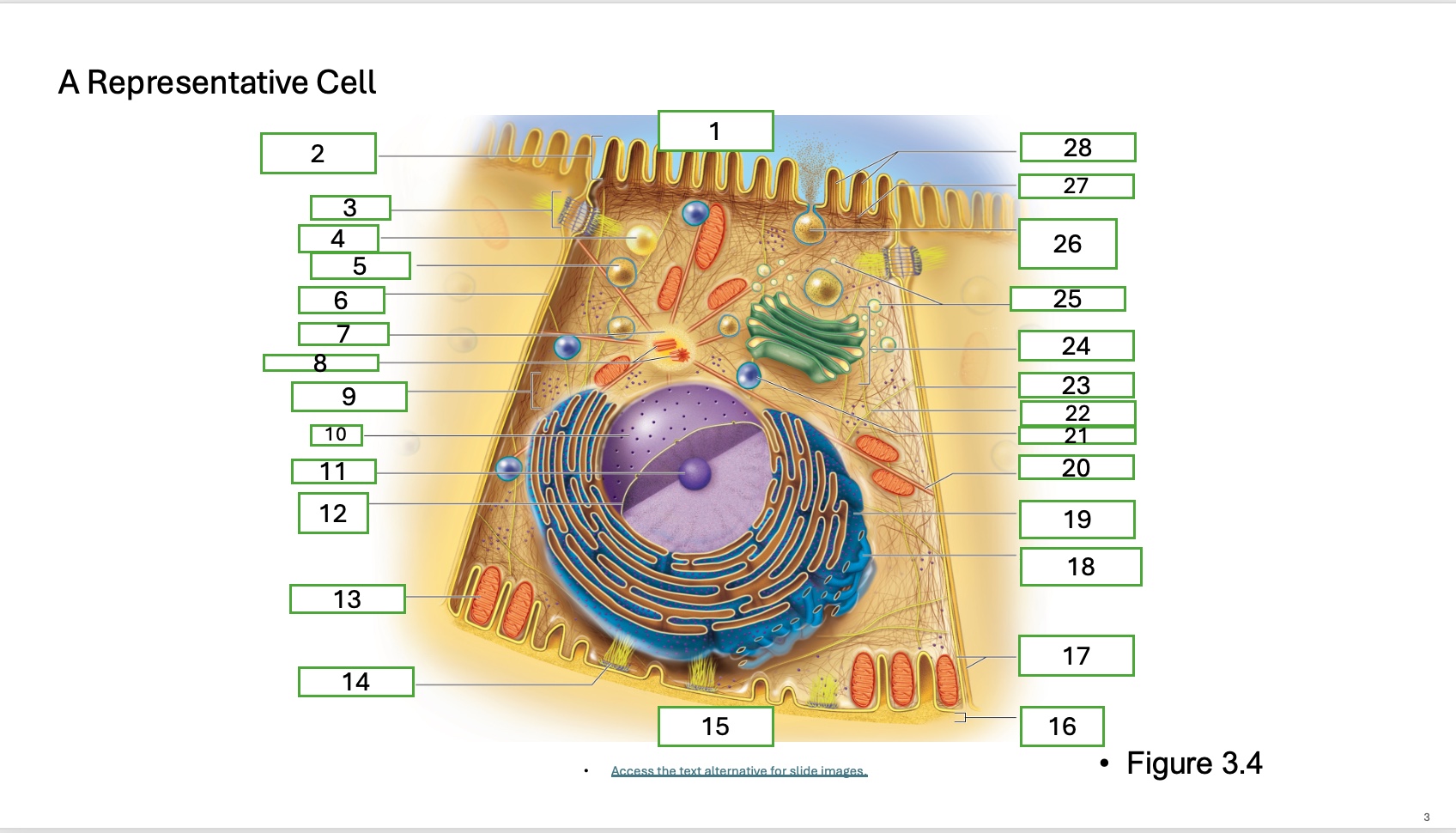
what is organelle 23
lateral cell surface
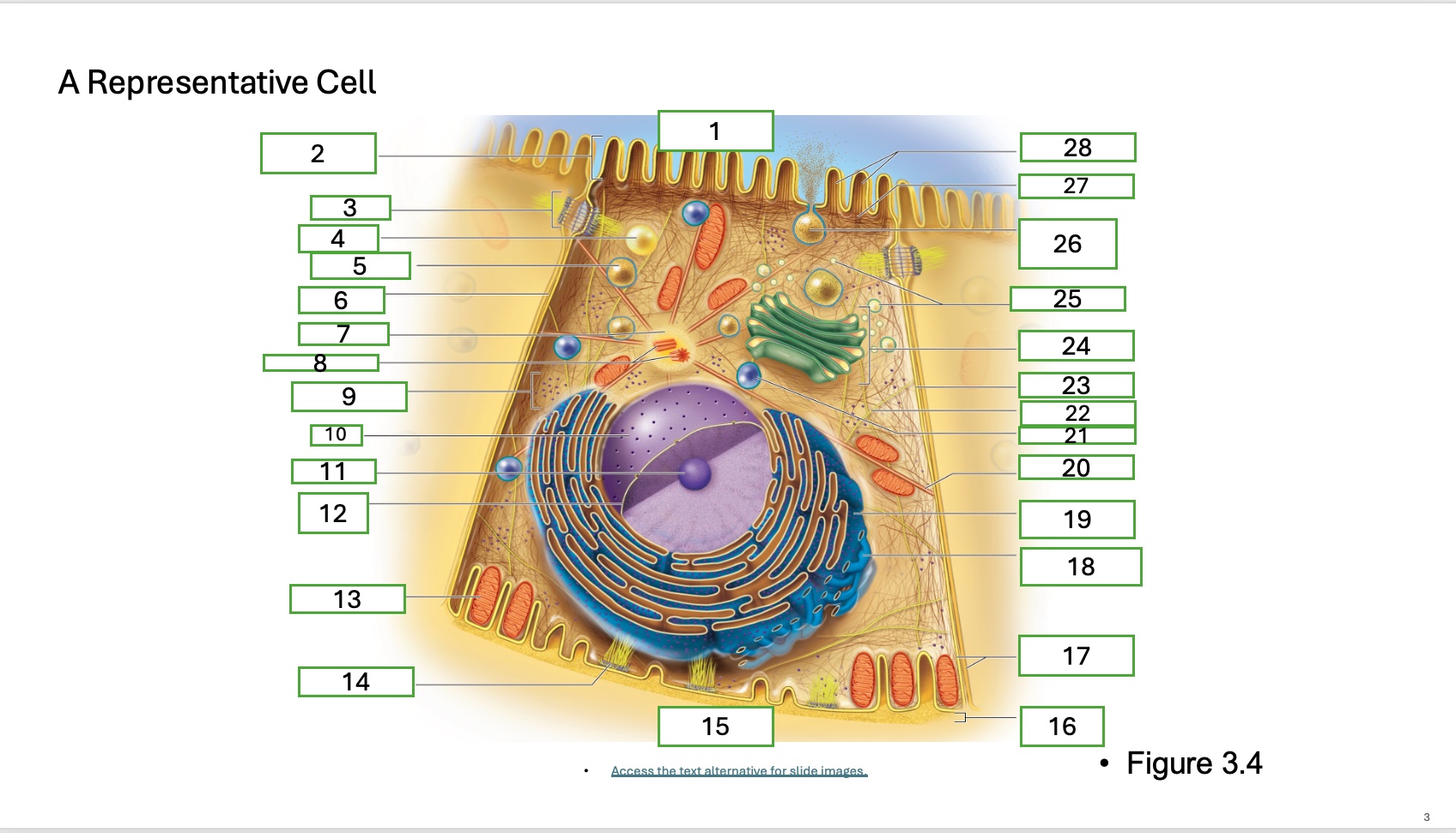
what is organelle 24
golgi complex/appartus
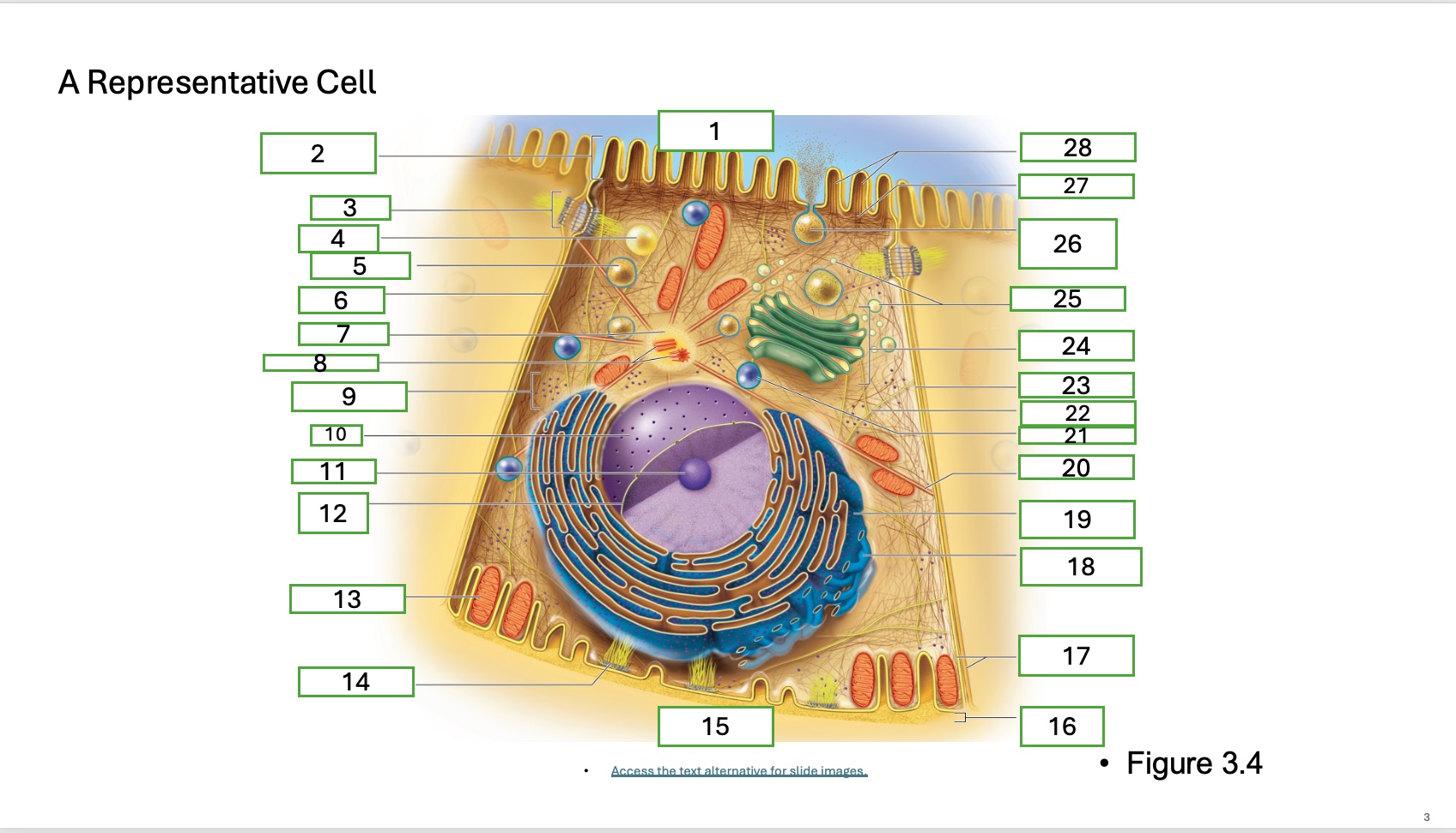
what is organelle 25
golgi vesicles
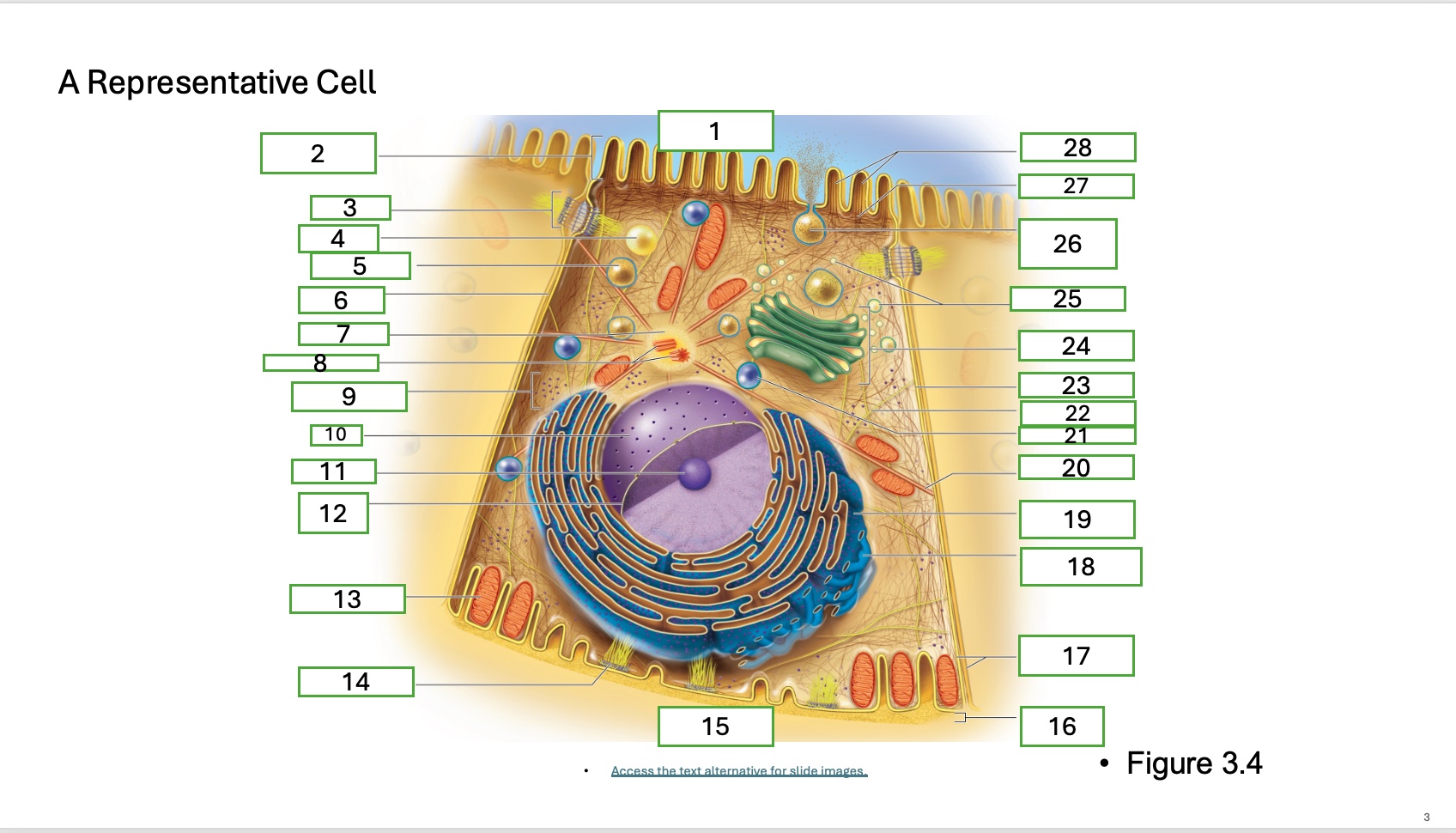
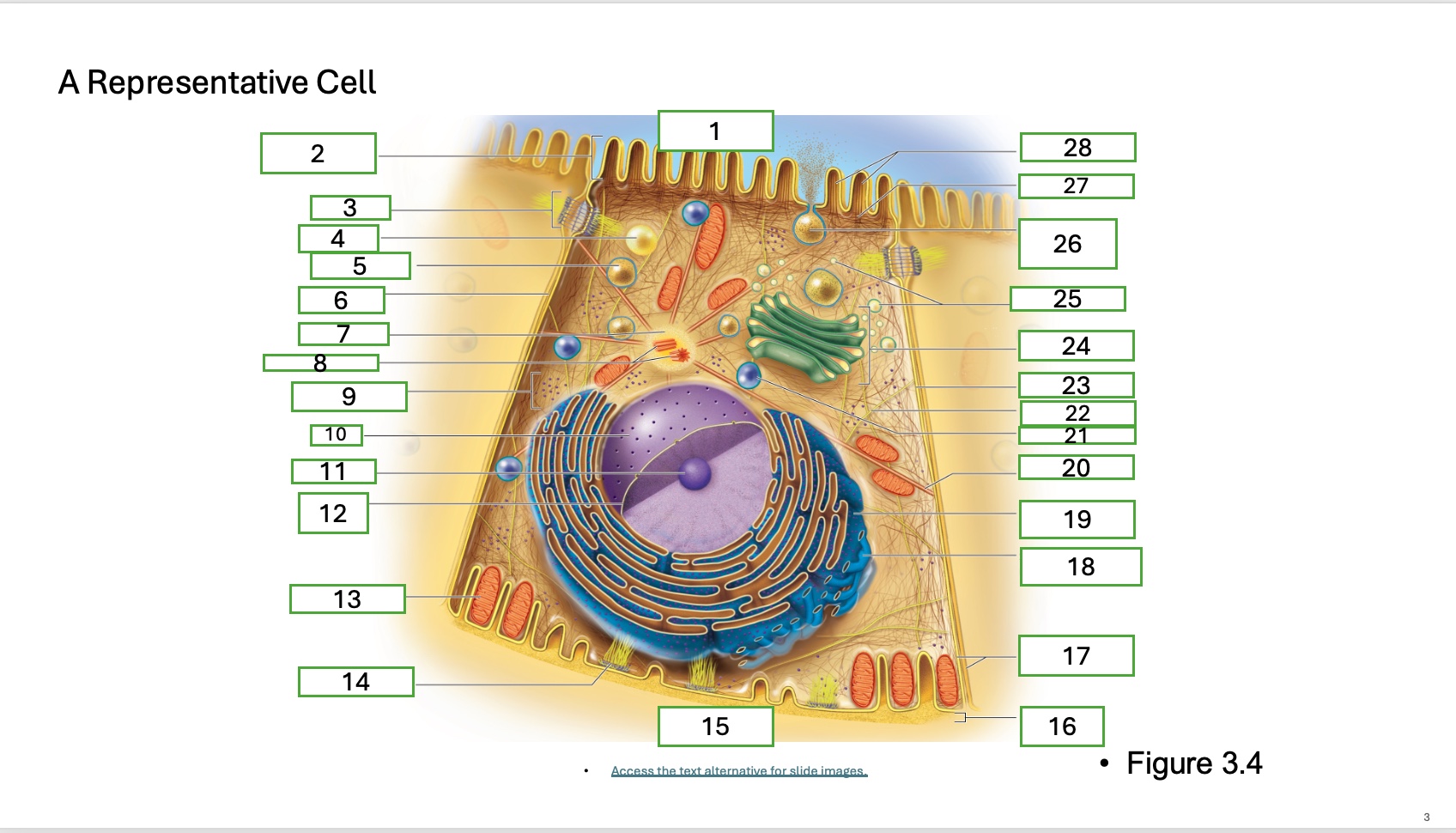
what is organelle 26
secretory vesicle undergoing exocytosis
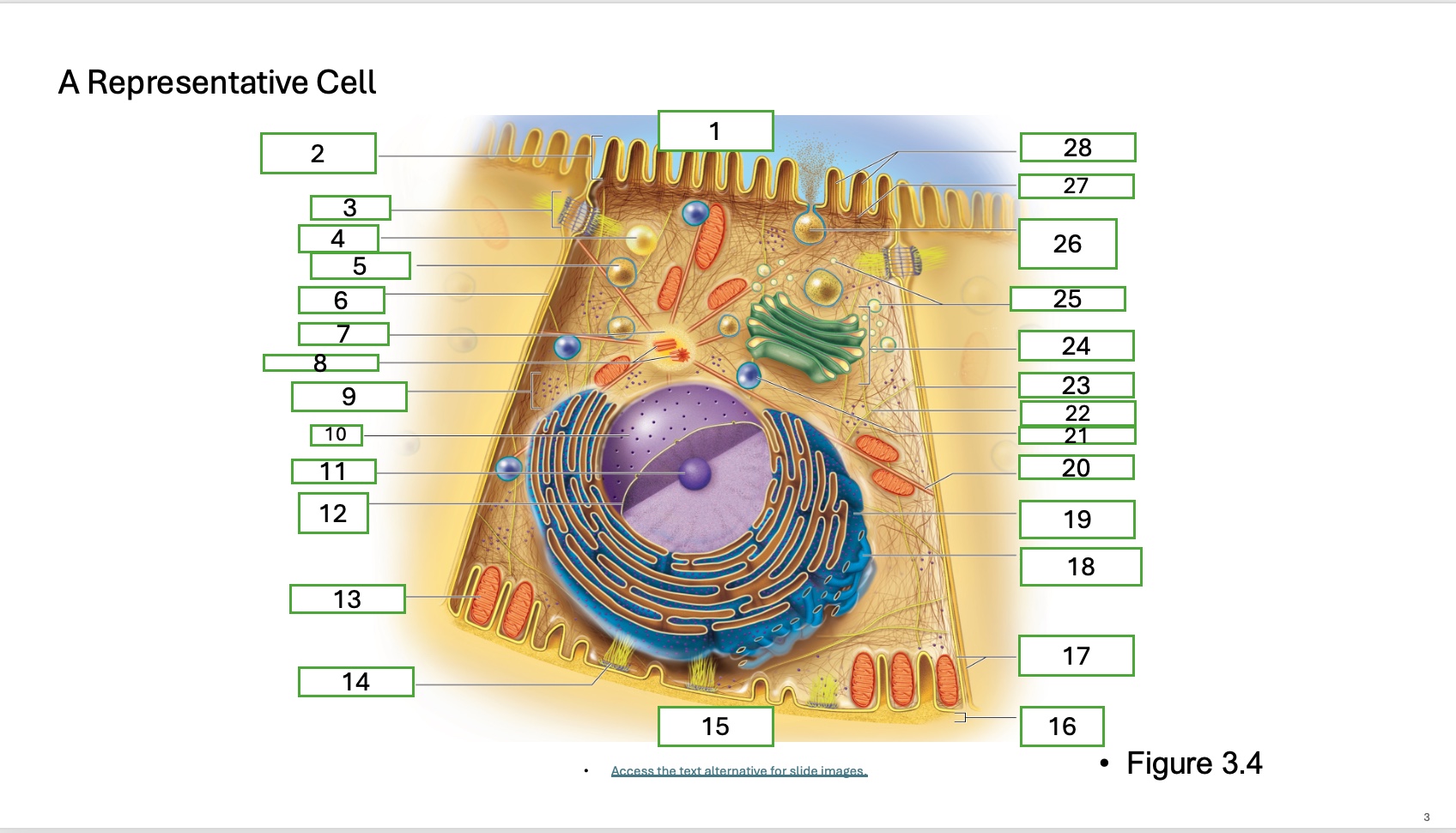
what is organelle 27
terminal web
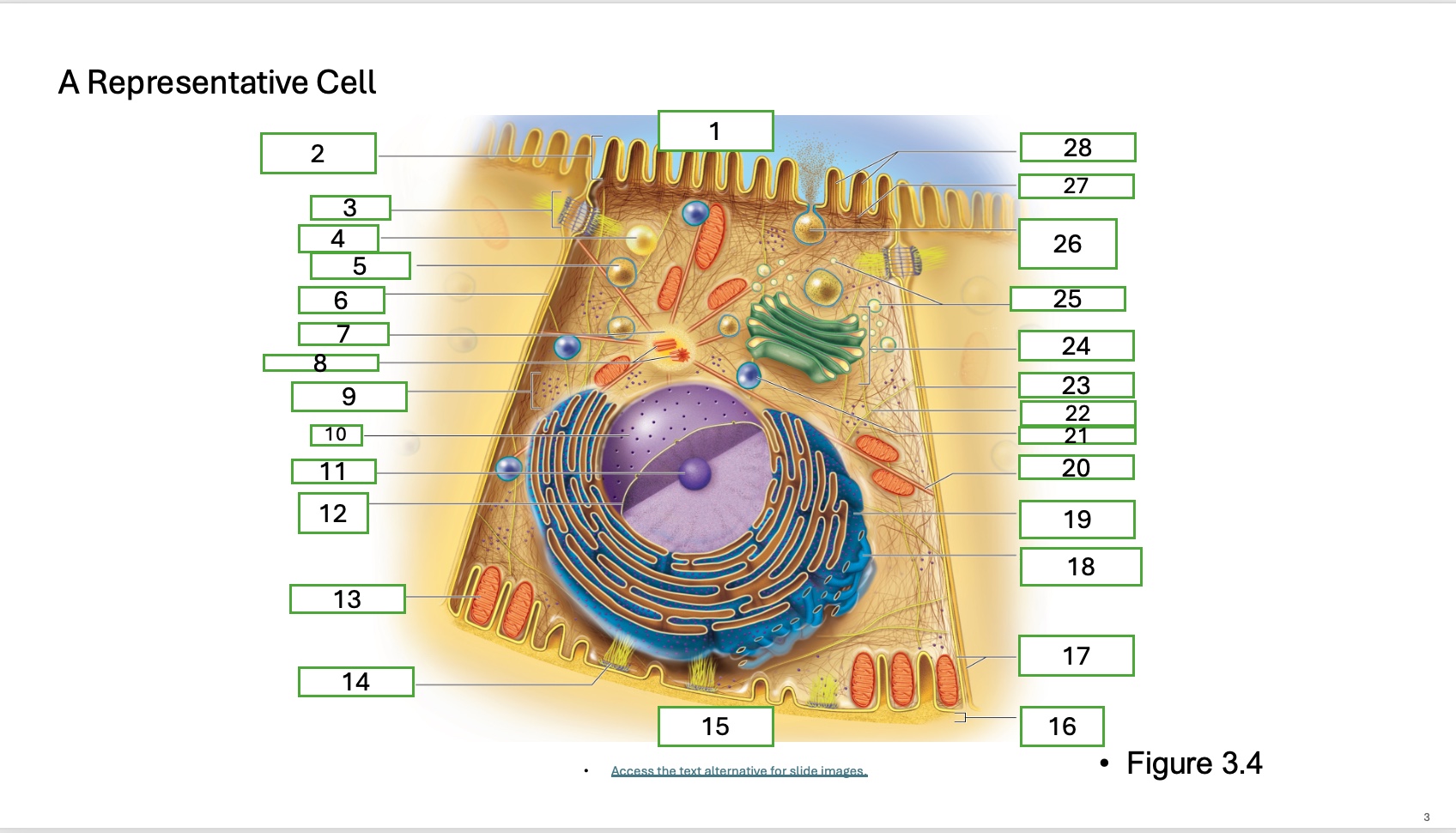
what is organelle 28
microfilaments
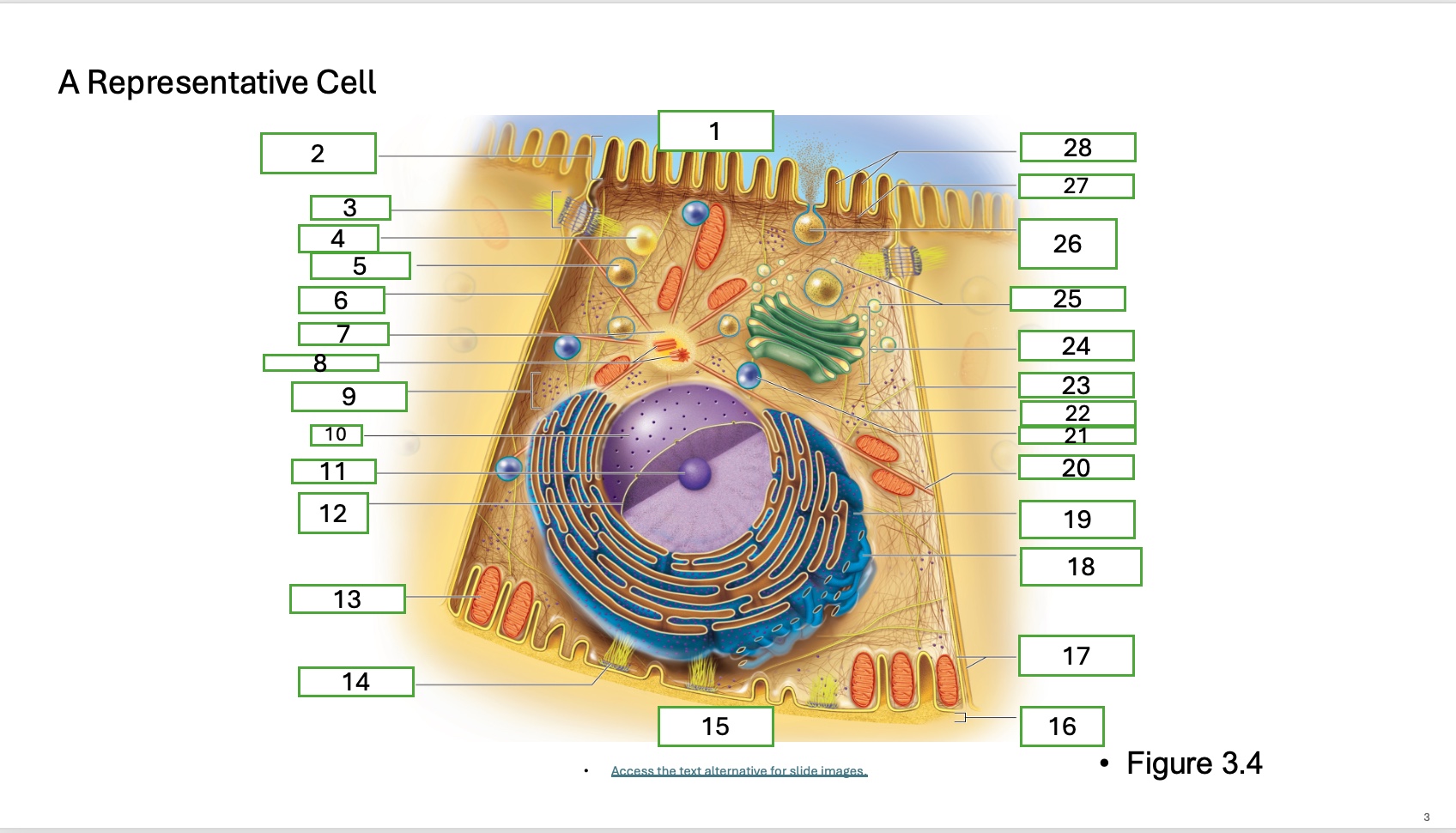
what is organelle 16
basement membrane
the cell cycle has two phases
interphase and mitotic phase
what are the subphases of interphase
First gap phase (G1). synthesis phase (S), & second gap phase (G2)
What are the subphases of the mitotic phase
prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, & cytokinesis
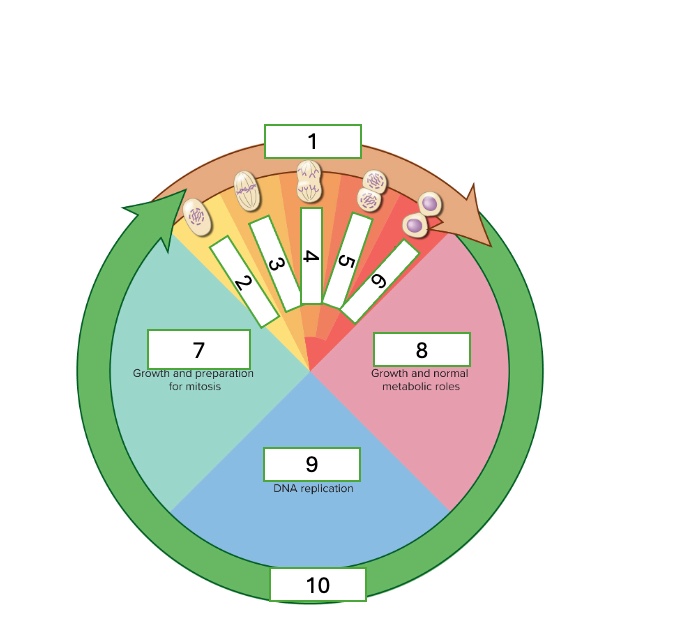
what cell cycle phase is 1?
metaphase
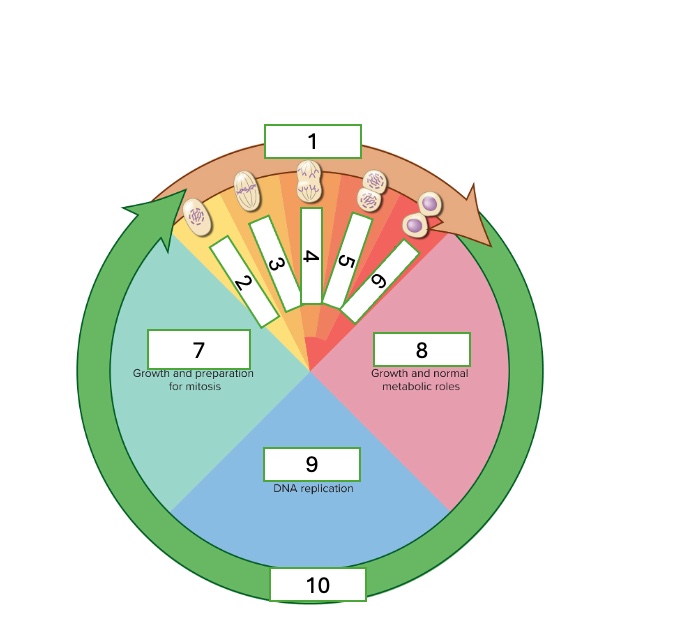
what cell cycle phase is 2
prophase
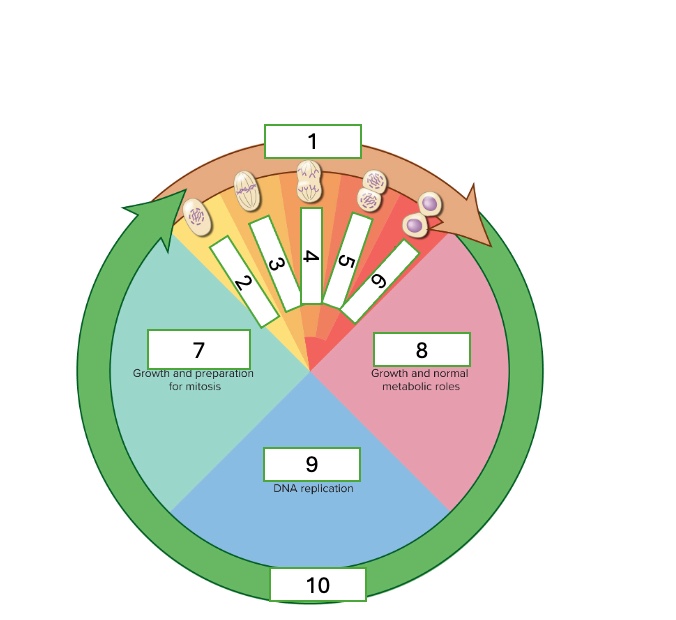
what cell cycle phase is 3
metaphase
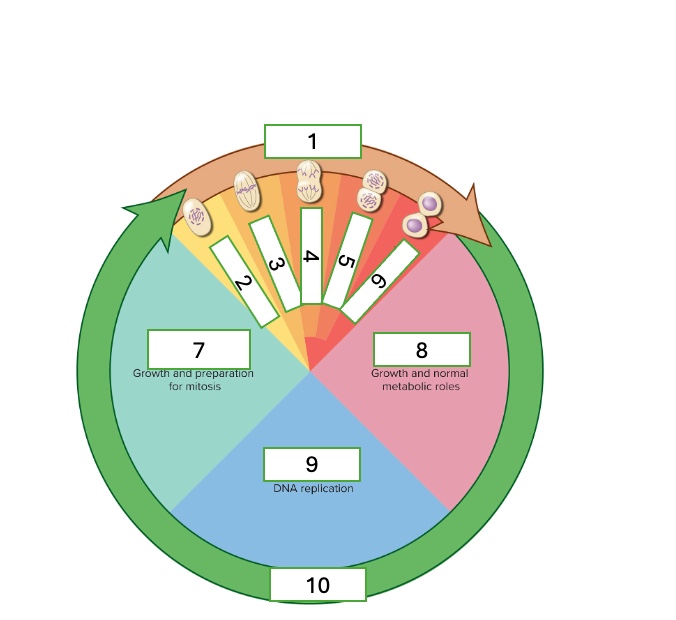
what cell cycle phase is 4
anaphase
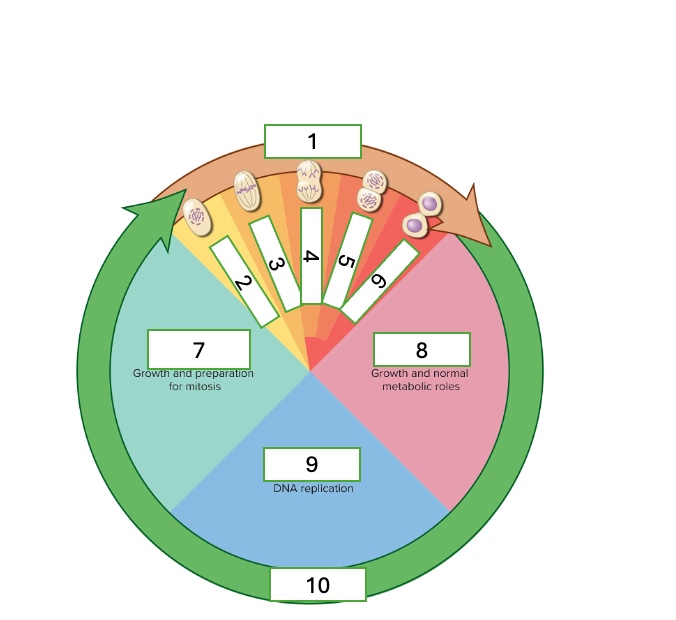
what cell cycle phase is 5
telophase
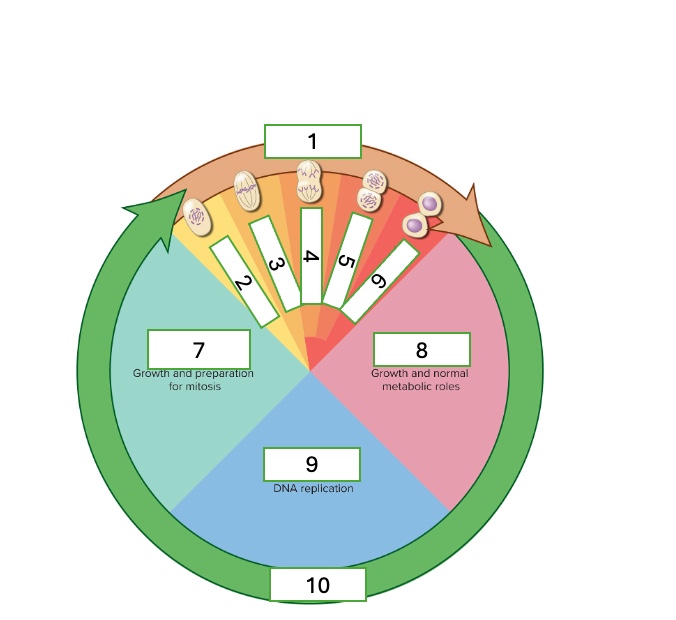
what cell cycle phase is 6
cytokinesis
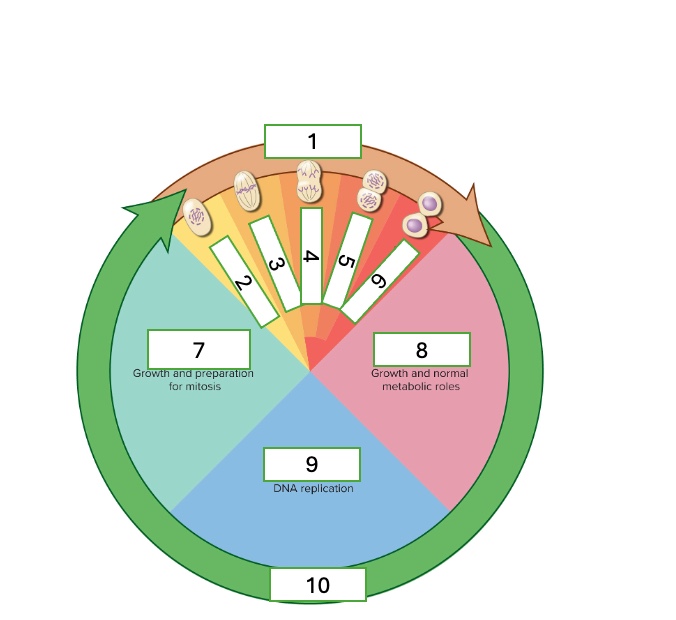
what cell cycle phase is 7
G2 — second gap phase
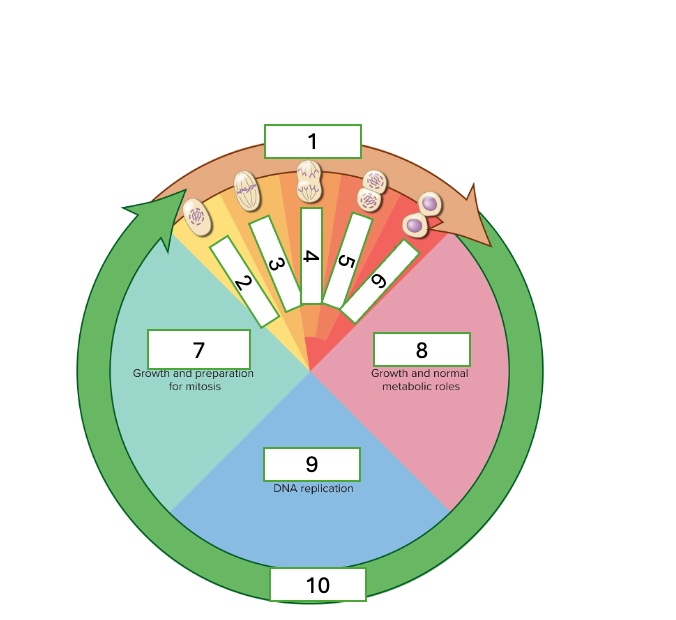
what cell cycle phase is 8
G1 — first gap phase
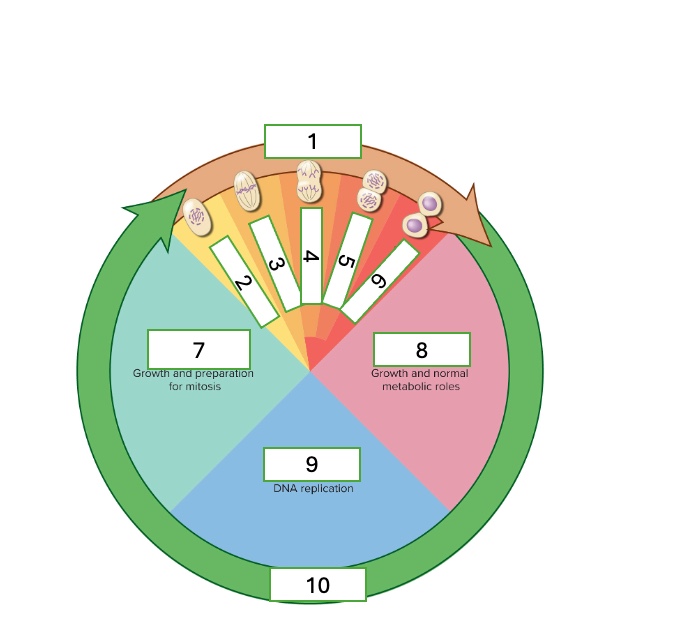
what cell cycle phase is 9
S — Synthesis phase
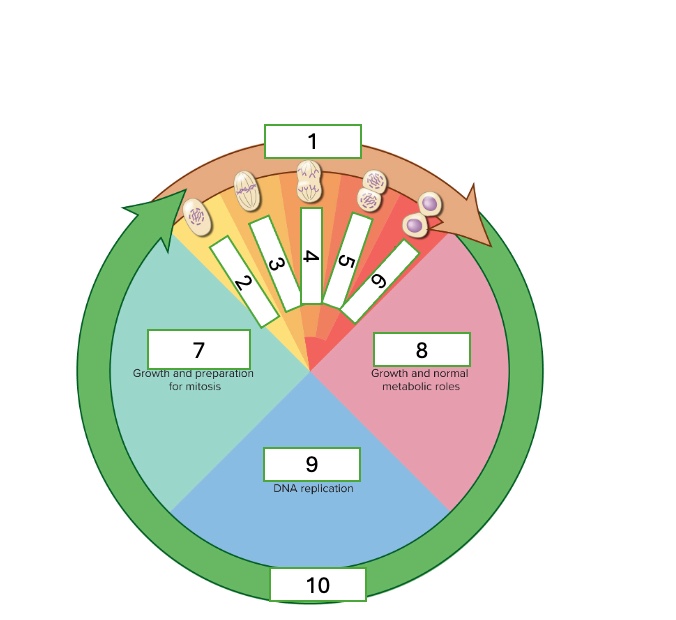
what cell cycle phase is 10
interphase
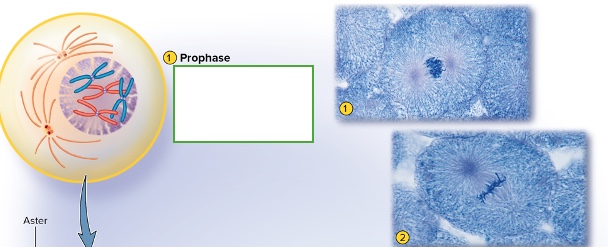
what happens in prophase
•DNA condenses into chromosomes
•Nuclear envelope disintegrates
•Spindle fibers push centrioles apart
what happens in prophase
•Chromosomes lined the equator/metaphase plate
•Centrioles on either side
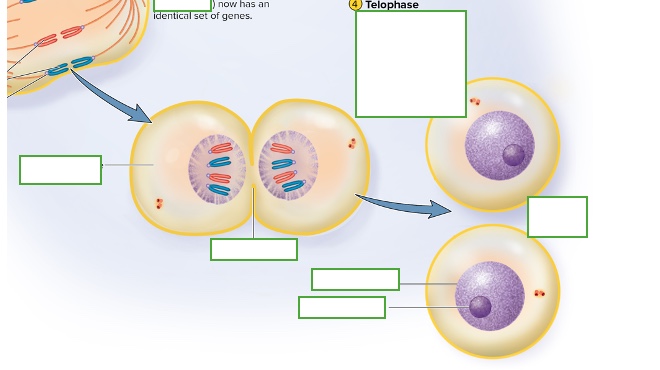
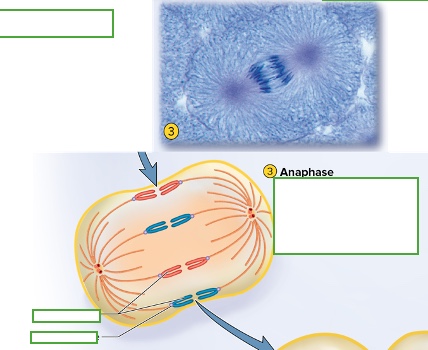
what happens in telophase & cytokinesis
Start to have cleavage furrow which means 2 distinct daughter cells are beginning to be made
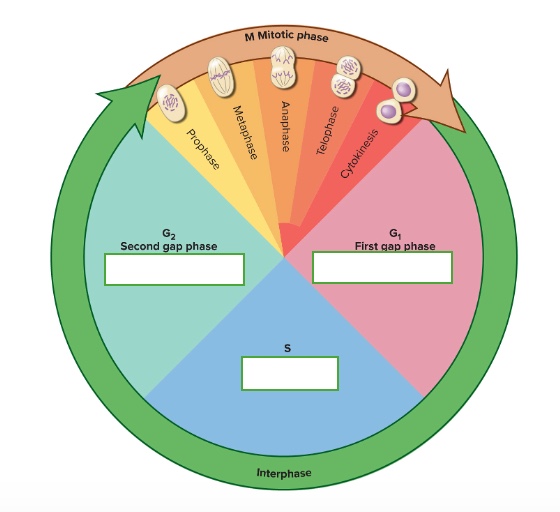
what happens in the G2 — Second gap phase
growth and preparation for mitosis
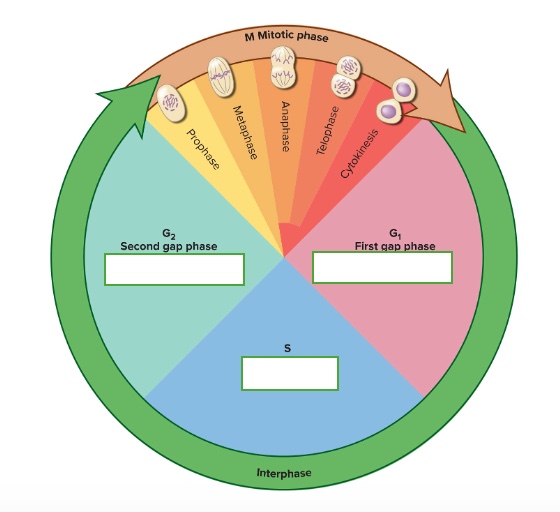
what happens in the G1 — First gap phase
growth and normal metabolic roles
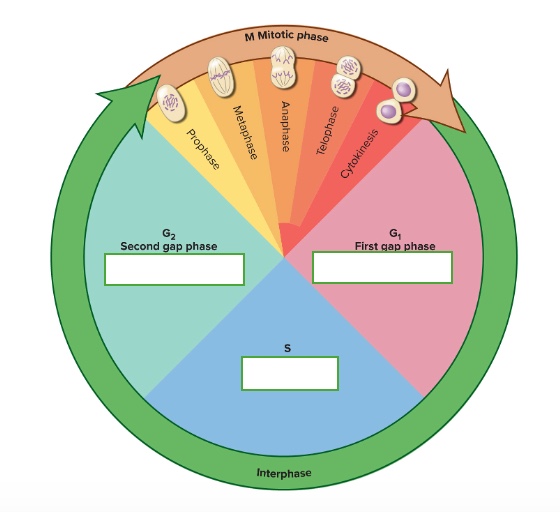
what happens in the S — Synthesis phase
DNA replication
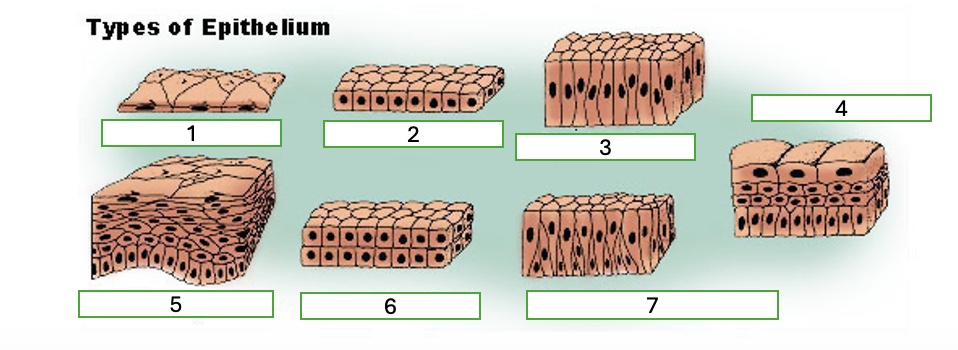
type 1 of epithelium
simple squamous
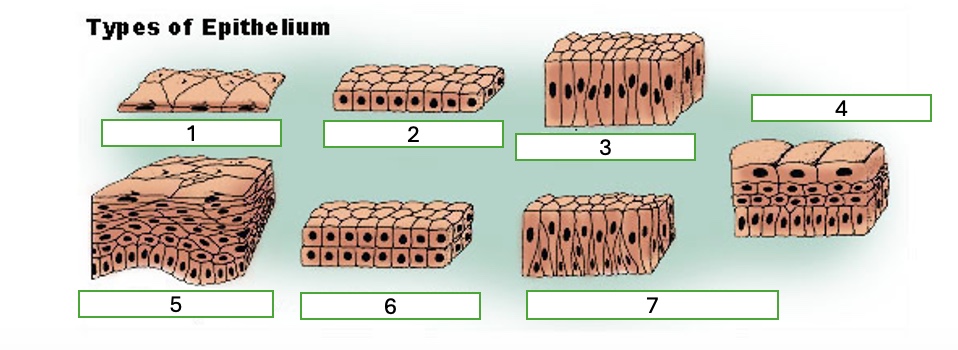
type 2 of epithelium
simple cubiodal
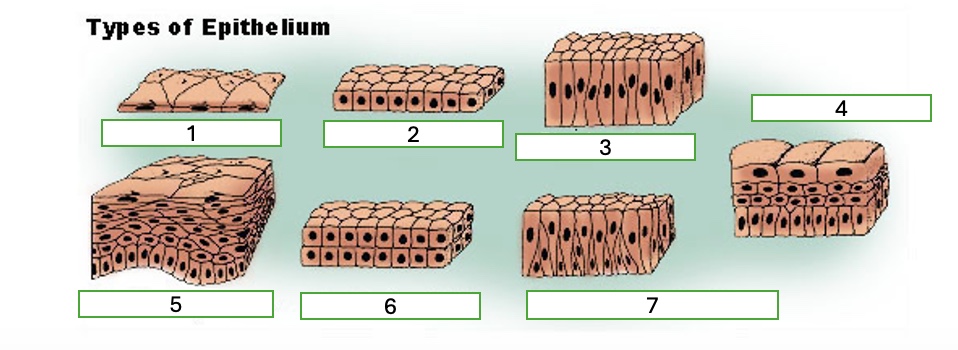
type 3 of epithelium
simple columnar
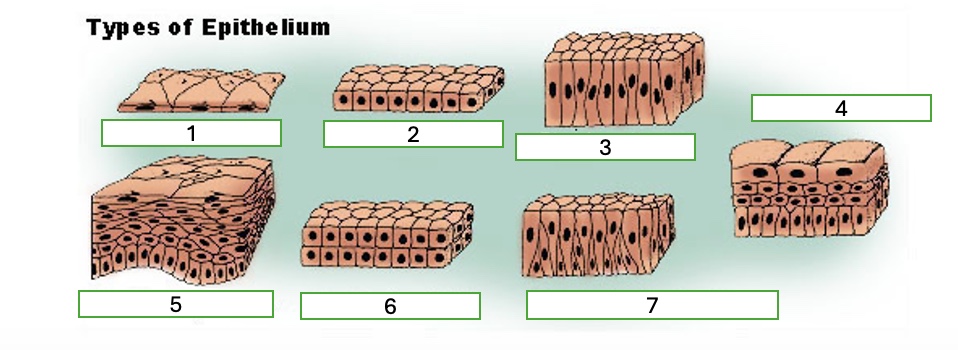
type 4 of epithelium
transitional
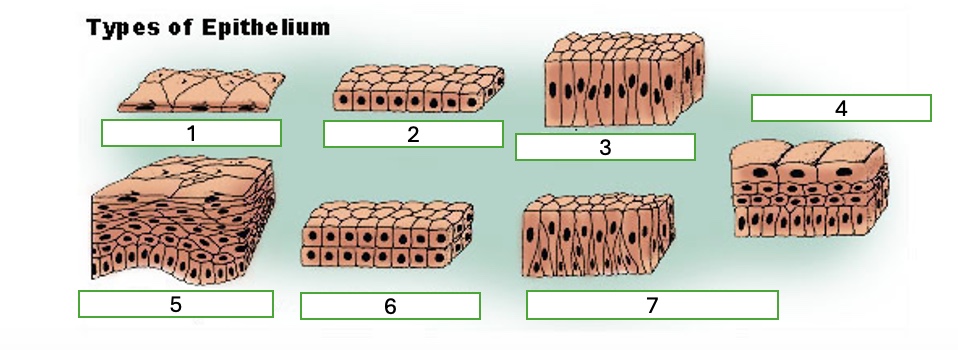
type 5 of epithelium
stratified squamous
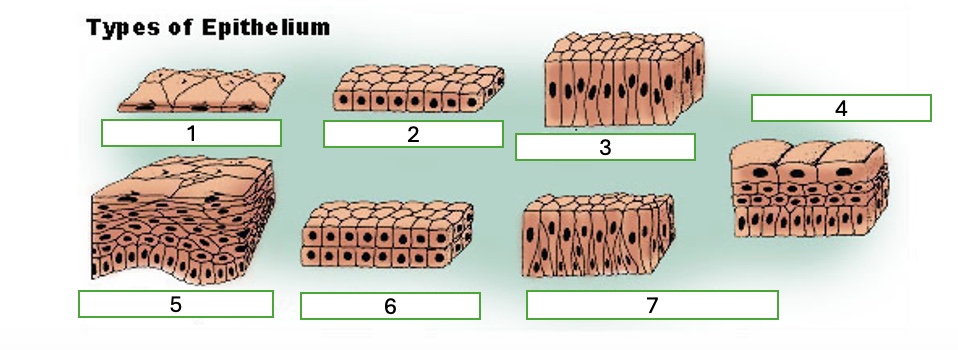
type 6 of epithelium
stratified cuboidal
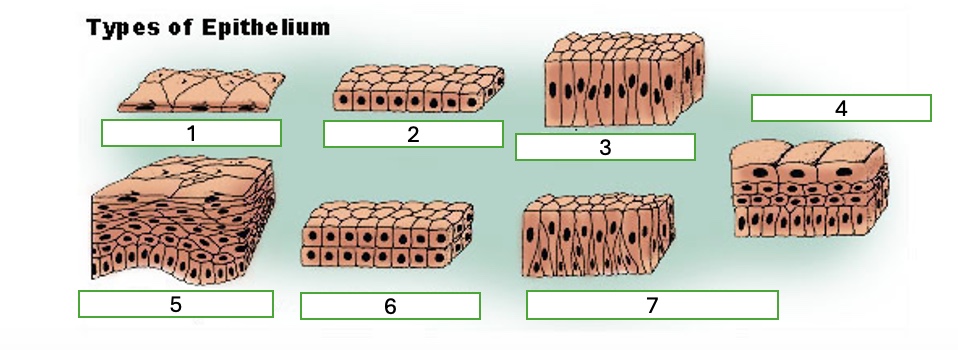
type 7 of epithelium
pseudostratified columnar
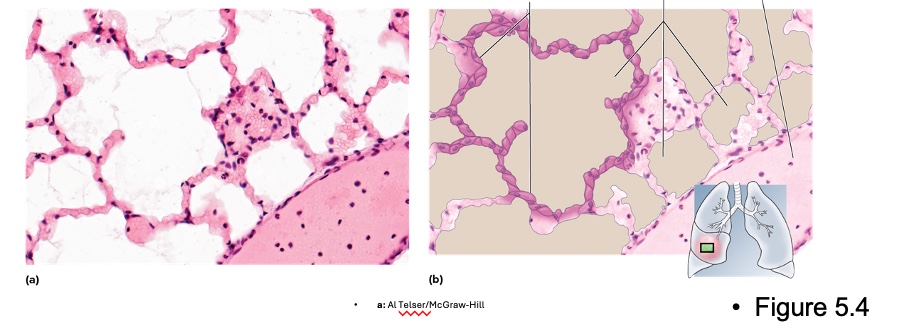
what type is this
simple squamous epithelium
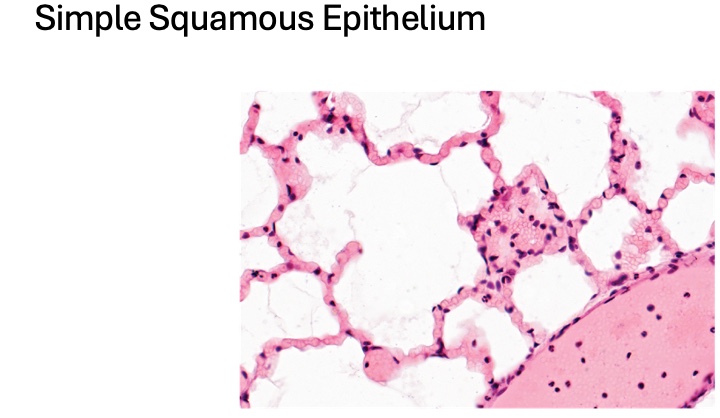
location of simple squamous epithelium
serosa
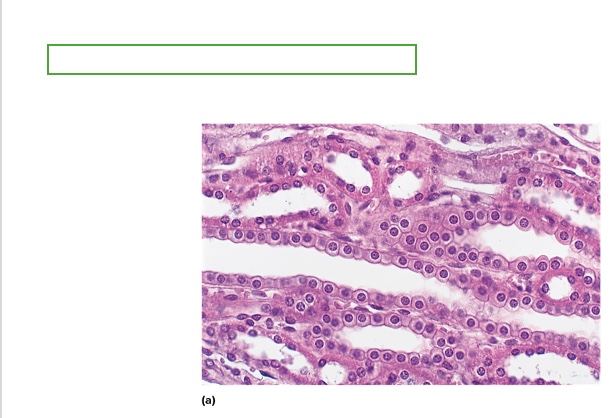
what type is this
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
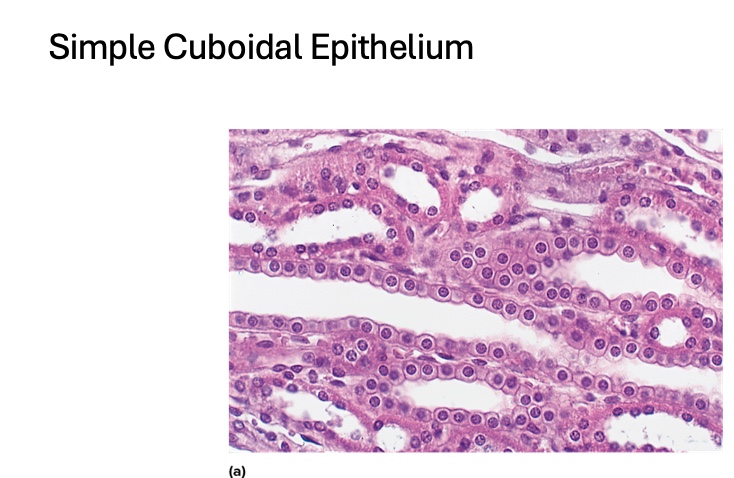
location of simple cuboidal epithelium
liver
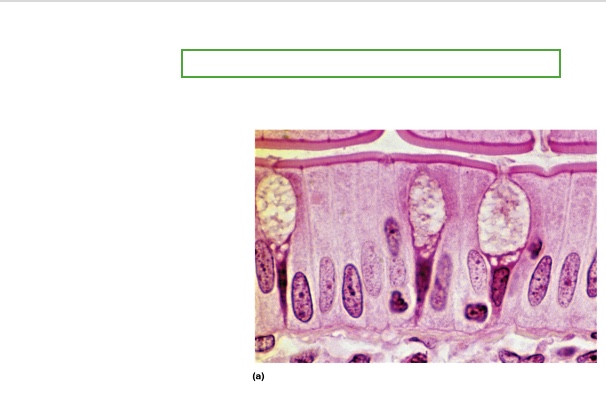
what type is this?
Simple Columnar Epithelium
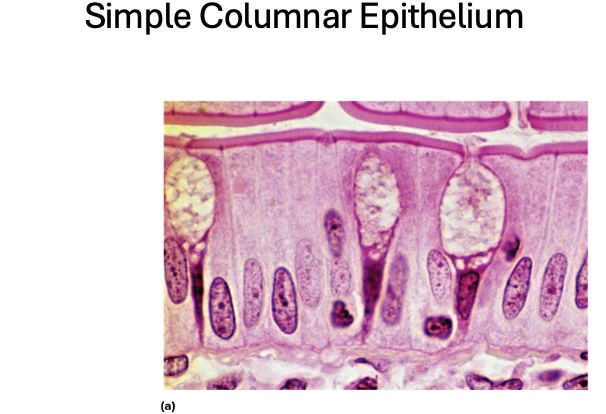
Simple Columnar Epithelium location
uterus
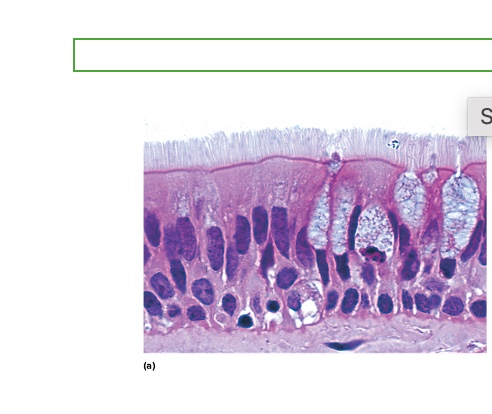
what type is this
Ciliated Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
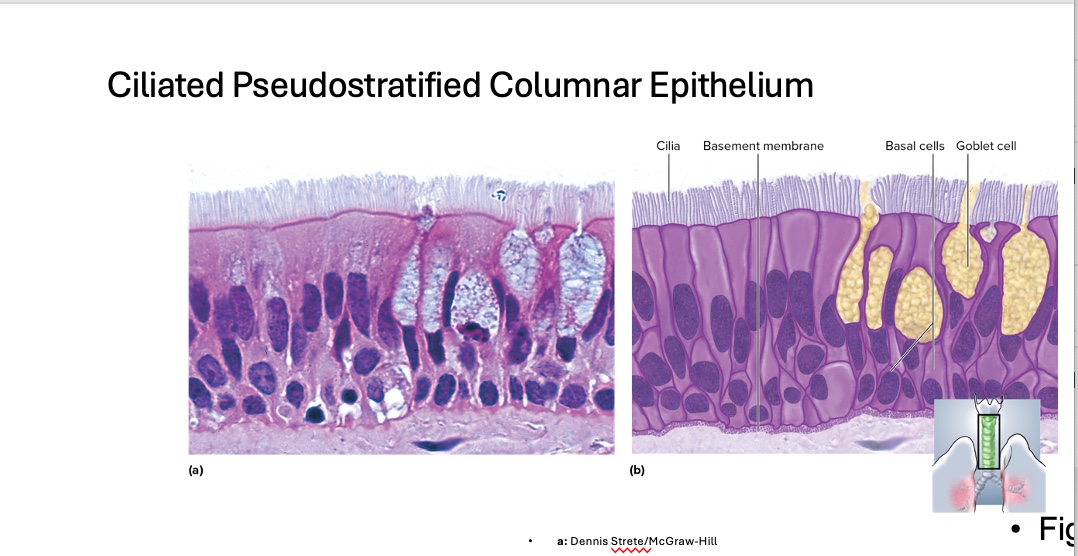
location of Ciliated Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
respiratory tract, including the trachea and bronchi
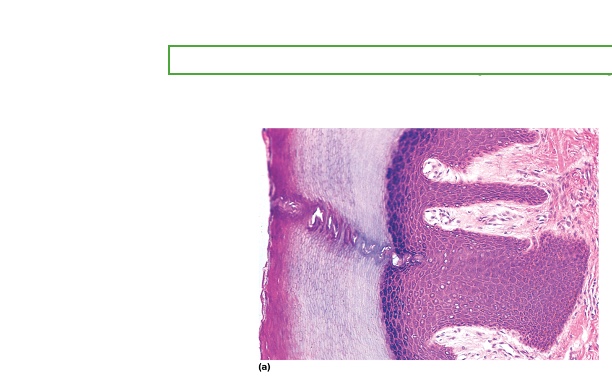
what type is this
Keratinized Stratified Squamous Epithelium
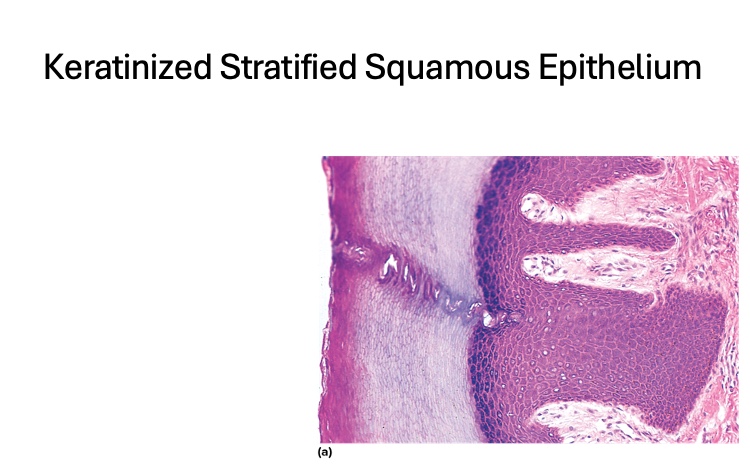
location of Keratinized Stratified Squamous Epithelium
epidermis. palms, soles
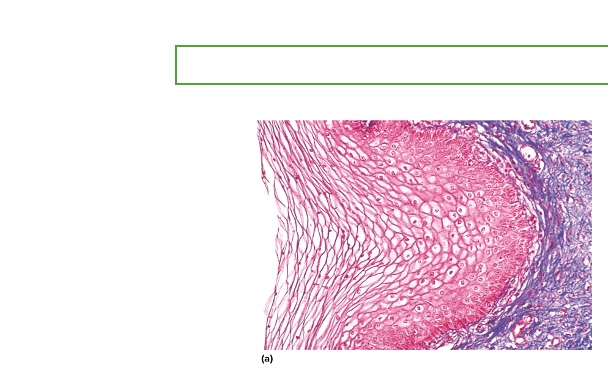
what type is this
Nonkeratinized Stratified Squamous Epithelium
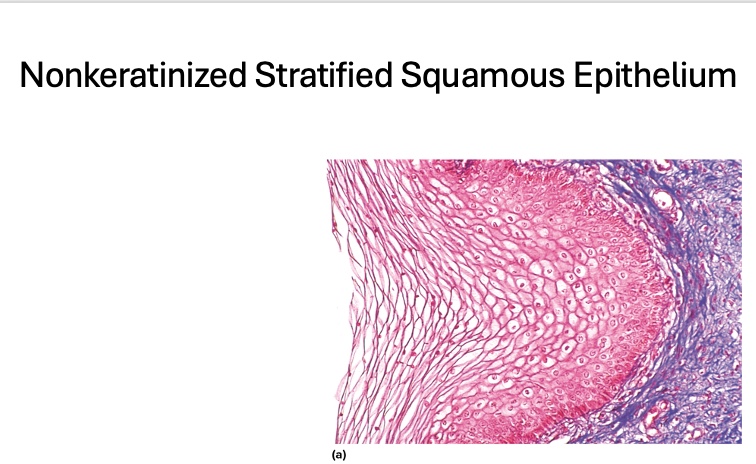
location of Nonkeratinized Stratified Squamous Epithelium
tongue, esophagus, vagina

location of Urothelium/Transitional epithelium
bladder, ureters, part of urethra
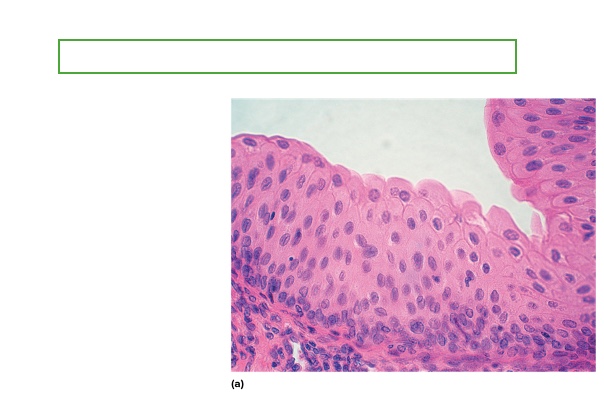
what type is this
Urothelium/Transitional epithelium
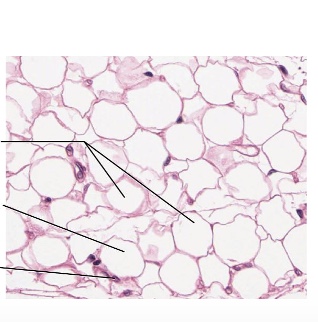
what type is this
adipose tissue
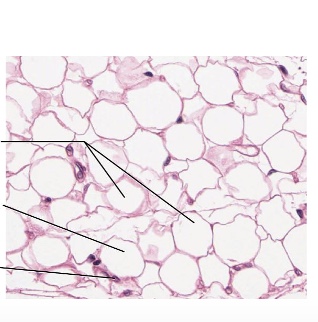
location of adipose tissue
found under the skin, around organs, and in bone marrow.
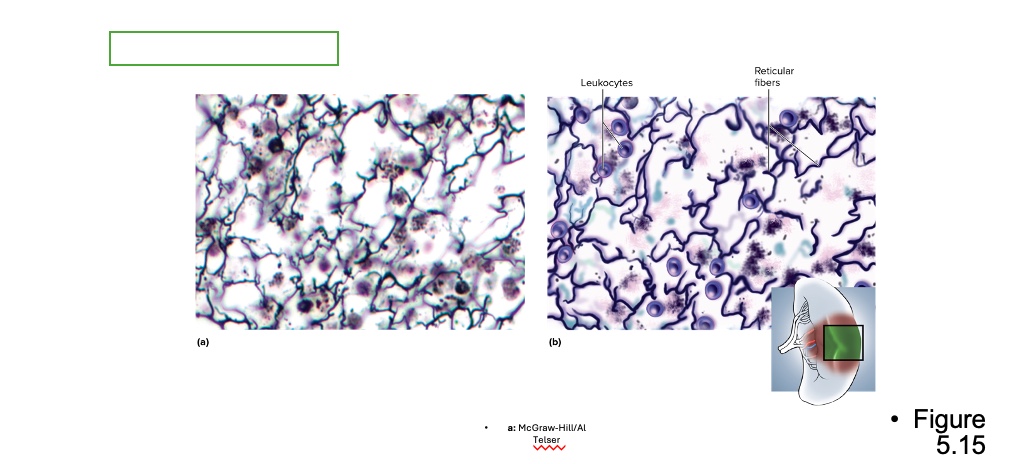
what type is this
reticular connective tissue
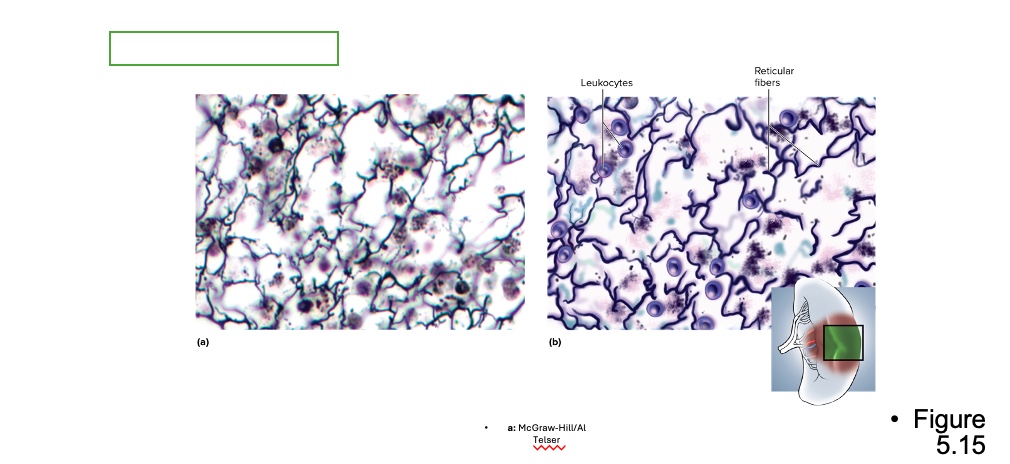
location for reticular connective tissue
bone marrow
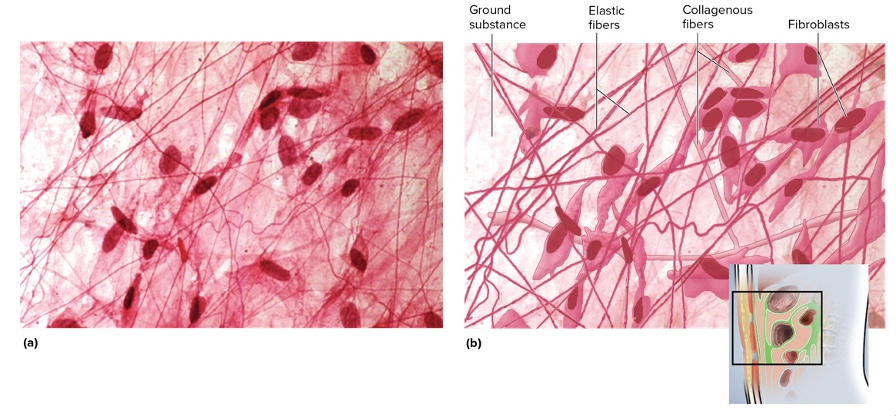
what type is this
areolar connective tissue
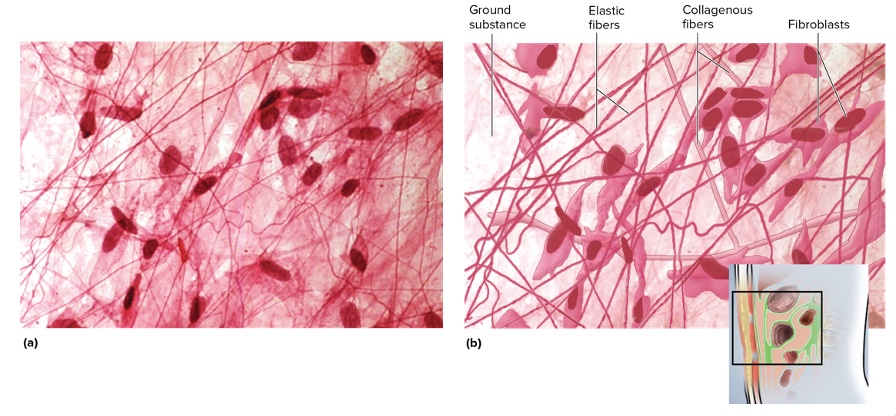
location areolar connective tissue
between muscles
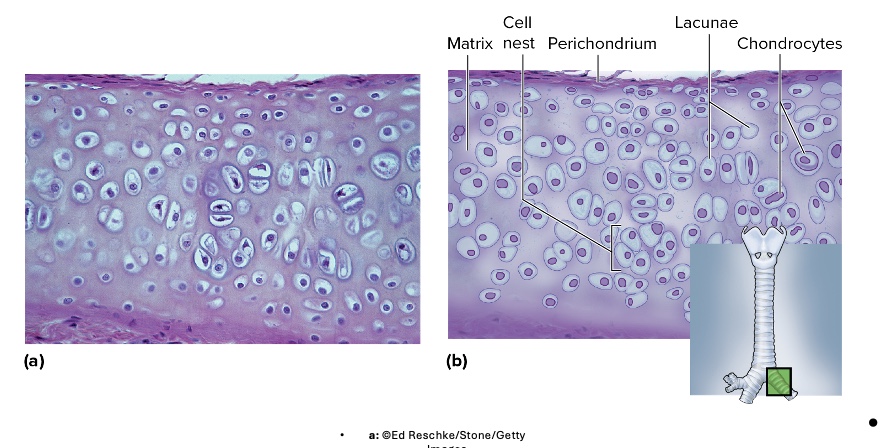
what type is this
hyaline cartilage
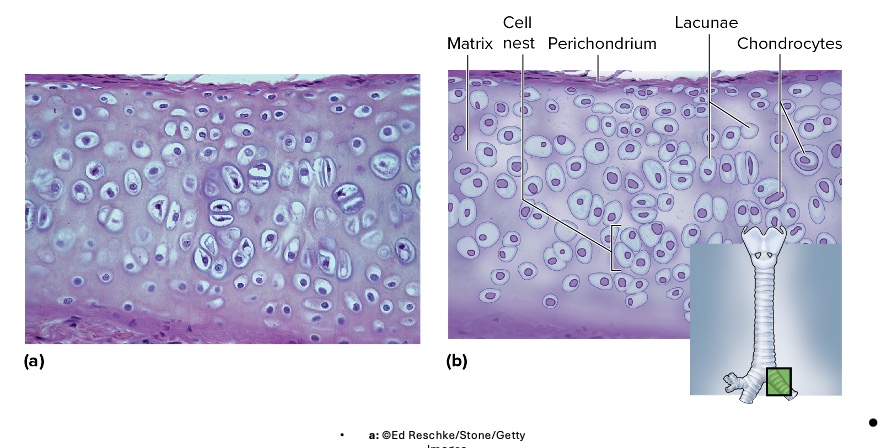
location of hyaline cartilage
trachea
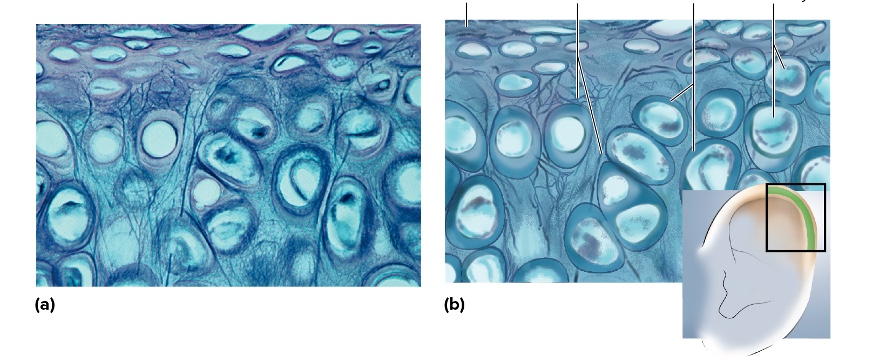
what type is this
elastic cartilage
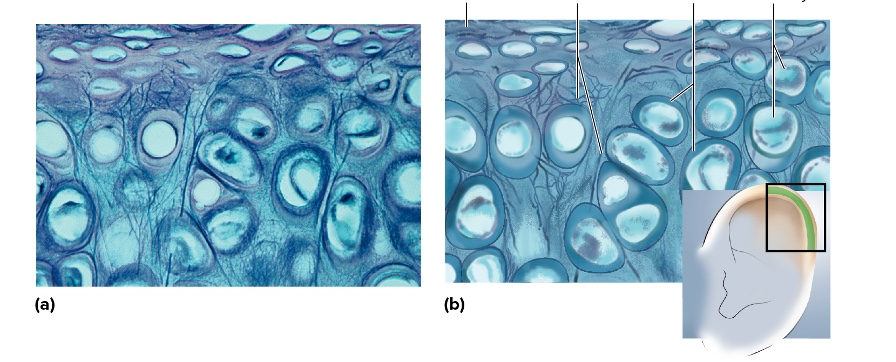
location of elastic cartilage
external ear and epiglottis
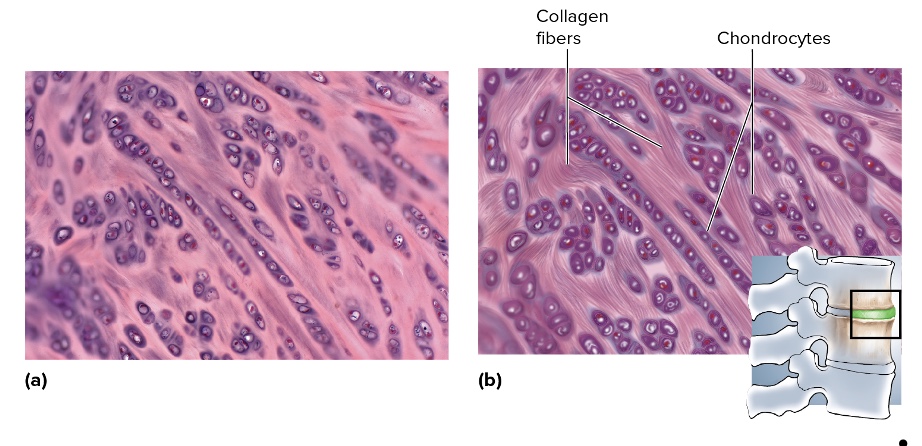
what type is this
fibrocartilage
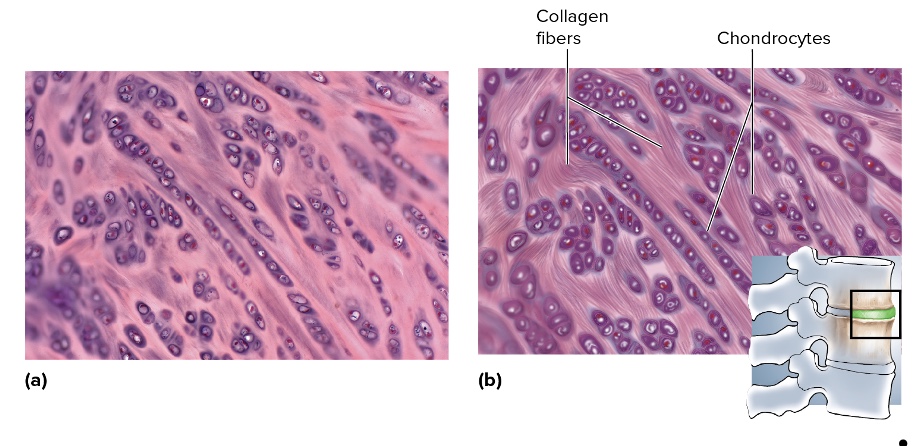
location of fibrocartilage
menisci, intervertebral discs, pubic symphysis
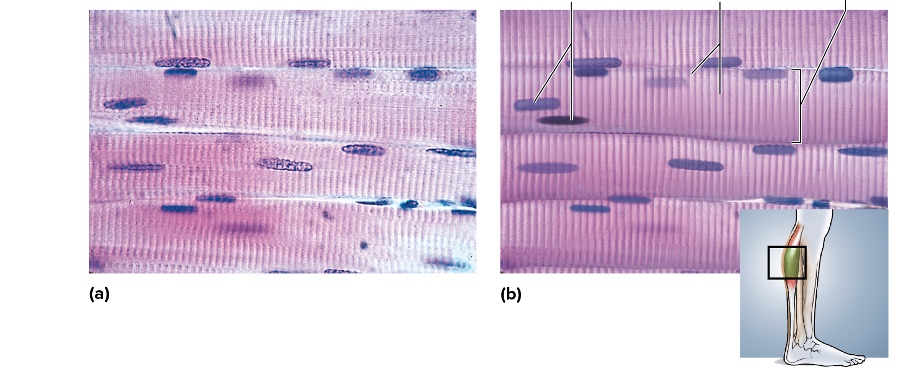
what type is this
skeletal muscle
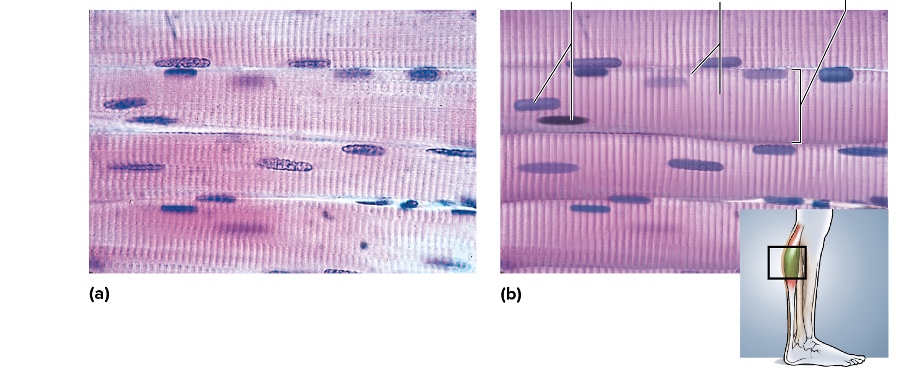
location of skeletal muscle
attached to bones
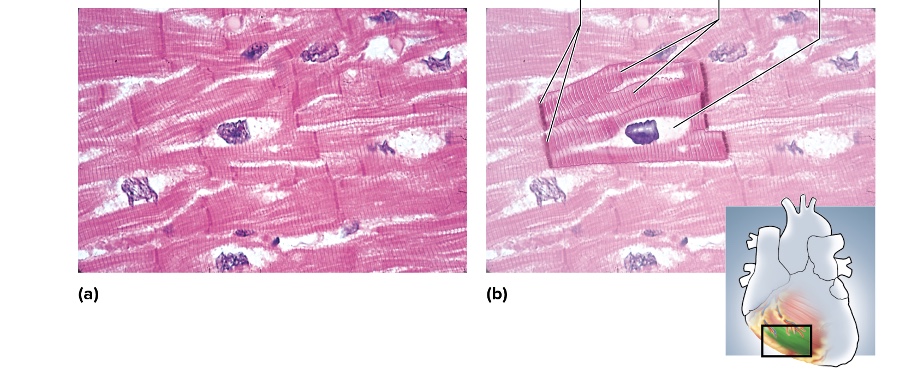
what type is this
cardiac muscle
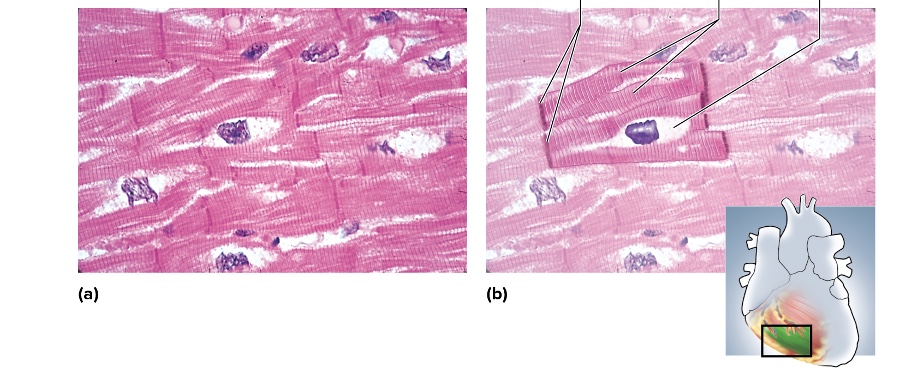
location of cardiac muscle
heart wall
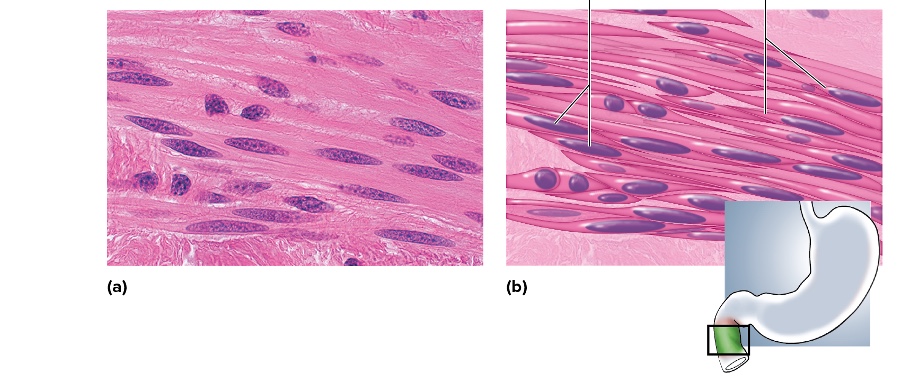
what type is this
smooth muscle
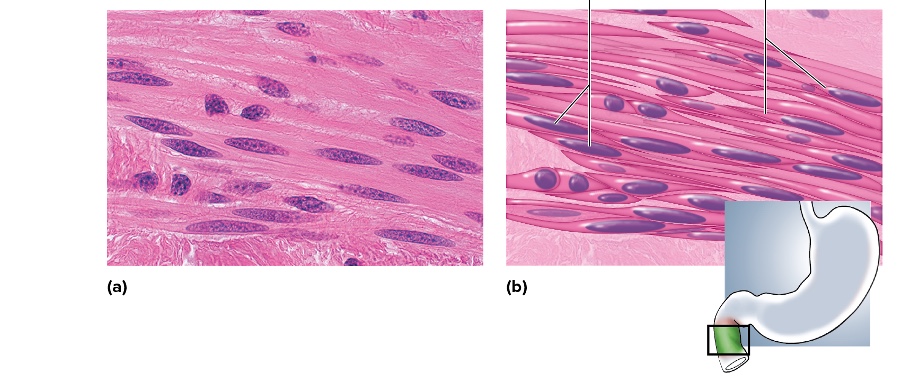
location of smooth muscle
found in the walls of hollow organs such as the intestines, blood vessels, and bladder.
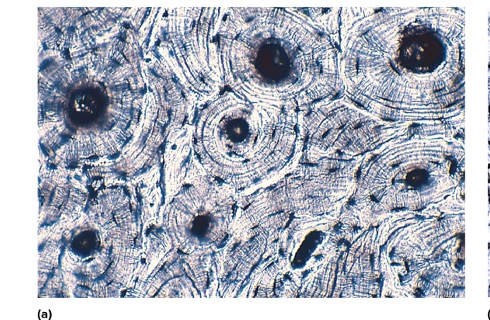
what type is this
compact bone
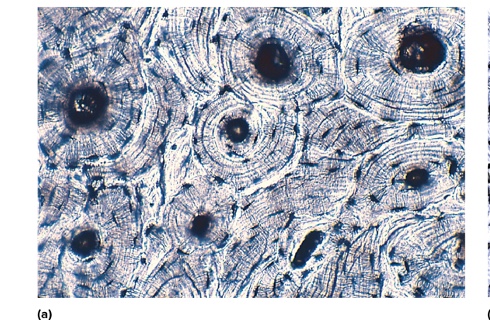
location of compact bone
found in the outer layers of bones, providing strength and structure.
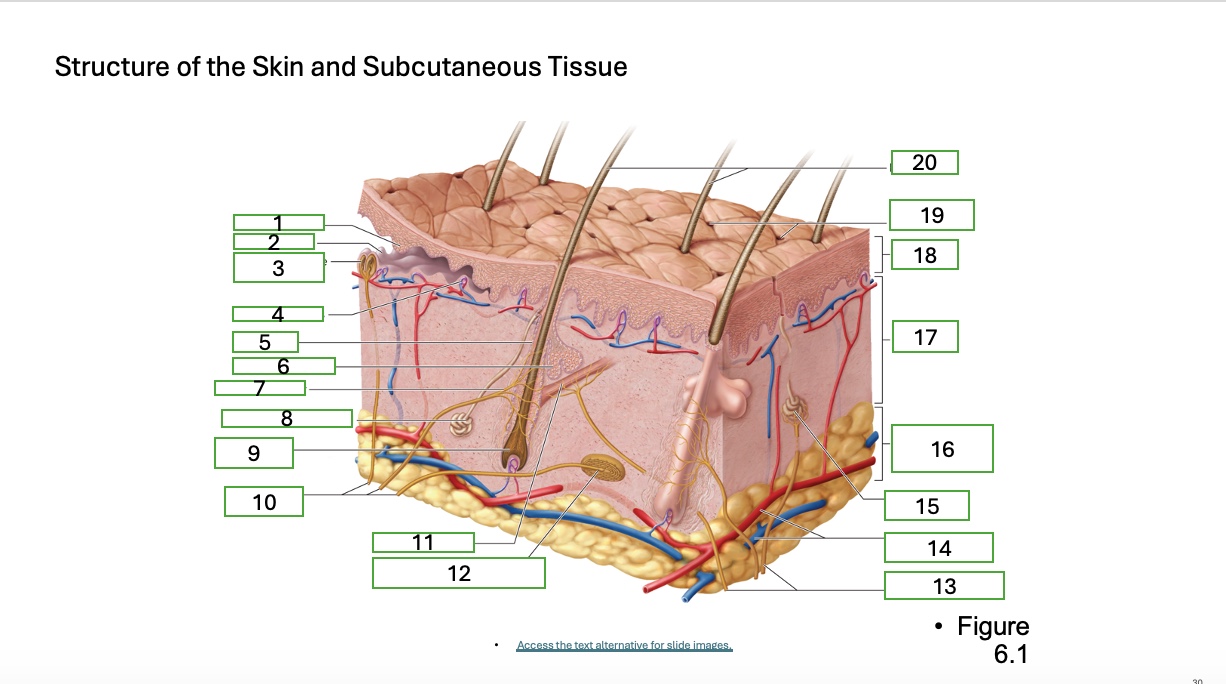
skin structure 1
epidermal ridge
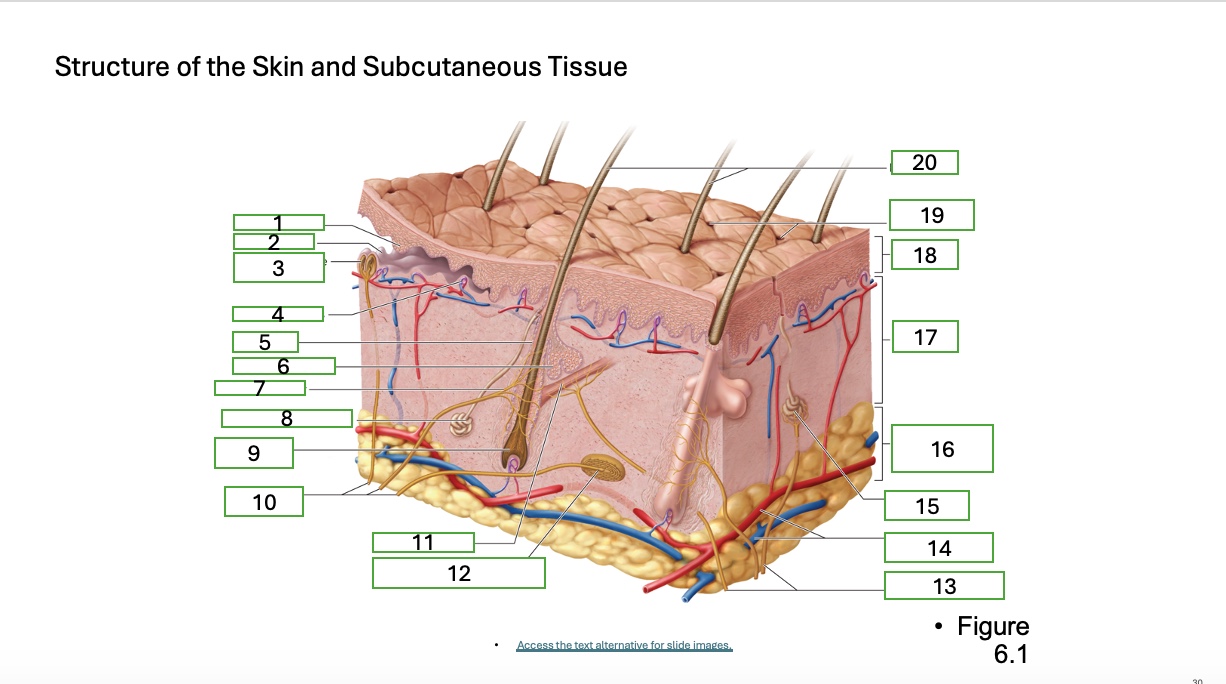
skin structure 2
dermal papilla
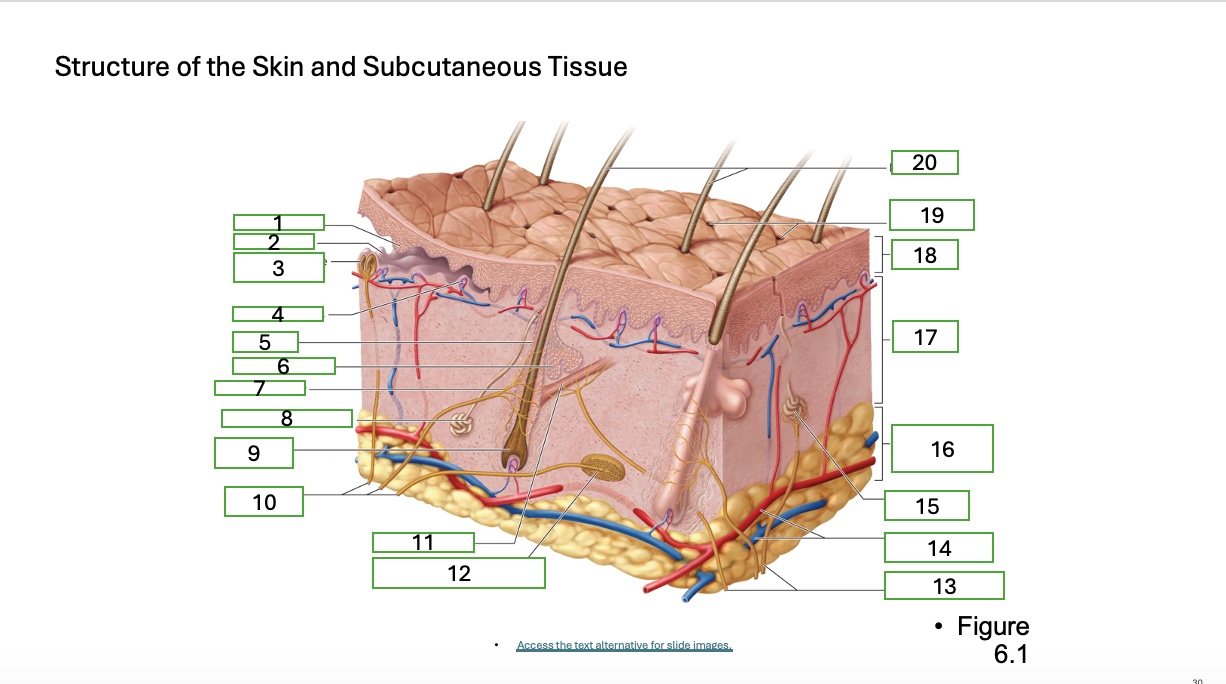
skin structure 3
tactile corpuscle (touch receptor)
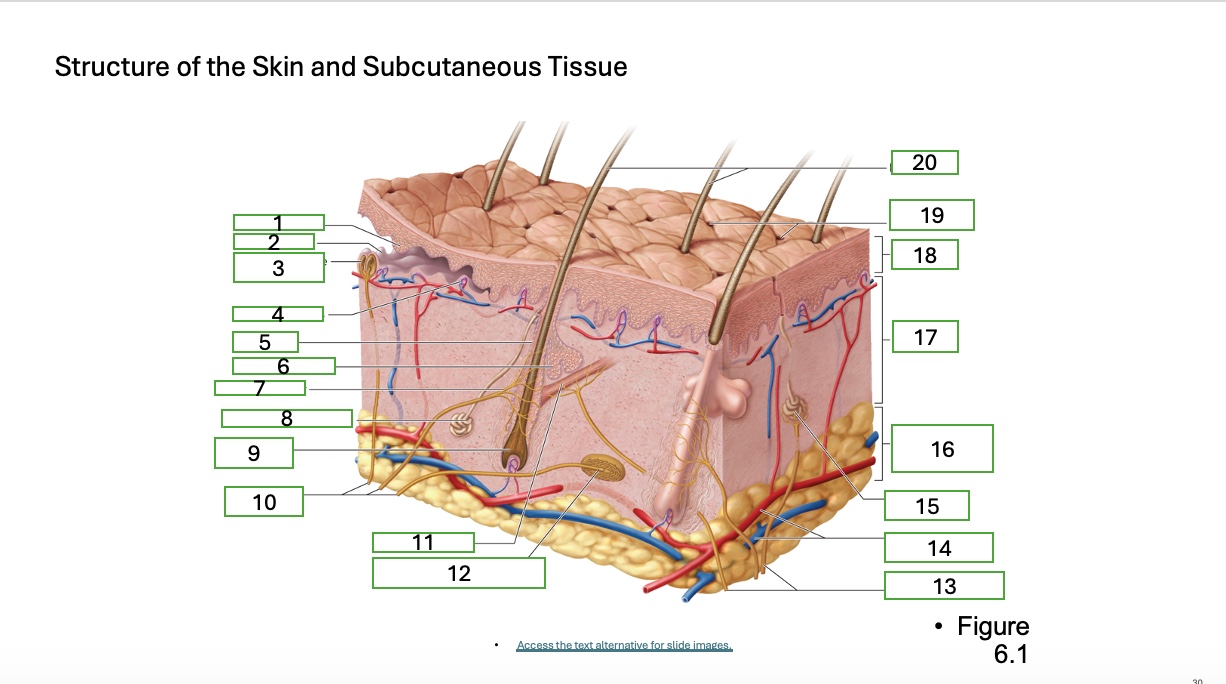
skin structure 4
blood capallaries
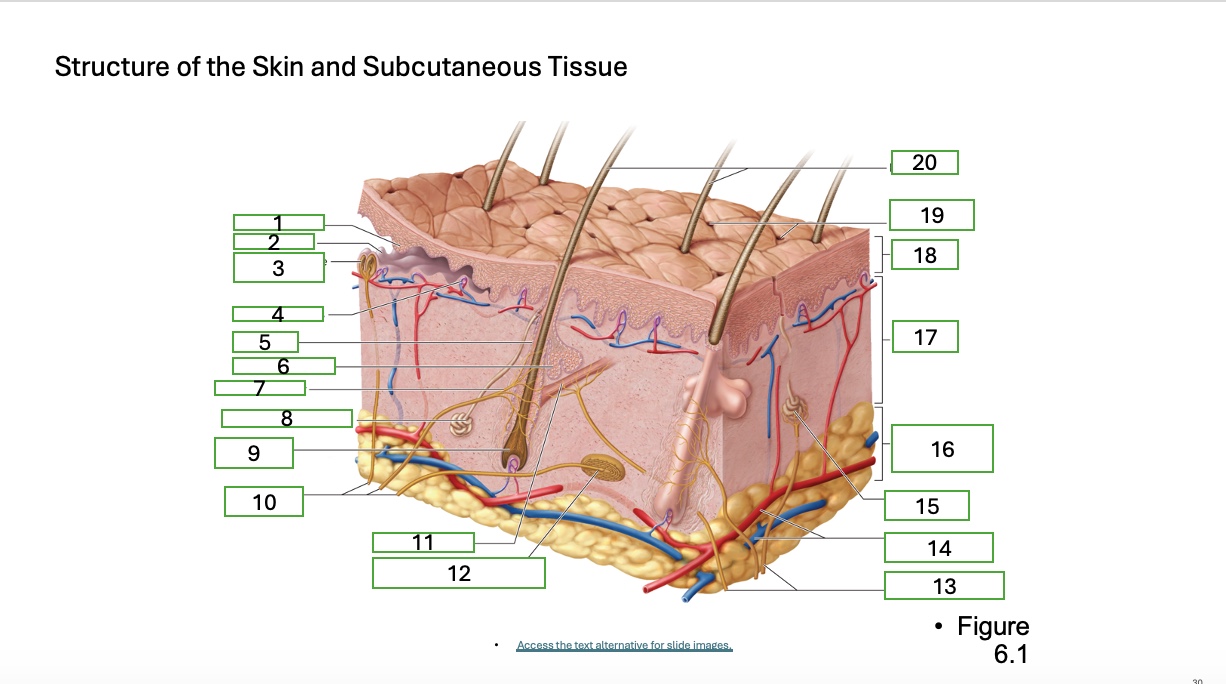
skin structure 5
hair follicle